Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Financial Services Material
Enviado por
rajsimiestDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Financial Services Material
Enviado por
rajsimiestDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Business Financial Services Meaning: Financial service is defined as a service provided by the financial group, which encompasses with
a broad range of organizations that deal with the management of money. This can be done in different forms like savings account, checking account, leasing, money transfer, and more. Generally all types of activities which are related to financial nature could be called as financial services. It also means that mobilizing and allocating savings. So, it includes all activities of transformation into investments. It is otherwise also called as intermediation because it is a place where funds are mobilizing from a huge number of savers to all those who are in need of money especially for the corporate consumers. Thus it is considered to be the key area for industrial developers. Definition: As per section 65(10) of the Finance Act, 1994, banking and financial services means the following services provided by a banking company or a financial institution including a non banking financial company, namely; financial leasing services including equipment leasing and hire-purchase by a body corporate; credit card services; merchant banking services; securities and foreign exchange (forex) broking; asset management including portfolio management, all forms of fund management, pension fund management, custodial depository and trust services, but does not include cash management; advisory and other auxiliary financial services including investment and portfolio research and advice, advice on mergers and acquisition and advice on corporate restructuring and strategy; and provision and transfer of information and data processing. Financial services can be defined as the products and services offered by institutions like banks of various kinds for the facilitation of various financial transactions and other related activities in the world of finance like loans, insurance, credit cards, investment opportunities and money management as well as providing information on the stock market and other issues like market trends Financial services refer to services provided by the finance industry. The
finance industry encompasses a broad range of organizations that deal with the management of money. Among these organizations are banks, credit card companies, insurance companies, consumer finance companies, stock brokerages, investment funds and some government sponsored enterprises. Functions of financial services 1. Facilitating transactions (exchange of goods and services) in the economy. 2. Mobilizing savings (for which the outlets would otherwise be much more limited). 3. Allocating capital funds (notably to finance productive investment).
4. Monitoring managers (so that the funds allocated will be spent as envisaged). 5. Transforming risk (reducing it through aggregation and enabling it to be carried by those more willing to bear it). Characterstics and Features of Financial Services i) Customer-Specific: Financial services are usually customer focused. The firms providing these services, study the needs of their customers in detail before deciding their financial strategy, giving due regard to costs, liquidity and maturity considerations. Financial services firms continuously remain in touch with their customers, so that they can design products which can cater to the specific needs of their customers. The providers of financial services constantly carry out market surveys, so they can offer new products much ahead of need and impending legislation. Newer technologies are being used to introduce innovative, customer friendly products and services which clearly indicate that the concentration of the providers of financial services is on generating firm/customer specific services. ii) Intangibility: In a highly competitive global environment brand image is very crucial. Unless the financial institutions providing financial products and services have good image, enjoying the confidence of their clients, they may not be successful. Thus institutions have to focus on the quality and innovativeness of their services to build up their credibility. iii) Concomitant: Production of financial services and supply of these services have to be concomitant. Both these functions i.e. production of new and innovative financial services and supplying of these services are to be performed simultaneously. iv) Tendency to Perish: Unlike any other service, financial services do tend to perish and hence cannot be stored. They have to be supplied as required by the customers. Hence financial institutions have to ensure a proper synchronization of demand and supply. v) People based services: Marketing of financial services has to be people intensive and hence its subjected to variability of performance or quality of
service. The personnel in financial services organisation need to be selected on the basis of their suitability and trained properly, so that they can perform their activities efficiently and effectively. vi) Market Dynamics: The market dynamics depends to a great extent, on socioeconomic changes such as disposable income, standard of living and educational changes related to the various classes of customers. Therefore financial services have to be constantly redefined and refined taking into consideration the market dynamics. The institutions providing financial services, while evolving new services could be proactive in visualising in advance what the market wants, or being reactive to the needs and wants of their customers. Scope of Financial Services Financial services cover a wide range of activities. They can be broadly classified into two, namely: i. ii. Traditional. Activities Modern activities.
i. Traditional Activities Traditionally, the financial intermediaries have been rendering a wide range of services encompassing both capital and money market activities. They can be grouped under two heads, viz. 1. Fund based activities and 2. Non-fund based activities. Fund based activities: The traditional services which come under fund based activities are the following: Underwriting or investment in shares, debentures, bonds, etc. of new issues (primary market activities). Dealing in secondary market activities. Participating in money market instruments like commercial Papers, certificate of deposits, treasury bills, discounting of bills etc. Involving in equipment leasing, hire purchase, venture capital, seed capital, Dealing in foreign exchange market activities. Non fund based activities Non fund based activities Financial intermediaries provide services on the basis of non-fund activities also. This can be called fee based activity. Today customers, whether individual or corporate, are not satisfied with mere provisions of finance.
They expect more from financial services companies. Hence a wide variety of services, are being provided under this head. They include: Managing the capital issue i.e. management of pre-issue and postissue activities relating to the capital issue in accordance with the SEBI guidelines and thus enabling the promoters to market their issue. Making arrangements for the placement of capital and debt instruments with investment institutions. Arrangement of funds from financial institutions for the clients project cost or his working capital requirements. Assisting in the process of getting all Government and other clearances. ii. Modern Activities Beside the above traditional services, the financial intermediaries render innumerable services in recent times. Most of them are in the nature of nonfund based activity. In view of the importance, these activities have been in brief under the head New financial products and services. However, some of the modern services provided by them are given in brief hereunder. Rendering project advisory services right from the preparation of the project report till the raising of funds for starting the project with necessary Government approvals. Planning for M&A and assisting for their smooth carry out. Guiding corporate customers in capital restructuring. Acting as trustees to the debenture holders. Recommending suitable changes in the management structure and management style with a view to achieving better results. Structuring the financial collaborations / joint ventures by identifying suitable joint venture partners and preparing joint venture agreements. Rehabilitating and restructuring sick companies through appropriate scheme of reconstruction and facilitating the implementation of the scheme. Hedging of risks due to exchange rate risk, interest rate risk, economic risk, and political risk by using swaps and other derivative products. Managing In- portfolio of large Public Sector Corporations. Undertaking risk management services like insurance services, buy-hack options etc.
Advising the clients on the questions of selecting the best source of funds taking into consideration the quantum of funds required, their cost, lending period etc. Guiding the clients in the minimization of the cost of debt and in the determination of the optimum debt-equity mix. Promoting credit rating agencies for the purpose of rating companies which want to go public by the issue of debt instrument. Undertaking services relating to the capital market, such as 1)Clearing services, 2)Registration and transfers, 3)Safe custody of securities, 4)Collection of income on securities. What Is Economic Environment? Introduction:- Various environmental factors such as economic environment, socio-cultural environment, political, technological, demographic and international, affect the business and its working. Out of these factors economic environment is the most important factor. Meaning of Economic Environment:- Those Economic factors which have their affect on the working of the business is known as economic environment. It includes system, policies and nature of an economy, trade cycles, economic resources, level of income, distribution of income and wealth etc. Economic environment is very dynamic and complex in nature. It does not remain the same. It keeps on changing from time to time with the changes in an economy like change in Govt. policies, political situations. Elements of Economic Environment:- It has mainly five main components:1. Economic Conditions 2. Economic System 3. Economic Policies 4. International Economic Environment 5. Economic Legislations Economic Conditions:- Economic Policies of a business unit are largely affected by the economic conditions of an economy. Any improvement in the economic conditions such as standard of living, purchasing power of public, demand and supply, distribution of income etc. largely affects the size of the market. Business cycle is another economic condition that is very important for a business unit. Business Cycle has 5 different stages viz. (i) Prosperity, (ii) Boom, (iii) Decline, (iv) Depression, (v) Recovery. Following are mainly included in Economic Conditions of a country:-
I. Stages of Business Cycle II. National Income, Per Capita Income and Distribution of Income III. Rate of Capital Formation IV. Demand and Supply Trends V. Inflation Rate in the Economy VI. Industrial Growth Rate, Exports Growth Rate VII. Interest Rate prevailing in the Economy VIII. Trends in Industrial Sickness IX. Efficiency of Public and Private Sectors X. Growth of Primary and Secondary Capital Markets XI. Size of Market Economic Systems:- An Economic System of a nation or a country may be defined as a framework of rules, goals and incentives that controls economic relations among people in a society. It also helps in providing framework for answering the basic economic questions. Different countries of a world have different economic systems and the prevailing economic system in a country affect the business units to a large extent. Economic conditions of a nation can be of any one of the following type:1. Capitalism:- The economic system in which business units or factors of production are privately owned and governed is called Capitalism. The profit earning is the sole aim of the business units. Government of that country does not interfere in the economic activities of the country. It is also known as free market economy. All the decisions relating to the economic activities are privately taken. Examples of Capitalistic Economy:- England, Japan, America etc. 2. Socialism:- Under socialism economic system, all the economic activities of the country are controlled and regulated by the Government in the interest of the public. The first country to adopt this concept was Soviet Russia. The two main forms of Socialism are: (a) Democratic Socialism:- All the economic activities are controlled and regulated by the government but the people have the freedom of choice of occupation and consumption.
(b) Totalitarian Socialism:- This form is also known as Communism. Under this, people are obliged to work under the directions of Government. 3. Mixed Economy:- The economic system in which both public and private sectors co-exist is known as Mixed Economy. Some factors of production are privately owned and some are owned by Government. There exists freedom of choice of occupation and consumption. Both private and public sectors play key roles in the development of the country. Economic Policies:- Government frames economic policies. Economic Policies affects the different business units in different ways. It may or may not have favorable effect on a business unit. The Government may grant subsidies to one business or decrease the rates of excise or custom duty or the government may increase the rates of custom duty and excise duty, tax rates for another business. All the business enterprises frame their policies keeping in view the prevailing economic policies. Important economic policies of a country are as follows:1. Monetary Policy:- The policy formulated by the central bank of a country to control the supply and the cost of money (rate of interest), in order to attain some specified objectives is known as Monetary Policy. 2. Fiscal Policy:- It may be termed as budgetary policy. It is related with the income and expenditure of a country. Fiscal Policy works as an instrument in economic and social growth of a country. It is framed by the government of a country and it deals with taxation, government expenditure, borrowings, deficit financing and management of public debts in an economy. 3. Foreign Trade Policy:- It also affects the different business units differently. E.g. if restrictive import policy has been adopted by the government then it will prevent the domestic business units from foreign competition and if the liberal import policy has been adopted by the government then it will affect the domestic products in other way. 4. Foreign Investment Policy:- The policy related to the investment by the foreigners in a country is known as Foreign Investment Policy. If the government has adopted liberal investment policy then it will lead to more inflow of foreign capital in the country which ultimately results in more industrialization and growth in the country.
5. Industrial Policy:- Industrial policy of a country promotes and regulates the industrialization in the country. It is framed by government. The government from time to time issues principals and guidelines under the industrial policy of the country. Global/International Economic Environment:- The role of international economic environment is increasing day by day. If any business enterprise is involved in foreign trade, then it is influenced by not only its own country economic environment but also the economic environment of the country from/to which it is importing or exporting goods. There are various rules and guidelines for these trades which are issued by many organizations like World Bank, WTO, United Nations etc. Economic Legislations:- Besides the above policies, Governments of different countries frame various legislations which regulates and control the business.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Hedge Fund Accounting PDFDocumento295 páginasHedge Fund Accounting PDFBalaji Mundhe100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
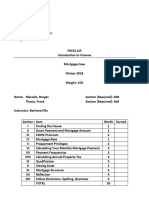
- 1 - Mortgage Case Winter 2018Documento8 páginas1 - Mortgage Case Winter 2018Marcelo BorgesAinda não há avaliações
- KFS3122 Entrepreneurship Slides 8Documento37 páginasKFS3122 Entrepreneurship Slides 8Poovarashan ManimaranAinda não há avaliações
- Somaliland Revenue Act 2016 English v2Documento129 páginasSomaliland Revenue Act 2016 English v2Mohamed DaudAinda não há avaliações
- 2009 Taxation Law ReviewerDocumento203 páginas2009 Taxation Law ReviewerDoctorGreyAinda não há avaliações
- 08) RCBC V Royal CargoDocumento2 páginas08) RCBC V Royal CargokathreenmonjeAinda não há avaliações
- (G.R. NO. 190144 - August 1, 2012) Bank of The Philippine Islands, Petitioner, v. CARLITO LEE, Respondent. DecisionDocumento105 páginas(G.R. NO. 190144 - August 1, 2012) Bank of The Philippine Islands, Petitioner, v. CARLITO LEE, Respondent. DecisionNikkiAinda não há avaliações
- Lupin FinalDocumento37 páginasLupin FinalShruti Mathur100% (1)
- 3 - Building A Problem-Solving Culture PDFDocumento7 páginas3 - Building A Problem-Solving Culture PDFJdalliXAinda não há avaliações
- How To Game Your Sharpe RatioDocumento21 páginasHow To Game Your Sharpe RatioCervino InstituteAinda não há avaliações
- Business Analysis ReportDocumento13 páginasBusiness Analysis Reporthassan_401651634Ainda não há avaliações
- BSBFIA412 - AssessmentPi 2Documento17 páginasBSBFIA412 - AssessmentPi 2Pattaniya KosayothinAinda não há avaliações
- Sunanda Jha & Dinabandhu BagDocumento4 páginasSunanda Jha & Dinabandhu Bagdinabandhu_bagAinda não há avaliações
- ACCTG 112 Chapter 2Documento1 páginaACCTG 112 Chapter 2C E DAinda não há avaliações
- FOREX Funded Account Evaluation My Forex Funds 2Documento1 páginaFOREX Funded Account Evaluation My Forex Funds 2SujitKGoudarAinda não há avaliações
- Olam Brokers' ReportDocumento9 páginasOlam Brokers' Reportsananth60100% (1)
- GAC+JD FinalsDocumento3 páginasGAC+JD FinalsAmod JadhavAinda não há avaliações
- IC 38 Short Notes (2) 61Documento1 páginaIC 38 Short Notes (2) 61Anil KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Agard Case SummaryDocumento4 páginasAgard Case SummaryQuerpAinda não há avaliações
- Selling and Sales Management - Chapter 5Documento45 páginasSelling and Sales Management - Chapter 5albgatmtyAinda não há avaliações
- Mica - 2019 03 en PDFDocumento116 páginasMica - 2019 03 en PDFrichaAinda não há avaliações
- Multinational Business Finance 15th Edition Eiteman Test BankDocumento14 páginasMultinational Business Finance 15th Edition Eiteman Test Bankmisavizebrigadeuieix100% (26)
- The Parable of The Pipeline PDFDocumento4 páginasThe Parable of The Pipeline PDFsusvarAinda não há avaliações
- Wallstreetjournalasia 20170621 The Wall Street Journal AsiaDocumento22 páginasWallstreetjournalasia 20170621 The Wall Street Journal AsiaKoutsoupisAinda não há avaliações
- Itad Bir Ruling No. 191-15 Uk VatDocumento8 páginasItad Bir Ruling No. 191-15 Uk VatKarla TigaronitaAinda não há avaliações
- Code of Business Ethics and ConductDocumento7 páginasCode of Business Ethics and ConductShane NaidooAinda não há avaliações
- Filing From Bondurant's Landlord, The Sun Marina Valley Development CorporationDocumento8 páginasFiling From Bondurant's Landlord, The Sun Marina Valley Development CorporationStefAinda não há avaliações
- A Simple Day Trading Strategy Using Bollinger & MACD - Trading Setups Review PDFDocumento15 páginasA Simple Day Trading Strategy Using Bollinger & MACD - Trading Setups Review PDFzooor100% (1)
- Cases - August 25, 2017Documento19 páginasCases - August 25, 2017nellafayericoAinda não há avaliações
- Advocacy Strategy ManualDocumento53 páginasAdvocacy Strategy ManualINFID JAKARTA100% (1)