Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
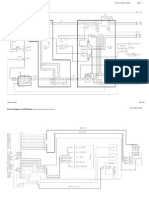
36 Isdn Exp
Enviado por
CauVong JustinDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
36 Isdn Exp
Enviado por
CauVong JustinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
www.sigmatrainers.
com
Since
21
Years
More
than
1500
Trainers
TRAINERS
SIGMA TRAINERS
AHMEDABAD (INDIA)
ISDN TRAINER
MODEL-ISDN100
EXPERIMENTAL MANUAL
INTRODUCTION
This trainer provides training of hardware and software theory of ISDN technology.
SPECIFICATION
(A) Computer Systems (2 Nos. ) (Optional)
1. CPU with fan : Intel Pentium IV 3. 0 GHz
2. Mother Board : 400 MHZ FSB
3. Memory (RAM) : 256 MB SDRAM
4. Display Adaptor card : On Board AGP 8 MB
5. Hard Disk : 80 GB ATA
6. Floppy Disk Drive : 1. 44 MB
7. Monitor : 15" Colour SVGA
8. Key board : 104 Keys Keyboard
9. Mouse : Logitech 1st Mouse with pad
10. SMPS : 200 Watts AT
(B) ISDN Hardware
1. Analog Telephones : 2 No.
2. ISDN Terminal Adaptor : 2 No.
3. ISDN Emulator : 1 No.
(C) Training Packages
1. ISDN Training software
User Manual 2 Port ISDN Simulator
1
Contents
Chapter 1: Important Information 3
General Disclaimer 3
Other Restrictions 3
Trademark Information 3
Patent information 3
Warranty 3
Limitation of Remedies and Damages 4
Important Safeguards 4
Regulatory Compliance 5
Chapter 2: Introduction 5
Unpacking 5
Fast Start for Advanced Users 5
About your ISDN Simulator 6
Chapter 3: Product Description 8
Ports / Interfaces 9
Power 10
Cabling 11
Controls 11
LEDs 11
Chapter 4: Conguring ISDN Simulator 12
Conguring the ISDN Simulator with ISDN Manager 12
Conguring ISDN Simulator via Terminal Server 15
SPID assignments 16
Upgrading Firmware 17
Chapter 5: ISDN Simulator and Cisco Routers 18
Layer 1 18
Layer 2 19
Troubleshooting 20
2 PorI lSDN SimulaIor User Manual
Chapter 6: Cisco Routers Conguration Examples 23
Basic-Net3 Switch Type Example 23
Basic-NI1 Switch Type Example 24
Chapter 7: Specications 25
2
Chapter 1: Important Information
General Disclaimer
No part of this document can be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, for any purpose without the written express permission from Virtual Console, LLC.
Under the law reproducing includes translating into another language or digital format.
As between the parties, Virtual Console, LLC retains title to, and ownership of, all proprietary rights with
respect to the software contained within its products. The software is protected by United States and
international copyright laws. Therefore, you must treat the software like any other copyrighted material.
Other Restrictions
You shall not and shall not allow any third party to decompile, disassemble, reverse-engineer or attempt to
reconstruct or discover any source code or underlying ideas or algorithms of the software by any means
whatsoever or remove any product.
Trademark Information
Virtual Console logo design is registered trademark in the United States and various other countries.
Microsoft, Windows are registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Every effort has been made to ensure that the
information in this manual is accurate. Information in this document is the subject to change without notice.
Patent Information
The accompanying product is protected by one or more U.S. and foreign patents and patents pending held by
Virtual Console, LLC
Warranty
Virtual Console, LLC warrants its products to be free of defects in materials and factory workmanship for a
period of twelve (12) months from date of purchase.
This warranty does not apply to damage to products resulting from accident, misuse, service or modication by
anyone other than a Virtual Console, LLC authorized service facility/dealer.
The warranty is limited to the original purchaser and is not transferable. Any liability of Virtual Console or its
suppliers with respect to the product or the performance thereof under any warranty, negligence, strict liability
or other theory will be limited exclusively to product repair or replacement as provided above.
3
2 Port ISDN Simulator
Except for the foregoing, the product is provided as is without warranty of any kind including without
limitation, any warranty of merchantability or tness for a particular purpose.
The entire risk of the quality and performance of the software programs contained in the system is with you.
Limitation of Remedies and Damages
Virtual Console, LLC, its agents, employees, suppliers, dealers and other authorized representatives shall
not be responsible or liable with respect to the product or any other subject matter related thereto under any
contract, negligence, strict liability or other theory for any indirect, incidental, or consequential damages,
including, but not limited to loss of information, business, or prots.
The law of certain states or nations does not permit limitation or exclusion of implied warranties and
consequential damages, so the above limitations, disclaimers, or exclusion may not apply to you. This
warranty gives you special legal rights. You may also have other rights that vary by state and nation.
Important Safeguards
Read and understand the following instructions before using the system:
Close supervision is necessary when the system is used by or near children. Do not leave unattended while in
use.
Always disconnect the system from power before cleaning and servicing and when not in use.
Do not spray liquids directly onto the system when cleaning. Always apply the liquid rst to a static free cloth.
Do not place this product onto unstable desk, cart or table. The product may fall causing serious damage to
the product.
Do not immerse the system in any liquid or place any liquids on it.
Do not disassemble this system (except as instructed in the manufacturers instructions). To reduce the risk of
shock and to maintain the warranty on the system, a qualied technician must perform service or repair work.
Connect this appliance to a grounded outlet.
Connect the system only to surge protected power outlets.
Keep ventilation openings free of any obstructions.
Unplug this product from the wall outlet and refer servicing to qualied service personnel under the following
conditions:
1. When the power supply adapter or plug is damaged or frayed.
2. If liquid has been spilled into the product.
3. If the product has been exposed to rain or water.
8. If the product has been dropped or the enclosure has been damaged.
9. If the product exhibits a distinct change in performance.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Regulatory Compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction
manual, may cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at
his own expense.
Chapter 2: Introduction
ISDN Simulator is a two port ISDN switch which was designed to ease testing, demonstration and
development of ISDN Basic Rate CPE (TE) equipment. It simulates two ISDN BRI lines reducing installation
and monthly charges from Telephone Company and provides full featured BRI lines for Voice, Data and Video
communications.
ISDN simulator is equipped with U (2 wire) and S/T (4 wire) interfaces, allowing to connect two devices with
either interface type, including mixed connection between U and S/T interfaces.
Unpacking
Carefully unpack the items in the shipping box and verify that you have received the following:
1. ISDN Simulator unit
2. Wall mount power adapter
3. ISDN Manager Conguration Diskette
4. DB9F-DB9M 6-ft RS-232 cable for connection to a PC.
Fast Start for Advanced Users
1. Plug the power adapter into a 120 VAC outlet, and connect the DC power cable to the power jack on
your simulator.
2. Make the physical connection(s) between the device(s) for which you want ISDN connections with the
ISDN simulator.
3. Connect the terminal port to a terminal, or a PC with a terminal emulator.
4. Issue commands or use ISDN Manager GUI interface to congure the switch type that you need to
simulate, and any options appropriate for that switch type.
About your ISDN Simulator
Virtual Consoles ISDN simulator is a two port ISDN switch that provides call switching services for Basic
Rate Interface (BRI) terminal equipment. All our ISDN simulators conform to the ISDN architecture and to
individually programmable switch types (Table 1). Our products are extensively used with Cisco equipment
and are tested for compatibility with most of the ISDN-capable Cisco routers, including the 1600, 1700, 2500,
2600 and 3600 series.
Table 1: Switch Types Emulated
Switch Type Cisco conguration command SPID required
National ISDN-1 isdn switch-type basic-ni1 Yes
NET3 isdn switch-type basic-net3 No
AT&T 5ESS isdn switch-type basic-5ess Optional
Nortel DMS-100 isdn switch-type basic-dms100 Yes
Figure 1: ISDN Functional Architecture
The ISDN simulator appears to the customer-side Functional Groupings as the Loop Termination (LT) at
the telephone central ofce. These Functional Groupings, examples of which are shown in, include ISDN-
compliant Terminal Equipment (TE1), Network Terminations (NT1 and NT1) and Terminal Adapters (TA).
To a TE1 or TA, the simulator provides the S/T interface. To an NT1, it provides the U interface. Over these
physical interfaces (Figure 2) ow the protocols described in Figure 3.
Figure 2: Examples of ISDN Devices supported by ISDN Simulator
Figure 3: ISDN Protocol Stack
While Q.931, the ISDN primary dialing protocol, usually is used to set up dynamic ISDN calls, ISDN simulator
also supports semi-permanent nailed up B channels that act like private leased lines.
Signaling for the D Channel
Before you congure signaling, you must have set the switch type. Once that is done, you will always need to
set the phone numbers (i.e., DN) and, if the congured switch type requires it, the SPIDs.
Caller ID, or, in formal ISDN terminology, calling number identication presentation, is always enabled.
Chapter 3: Product Description
The Virtual Consoles ISDN simulator provides a telco in a box for a variety of device testing scenarios.
Figure 4: Functional Applications of the Virtual Console Simulator
The device has the most common connectors and indicators on its front panel. In a rack installation with
routers, you would typically want the front panel on the same side as the router interface connectors. Less
frequently used connectors and switches are on the back. Do note that the Reboot button function can be
invoked remotely through the ISDN Manager interface.
Figure 5: Front and Rear Views of the ISDN Simulator
Ports / Interfaces
There are both S/T and U interfaces for each port of the simulator, but only one interface type can be active for
each port. Again, remember that a TE1 or TA device plugs into the S/T interface jack, while a NT device plugs
into the U interface jack.
Figure 6: Connectivity Options
Power
ISDN Console simulator is powered from a 9 DC or AC, 500 mA supply that plugs into a standard 120 VAC
household outlet. Equivalent supplies are available if you need to use the device in a country with 220 VAC.
The power supply may be slightly warm when operating.
The simulator does not provide inline power to connected ISDN devices. They will need independent power
sources.
Cabling
Straight-through RS-232 cable with DB9 connectors is supplied with each ISDN Simulator for the ISDN
Manager or console management. To connect ISDN devices to the simulator, also use a straight-through CAT3
or CAT5 cable with RJ45 connectors.
Controls
A hardware Reset button is on the back panel of the ISDN Simulator. You can also Reboot ISDN Simulator
remotely using ISDN Manager or AT commands sent via console port.
LEDs
Your simulator has four status LEDs (Table 2), numbered from left to right. Two are global to the simulator and
two are specic for ports.
Table 2: LED Denitions
LED number Function
1 Port A Status
2 Power Indicator
3 Device Mode
4 Port B Status
LED status indications are the fastest way to tell the status of the device.
Table 3: Interpreting the ISDN Simulator LEDs
LED Color LED 1 & 4 (Port)
LED 2
(Power)
LED 3 (Mode)
Off No connection No power No Calls in Progress or established
Red
Physical handshaking on the U
interface
Hardware
Failure
N/A
Yellow
Physical link established, data
link not active
N/A Call negotiation in progress
Green Data link active Power ON Call in progress
Blinking
green
SPID received, not matching N/A N/A
Green /
Red
N/A N/A Data transfer in progress
Chapter 4: Conguring ISDN Simulator
Your simulator is controlled by ISDN Manager Win32 application. We recommend that you use ISDN Manager,
which provides a graphic interface with several convenient click buttons. In test racks, you may nd it more
convenient to control the simulator with a reverse Telnet server by issuing AT-style conguration commands.
Conguring the ISDN Simulator with ISDN Manager
Virtual Consoles ISDN Manager is the principal means of conguring and controlling ISDN simulators. It
is a Windows application supported for Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 2000 and Windows XP. ISDN
Manager application is provided with each ISDN simulator
Figure 7: ISDN Manager Screens
When you bring up ISDN Manager, you can set the appropriate COM port for it to communicate with the
simulator with the settings tab (Figure 8). The gather low-level diagnostics is used only when working with
the technical support.
Figure 8: Setting the COM port for ISDN Manager
Your PC COM port must be congured with the settings in Table 4
Table 4: COM port settings for ISDN Manager
Parameter Value
Baud rate 115200 bps
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow Control Hardware
Once you are in communications with the ISDN simulator, you can click the About tab to check rmware and
software versions (Figure 9). See Upgrading Firmware for the upgrade procedure, which will give you a
new version of the TMS code. The AVR and Hardware elds in the gure are for factory use.
Figure 9: Version information from ISDN Manager About tab
On the main screen, you set the switch-type (see Table 1).
To set individual port characteristics, click on the appropriate Port tab. The screen will then show the current
phone number and, when applicable, SPID settings (see Table 7) for each B channel on the port. You can then
set the values as required.
If you need to congure a B channel in nailed up, semi-permanent, or dedicated line mode, check the
appropriate box at the top of the ISDN Manager screen.
Conguring ISDN Simulator via Terminal Server
Many test environments control all devices from a single point, using a reverse Telnet server to connect to all
devices at a remote site. You can control the ISDN simulator in this manner. You must set the asynchronous
interface on the reverse Telnet server to the values in Table 5, and send the codes in Table 6.
Table 5: Interface Settings for Reverse Telnet
Parameter Value
Baud rate 115200 bps
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow Control Hardware
From a terminal server, since you cannot press display buttons, modem-style AT commands must be issued
for all functions.
Table 6: Conguring the ISDN Simulator via Terminal Interface
Function Command Example
Reboot ATZ
Save current conguration AT&W
Display rmware version ATI7
Assign Phone 1 for port A ATN0=1234567
Assign Phone 2 for port A ATN4=1234567
Assign SPID1 for port A ATP0=1234567
Assign SPID2 for port A ATP4=1234567
Assign Phone 1 for port B ATN1=1234567
Assign Phone 2 for port B ATN5=1234567
Assign SPID1 for port B ATP1=1234567
Assign SPID2 for port B ATP5=1234567
SPID assignments
Some ISDN switches, or provider implementations of switches, require Service Provider Identiers (SPID).
You need to know the type required for your reference conguration, and, if you are using a Cisco device, the
Cisco device must be congured to match the switch being simulated.
You can use any SPID numbering scheme that matches your requirement. We support three types of SPID
numbering (Table 7). Whenever you change the SPID, reboot the simulator and preferably the TE device.
Table 7: SPID Formats
SPID format Switch type Comment
All SPIDs are 0
Matches any SPID on the TE side
Supported by NI-1, DMS-
100, 5ESS
Troubleshooting use
All SPID are empty Supported by NET3 only Standard
Any sequence of 40 digits.
Supported by NI-1, DMS-
100, 5ESS
Standard
Upgrading Firmware
Virtual Consoles will periodically publish software upgrades. Check the website for new versions of the
upgradable TMS le shown in Figure 9. When you download new rmware, check if there is a newer version
of ISDN Manager and upgrade that as well.
Clicking the upgrade tab for your product will download a ZIP le containing three les (Table 8). XLOAD is
the actual loader.
Table 8: Firmware Upgrade
File Function & comments
XLOAD.EXE Firmware loader
XXXXX.XMD Firmware, where XXXXXX is a platform specic designation.
DEV.CFG Device default conguration le
To load new rmware with the XLOAD program, connect a COM port of a PC to the console port of the
simulator. The XLOAD program must have exclusive use of the COM port; no other application may use it
while the upgrade program is running.
Example:
XLOAD.EXE P2US.XMD /Com:1 /Cfg:DEV.CFG
at the Windows DOS command prompt. In this example, the Virtual Console device is connected to COM1
port and loads the default settings from the DEV.CFG le.
Chapter 5: ISDN Simulator and Cisco Routers
Since many simulator users intend to use their product with Cisco routers, we will illustrate practical setup
and troubleshooting with Cisco examples. The simulator supports physical connectivity for the two Basic Rate
Interface types, the S/T Reference Point used inside customer premises, and the U Reference Point between
the customer premises and the provider end ofce.
A good starting point is to remember that the isdn switch-type congured, as a global command in the router,
must match one of the types in Table 1 if you are to have any success in operations.
Obviously, you can look at the Cisco conguration for switch-type commands, but, in a lengthy conguration, it
can sometimes be hard to nd the right line.
An alternative is to use the show isdn status command. This is a good command to check for success at
each successive stage of conguration: global, layer 1, layer 2 and layer 3. The switch type is set globally for
the entire router. Layer 1
Figure 10 for an example of show isdn status output before the switch type is set.
Layer 1
Figure 10: Show ISDN Status with undened Switch Type
Router#sh isdn stat
**** No ISDN Switchtype currently dened ****
ISDN BRI0 interface
Layer 1 Status:
DEACTIVATED
Layer 2 Status:
Layer 2 NOT Activated
Layer 3 Status:
0 Active Layer 3 Call(s)
Activated dsl 0 CCBs = 0
The Free Channel Mask: 0x80000003
Total Allocated ISDN CCBs = 0
Once you have the switch type dened, you should see the Yellow LED light and the following output from the
show isdn status command.
Figure 11: Cisco display for active physical layer
Router#sh isdn stat
The current ISDN Switchtype = basic-ni1
ISDN BRI0 interface
Layer 1 Status:
ACTIVE
Spid Status:
TEI Not Assigned, ces = 1, state = 1(terminal down)
spid1 congured, spid1 NOT sent, spid1 NOT valid
TEI Not Assigned, ces = 2, state = 1(terminal down)
spid2 congured, spid2 NOT sent, spid2 NOT valid
Layer 3 Status:
0 Active Layer 3 Call(s)
Activated dsl 0 CCBs = 0
See Table 9 for other possible states following setting the switch type.
Table 9: Cisco Layer 1 States
Layer 1 Status General Meaning
DEACTIVATED No Layer 1 connection has been established
ACTIVE A Layer 1 connection is up and running
GOING DOWN
Normally a transient state. If it persists, try a
clear interface BRI number command. If it
still persists, check cabling, then reload the
router and the simulator
INIT
TESTING
REBOOT
DELEATED (sic)
SHUTDOWN
ACTIVATING
ACTIVE_ErrorInd
Layer 2
After TEI negotiation is complete, you will see a Cisco display like that in Figure 12.
Figure 12: Status display after Layer 2 Initialization
Router#show isdn status
The current ISDN Switchtype = basic-ni1
ISDN BRI0 interface
Layer 1 Status:
ACTIVE
Layer 2 Status:
TEI = 64, SAPI = 0, State = MULTIPLE_FRAME_ESTABLISHED
TEI = 66, SAPI = 1, State = MULTIPLE_FRAME_ESTABLISHED
Layer 3 Status:
0 Active Layer 3 calls
Activated dsl 0 CCBs = 0
Total Allocated ISDN CCBs = 0
While the Virtual Console simulator will stay up, some DMS implementations may shut down ISDN layer 1 or 2
if there are no active calls. With the actual switch, rather than the simulator, it may be necessary to dial out, or
arrange to receive a call, for the lower layers to activate.
In operation with the real switch, rather than the simulator, if you are operating in DMS mode and the switch is
implemented in this manner, you may need to congure the Cisco interface subcommand
isdn tei-negotiation rst-call This is most commonly seen in European switch implementations where the
switch initiates TEI negotiation as part of power-up handshaking.
Troubleshooting
Be systematic in your troubleshooting, from the environmental and then bottom-up from layer 1 upwards.
Environmental
Table 10: Symptoms and Recommended Actions
Power LED (2) does not light
Check power cabling, and the power supply. Verify
the outlet has power
Port LED (1 or 4) does not light
1. Check power LED. If it is OFF, check power
cabling, and the power supply
2. Check that the NT or TE are enabled
3. Check device cabling. Verify interface type.
3. Try the other port. If the other LED does not light,
contact technical support
Layer 1 Troubleshooting with Cisco routers
If the connected router fails to enter the ACTIVE state, as shown in Figure 13, you will need to troubleshoot.
Figure 13: Show isdn status output immediately after setting the switch type
Router#show isdn status
The current ISDN Switchtype = basic-ni1
ISDN BRI0 interface
Layer 1 Status:
ACTIVE
Layer 2 Status:
TEI = 64, SAPI = 0, State = TEI_ASSIGNED
Layer 3 Status:
0 Active Layer 3 calls
Activated dsl 0 CCBs = 0
Total Allocated ISDN CCBs = 0
Try the following troubleshooting steps:
1. Verify the switch types are set and consistent. If you change from the current settings, reboot the
simulator and preferably the router.
2. Issue a shutdown followed by a no shutdown command
3. Issue a clear interface bri number command.
4. Reboot the router.
5. Check that the BRI interface does not have a backup interface subcommand; remove it if
present.
6. Be sure that the physical interface (i.e., S/T or U) on the device under test matches the Simulator
jack to which it is connected. On a Cisco router, use show version or show controllers to
conrm the interface type.
Layer 2 Troubleshooting with Cisco routers
Once you have conrmed layer 2 is working but layer 2 either is down or cannot stay up, you need to debug
Q.921, the layer 2 protocol used for ISDN signaling on the D channel.
Figure 14: Example of Layer 2 Debugging
router#debug isdn q921
ISDN Q921 packets debugging is on
router#conf t
r2(cong)#
r2(cong)#int bri 0
r2(cong-if)# no shut
%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface BRI0, changed state to up
ISDN BR0: TX -> IDREQ ri = 33114 ai = 127
ISDN BR0: RX <- IDDENY ri = 33114 ai = 127
ISDN BR0: RX <- IDCKRQ ri = 0 ai = 127
ISDN BR0: RX <- IDCKRQ ri = 0 ai = 127
ISDN BR0: TX -> IDREQ ri = 38651 ai = 127
ISDN BR0: RX <- IDREM ri = 0 ai = 82
ISDN BR0: RX <- IDREM ri = 0 ai = 83
ISDN BR0: TX -> IDREQ ri = 1708 ai = 127
ISDN BR0: RX <- IDASSN ri = 1708 ai = 85
ISDN BR0: TX -> SABMEp sapi = 0 tei = 85
ISDN BR0: RX <- UAf sapi = 0 tei = 85
ISDN BR0: TX -> INFOc sapi = 0 tei = 85 ns = 0 nr = 0 i = 0x08007B3A0A30383335383636323031
ISDN BR0: RX <- INFOc sapi = 0 tei = 85 ns = 0 nr = 1 i = 0x08007B080382E43A
ISDN BR0: TX -> RRr sapi = 0 tei = 85 nr = 1
ISDN BR0: TX -> IDREQ ri = 29037 ai = 127
ISDN BR0: RX <- IDASSN ri = 29037 ai = 86
ISDN BR0: TX -> SABMEp sapi = 0 tei = 86
ISDN BR0: RX <- UAf sapi = 0 tei = 86
ISDN BR0: TX -> INFOc sapi = 0 tei = 86 ns = 0 nr = 0 i = 0x08007B3A0A30383335383636343031
ISDN BR0: RX <- INFOc sapi = 0 tei = 86 ns = 0 nr = 1 i = 0x08007B080382E43A
ISDN BR0: TX -> RRr sapi = 0 tei = 86 nr = 1
Layer 3 Troubleshooting with Cisco routers
One of the most important Cisco tools for debugging ISDN layer 3 problems is:
debug isdn q931
As with any use of debug, be careful when using it on a production router.
When you are interconnecting two routers through the Simulator, you might encounter problems because the
called router is not congured correctly.
See Figure 15 for a representative debug isdn q931 output associated with a failed call. The call is initiated
by the ping to the remote router.
Figure 15: Layer 3 failure due to called router misconguration.
router#debug isdn q931
ISDN Q931 packets debugging is on
router#ping 192.168.0.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echoes to 192.168.0.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
ISDN BR0: TX -> SETUP pd = 8 callref = 0x10
Bearer Capability i = 0x8890
Channel ID i = 0x83
Called Party Number i = 0x80, 8358661
ISDN BR0: RX <- RELEASE_COMP pd = 8 callref = 0x90
Cause i = 0x82EF - Protocol error, unspecied
ISDN BR0: Event: incoming ces value = 1.
Chapter 6: Cisco Routers Configuration Examples
The following congurations can be used as a typical implementation of ISDN Simulator with two Cisco
routers.
Basic-Net3 Switch Type Example
Note: NET3 does not use SPID numbers
Router 1
hostname R1
isdn switch-type basic-net3
!
interface BRI0
! this interface should be in the simulator Port A
no shutdown
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
dialer map ip 10.10.10.2 broadcast 4082222222
dialer-group 1
isdn switch-type basic-net3
!
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
!
end
Router 2
hostname Router2
!
isdn switch-type basic-net3
interface BRI0
! this interface should be in the simulator Port B
no shutdown
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0
dialer map ip 10.10.10.1 broadcast 4081111111
dialer-group 1
isdn switch-type basic-net3
!
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
Basic-NI1 Switch Type Example
Note: This common switch type require SPID numbers.
Router 1
hostname R1
!
isdn switch-type basic-ni1
!
interface BRI0
! this interface should be in the simulator Port A
no shutdown
isdn spid1 408111111101
isdn spid2 408111111102
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
dialer map ip 10.10.10.2 broadcast 4082222222
dialer-group 1
isdn switch-type basic-ni1
!
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
!
end
Router 2
hostname Router2
!
isdn switch-type basic-ni1
!
!
interface BRI0
! this interface should be in the simulator Port B
no shutdown
isdn spid1 408222222201
isdn spid2 408222222202
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0
dialer map ip 10.10.10.1 broadcast 4081111111
dialer-group 1
isdn switch-type basic-ni1
!
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
Chapter 7: Specifications
Power Adapter: Input: 110/220 VAC Output: 9 VDC,
600mA. 2.5mm jack
U Interface: RJ-45, 8-pin modular jack
U Interface protocol: 2B1Q (2 Binary 1 Quaternary)
S/T Interface: RJ-45, 8-pin modular jack
S/T Interface protocol: ASI (Alternate Space Inversion)
Maximum cable drop: 1600 meters (U Interface), 100 meters
(S/T interface)
RS-232 Interface: DB-9 Female
Storage Temperature: -40 to +55C
Operating Temperature: 0 to 50 C
Humidity Max: 75%
Dimensions: 1.5H x 5D x 7W
Weight: 1 lb (500g)
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 1
DMI-128ESU+
ISDN TERMINAL ADAPTER (TA)
Users Guide
Rev.01 (February, 2004)
LIMITED WARRANTY
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 6
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Introduction ........................................................................................................................8
2. Features.............................................................................................................................9
3. Outlet Description ............................................................................................................10
3.1 FRONT PANEL .................................................................................................................................................................................... 10
3.2 REAR PANEL CONNECTION................................................................................................................................................................. 11
3.3 SIDE PANEL........................................................................................................................................................................................ 11
4 Connection Method...........................................................................................................12
4.1 CONNECTION PROCEDURES ............................................................................................................................................................... 12
4.2 CONNECTION WITH TELEPHONEFAX................................................................................................................................................ 12
4.3 CONNECTION WITH PC ...................................................................................................................................................................... 12
4.4 CONNECTION WITH MODEM................................................................................................................................................................ 13
4.5 MULTIDROP CONNECTION .............................................................................................................................................................. 13
4.6 CONNECTION NOTIFICATION ............................................................................................................................................................... 13
5 Installing The TA...............................................................................................................14
5.1 PACKING LIST .................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
5.2 WHAT ELSE YOU NEED ...................................................................................................................................................................... 15
5.3 INSTALLING THE TA............................................................................................................................................................................ 15
5.4 TIPS ON CONFIGURING WINDOWS 98/NT/2000................................................................................................................................... 15
5.5 Windows 98/2000 and USB......................................................................................................................................................... 17
5.5.1 Linux operating systems with RS 232....................................................................................................................................... 18
5.5.2 USB installation Procedure 19
5.5.4 Tips on configuring your Dial Up Network 25
5.6 VERIFYING YOUR CONNECTION .......................................................................................................................................................... 27
6. AT COMMAND ................................................................................................................28
6.1 DESCRIPTION OF AT COMMAND.......................................................................................................................................................... 28
6.1.1 AT Command .......................................................................................................................................................................... 28
6.2 AT COMMAND.................................................................................................................................................................................... 29
6.2.1 AT Command Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 29
6.2.2 AT Command List ................................................................................................................................................................... 31
6.3 S REGISTER....................................................................................................................................................................................... 35
6.4 RESULT CODE.................................................................................................................................................................................... 36
7. Easy Setup From Telephone Keypad..............................................................................37
7.1 ENTERING PROGRAMMING MODE........................................................................................................................................................ 38
7.2 SETUP CONFIGURATION ..................................................................................................................................................................... 38
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 7
7.3 STORING THE SETTING....................................................................................................................................................................... 38
8. Re-Flash the New Software.............................................................................................39
8.1 NORMAL RE-FLASH PROCEDURE........................................................................................................................................................ 39
8.2 FAILED RE-FLASH PROCEDURE .......................................................................................................................................................... 40
9 Trouble Shooting...............................................................................................................42
9.1 POWER SWITCH ON BUT POWER LED IS NOT LIT. ............................................................................................................................. 42
9.2 DTR LED NOT LIT, AND THE TA DOES NOT CONNECT. ......................................................................................................................... 42
9.3 TYPE AT, BUT THE TA DOES NOT RESPOND WITH OK MESSAGE....................................................................................................... 43
9.4 USING ATD TO CALL, BUT NO CARRIER IS DISPLAYED.................................................................................................................... 44
9.5 CANNOT ACCEPT INCOMING DATA CALL.............................................................................................................................................. 45
9.6 UNABLE TO ACCEPT INCOMING VOICE CALL ........................................................................................................................................ 46
9.7 CAN NOT USE CALL WAITING ............................................................................................................................................................. 47
9.8 SELF DIAGNOSTICS ............................................................................................................................................................................ 48
10. Supplementary Service Function 50
APPENDIX...........................................................................................................................54
APPENDIX 1 DCE 9PIN D TYPE CONNECTOR DEFINITION...................................................................................................................... 54
APPENDIX 2 DISCONNECT CAUSE INDICATION....................................................................................................................................... 50
APPENDIX 3 SPECIFICATION ................................................................................................................................................................. 56
APPENDIX 4 REGISTRATION CARD. 58
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 8
1. Introduction
The ISDN TA (Integrated Service Digital Network Terminal Adapter) is a communication product
for the Internet and digital communication era. It provides high speed and high quality
transmission. The TA supports two analogs and one digital port. The two analog ports act like two
regular telephone lines, which can be connected to regular telephone, answering machine, fax and
modem products. Also, the TA can provide flexible functions like: supplementary service, call
screening, speed dial and global call function to meet users requirements. The digital port with
the RS232 link can be connected to PC to support data communication with remote site. It
supports many protocol selection such as V.110, V.120, X.75, X.25 on D channel, PPP (Point-to-
Point Protocol), MLPPP (Multi-Link PPP), BACP (Bandwidth Allocation Control Protocol) /
BOD (Bandwidth On Demand) function. With the MLPPP, the entire 128k ISDN bandwidth can
be used to access the Internet. The BOD function can utilize dynamic bandwidth demand under
MLPPP connection. Under MLPPP data connection, the TA will automatically release one B
channel for voice communication when the user picks up the phone to make a call and returns to
two B channels for MLPPP when the phone hangs up. With the BACP function, the 128k capacity
of ISDN can be utilized fully. The TA is equipped with channel bundling feature which allows the
user to use both B channels to maximize the 128k bandwidth for data transmission.
The TA complies with ITU-T Q.921, Q.931 for D channel protocol, and provides switching type
selections for different countries. Following are the switch types supported by the TA:
*Euro-ISDN EDSS1
The TA is equipped with flash EPROM for easy future software upgrade through RS232 port.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 9
2. Features
Support MLPPP to utilize the full 128K ISDN capacity
Support BACP/BOD for dynamic bandwidth demand
Up to 230.4K DTE speed
One standard RJ11 modular jack for U interface
Selectable terminating resistance (100 Ohm) inside battery pack
1 standard RJ45 modular jack for S/T interface to NT1 (EURO ISDN)
Two analog ports with RJ11 modular jack
One RS232 data port with DB9-Sub male connector
One USB -port for Windows 98SE/ ME /XP and Windows 2000
LED indication
Inner Communication
Receive Priority, Call Screen, Speed Dialing function
ITU-T V.110, V.120, X.75, X.25 on D protocol
Channel bundling function
Switching type selection
Hardware CTS/RTS, Software Xon/Xoff Flow Control
Network supplementary service
Local supplementary service
Easy setup from telephone keypad for analog phones
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 10
3. Outlet Description
3.1 Front Panel
LED indications on Front Panel along with their colour description
1. POWER: ON- GREEN means TA is working on Mains Power.
ON -RED means TA is working on Battery Power.
2. CONNECT: ON -GREEN means TA is connected to the network at 64K.
ON- RED means TA is connected to the network at 128K (MLPPP).
3. DTR/USB: ON RED means terminal is connected to PC via DTE (Serial Port).
ON GREEN means terminal is connected to PC via USB port.
4. TX/RX: This LED becomes ON when data is being sent or received.
5. LINE: ON-When TA is connected to S/T interface of NT1. (S0 bus)
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 11
3.2 Rear Panel Connection
1. DTE DB9-SUB male connector RS232 and USB
Connect to PC or DTE equipment.
Use only one connection port (USB / Serial) at a time to connect to PC.
2. Analog Port TEL-A, TEL-B
Connect to the regular telephone, answering machine or fax machine.
3. AC Power plug
Connect to DC 5V adapter
4. ST
ST interface connection. You can connect to ST interface of NT1 (of ISDN Line), or connect
other ISDN TA phone with S/T interface to make a multi-drop bus connection.
5. FG (Frame Ground)
Optional and not connected in this model
3.3 Side panel
Battery Backup
In case of sudden loss of local power, the TA has a battery power backup solution. A total of 6 AA
batteries are required to backup the TA. Please make sure all 6 batteries are placed correctly, in
the correct polarity. (Use Alkaline Batteries for proper operation)
Battery Mode Operation
In case of sudden loss of local power, the TA will switch to battery backup mode automatically. (If
all 6 batteries had been installed properly.) Under the battery backup mode, all 3 data and analog
ports can be operated normally.
In battery backup mode, with average brand new batteries, the TA can last at least 6 hours in
standby or it can run one analog port continuously for about 1 hours.
Changing Batteries
Please inspect batteries if the TA does not work properly under battery backup mode. If the battery
is low, please replace batteries. We suggest the user to replace all 6 batteries together.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 12
4 Connection Method
4.1 Connection Procedures
1. Plug in AC power adapter DC 5V 2.8A
2. Connect the ST interface RJ45 modular jack to ISDN port with the RJ45 cable.
3. Connect RS232 cable between TA and PC or TA and USB but not both.
4. Plug in the regular telephone to analog port A or B with RJ11 cable.
5. Connect other ST ISDN phone or TA device with RJ45 cable
A. With this connection method user can use V110, V120, X.75, X.25 protocol to
communicate with other TA.
B. Use PPP or MLPPP to connect with ISP (Internet Service Provider) for Internet access.
C. Use regular telephone make calls
D. Use inner communication between analog port TEL-A and TEL-B.
4.2 Connection With Telephone / Fax
Locate an available RJ11 modular jack telephone outlet.
Take one end of the modular cord supplied with the TA and plug it into the analog port
TEL-A or TEL-B modular jack on the back of the TA.
Plug the other end of the modular cord into the modular jack on the regular telephone/fax.
4.3 Connection With PC
Use the attached RS232 cable to connect TAs DTE port and PCs RS232 port or use
USB port with Windows 98 SE/Me/2000/XP
If the connector type of PCs RS232 port does not match, you may need to use the 9-to-25
gender changer to connect between the RS232 cable and PC
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 13
4.4 Connection With Modem
Connect the telephone to modems port labeled with PHONE then connect modems
LINE port to TAs TEL A or TEL B port
4.5 Multi-Drop Connection
To make a multi-drop bus connection, you can connect the two TAs by the RJ45 cable
4.6 Connection Notification
Do not connect two or more telephones on the same port. It will affect the Impedance of the telephone set.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 14
5 Installing The TA
5.1 Packing List
Unpack your TA and make sure that you have the following items:
TA main unit
Female RS232 cable and USB cable
Power adapter 230 V ac DC 5V 2.8A
S/T interface cable
Users manual
Windows driver disk
When you opened your package, make sure that all of the above items are included in good
order. If any of the components were damaged, please contact your dealer immediately.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 15
5.2 What Else You Need
In order to complete your data communication system, you will need the following items:
1. Some type of communication software, if not included (like dialup network).
2. An ISDN U-interface line from the local PTT NT1. This TA gets connected to the ST
interface of the NT1 (which is supplied by your PTT).
5.3 Installing The TA
The following instruction explained how to install the TA with a PC or PC compatible
computer. If you install the TA into a different computer, refer to the manual that came with
or contact your dealer for instructions and assistance.
IMPORTANT:
In PC environment, two serial devices configured to use the same COM port or IRQ
may conflict. Existing multi-I/O cards usually occupies COM1 and COM2 using IRQ4
and IRQ3 respectively. Whereas the COM port setting must be unique, the IRQ can be
shared provided that the related COM port is not being used. For example, if the PCs
COM2 which uses IRQ3 is not attached to any device (print or mouse, etc.), then your
TA can be set to use COM4 with IRQ3. For maximum flexibility, your PC supports
IRQ2, 3, 4, 5, and 7. However, IRQ2, 5 and 7 should be used only if you have no other
choice. Not all PCs and DOS versions support these IRQs. IBM PC/AT computers and
compatibles should be able to use IRQ5 or 7. Check with your PC dealer or PC manual
for more information.
Turn off the power on the personal computer.
Refer to section 4 to select the adequate method for connection.
5.4 Tips On Configuring Windows 98SE/Me/NT/2000/XP
The following tips will guide you through configuration of the TA on your PC, in the
Windows environment, in a step-by-step manner, with windows screen shots. Proceed with
choosing the correct COM port for your TA.
While installing the ISDN TA through USB port, first install the USB -to-Serial converter
drivers. Then follow the same procedure of installing the modem as shown in Windows
98SE/Me/NT4/2000/XP (RS232 cable connected) procedure.
For other DTE configurations, please refer to the PC manufacturer manual or contact your
local dealer.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 16
5.4.1 Window 98SE/Me/NT4/2000 (RS232 cable connected)
1. Choose My Computer
icon.
2. Open the Control Panel
menu box as shown on the
right hand side.
3. After double click Modem
icon, Modems Properties
box appear and show the
existing modems, which has
been installed previously.
4. Click Add button to add
the TA.
5. Tick the box (Dont
detect my modem)
Click Next to
select TAs driver.
6. In Install New Modem,
click on Have Disk button
and put ISDN TA driver
disk to corresponding drive.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 17
7. Press OK if the location of
driver disk is correct.
Otherwise you may press
Browse button to change.
8. Select the modem to be
installed.
For 64K select ISDN TA
(PPP-64K)
For 128K select ISDN TA
(MLPPP-128K)
Click Next to continue.
9. Choose an available COM
port which is available
(It should not conflict
other devices) and click
Next button.
** IN CASE OF USB port
installation, select the
USB port, shown in the
drop down list .. after
the USB-to-serial
converter is installed
10. Press Finish to
complete setup.
5.5 Windows 98SE/Me/2000/XP (USB cable connected)
1. Power Plug into power plug and wait 5 seconds and the plug USB cable
into USB connector of PC and DMI-128ESU+.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 18
2. Windows will recognise the new USB device and will ask drivers for for
new USB device. Correct path is Floppy A:. So define search path so that
you specify the installation drivers path A:\.
3. After USB -drivers installed just add the modem driver into system as
you installed in previous section and select the COM -port, which was
created By USB to Serial driver installation.
4. Power adapter is needed when USB -connector in use because of
Analog ports ringing signals
5.5.1 Linux operating systems with RS 232
1. Use KPPP program and directly TTY port where TA is installed
Or any similar
2. Set port 230400 or 115200 DTE speed 8, N, 1
3. CTS/RTS setting ON
4. PPP / 64K connection AT%A2=5
5. ML PPP 128K AT%2=6
6. In this case do not use IP -header compression
7. If device is not working the slow down AT -command sending speed and
response wait time.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 19
5.5.2 USB Installation Procedure for Win 2000
(USB SERIAL CONVERTER):
1.Win2000 will detect the DMI-128ESU+ and
bring you to the Found New Hardware Wizard.
2.Click Next to continue.
3.Select the first item-Search for a suitable
driver for my device [recommended]
4.Click Next to continue
5.Click the Specific location in the
Checkbox.
Click Next to continue.
6.Click the Browse button.
7.Choose the location as A:\USB Drivers.
Select the file ftdibus.inf and click open.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 20
8.Click OK button.
9.Click Next to continue.
Note: For correct Locations on the screen, please follow remarks indicated on the side of the
screen snap-shots.
10.The USB Serial
Converter is now installed.
Click Finish button
Installation of USB Serial Port (In Win 2000)
1.Win2000 will detect the USB Serial Port
and bring you to the Found New Hardware
Wizard
2.Click Next to continue.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 21
3.Select the first item-Search for a suitable
driver for my device [recommended]
4.Click Next to continue
5.Check the Specify a location checkbox.
Click Next to continue.
6.Click the Browse button.
7.Choose the location as A:\USB Drivers.
Select the file FTDIPORT and click Open.
8.Click OK button.
9.Click Next to continue.
Note: For correct Locations on the screen,
please follow remarks indicated on the side of
the screen snap-shots.
10.The USB Serial Port is now installed.
Click Finish button
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 22
11.Go to the Control Panel, and in System,
to ensure correct installation of the USB
modem
To Ensure that correct installation has taken place, check that in Device manager, when you
expand Universal Serial Bus Controllers you get USB Serial Converter and when you
expand Ports(COM &LPT) you get USB Serial Port(COM 3).
This installation procedure is similar for the WIN 98 SE and WIN ME environment.
AFTER THIS, FOLLOW THE PROCEDURE IN SECTION 5.4.1 FOR INSTALLING THE
MODEM DRIVERS.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 23
5.5.3 USB Installation Procedure for Win XP
(USB SERIAL CONVERTER):
1. Win XP will detect the DMI-
128ESU+ and bring you to the Found
New Hardware Wizard.
2. Select the second checkbox and give the
correct path for the drivers, A: if the drivers are
on floppy disc.
3.Click Next to continue
4. This wizard will search for the
required drivers in the given path.
5. Click Continue anyway to proceed
to install the USB High Speed Serial
Converter.
6. The USB High Speed Serial Converter is
now installed. Click Finish button
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 24
Installation of USB Serial Port (In Win XP)
1. After installing USB High Speed Serial
Converter DMI-128ESU+, the wizard will
bring you to the Found New Hardware
USB Serial Port.
2. Select the second checkbox and give the correct
path for the drivers, A: if the drivers are on floppy
disc.
3.Click Next to continue
4. This wizard will search for the required
drivers in the given path.
5. Click Continue anyway to proceed to
install the USB Serial Port.
6. The USB Serial Port is now installed. Click
Finish button
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 25
5.5.4 Tips on configuring your Dial-Up Network
After you setup the ISDN TA driver completely. The next step is going to have your Dial-Up
network working. Following tips will guide you how to configure your Dial-Up Network
with Windows 98SE/Me/2000
1. 1) Ensure that you have
installed Dialup server and
Dial-Up Networking in
your windows
environment (Win 98SE).
2) In Win NT ensure that
RAS (Remote Access
Server) is installed.
3) Choose Dial-Up
Network icon from My
Computer window.
2. Click the Make New
Connection icon
twice to create a connection.
3. Choose a protocol for
ISDN TA and give a
name for this connection
and press Next button.
Note! If you use ML PPP 128K driver then TCP/IP header compression has to be off
And DNS -values has to be set up correctly in TCP/IP properties.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 26
4. Enter the correct
country, area code
and phone number
(The phone number
depends on the ISP
you selected) Then
press Next ,if asked
5. Reconfirm the New
connection and press
Finish button.
6. The new connection of
ML-PPP has been
completed and a new icon
will appear. You may
make future modifications
by checking the contents
of function.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 27
5.6 Verifying Your Connection
Start a communication program (HyperTerminal) and place the computer in terminal mode.
Refer to your computer manual to find out the appropriate commands to do so.
Follow these procedures to verify your installation:
1. Type
AT [Enter]
If your system is operating properly, the TA will respond with OK message to your
screen and will wait for the next command.
2. Use your communication software to prepare your computer to dial a data call.
For example, you can test the data connection under V.110 protocol with the following
procedures.
AT%A2 = 1 ; Select V.110 communication protocol.
ATD 5552121 ; Where 5552121 is the called partys telephone number with V.110
protocol setting.
After ATD5552121 you can see the TX/RX LED is lighted and then, the CONNECT or
NO CARRIER message will be displayed.
CONNECT; Means TA connected with the Called Party.
NO CARRIER; Means TA did not connect with the Called Party, may be due to
Called Party busy.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 28
6. AT COMMAND
6.1 Description of AT Command
Hayes command set is a standard for Hayes modem commands for its Smart modem 300. Most
modem manufactures adopted this command set in order to have Hayes compatible. The command
set used by the Smart modem 300, as well as most modems or TAs today (with a few additional
new advanced commands), is known as the AT command set. AT stands for attention, and is
placed in front of actual content of command so that the TA knows what follows is an command
directed at the modem or TA. With the exception of some A/ and +++ command, AT
command is the process to place command to the TA.
Different modems or TAs may have slightly different command sets, but generally speaking, most
of the TAs follow the standard set by Hayes.
6.1.1 AT Command
When you connect terminal equipment (like PC) with the TA, after typing AT command ending
with [ENTER] key, TA will process the command and then return the result code to the terminal
equipment. Each AT command must starts with AT and end with [ENTER] key (with the
exception of A/ and +++ commands).
Command Format
The following is the format of AT command:
AT
Command Value Command Value CR LF
Result code has two styles (Verbose and Numeric). The following are their formats:
CR LF Result
code(Verbose)
CR LF
Result code (Numeric) CR
S register
The S register is used to store the settings including
auto answer mode
escape sequence character
V.110 connect speed ..... etc.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 29
If you want to change the value of S register, you can use the ATS command.
6.2 AT Command
6.2.1 AT Command Overview
Command Description Default
ATA Manual answer
ATD Dialing
ATEn Echo command ATE1
ATH Hang up
ATIn Interrogate the TA product status
ATL Dialing the latest number
ATO Return to on line state
ATQn Return result codes select ATQ0
ATSn=x Set S register
ATVn Verbose mode ATV1
ATWn Connection message format select ATW0
ATXn Result code set select ATX0
ATZn Reset recall user profile
AT&Cn CD signal control AT&C1
AT&Dn ER signal control AT&D2
AT&F Recall factory default setting
AT&Kn Flow control AT&K3
AT&Sn DR signal control AT%S0
AT&Vn Display system configuration
AT&Wn Write user profile
AT&Yn Load user configuration when power on AT&Y0
AT%A2=n Data port protocol selection Default is PPP 64K AT%A2=5
AT%A5=n Set enbloc or overlap sending mode when dialing telephone number AT%A5=0
AT%D Data port setting display
AT%DC Show disconnect cause, source, charge
AT%FAPPS Re-Flash the new software
AT%N=x Set data port directory number / sub-address
AT%Sn Data port call screen function enable AT%S1
AT%Z1 Software reset
AT$AAn Set analog port A voice information capability in answer mode AT$AA2
AT$AN=x Set analog port A directory number / sub-address
AT$AOn Set analog port A voice information capability in originate mode AT$AO0
AT$APn Dial pause set up for analog port A AT$AP1
AT$ASn Screen incoming call for analog port A AT$AS1
AT$BAn Set analog port B voice information capability in answer mode AT$BA2
AT$BN=x Set analog port B directory number / sub-address
AT$BOn Set analog port B voice information capability in originate mode AT$BO0
AT$BPn Dial pause set up for analog port B AT$BP1
AT$BSn Screen incoming call for analog port B AT$BS1
AT$CC Display advice of accumulate charge
AT$CD Display all analog port setting
AT$CGn Global call select setting AT$CG2
AT$CIn Enable inner communication AT$CI1
AT$CPn Receiver priority setting AT$CP1
AT$CSn Select supplementary service function AT$CS1
AT$CZn Initialize charge
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 30
AT$CFn Call forwarding function select AT$CF1
AT*CFAn Enable call forwarding for analog port A AT*CFA0
AT*CFBn Enable call forwarding for analog port B AT*CFB0
AT*CFGn Enable call forwarding under global call AT*CFG0
AT*CFA= Set call forwarding number for analog port A
AT*CFB= Set call forwarding number for analog port B
AT*CFG= Set call forwarding number for global call
AT$EUn Set a-law or u-law coding AT$EU1
AT$ESN DTMF START CODE A AT$ES1
AT$ERN Set CID between 1
st
and 2
nd
ring AT$ER1
AT$ACn Enable to send caller ID for analog port A AT$AC1
AT*BCn Enable to send caller ID for analog port B AT$BC1
AT*IDn Enable to send caller ID for data port AT*ID1
AT$EDN Setup DTMF caller ID or FSK AT$ED1
AT*W=n Save settings to flash memory
ATUn Resource BOD setup ATU1
A/ Repeat last command
+++ Escape sequence from data mode
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 31
6.2.2 AT Command List
* means default setting
Command Description Value Remark
ATA Manual answer
Answer an incoming data call
ATD Dialing
Dial the destination number
Max main address: 20 digits
Max sub-address: 5 digits
0-9
+
ATD4125678+ 123
Dialing digits
Sub-address delimiter
ATDSn Speed dialing 0-19 Speed dialing number
ATEn Echo command
Define whether characters are echoed back
from the TA to the DTE within command
mode.
0
*1
No echo
Echo
ATH Hang up
Hang up the connection
Type ATH during the RING will reject the
call
ATIn Interrogate the TA product status 0
1
3
6
Requests the TA product code
Checksum value
ROM Part Numbers and Revision
Supported switching type
ATL Dialing the latest number ATD4125678
Then ATDL will dial 4125678 again
ATO Return to on-line state Return from command mode to data mode
ATQn Return result codes select
Defines whether or not the TA will issue
result codes to the DTE
*0
1
Result code returned
Not returned
ATSn=x Set S register
Change S register value
n
x
S register number
Setting value
ATVn Verbose mode
Defines the form of result codes returned by
the TA
0
*1
Numeric form responses enabled
Verbose responses enabled (English
responses)
ATWn Connection message format select
Defines the type of (extended) negotiation
result codes to return.
*0
1
Negotiation codes reported in 1
line format : (CONNECT)
3 line format (Hayes format)
(CONNECT xxx)
(PROTOCOL xxx)
(CARRIER xxx)
ATXn Result code set select
Description Select the result code set.
*0
1
Data result codes 0-4 enabled
All supported data result codes
Enabled
ATZn Reset/recall user profile
The user configuration stored in the non-
volatile memory is recalled to become the
active configuration.
0
1
Reset the TA and recall user profile
Reset the TA and load default value
(Except stored dial number, own-
address, sub-address and
accumulated charge)
AT&Cn CD signal control
Defines what the TA outputs as the DCD
(CD) signal on the DTE interface
0
*1
DCD (CD) signal on at all time.
(TAs DCD signal follow PCs DTR)
DCD (CD) signal on at only
communication time.(DCD signal
high during communication time)
AT&Dn DTR signal control
Defines how the DTR (ER) signal is
interpreted by TA.
0
*2
DTR signal consider on at all
time.
(TA wont detect DTEs DTR,
TA consider DTR is always on)
TA will detect DTEs DTR (ER) Signal
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 32
AT&F Recall factory default setting The factory configuration contained in the
ROM is loaded to become the TAs
configuration.
AT&Kn Flow control 0
*3
4
No flow control
Hardware flow control (RTS/CTS)
Software flow control (Xon/Xoff)
AT&Sn DR signal control
Defines how the DSR (DR) signal is
handled by the TA
*0
1
TAs DSR (DR) signal follows DTEs
DTR
DSR (DR) signal on at only
communication time.
(DSR signal high during
communication time)
AT&Vn Display system configuration
Cause the TA to display its current
configuration
0
2
Displays the current
configuration
Display Directory Numbers and all
stored phone numbers
AT&Wn Write user profile
The TA s active configuration will
be stored into the non-volatile
memory as User profile
0
1
Write user profile 0
Write user profile 1
AT&Yn Load user configuration when power on 0
1
Use user profile 0 as active Profile
when power up
Use user profile 1 as active Profile
when power up
AT&Zn=x Register speed dial number n
x
n = 0-19
x = telephone number
AT%A2=n Data port protocol selection
Select the protocol on BOD channel
1
2
4
*5
6
8
14
V.110
V.120
X.25 on D
PPP
MLPPP
X.75
Channel Bundling
AT%A5=n Enbloc/overlap sending mode
Select the sending method for telephone
number (refer also AY*W0, AT*W1)
*0
1
Overlap sending
The dialing telephone will be sent to
network after TA detect the ending digit
Enbloc sending
The dialing telephone number will be
sent to network immediately whenever
the user dialing each digit
AT%D Data port setting display Display all corresponding setting
AT%DC Show disconnect cause, source, charge Display the disconnect reason and
connection fee
AT%FAPPS Re-Flash the new software
AT%N=x Set data port directory number / sub-
address
(eg. AT%N=12345678 + 12345)
x x=telephone number
main - address: max 20 digits
sub - address: max 5 digits
AT%Sn Data port call screen function enable 0
*1
Accept incoming call if the calling
party number is in the call screen table.
Accept all incoming call
AT%Z1 Software reset Reset all internal state of TA
AT$AAn Set analog port A voice information
capability in answer mode
0
1
*2
Accept speech
Accept 3.1kHz audio
Accept both
AT$AN=x Set analog port A directory number / sub-
address (Not used in Finland)
Eg. AT$AN1234567812345
x X = telephone number
Main - address: max 20 digits
Sub - address: max 5 digits
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 33
AT$AOn Set analog port A voice information
capability in originate mode
*0
1
Select speech
Select 3.1kHz audio
AT$APn Dial pause set up for analog port A *1
2
3
4
5sec
9sec
11sec
13sec
AT$ASn Screen incoming call for analog port A 0
*1
Accept incoming call if the calling
party number is in the call screen table.
Accept all incoming call
AT$BAn Set analog port B voice information
capability in answer mode
0
1
*2
Accept speech
Accept 3.1kHz audio
Accept both
AT$BN=x Set analog port B directory number / sub-
address
(eg. AT$BN=12345678 + 12345)
x x = telephone number
main - address: max 20 digits
sub - address: max 5 digits
AT$BOn Set analog port B voice information
capability in originate mode
*0
1
Select speech
Select 3.1kHz audio
AT$BPn Dial pause set up for analog port B *1
2
3
4
5sec
9sec
11sec
13sec
AT$BSn Screen incoming call for analog port B 0
*1
Accept incoming call if the calling
party number is in the call screen table.
Accept all incoming call
AT$CC Display advice of accumulate charge Display advice of accumulate charge (data
port, analog port A, analog port B)
AT$CD Display all analog port setting Display all of the setting for analog port A
and B
AT$CGn Global call select setting
If the incoming call did not contain the
called party number then TA had to
determine ring mechanism
0
1
*2
Ring TEL-A only
Ring TEL-B only
Ring both TEL-A and TEL-B
AT$CIn Enable inner communication 0
*1
Disable inner communication
Enable
AT$CPn Receiver priority setting
This function only available when
set AT$CG2
*1
2
3
Ring TEL-A/B alternatively
Ring TEL-A 10 times first
Ring TEL-B 10 times first
AT$CSn Select supplementary service function Note: Follow chapter 10.
AT$CZn Initialize charge
AT$CZn =MM-DD-YY
1
2
3
Initialize TEL-A to zero charge
Initialize TEL-B to zero charge
Initialize data port to zero charge
AT$CFn Call forwarding function select
Select call forwarding by local or
Network.
*1
2
3
4
5
Local call forwarding
Network forwarding, ID=32
Network forwarding, ID=33
Network forwarding, ID=34
Network forwarding, ID=35
AT*CFAn Enable call forwarding for analog port A *0
1
No forwarding
If the incoming call is for TEL-
A, it will forward automatically
to the phone number defined by
AT*CFA=xxxxxx
AT *CFBn Enable call forwarding for analog port B *0
1
No forwarding
If the incoming call is for TEL-
B, it will forward automatically
to the phone number defined by
AT*CFB=xxxxxx
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 34
AT*CFGn Enable call forwarding under global call *0
1
No forwarding
If the incoming call is a global
call it will forward automatically
to the phone number defined by
AT*CFG=xxxxxx
AT*CFA=x Set call forwarding number for analog port
A
x x=forward phone number
AT*CFB=x Set call forwarding number for analog port
B
x x=forward phone number
AT*CFG=x Set call forwarding number for global call x x=forward phone number
AT*Ln
Or
AT$EU1
A-law or u-law coding select *0
1
A-law coding
For European, China, Australian and
etc
U-law coding
For American, Japan and etc
AT*W0=n Set the dialing interpretation of # *0
1
2
# is interpreted as a normal digit
# is interpreted as a sub-address
delimiter
# is interpreted as an ending digit. In
enbloc sending mode TA will send the
dialing number after received the
ending digit or after timeout
AT*W1=n Set the dialing interpretation of * *0
1
2
* is interpreted as a normal digit
* is interpreted as a sub-address
delimiter
* is interpreted as an ending digit. In
enbloc sending mode TA will send the
dialing number after received the
ending digit or after timeout A-law
coding
For European, China, Australian and
etc
AT$EDx Set DTMF caller id to analog ports 0
*1
Fsk caller ID
DTMF caller ID (Finland)
AT$Esx DTMF CALLER ID start code D
*A
B
A -LETTER START CALLER ID
SEQUENCE IN FINLAND
AT$ER1 Caller ID between 1
st
and 2
nd
ring Forced Default always
AT$ACx Enable to send caller ID for analog port A 0
*1
Not to send TEL - A telephone number
under outgoing call
Send TEL - A telephone number
AT$BCx Enable to send caller ID for analog port B 0
*1
Not to send TEL - B telephone number
under outgoing call
Send TEL - B telephone number
AT*Idn Enable to send caller ID for data port 0
*1
Not to send data port telephone number
under outgoing call
Send data port telephone number
ATUn Resource BOD setup
Enable/Disable the resource BOD function
*0
1
Disable resource BOD function
Enable resource BOD function
A/ Repeat last command
TA will re-execute the most recently
received command line
This command does not use the AT prefix
nor does it require a carriage return to enter
+ + + Escape sequence from data mode Escape from the data mode
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 35
6.3 S Register
Number Meaning Range Unit Description Default
0 Auto answer 0
1 - 255
Time Manual answer
Auto answer the incoming data
call after defined counting
0
1 RING count 0 - 255 Time Stored the RING count 0
2 Escape character 0
0 - 127
ASCII Disabled
Use the ASCII value as escape
character
43
3 Carriage Return 0 - 127 ASCII Use the ASCII value as CR 13
4 Line Feed 0 - 127 ASCII Use the ASCII value as LF 10
5 Back Space 0 - 32 ASCII Use the ASCII value as BS 8
12 Escape sequence
Prompt time
0
1 - 255
20ms Do not check guard time
Check guard time
50
25 DTR detection time 0 - 255 0.01sec DTR recognized time 20
26 CS delay time 0 - 255 0.01sec Delay between lost carrier and
Hang up (RTS to CTS)
1
37 V.110 speed set 5
6
15
17
27
50
5 = 1200bps
6 = 2400bps
15 = 4800bps
17 = 9600bps
27 = 19200bps
50 = 38400bps
50
107 Throughput BOD
criteria (monitor B -
ch throughput)
0 - 6 10kbps 0 = do not monitor
1 = 10kpbs
2 = 20kbps
3 = 30kbps
4 = 40kbps
5 = 50kbps
6 = 60kbps
0
141 BOD - Add monitor
Time
0 - 255 Sec Average calculation time for adding one
B - ch
5
143 BOD - Add last time 0 - 255 Sec The throughput must greater than S107
and lasted S143 time, after
Such criteria, TA will add one B-ch
connection
30
144 BOD - Cut monitor
Time
0 - 255 Sec Average calculation time for dropping
one B-ch
5
146 BOD - Cut last time 0 - 255 Sec The throughput must less than S107 and
lasted S146 time, after such criteria, TA
will drop one B-ch connection
30
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 36
6.4 Result Code
Data Result
Code
Word Format Description
0 OK Normal response
1 CONNECT Connected
2 RING Incoming call ringing
3 NO CARRIER No carrier detected
4 ERROR Error operation
7 BUSY Busy state
5 CONNECT 1200 1200bps connection
10 CONNECT 2400 2400bps connection
11 CONNECT 4800 4800bps connection
12 CONNECT 9600 9600bps connection
14 CONNECT 19200 19200bps connection
28 CONNECT 38400 38400bps connection
18 CONNECT 57600 57600bps connection
19 CONNECT 64000 64000bps connection
20 CONNECT 115200 115200bps connection
21 CONNECT 230400 230400bps connection
46 CARRIER 1200 1200bps carrier detected
47 CARRIER 2400 2400bps carrier detected
48 CARRIER 4800 4800bps carrier detected
50 CARRIER 9600 9600bps carrier detected
54 CARRIER 19200 192000bps carrier detected
56 CARRIER 38400 384000bps carrier detected
39 CARRIER 48000 48000bps carrier detected
57 CARRIER 57600 57600bps carrier detected
59 CARRIER 64000 64000bps carrier detected
83 PROTOCOL: V.120 V.120 connection
85 PROTOCOL: V.110 V.110 connection
86 PROTOCOL: PPP PPP connection
88 PROTOCOL: MLPPP MLPPP connection
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 37
7. Easy Setup From Telephone Keypad
The TA provides an easy configuration way through the analog port. If you use TEL-A port then
you can setup the corresponding attributes only for TEL-A. If you are using TEL-B then you can
setup the configuration for TEL-B only.
Easy Setup
Operation
Meaning Value Description
Press Flash /
R first
** 1 2 8
Enter into programming
Mode
Instruct TA to enter into
programming mode
Flash/
On-hook
Cancel setting Cancel the current operation
* * Store setting into active
profile
Save the current setting into
active memory profile
# * # Store setting into
Non-volatile memory
Save the current setting into
NV-RAM
n=0 Ring TEL-A only
1 Ring TEL-B only
0 0 * n Global Call Select
2 Ring TEL-A and TEL-B
n=0 Disabled inner communication 0 1 * n Inner Communication
1 Enabled
n=1 No receive priority
2 Ring TEL-A first
0 2 * n Receive Priority
3 Ring TEL-B first
0 5 * n Factory Default
n=1 Call is forwarding when received an
incoming global call (without called
party number)
2 Call is not forwarding when received
an incoming global call
3 Call is forwarding when received an
incoming call for
TEL-A
4 Call is not forwarding when received
an incoming call for
TEL-A
5 Call is forwarding when received an
incoming call for
TEL-B
0 7 * n Call Forwarding Criteria
6 Call is not forwarding when received
an incoming call for
TEL-B
n=1 Local call forwarding
2 Network forwarding, ID=32
3 Network forwarding, ID=33
4 Network forwarding, ID=34
0 8 * n Local/Network Call
Forwarding
5 Network forwarding, ID=35
n=1 Global call forwarding no.
2 TEL-A call forwarding no.
0 9 * n * x Forwarding Number
3 TEL-B call forwarding no.
1 0 * x Register Telephone
Number
x=tel
number
Register telephone number for
TEL-A/TEL-B
1 1 * n * x Register Call Screen
Number
n=1-5
x=tel
number
Register call screen number for TEL-
A/TEL-B
n=0 Do not send out caller-ID when
made an outgoing call
1 2 * n Enable Caller-ID
1 Send out caller-ID when made
Outgoing call
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 38
7.1 Entering Programming Mode
To enter into the programming mode from telephone sets, please follow the steps below:
A) Use regular telephone set with DTMF -codes and plug into analog port A (TEL-A) or B (TEL-
B) Pick up the telephone you and wait for dial tone.
C) Press flash / R -button and then ** 1 2 8 one the telephone keypad then you
will hear a confirmation tone which indicate that the TA is now under the programming mode.
7.2 Setup Configuration
To setup the corresponding settings, please check the above Easy Setup Table and execute the
following steps.
A). Press 0 0 * 0 to set global call select - ring TEL - A only (for example)
B). Press * * to store the setting into active profile.
C). Repeat the procedure A) and B) for other settings.
D). When finished with all settings, press * # * to store all the updated settings into the
non - violate Memory.
7.3 Storing The Setting
After you performed the * # * sequence, even when there is a power outage. The modified settings
will still stored in the non-violate memory. After power resumes, you can recall the setting from
user profile 0 or 1. If you hang up the phone before you execute the * # * sequence, then the TA
will abort from the programming mode and return to idle mode.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 39
8. Re-Flash the New Software
8.1 Normal Re-Flash Procedure
To provide the upgraded software function in the future. The TA had been installed with the flash
EPROM for re-flash the new software function. Usually you should get the zipped (.ROM) file
from your local dealer directly or from your local agents Web Home Page. After you get the
.ROM file please follow the following procedure carefully.
(1) Use any terminal program that support ASCII file transfer function, like HyperTerminal.
(2) Enter into the terminal mode and make sure that the terminal program had set the following
configuration.
. 115200-baud rate
. 8 data bit, no parity, 1 stop bit (8N1)
. CTS/RTS hardware flow control
(3) Type AT and check TA responded with OK
(4) Type AT%FAPPS the screen will display the following message.
AT%FAPPS Application Upgrade
FLASH PROGRAM VERSION 1.4
Erase and reprogramming flash EPROM contents (y/n)?
(5) If you enter n then screen displayed
Reset modem to continue.
You need to power off and power on AFTER flashing TA to restart.
If you type y the screen will display:
*** WARNING ***
Erasing Flash Memory
Flash EPROM Upgrade Procedure
Ready for ASCII download
CTS (hardware) flow control
38400,8,N,1
>
(6) After you see the > character is appeared, you should select the new upgraded
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 40
software from the correct path. Select Transfer ->> Send Text File. Here give path of the .rom
file (*.ROM). Then click OK to start download. The screen will show the >>>>>>>>>> and
<<<<<<<<<< alternatively to indicate TA is downloading now.
(7) After finished the download new software, screen will display
Code update successful
OK
Normally it takes about 10 minutes to finish re-flash.
(8) After you see the message it means the download is completely already. You
need to power off and power on TA again to restart.
(9) Type ATI3 to inspect the new software version.
8.2 Failed Re-Flash Procedure
Sometimes during the re-flash procedure, due to some accidents like: local power is off; PC is shut
down, RS232 cable is disconnected and etc. To prevent any kind of failed re-flash operation, TA
provides a so-called Minimum Operating Mode. When you failed to re-flash the new software,
TA will detect the failed re-flash internally.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 41
You must follow the procedures as below step-by-step.
(1) Power off TA.
(2) Check the RS232 cable is connected with PC well.
(3) Change the Terminal program to 38400 baud, 8N1, CTS/RTS hardware flow control.
(4) Entering the terminal mode again.
(5) Power on TA again, you will see the screen display:
Erase and reprogramming flash EPROM contents (y/n) ?
(6) Enter y and follow the steps from 8.1 (6) as stated above. Then you can still
finish the re-flash procedure. And you will see 38400, 8, N, 1 instead of
115200, 8, N, 1. Due to the baud rate is slower therefore it takes about 10
minutes to finish re-flash.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 42
9 Trouble Shooting
Here are some flow charts of troubleshooting, which may help you resolve frequently encountered installation
problems.
9.1 Power Switch On but POWER LED is not lit.
9.2 DTR LED not lit, and the TA does not connect.
Please Check Power. Does the
power cord connected ?
Connect the power cord.
Are all connections to the TA
properly and correctly
connected?
Yes
1. Please confirm that the
S/T line to local switch
center is connected
properly.
2. Confirm that the S/T of
local switch center is
working.
Turn off the TA. Reconnect all
connectors before turning on
the TA.
No
No
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 43
9.3 Type AT, but the TA does not respond with OK message
Is the POWER LED lit? Turn on the power to the
TA
No
Yes
Does the attention code
contain both upper and lower
case letters? (i.e. aT or At?)
Use only one case in
attention code.
Yes
Is COM Port Setting
correct?
Retrieve and review COM
Port setting.
Tx/Rx LED does not flash
when entering command
from terminal (DTE)
Check the connection between
TA and DTE.
1. Check the socket connections.
2. Use the connection cord
provided with the TA.
3. Make sure the cord is in good
condition.
4. Make sure the Ta is
connected to the correct COM
Port on the PC.
Is the DTR LED lit? Enter AT command of
AT&D0
Does the Tx/Rx LED
flash when enter
AT<CR> ?
Reconfirm COM Port.
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 44
9.4 Using ATD to call, but NO CARRIER is displayed.
Capable of dialing an
outgoing call?
Reconfirm settings on
the two previous
Does the CONNECT
LED light up when
receiving an incoming call?
1. Please confirm the
telephone is functioning
properly on the other end.
2. Confirm Data bits; stop
bits, Parity and Flow
control type settings.
3. Reset service functions to
the same settings on both
calling side and called
side.
Does the PC indicate
RING?
1. Refer to previous
section and check all
settings.
2. Reset after enters the
command of ATQ0.
3. The command ATA
can make TA to auto
answer mode.
Yes
No
No
No
Yes
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 45
9.5 Can not Accept Incoming Data Call
Can out going calls be
made?
Confirm settings on the
2
nd
and third section of
troubleshooting.
Does the LINE LED
light up when receiving
an incoming call?
1. Please confirm the
telephone is
functioning properly
on the other end.
2. Confirm Data bits;
stop bits, Parity and
Flow control type
settings.
3. Reset service
functions to the same
settings on both
calling side and called
side.
Does the PC indicate
RING?
1. Refer to previous
section and check all
settings.
2. Reset after enter the
command of ATQ0.
3. The command ATA
can make TA to auto
answer mode.
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 46
9.6 Unable to Accept Incoming Voice Call
Is there dial tone when
headset is removed from
the hook?
Go through checks
outlined in section 2 and 3
of this trouble-shooting
manual. Contact the phone
manufacturer if the phone
still fails to work.
Is the incoming calls
being rejected?
1. Please confirm the
telephone is functioning
properly on the other
end.
2. Confirm Data bits; stop
bits, Parity and Flow
control type settings.
3. Reset service functions
to the same settings on
both calling side and
called side.
4. Terminate Call Screen
function.
Is this analog port
connected to more than
one telephone and/or fax?
Only one telephone set or
one fax machine can be
connected to one analog
port. Please disconnect all
additional devices.
No
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 47
9.7 Can Not Use Call Waiting
Does incoming tone appear
during calls?
Confirm local switch
provides Call Waiting
Make sure that when
hang up or use the
flash key to switch
calls, the duration is
about one second.
Yes
No
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 48
9.8 Self Diagnostics
Power On Self-Diagnostic
The TA is installed with power-on self-diagnostic functions. After the power is switched
on, the TA will perform the following self-test diagnostics.
Item Description
ROM Inspect ROMs to CHECK ROM size
RAM Inspect RAMs read/write operations
Do not turn off power during self-diagnostic.
If a problem occurs during self-diagnostic, the POWER LED will
continue flashing after the test.
Before you test the ISDN TA, there are some things need to be noted as shown below:
1. Select the correct transfer
protocol you are going to dial,
make sure that these models have
been set already. (See Chapter 5.6
for reference)
2. Make sure the right User
name, Password and Dial-Up
number (i.e. Telephone
number provided by ISP) are
used and click the connect
button.
3. The Dialog Box
shows dialing the
connection.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 49
4. Ensure the following Properties in the Dial-Up Netwoking.
Fig: 1 fig: 2 fig: 3
Fig: 4 fig: 5 fig: 6
In fig 2-Uncheck Enable software
compression.
In fig 3- Uncheck Use IP header
compression.
In fig 6- Select the correct port where ISDN
TA is installed.
Fig: 7
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 50
10. Supplementary Service Function
The supplementary services will require Analog phone having flash timing set to 600 msec.
(flash=600 msec). Check with your Telco (PTT) for supplementary service availability.
Follow the AT Command in Chapter 6 along with this procedure.
10.1 Definition
AT$CI1 Set inner communication enable
AT$CS1 No Network/Local supplementary service function provided
AT$CS2 Only Network supplementary service function provided
AT$CS3 Only Local supplementary service function provided
LIT Local incoming
tone
400Hz tone
0.125sec on, 0.1sec off, 0.125sec on, 0.1sec off,
3.55sec off repeated
BT Busy tone 400Hz tone
0.5sec on, 0.5sec off continually
DT Dial tone 400Hz tone
Continual
RBT Ring-back tone Receive from Network ISDN switch
IRBT Inner ring-back
tone
60ms on, 50ms off, 60ms on, 3250ms off,
repeated
400 HZ tone
IR Inner ring 25Hz ring signal
When TA detects an inner communication and
sends ring signal to TEL-A/B by clicking the
ringing relay
Ringing period is same as IRBT
ICR Incoming ring 25Hz ring signal
When TA accepts an incoming call and sends
ring signal to TEL-A/B/C by clicking the
ringing relay
Ringing period is 1sec on, 2sec off repeated
HT Holding tone Send by Network ISDN switch
Waiting first dial digit time After TEL-A/B off hook, TA sends DT to TEL-
A/B
If after 25 seconds TA did not receive any
dialing digit, TA send BT to POTS-A/B
Flash signal recognition time TA detects Flash-Hook signal from TEL-A/B
Flash timing to be set to 600 msec on POTS
A/B for correct operation.
DMI-128ESU+ DMI 128 ESU+
A
B
C
D
ISDN
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 51
On-Hook signal recognition
time
TA detects a Flash-Hook signal from TEL-A/B
If Flash-Hook time >=2.2 sec then it is a correct
On-Hook signal
Ideal mode On-hook, disconnected and no any event
occurred to the POTS interface
Talk mode Off-Hook and talking with only one other party
10.2 Making an Outgoing Call
Case No Representation
0 When A is in the idle mode
1. A off-hook
2. A hears TAs DT
3. A dials the telephone number of C
4. TA2 rings C (if C is in idle mode, TA2 sends ICR to C)
5. A hears Networks RBT
6. C off-hook (TA2 stops ICR)
7. A talks to C (A is in talk mode with C)
1 When A at Case 0, step 3
1. If C is busy
2. A hears TAs BT
3. A on hook
4. A returns to idle mode
1.1 When A at Case 1, step 2
1. A flash
2. A go to Case 0, step 2
2 When A at Case 0, step 2/3/4/5/6
1. A on-hook
2. A is disconnected
3. A returns to the idle mode
3 When A at Case 0, step 4
1. A flash
2. TA2 stops to ring C
3. A go to Case 0, step 2
4 When A at Case 0, step 6/7
1. A flash
2. C is disconnect
3. C hears Other TAs BT
4. A go to Case 0, step 2
5 When A at Case 0, step 7 (talk mode)
1. A on-hook
2. C hears Other TAs BT
3. A is disconnected
4. A returns to idle mode
6 When A at Case 0, step 7 (talk mode)
1. C on-hook
2. C is disconnected
3. A go to Case 1, step 2
To hear the PTT telephone line dial tone on lifting the telephone A or B OFF-HOOK, use the following
command in HyperTerminal. i.e. AT%A5=0.
To hear the ISDN TAs internal dial tone on lifting the telephone A or B OFF-HOOK, use the following
command in HyperTerminal. i. e. AT%A5=1.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 52
10.3 Making an Incoming Call
Case No Representation
0 When A is in idle mode
1. TA receives an incoming call to A
2. TA rings A (TA sends ICR to A)
3. A off-hook
4. A talks to the originated party (talk mode)
1 When A is in (1) Outgoing call, Case 0, step 1/2/3
1. TA receives an incoming call to A
2. TA reject the incoming call
3. A still at (1) Outgoing call, Case 0, step 1/2/3 (As state is not
changed)
10.4 Making an Inner Communication
. TEL-A calls TEL-B by dialing * * 0
. TEL-B calls TEL-A by dialing * * 0
To enable inner communication give the following command in HyperTerminal. i.e. AT%A5=1&W (after
using this command, you will save the current inner communication settings even after powering OFF the TA)
10.5 Making a Local Call Waiting
Case No Representation
0 When A is in talk mode with C
1. A Talks to C (occupy one B-ch for example B1-ch)
2. D calls A
3. A hears TAs ICT
4. A flash
5. C holds (C hears LHT from TA)
6. A talks to D (B2-ch, if C use B1-ch then D should use B2-ch)
7. A flash
8. D holds (D hears silent from TA)
9. A go to Case 0, step 1
10.6 Making a Local Call Transfer
Case No Representation
0 When A is in talk mode with C
1. A talk to C
2. A flash +2
3. C hold (hears silent from TA)
4. A dial * * 0
5. TA rings B
6. B off-hook
7. B talks to C
8. A hears TAs BT
9. A returns to idle mode
1 When A at Case 0, step 5
1. if B is busy (off-hook or talking with somebody)
2. A hears TAs BT
3. A flash
4. A talks to C (A is in talk mode with C)
2 When A at Case 1, step 2
1. A on hook
2. TA rings A
3. A off-hook
4. A talks to C (A is in talk mode with C)
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 53
10.7 Making a Local 3 Party Conference
Same operating sequence with network 3 party conference.
Case No Representation
0 When A and D is in talk mode
1. A talks to D
2. A press flash key then press 1
3. D hears holding tone
4. A hears TA1s dial tone
5. A calls C
6. C off-hook
7. A and C is in talk mode
8. A press flash then press 0
A, D, C are in 3 party conference
10.8 Making a Local Call Forwarding
Case No Representation
0 1. Set AT$CF1 for local call forwarding
2. Set AT*CFG1 to enable global call forwarding
1. Set AT*CFA1 to enable call forwarding for A
2. Set AT*CFB1 to enable call forwarding for B
3. Set AT*CFG=xxxxxx for the global call forwarding number
(If TA received an incoming call but without called party
number then this call is named global call)
4. Set AT*CFA=xxxxxx for A call forwarding number only
5. Set AT*CFB=xxxxxx for B call forwarding number only
1 When TA received an incoming global call
1. TA will inform network to forward this incoming call to the
number specified by AT*CFG=xxxxxx
(For example, if set AT*CFG= to D then D will be ringed)
Note:
If there is no B-ch available, then TA will reject the local
call forwarding. Calling party will hear BT.
2 When TA received an incoming call directly for A
1. TA will inform network to forward this incoming call to the
number specified by AT*CFA=xxxxxx
(For example, if set AT*CFA= to D then D will be ringed)
Note:
If there is no B-ch available, then TA will reject the local
call forwarding. Calling party will hear BT.
3 When TA received an incoming call directly for B
1. TA will inform network to forward this incoming call to the
number specified by AT*CFA=xxxxxx
(For example, if set AT*CFA= to D then D will be ringed)
Note:
If there is no B-ch available, then TA will reject the local
call forwarding. Calling party will hear BT.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 54
APPENDIX
APPENDIX 1 DCE 9Pin D Type Connector Definition
1 2 3 5 4
6 7 8 9
Pin Signal Name Direction Description
3 SD, Send Data DTE send data to TA
2 RD, Receive Data TA send data to DTE
7 RS, Request to Send DTE request to send data
8 CS, Clear to Send TA inform DTE can to send data
6 DR, Data Set Ready TA is ready receiving command from DTE
5 SG, Signal Ground TA signal ground (GND)
1 CD, Carrier Detect TA inform DTE that has a call incoming already
4 ER, Data Terminal Ready
DTE is ready, it can working now
9 CI, Ring Indication Incoming ring indication
Terminating Resistor Settings (DIP Switch inside Battery Compartment)
Switch SW2
DIP Switch 1,2 - ON (default) =100 ohm Terminating
Resistor
DIP Switch 1,2 - OFF =0 ohm Terminating
Resistor
DIP Switch 3 - OFF (default) =N.A Keep in OFF Mode
DIP Switch 4 - OFF (default) =N.A Keep in OFF Mode
The Terminating Resistor of 100 ohm should be set in the
DMI-128ESU+, when your NT1 is set to 100 ohms, in the
point-to-point connection, between NT1 and TA.
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 55
APPENDIX 2 Disconnect Cause Indication
Class No. Description
001 Unassigned (unallocated) number
002 No route to specified transit network
003 No route to destination
006 Channel unacceptable
007 Call awarded and being delivered in an established channel
016 Normal call clearing
017 User busy
018 No user responding
019 User alerting no answer
021 Call rejected
026 Non-selected user clearing
027 Destination out of order
028 Incomplete number
029 Facility rejected
030 Response to STATUS ENQUIRY
Normal
Event
031 Normal, unspecified
034 No circuit/channel available
038 Network out of order
041 Temporary failure
042 Switching equipment congestion
043 Access information discarded
044 Requested circuit/channel not available
Resource
Unavailable
047 Resource unavailable, unspecified
049 Unable to use QOS
050
057 Bearer capability no authorized
058 Bearer capability not presently available
Service or
option not
available
063 Service or option not available
065 Bearer capability not implemented
066 Channel type not implemented
069 Requested facility not implemented
070 Only restricted digital information bearer capability is available
Service or
option not
implemented
079 Service or option not implemented, unspecified
081 Invalid call reference value
082 Identified channel does not exist
083 A suspended call exists, but this call identity does not
Exist
085 No call suspended
086 Call having the requested call identity has been cleared
088 Incompatible destination
091 Invalid transit network selection
Invalid
message
095 Invalid message, unspecified
096 Mandatory information element is missing
097 Message type non-existent or not implemented
098 Message not compatible with call state or message type non-existent
or not implemented
099 Information element non-existent or not implemented
100 Invalid information element contents
101 Message not compatible with call state
102 Recovery on time expiry
Protocol error
111 Protocol error, unspecified
Inter-working 127 Inter-working, unspecified
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 56
APPENDIX 3 Specification
Rate 2B +D Basic Rate (BRI)
Type External
S/T interface ITU-T I.430 S/T-interface
4-wire
2 x S/T-interface port
AMI line coding
RJ45 modular jack
Terminating resistance selectable for 100 Ohm or none
Connection (To NT1) Point-to-multipoint, point to point.
Analog port 2 x analog ports
RJ11 modular jack
ITU-T G.711 a-law
25Hz, 59Vrms ringing signal: 1-sec on, 2-sec off
Tone Generation
Dial tone: 400 +/- 20 Hz
Busy tone
Holding tone
Incoming tone
-59VDC
DTMF dialing
DTMF Caller ID
Data port 1 x data port
DB - 9SUB male connector or USB for Windows 98/2000
Auto - baud detection
DTE speed
1200/2400/4800/9600/19200/38400/57600/115200/230400 bps
Communication speed
Sync: 64000/128000 bps
Async: 1200/2400/4800/9600/19200/38400 bps
Hardware RTS/CTS flow control
Software Xon/Xoff flow control
1 * USB port
Protocol V.110
V.120
PPP 64K
ML-PPP 128K
X.75
X.25 on D
Soft-Fax
Channel bundling
BACP/BOD
D-LINK ISDN TA DMI-128ESU+ 57
Switching Euro ISDN (EDSS1)
LED Power: Power on indication
CONNECT: connected to ISDN Network
DTR: DTE ready
TX/RX: Data transmitting/receiving
LINE: ISDN Line is connected to TA
Power 230VAC, 50-60 Hz, o/p: DC 5V 2.8A
6 x AA battery (Alkaline)
Maintenance Power on self-diagnostic
Flash EPROM for software upgrade
Minimum operation mode
Factory default setting
User profile saving in non-volatile memory
EMI CE EMI Class-2
Operation 0 to 40 degree C
Humidity 10 to 95% RH
Dimension 55mm(W) x170mm (D) x155mm (H)
Weight 0.8Kg
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- 41 Mobile100 TechnicalDocumento107 páginas41 Mobile100 TechnicalCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 40 Inet100 IndexDocumento7 páginas40 Inet100 IndexCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- Block Diagram of System/RF Blocks: NSE-1 System Module UP8RDocumento15 páginasBlock Diagram of System/RF Blocks: NSE-1 System Module UP8RCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- Bài Gi NGK Thu Tvix LýDocumento11 páginasBài Gi NGK Thu Tvix LýCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- Wide Area Network (Wan) TrainerDocumento111 páginasWide Area Network (Wan) TrainerCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- Data Conditioning & Carrier Modulation Transmitter & Data Reconditioning & Carrier Demodulation ReceiverDocumento49 páginasData Conditioning & Carrier Modulation Transmitter & Data Reconditioning & Carrier Demodulation ReceiverCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 34 Modem100Documento16 páginas34 Modem100CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- Model-Dpcm100: Differential Pulse Code Modulation/Demodulation TrainerDocumento15 páginasModel-Dpcm100: Differential Pulse Code Modulation/Demodulation TrainerVăn Tấn ĐìnhAinda não há avaliações
- Local Area Network (Lan) TrainerDocumento36 páginasLocal Area Network (Lan) TrainerCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- MODEL-TRL200: Transmission Line TrainerDocumento6 páginasMODEL-TRL200: Transmission Line TrainerCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 30 Phone100Documento41 páginas30 Phone100CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Transmission Receiver Fiber Optic Trainer: MODEL-FOT102Documento5 páginasDigital Transmission Receiver Fiber Optic Trainer: MODEL-FOT102CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 3-Com116 PSKDocumento9 páginas3-Com116 PSKVăn Tấn ĐìnhAinda não há avaliações
- 2-Com115 FSK PDFDocumento9 páginas2-Com115 FSK PDFChauthanh94Ainda não há avaliações
- 20 Com208Documento16 páginas20 Com208CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Com123n TXDocumento7 páginas12 Com123n TXCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 16 17 Com411 Com412Documento19 páginas16 17 Com411 Com412CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Osc06Documento7 páginas05 Osc06CauVong Justin100% (1)
- 03 PLL02Documento8 páginas03 PLL02CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 09 Com104Documento8 páginas09 Com104CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Com306Documento19 páginas01 Com306trantrieuvnAinda não há avaliações
- Phase Lock Loop: Model-Plldm100Documento9 páginasPhase Lock Loop: Model-Plldm100CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 04 Osc100Documento17 páginas04 Osc100CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- DX 1227Documento11 páginasDX 1227Marcos Daniel Muñoz ToledoAinda não há avaliações
- McKenzie ThesisDocumento135 páginasMcKenzie Thesispreeti200726Ainda não há avaliações
- 49 43UJ6300-SA 0002 4602 WebOS3.5 PDFDocumento48 páginas49 43UJ6300-SA 0002 4602 WebOS3.5 PDFoskrrg100% (1)
- Release Note Update7 For Gateway3.12Documento9 páginasRelease Note Update7 For Gateway3.12kotrex3Ainda não há avaliações
- Rotary Encoder Basics: If Both Switches Are ClosedDocumento7 páginasRotary Encoder Basics: If Both Switches Are ClosedMohammed El-AwamryAinda não há avaliações
- Veronica PLL Parts ListDocumento4 páginasVeronica PLL Parts ListitutdswAinda não há avaliações
- SITEC-PM180-Datasheet 16Documento1 páginaSITEC-PM180-Datasheet 16Thriloknath PallaAinda não há avaliações
- WDM and DWDM MultiplexingDocumento113 páginasWDM and DWDM MultiplexingtonzkosgeiAinda não há avaliações
- Some Basic Microwave ComponentDocumento6 páginasSome Basic Microwave ComponentSuper SpecialAinda não há avaliações
- Dronacharya College of Engineering, GR - Noida.: Q6.Explain Bridges, Routers, Gateways and Different LevelDocumento4 páginasDronacharya College of Engineering, GR - Noida.: Q6.Explain Bridges, Routers, Gateways and Different Levelshyamsagar15Ainda não há avaliações
- Smart Attendance System Based On Face RecognitionDocumento23 páginasSmart Attendance System Based On Face Recognitiony jayarajuAinda não há avaliações
- Labeltac 4 Pro - Data Sheet: Lifetime WarrantyDocumento1 páginaLabeltac 4 Pro - Data Sheet: Lifetime WarrantyTerryAinda não há avaliações
- Sonora Design 5SATPL Power Inserter Polarity LockerDocumento5 páginasSonora Design 5SATPL Power Inserter Polarity LockerDavid WardAinda não há avaliações
- Product Feature: Single Phase RectifierDocumento2 páginasProduct Feature: Single Phase RectifierIgorTAinda não há avaliações
- CMQEE 3440A Data SheetDocumento5 páginasCMQEE 3440A Data Sheetnd2b8f4djmAinda não há avaliações
- Acer Aspire 4935 Compal La 4492p Kal90 Kalh0 Laptop Schematics Diagram PDFDocumento52 páginasAcer Aspire 4935 Compal La 4492p Kal90 Kalh0 Laptop Schematics Diagram PDFOgan AltrkyAinda não há avaliações
- REF54 Tob 750443 ENhDocumento158 páginasREF54 Tob 750443 ENhUday PowarAinda não há avaliações
- A High-Efficient Nonisolated Single-Stage On-Board Battery Charger For Electric Vehicles 2013Documento12 páginasA High-Efficient Nonisolated Single-Stage On-Board Battery Charger For Electric Vehicles 2013Léo NotzAinda não há avaliações
- Ida8S: Ida8 Networkable Pava System - Slave UnitDocumento4 páginasIda8S: Ida8 Networkable Pava System - Slave UnitAdrian PuruggananAinda não há avaliações
- MCB Discrimination-Practical ExercisesDocumento9 páginasMCB Discrimination-Practical ExercisesMan Swakarya UbattaAinda não há avaliações
- TP-Link Media Converter DatasheetDocumento10 páginasTP-Link Media Converter Datasheethery014405Ainda não há avaliações
- Wharfedale EVP X15PDocumento12 páginasWharfedale EVP X15PttnaingAinda não há avaliações
- EL 01190604701000-A SBMXGM120235 Electrical BlowerDocumento673 páginasEL 01190604701000-A SBMXGM120235 Electrical BlowerAli TradAinda não há avaliações
- On EIRP Control in Downlink Precoding For Massive MIMO ArraysDocumento5 páginasOn EIRP Control in Downlink Precoding For Massive MIMO ArraysdrphraoAinda não há avaliações
- Micropc Vortex86Dx™ 600 MHZ Cpu Module: Technical SpecificationsDocumento3 páginasMicropc Vortex86Dx™ 600 MHZ Cpu Module: Technical Specificationsvi naryAinda não há avaliações
- PIC Training System Manual - Rev2 - PICKit2 - 3 - 18 - 14 PDFDocumento47 páginasPIC Training System Manual - Rev2 - PICKit2 - 3 - 18 - 14 PDFJoseAinda não há avaliações
- ITSIMM CH 1Documento74 páginasITSIMM CH 1Jamile Katiuska García Zarcos100% (1)
- Turntable ManualDocumento2 páginasTurntable Manualreneleones0% (1)
- BC 300 ManualDocumento24 páginasBC 300 ManualFreddyo59100% (1)
- Philips Bulletins 2002Documento70 páginasPhilips Bulletins 2002mazzideAinda não há avaliações