Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
MRSM 2011paper 2
Enviado por
Sim Kwang YawDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MRSM 2011paper 2
Enviado por
Sim Kwang YawDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MRSM 2011
PAPER 2
1. Solve the following simultaneous equations:
3x + y + 1 = 0
x
2
+ y
2
= 3 xy
[x = 0.2319, y = 1.6957, x = 1.2319, y =
2.6957]
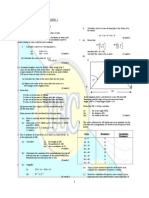
2. Diagram 2 shows a cuboid of volume 72
cm
3
.
(a) Show that the total surface area of the
cuboid, A cm
2
, is given by
A = 4x
2
+
216
x
(b) Hence, find the minimum total surface
area, in cm
2
, of the cuboid.
[108 cm
2
]
3. (a) Prove that
2
2tan
sec
x
x
= sin 2x
(b) (i) Sketch the graph of y = sin2x
for 0 x 2t.
(ii) Hence, using the same axes,
sketch a suitable straight line to
find the number of solutions to
the equation
2
4tan
sec
x
x
= 2
x
for
0 x 2t.
[(b)
4. Table 4 shows the cumulative frequency of
the scores of a group of students in a quiz.
Scores 6 7 8 9 10
Cumulative
frequency
3 7 y 15 20
The mean score is 8.1
Find
(a) the range of the scores,
(b) the value of y,
(c) the standard deviation of the scores.
[(a) 4 (b) 13 (c) 1.375]
5. Diagram 5 shows a number of rectangles
made of wire. All the rectangles have a
height of 5 cm.
The area of the 6
th
rectangle is 80 cm
2
.
(a) Find the value of x.
(b) Hence, find the maximum number of
rectangles which can be formed using a
wire of length 450 cm.
[(a) 6 (b) 10]
6. Diagram 6 shows a triangle RST.
Point L lies on the straight line TS such that
TS = 3TL. It is given that 8 RT x =
,
6 , 4 RK y KS y = =
and RQ nRL =
(a) Express in terms of x
and y
for
(i) TS
(ii) TK
(b) (i) Express TQ
in terms of n, x
and
y
(ii) Hence, find the value of n if points
T, Q and K are collinear.
[(a) (i) 10 8 y x
(ii) 6 8 y x
(b) (i)
16 10
8
3 3
n n
x y
| |
+
|
\ .
(ii)
9
11
]
SECTION B
7. Table 7 shows the values of two variables,
x and y, obtained from an experiment.
8 solutions
Variables x and y are related by the
equation y =
3
6 px q +
, where p and q are
constants.
x 2 3 4 5 6
y 2.6 3.3 4.6 6.7 14.3
(a) Plot
1
y
against x using a scale of 2 cm
to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 0.05
unit on the
1
y
-axis. Hence, draw a line
of best fit.
(b) Use the graph in 7(a) to find the value
of
(i) p
(ii) q
(iii) y, when x = 1.
[(b) (i) 0.23 (ii) 0.27 (iii) 2.2]
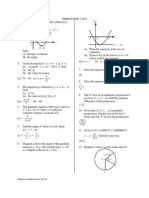
8. In Diagram 8, O is the centre of a
semicircle ABC with radius 12 cm and
OED is a right-angled triangle.
The length of arc AB is 10t cm and CE = 6
cm.
Find
[Use t = 3.142]
(a) the value of u, in radian,
(b) the perimeter, in cm, of the shaded
region P,
(c) the area, in cm
2
, of the shaded region Q.
[(a)
6
rad (b) 31.46 cm (c) 152.5
cm
2
]
9. (a) In an archery training, the probability
that Saiful hits the target is p. He made
10 trials and the mean of the number
of trials that hit the target is 3.5
Find
(i) the value of p,
(ii) the probability that he hits the
target at least twice.
(b) The mass of milk in packets produced
by a factory is normally distributed
with a mean of 300 g and a standard
deviation of 4 g.
(i) If a packet of milk is chosen at
random, find the probability that
the mass of milk in the packet is
between 298 g and 303 g.
(ii) The packet that contains less than
k g of milk cannot be marketed. If
0.5% of the milk cannot be
marketed, find the value of k.
[(a) (i) 0.35 (ii) 0.1757 (b) (i) 0.4649 (ii)
2289.7 kg]
10. Diagram 10 shows a trapezium ABCD.
Points A and D lie on the y-axis and DC is
parallel to AB.
It is given AB is perpendicular to BC and
the gradient of AB is
3
2
.
Find
(a) the equation of BC,
(b) the equation of DC and hence, find the
coordinates of C,
(c) the area of the shaded region OBCD,
(d) the equation of the locus of point P that
moves such that its distance from B is
always 10 units.
[(a) 3y + 2x = 32 (b) y =
3
11
2
x C(10, 4)
(c) 87 unit
2
(d) x
2
+ y
2
8x 16y 20 = 0]
11. Diagram 11 shows part of the curve y = x
2
4 which intersects the straight line y = x +
2 at point A.
Find
(a) the coordinates of A,
(b) the area of the shaded region Q,
(c) the volume generated, in terms of t,
when the shaded region P is revolved
360
o
about the y-axis.
[(a) (3, 5) (b) 8
1
6
unit
2
(c) 8t unit
3
]
SECTION C
12. Particle P and particle Q move
simultaneously along a straight line. The
displacement of P, s
p
m, from a fixed point
O, after t seconds is given by s
p
= t
3
8t
2
12t.
[Assume motion to the right as positive.]
(a) Find
(i) the displacement of P from O
when it stops momentarily,
(ii) the range of values of t when the
velocity of P is decreasing.
(b) It is given that the acceleration of Q, a
Q
m s
-2
, after t seconds, is given by a
Q
=
3t + 2 and its velocity is v
Q
ms
-1
. Both
particles P and Q have the same
velocity after 4 seconds.
Express v
Q
in terms of t.
[(a) (i) 144 m (ii) t <
8
3
(b) v
Q
=
2
3
2
t
+ 2t
60]
13. Diagram 13 shows a quadrilateral KLMN
where KM and LN are straight lines.
It is given that ZKLM is an obtuse angle
and the area of triangle KLM is 6 cm
2
.
Calculate
(a) ZKLM
(b) the length, in cm, of KM,
(c) ZKNM,
(d) the area, in cm
2
, of triangle KNM.
[(a) 121
o
(b) 6.532 cm (c) 51
o
51' (d)
21.81 cm
2
]
14. Table 14 shows the prices and price indices
of four ingredients, P, Q, R and S used in
making a particular type of bread.
Ingredient
Price per kg
(RM)
Price index
in the year
2008 based
on 2006
Weightage
2006 2008
P 0.80 1.00 125 k
Q y 2.80 140 5
R 0.40 0.60 x 3
S 0.50 z 80 2k
(a) Find the value of x, y and z.
(b) The composite index for the cost of
making the bread in the year 2008
based on the year 2006 is 114.5.
Calculate the value of k.
(c) The total cost for making these breads
in the year 2008 is RM2061, find the
corresponding total cost in the year
2006.
(d) The cost of making these breads is
expected to increase by 20% from the
year 2008 to the year 2010. Find the
expected composite index for the year
2010 based on the year 2006.
[(a) x = 150, y = 2 z = 0.40 (b) 4 (c)
1800 (d) 137.4]
15. A bookstore sells two types of calculators,
A and B. The cost price for a unit of
calculator A and calculator B is RM40 and
RM30 respectively. The bookstore ordered
x type A calculators and y type B
calculators based on the following
constraints:
I: The total number of calculators is at
least 35.
II: The total cost price is at most RM2400.
III: The number of type B calculators must
be at most twice the number of type A
calculators.
(a) Write three inequalities, other than x
0 and y 0 which satisfy all the above
constraints.
(b) Using a scale of 2 cm to 10 calculators
on both axes, construct and shade the
region R which satisfies the above
constraints.
(c) Use your graph in 15(b) to answer the
following questions:
(i) If 30 type A calculators are
ordered, find the minimum
number of type B calculator
which can be ordered.
(ii) The profit for selling a unit of
type A and type B calculator is
RM10 and RM15 respectively.
Find the maximum profit which
can be obtained.
[(a) x + y 35, 4x + 3y 240, y 2x
(c) (i) 5 (ii) RM960 when x = 24, y = 48]
Você também pode gostar
- Selangor 2011 P2Documento4 páginasSelangor 2011 P2Sim Kwang YawAinda não há avaliações
- SPM 2011 Paper 2Documento4 páginasSPM 2011 Paper 2Sim Kwang YawAinda não há avaliações
- SPM Additional Mathematics Paper 2 + AnsDocumento3 páginasSPM Additional Mathematics Paper 2 + AnsSim Kwang Yaw46% (13)
- Times 2012 Paper 2Documento5 páginasTimes 2012 Paper 2kysimAinda não há avaliações
- June 1988 - June 1997 Maths Paper 2Documento38 páginasJune 1988 - June 1997 Maths Paper 2Jerilee SoCute Watts0% (1)
- Maths Paper 2 November 2005Documento10 páginasMaths Paper 2 November 2005sandieletasAinda não há avaliações
- Add Maths Form 5 2013Documento2 páginasAdd Maths Form 5 2013Rohana YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of SPM Questions Form 4Documento8 páginasAnalysis of SPM Questions Form 4Jarnice Ling Yee ChingAinda não há avaliações
- Times Paper 1 2012Documento3 páginasTimes Paper 1 2012kysimAinda não há avaliações
- Add Maths Form 5 - First Monthly TestDocumento2 páginasAdd Maths Form 5 - First Monthly TestSerene Ser100% (1)
- Mathematics CXC 2011Documento12 páginasMathematics CXC 2011dggoode100% (1)
- 4exp AM Prelim7 P1Documento4 páginas4exp AM Prelim7 P1John GohAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Paper 2 June 2000Documento12 páginasMaths Paper 2 June 2000Tinashe KamusaireAinda não há avaliações
- Revision W9TueDocumento3 páginasRevision W9Tuemohamad_bidariAinda não há avaliações
- Kcse 2010 Mathematics Paper 2Documento6 páginasKcse 2010 Mathematics Paper 2isaacAinda não há avaliações
- Additional Mathematics 2002 November Paper 1Documento8 páginasAdditional Mathematics 2002 November Paper 1lornarifaAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Series 3 P2Documento3 páginasPractice Series 3 P2Ravendran MunianAinda não há avaliações
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education MathematicsDocumento8 páginasUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education MathematicsnshoulyAinda não há avaliações
- Answer All Questions 1Documento16 páginasAnswer All Questions 1Anonymous NRauXdoGAinda não há avaliações
- ICSE Math 2Documento6 páginasICSE Math 2Sanjay SuryadevraAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Paper 2 June 2001Documento11 páginasMaths Paper 2 June 2001Shelin FarmerAinda não há avaliações
- s4 General Graded MathsDocumento96 páginass4 General Graded MathsAnonymous R7NoMuy8Ainda não há avaliações
- 4exp AM Prelim2 P1Documento3 páginas4exp AM Prelim2 P1John GohAinda não há avaliações
- Gerak Gempur 4Documento23 páginasGerak Gempur 4Ru FangAinda não há avaliações
- Thirty: Time: Hours Minutes Instruction: A, All Four From B AltDocumento6 páginasThirty: Time: Hours Minutes Instruction: A, All Four From B AltsewcinAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Paper 1 Part 1 Questions & Answers O'levelDocumento110 páginasMathematics Paper 1 Part 1 Questions & Answers O'levelSsonko EdrineAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Form 2Documento22 páginasMaths Form 2HaziraAzlyAinda não há avaliações
- Untitled DocumentDocumento4 páginasUntitled DocumentAnany SinghAinda não há avaliações
- S4 N5 BT1 Revision SheetDocumento11 páginasS4 N5 BT1 Revision SheetMarisa VetterAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 3 - Linear FunctionDocumento3 páginasTutorial 3 - Linear FunctionWan Muhammad Abdul HakimAinda não há avaliações
- Modul SPM Set 8 (Latih Tubi)Documento8 páginasModul SPM Set 8 (Latih Tubi)nizafzAinda não há avaliações
- Differentiation 3Documento11 páginasDifferentiation 3Sc KhooAinda não há avaliações
- ICSE 10th Class MP-IIIDocumento8 páginasICSE 10th Class MP-IIIJotham SolomonAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Addmaths SPM: K HX X X FDocumento2 páginasRevision Addmaths SPM: K HX X X Fmohamad_bidariAinda não há avaliações
- Ajc H2 Math P1Documento6 páginasAjc H2 Math P1jimmytanlimlongAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics (4024) Dec 2001 Paper 2Documento12 páginasMathematics (4024) Dec 2001 Paper 2Jones Cheche100% (1)
- Maths Form2 - RevisionDocumento23 páginasMaths Form2 - RevisionNK2884% (49)
- Mathematics, Sum M Ative Assessm Ent - Ii Class X D Esign of The Question PaperDocumento17 páginasMathematics, Sum M Ative Assessm Ent - Ii Class X D Esign of The Question PaperSwaapnil ShindeAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 James Ruse Agricultural HS Ext 2Documento26 páginas2015 James Ruse Agricultural HS Ext 2omhreemaimhreemAinda não há avaliações
- Core 2 Revision Pack PDFDocumento55 páginasCore 2 Revision Pack PDFcandimathsAinda não há avaliações
- Retyped by Mr. Sim Kwang YawDocumento3 páginasRetyped by Mr. Sim Kwang YawtheuniquecollectionAinda não há avaliações
- Additional Mathematics 2003 November Paper 1Documento8 páginasAdditional Mathematics 2003 November Paper 1lornarifaAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Paper 2 November 1999Documento12 páginasMaths Paper 2 November 1999Peaarson GuveyaAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics: Higher School Certificate ExaminationDocumento16 páginasMathematics: Higher School Certificate ExaminationAlan TruongAinda não há avaliações
- S4 MathsDocumento5 páginasS4 Mathsbulemuibrahim6746Ainda não há avaliações
- IB Math SL Review Worksheet Packet 14Documento10 páginasIB Math SL Review Worksheet Packet 14Rebe SerranoAinda não há avaliações
- Class 2 Maths AssessmentDocumento19 páginasClass 2 Maths Assessmentthird100% (1)
- RevisionDocumento1 páginaRevisionhpchen9407Ainda não há avaliações
- Set 2 MathDocumento6 páginasSet 2 Mathgassygowri11Ainda não há avaliações
- 10icse Prelim PaperDocumento7 páginas10icse Prelim PapertraderprabhakarAinda não há avaliações
- X - B y - 10 Have A Solution X 2, y 3.: DX Dy DX DyDocumento3 páginasX - B y - 10 Have A Solution X 2, y 3.: DX Dy DX DyJohn GohAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics 4016/02: School BDocumento10 páginasMathematics 4016/02: School BJoanne ErAinda não há avaliações
- Blue Print: Sa-Ii (Ix) : Mathematics.: MensurationDocumento19 páginasBlue Print: Sa-Ii (Ix) : Mathematics.: Mensurationapi-243565143Ainda não há avaliações
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 7 Maths Set 3: All Questions Are CompulsoryDocumento4 páginasCBSE Sample Paper Class 7 Maths Set 3: All Questions Are Compulsorysupriya028Ainda não há avaliações
- Acs I Y4 Prelim Em2 2010Documento10 páginasAcs I Y4 Prelim Em2 2010math3matics3Ainda não há avaliações
- Kerala MATHEMATICS X STANDARD-SET 2Documento10 páginasKerala MATHEMATICS X STANDARD-SET 2naeblahblahAinda não há avaliações
- Sky Trial Exam p1Documento3 páginasSky Trial Exam p1kysimAinda não há avaliações
- Sky Trial Examination p2Documento4 páginasSky Trial Examination p2kysimAinda não há avaliações
- Sky Trial Examination p2Documento4 páginasSky Trial Examination p2kysimAinda não há avaliações
- Pulau Pinang 2011 p1Documento3 páginasPulau Pinang 2011 p1Sim Kwang YawAinda não há avaliações
- Examples - Combined StressDocumento14 páginasExamples - Combined Stressamdeva100% (1)
- Chapter No 3 Dynamics Class 9thDocumento53 páginasChapter No 3 Dynamics Class 9thKaka KAinda não há avaliações
- General Physics 1: Laws of MotionDocumento4 páginasGeneral Physics 1: Laws of MotionRobert RosarioAinda não há avaliações
- Dynapocket: Pocket-Size Hardness Tester Standardized To ASTM A 956Documento4 páginasDynapocket: Pocket-Size Hardness Tester Standardized To ASTM A 956napster386Ainda não há avaliações
- Vishal Chemistry Project CompleteDocumento16 páginasVishal Chemistry Project CompleteKislaya Mishra0% (1)
- Orbiting Solar Observatory Satellite OSO-1 The Project SummaryDocumento310 páginasOrbiting Solar Observatory Satellite OSO-1 The Project SummaryBob Andrepont100% (1)
- Pig OlgaDocumento24 páginasPig OlgaCitlalli QuetzalcoatlAinda não há avaliações
- Singular Value Decomposition - Lecture NotesDocumento87 páginasSingular Value Decomposition - Lecture NotesRoyi100% (1)
- Introduction To Numerical Methods in Chemical Engineering. Pradeep Ahuja. PHI Learning, India, 2010Documento299 páginasIntroduction To Numerical Methods in Chemical Engineering. Pradeep Ahuja. PHI Learning, India, 2010Anonymous 8mxTh1m60% (5)
- Agitator Vessel (Design&Costing)Documento34 páginasAgitator Vessel (Design&Costing)imrancenakk100% (2)
- Color and PleochroismDocumento22 páginasColor and PleochroismdeshmukhgeolAinda não há avaliações
- 93x1B - 000-107e-10.10 - Data SheetDocumento5 páginas93x1B - 000-107e-10.10 - Data SheetCostel CostescuAinda não há avaliações
- Matrices For Linear TransformationsDocumento31 páginasMatrices For Linear TransformationsPilar ZárateAinda não há avaliações
- Origin of The Universe 101 - National GeographicDocumento2 páginasOrigin of The Universe 101 - National GeographicColeen Jade CondinoAinda não há avaliações
- (Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances 12) Klaus Florey (Eds.) - Academic Press (1983) PDFDocumento736 páginas(Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances 12) Klaus Florey (Eds.) - Academic Press (1983) PDFngochieu_909Ainda não há avaliações
- PhysicsDocumento283 páginasPhysicsBogdan GlodeanuAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Chemistry Lecture 2Documento62 páginasApplied Chemistry Lecture 2Muhammad RafayAinda não há avaliações
- Polarity of MoleculesDocumento10 páginasPolarity of MoleculesglennAinda não há avaliações
- Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes The Solid StateDocumento21 páginasClass 12 Chemistry Revision Notes The Solid StateAfreen AnzAinda não há avaliações
- Amca 99Documento85 páginasAmca 99simonlia100% (5)
- 02 Chapter 2 - Force VectorDocumento20 páginas02 Chapter 2 - Force VectorShaun KerouacAinda não há avaliações
- Coordination Compound - Theory, Solved Ex. Module-3-2Documento23 páginasCoordination Compound - Theory, Solved Ex. Module-3-2Raju SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Gas LawsDocumento66 páginasGas LawsLorilieAinda não há avaliações
- The Principle of Uncertainty - GamowDocumento9 páginasThe Principle of Uncertainty - GamowPPAAAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Square Footing (Final)Documento10 páginasDesign of Square Footing (Final)Atta E Mustafa MughalAinda não há avaliações
- Notes 20 DC 20 MetersDocumento15 páginasNotes 20 DC 20 MetersAnonymous NFTqyEfoPAinda não há avaliações
- M SC Syllabus Applied Mathematics PhysicsDocumento20 páginasM SC Syllabus Applied Mathematics PhysicsComradeAinda não há avaliações
- Cylindrical Tubular Members: 7.1 General RemarksDocumento22 páginasCylindrical Tubular Members: 7.1 General RemarksfirmanrusydiAinda não há avaliações
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocumento6 páginasDiffusion and OsmosisWacoomo TaroomaAinda não há avaliações
- Cov MainDocumento33 páginasCov MainSugunaAinda não há avaliações