Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Bench Marking
Enviado por
Renuga DeviDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Bench Marking
Enviado por
Renuga DeviDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
BENCHMARKING Benchmarking is the process of comparing one's business processes and performance metrics to industry bests and/or best
practices from other industries There is no single benchmarking process that has been universally
adopted. The wide appeal and acceptance of benchmarking has led to the emergence of various benchmarking methodologies The 12 stage methodology consists of: 1. Select subject 2. Define the process 3. Identify potential partners
4. Identify data sources 5. Collect data and select partners 6. Determine the gap 7. Establish process differences 8. Target future performance 9. Communicate 10.Adjust goal 11.Implement 12.Review and recalibrate
Types Process benchmarking - the initiating firm focuses its observation and investigation of business processes with a goal of identifying and observing the best practices from one or more benchmark firms. Activity analysis will be required where the objective is to
benchmark cost and efficiency; increasingly applied to back-office processes where outsourcing may be a consideration. Financial benchmarking performing a financial analysis and comparing the results in an effort to assess your overall competitiveness and productivity.
Benchmarking from an investor perspective- extending the benchmarking universe to also compare to peer companies that can be considered alternative investment opportunities from the perspective of an investor. Performance benchmarking - allows
the initiator firm to assess their competitive position by comparing products and services with those of target firms. Product benchmarking - the process of designing new products or upgrades to current ones. This process can sometimes involve reverse engineering
which is taking apart competitors products to find strengths and weaknesses. Strategic benchmarking involves observing how others compete. This type is usually not industry specific, meaning it is best to look at other industries. Functional benchmarking - a
company will focus its benchmarking on a single function to improve the operation of that particular function. Complex functions such as Human Resources, Finance and Accounting and Information and Communication Technology are unlikely to be directly comparable in cost and
efficiency terms and may need to be disaggregated into processes to make valid comparison. Best-in-class benchmarking involves studying the leading competitor or the company that best carries out a specific function. Operational benchmarking -
embraces everything from staffing and productivity to office flow and analysis of [4] procedures performed. Energy benchmarking - developing an accurate model of a building's energy consumption with the purpose of measuring reductions in usage.
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
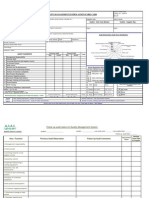
- QMS Audit Check SheetDocumento7 páginasQMS Audit Check Sheetaboo2uAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- 360 Degree Appraisal Feedback FormDocumento2 páginas360 Degree Appraisal Feedback FormSamantha Ysabel PasayloAinda não há avaliações
- Management Leading and Collaborating in A Competitive World 13th Edition Bateman Solutions ManualDocumento25 páginasManagement Leading and Collaborating in A Competitive World 13th Edition Bateman Solutions ManualMichaelPruittewnr100% (57)
- The Boston Consulting GroupDocumento9 páginasThe Boston Consulting GroupVipul AggarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Managing Quality Integrating The Supply Chain 5th Edition by Foster - CramDocumento62 páginasTest Bank For Managing Quality Integrating The Supply Chain 5th Edition by Foster - Cramzahid aliAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Value Chain AnalysisDocumento10 páginasWhat Is Value Chain Analysiskellykat64100% (15)
- Technological Innovation: Melissa A. SchillingDocumento10 páginasTechnological Innovation: Melissa A. SchillingSam100% (1)
- 01-Marketing Channel ConceptsDocumento27 páginas01-Marketing Channel ConceptsAshi GargAinda não há avaliações
- PSWDocumento1 páginaPSWIonut EduardAinda não há avaliações
- Relevant Cost For Decission MakingDocumento17 páginasRelevant Cost For Decission MakingMichelle Pratiwi TjioeAinda não há avaliações
- Department of CSIT: ON Hospital Management SystemDocumento17 páginasDepartment of CSIT: ON Hospital Management SystemVikas NayakAinda não há avaliações
- Performance Appraisal Officer: Procurement TeamDocumento1 páginaPerformance Appraisal Officer: Procurement TeamTasneva TasnevaAinda não há avaliações
- AMBOTDocumento2 páginasAMBOTAngelyn SamandeAinda não há avaliações
- An Integrated System ApproachDocumento20 páginasAn Integrated System ApproachEhsan AlikhaniAinda não há avaliações
- 487.assignment Brief 2 (V6.2020 - 2021)Documento3 páginas487.assignment Brief 2 (V6.2020 - 2021)Le Minh ThanhAinda não há avaliações
- AMAN CHUGH (10P125) Amrita Nadkarni (10P126) RAHUL KUMAR (10P162) RAHUL SHARMA (10P163) MOHIT GUPTA (10P151) Preety Bansal (10Fpm58)Documento11 páginasAMAN CHUGH (10P125) Amrita Nadkarni (10P126) RAHUL KUMAR (10P162) RAHUL SHARMA (10P163) MOHIT GUPTA (10P151) Preety Bansal (10Fpm58)Amrita NadkarniAinda não há avaliações
- Organizational Development PDFDocumento1 páginaOrganizational Development PDFMohammed Razwin K P0% (1)
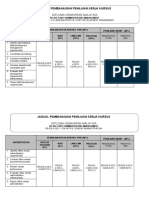
- Jadual Pembahagian Penilaian Kerja Kursus L4Documento4 páginasJadual Pembahagian Penilaian Kerja Kursus L4Izzati SalbiyanaAinda não há avaliações
- Session - 2 - Relation MarketingDocumento25 páginasSession - 2 - Relation MarketingFarhan Islam100% (1)
- Supplier Selection Assessment Check List - DBUDocumento26 páginasSupplier Selection Assessment Check List - DBUnathisonsAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Financial Accounting Canadian Canadian 7th Edition Beechy Solutions Manual 1Documento87 páginasAdvanced Financial Accounting Canadian Canadian 7th Edition Beechy Solutions Manual 1gilbertAinda não há avaliações
- Table of ContentDocumento6 páginasTable of ContentMohammad C. DatuganAinda não há avaliações
- MM 18-19Documento2 páginasMM 18-19BrijmohanAinda não há avaliações
- A Case Study of Mitsubishi Motor Sales: Presented To: Presented byDocumento10 páginasA Case Study of Mitsubishi Motor Sales: Presented To: Presented byMukesh Patel100% (2)
- Jan Kusters Modern Looking CVDocumento1 páginaJan Kusters Modern Looking CVJohnny Ronald Raymundo OliveraAinda não há avaliações
- IMSTDocumento2 páginasIMSTgssgopi9_389290943Ainda não há avaliações
- CRM in Sustainable Customer Loyalty Cathay PacificDocumento19 páginasCRM in Sustainable Customer Loyalty Cathay PacificHTMi Switzerland100% (2)
- CE511-Topic-1a Introduction Project Managment-352Documento25 páginasCE511-Topic-1a Introduction Project Managment-352leena samuelAinda não há avaliações
- Coal India LTDDocumento3 páginasCoal India LTDalone_readerAinda não há avaliações
- Domino's Case SolutionDocumento2 páginasDomino's Case SolutionPrachi Rajan100% (1)