Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Introduction
Enviado por
r2b2mDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Introduction
Enviado por
r2b2mDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
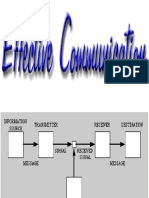
Introduction: Navigation is a art of science of conducting an aircraft/vehicle from one point to another point. U.S.
S. Dept of Defense decided to establish, develop, test, acquire and deploy GPS -1973 NAVSTAR GPS (Navigation Satellite Timing And Ranging Global Positioning System) GPS is a all weather Space based Navigation System GPS Satellites contains Radio transmitters, Atomic clocks, Various Equipment for Positioning, Military projects (atomic flash detection)
What is GPS? Global Positioning System(GPS) is technology that can be your accurate position anywhere on the earth (latitude/longitude). You need a special GPS receiver that can receive signals from satellites.
Satellite Information: Weighs approximately 2,000 lbs Travels 7,000 mph 17 feet across with solar panels extended Last 10 years Orbit 12,500 miles above Earth Circle the Earth twice daily.
How it works:
Satellite circles the Earth and transmits signal
Signal contains time it was sent and its location All satellites send their signal at the same time Difference in time to reach receivers is used to determine location. Formula: Distance = Speed x Time Signal travels at the speed of light 186,282.3976 miles per second Speed and Time are known, use to calculate Distance
NEED FOR GPS DEVICE A GPS device can be used for many things. From giving you turn-by-turn directions on a map to measuring time with great accuracy. The GPS provides quickly,accurately the time position &velocity of the object any where on the global at any time.
Principles of GPS GPS employs time of arrival(TOA) ranging for user position determination Three dimensional position location via intersection of multiple spheres How to GPS works: The GPS system consists of three pieces.There are the satellites that transmit the position information, there are the ground stations that are used to control the satellites and update the information,and finally there is the receiver that you purchased. It is the receiver that collects the data from satellites and computes its location anywhere in the world based on information it gets from satellites. GPS satellite system: The 24 satellites that make up the GPS space segment are orbiting the earth about 12,000 miles above us. They are constantly moving, making two complete orbits in less than 24 hours. These satellites are travelling at speeds of roughly 7,000 miles an hour.
GPS satellites are powered by solar energy. They have backup batteries onboard to keep them running in the event of a solar eclipse, when there's no solar power. Small rocket boosters on each satellite keep them flying in the correct path. Here are some other interesting facts about the GPS satellites (also called NAVSTAR, the official U.S. Department of Defense name for GPS): The first GPS satellite was launched in 1978.
A full constellation of 24 satellites was achieved in 1994. Each satellite is built to last about 10 years. Replacements are constantly being built and launched into orbit. A GPS satellite weighs approximately 2,000 pounds and is about 17 feet across with the solar panels extended. Transmitter power is only 50 watts or less.
GPS Space Segment: Consists of 24 satellites in circular orbits In 6 orbital planes equispaced 600 a part Period of 12 hours siderial time Semimajor axis of 26500 kms Four satellites in one plane, unevenly placed Eccentricity < 0.02 Inclination 550
This constellation allows atleast 4 satellites to be visible to a user on the earth, anywhere anytime (typically 6-8 satellites are visible at a time) GPS Satellite:
Uses of GPS: Locating Tracking Navigating Mapping Timing.
Impact of GPS: All weather, works in rain, clouds, sun and snow. High accuracy 3D position, velocity and time. 24 hours and world-wide availability. GPS has an impact in all related fields in geo-sciences and engineering. GPS equipment is very expensive compared with other equipment.
Sources of error in GPS :
Atmospheric Effects :
DGPS
GPS Signal 1 GPS Signal 4 GPS Signal RR Roving Receiver 1 Error correction message 1 Error correction message 4 Satellite GPS Signal 2 GPS Signal 3
Error correction message 2 Error correction message 3
Roving Receiver 2 Reference Receiver RR
Roving Receiver 4
Roving Receiver 3
DGPS APPLICATIONS Precision Agriculture
* * * * * * * * * *
Industrial Geodetic Surveying Marine and Air navigation Vehicle Guidance Military Fleet Management Forest/land asset Management Automatic Vehicle Location Aircraft landings GIS and Map Making
Why GPS / WAAS / LAAS? To provide an inexpensive and reliable global area navigation capability. This is the cornerstone of free flight. To provide an inexpensive precision approach capability everywhere. This is a significant safety benefit. To do this, we have to deliver a navigation system capable of these services without reliance on other navigation systems. That is the purpose of WAAS and LAAS. Atmospheric Errors: Signal propagates through Ionosphere and Troposphere Ionosphere extends from 70 1000 km. Troposphere extends up to 20 km from the ground level Ionospheric delay is freq. Dependent and can be removed by dual freq. Receiver Kloubuchar model gives 50% of the delay Trophospheric delay is independent of frequency
I t consists of dry component and Wet component Tropospheric delay can be successfully modeled Models by Hopfield, Black and Saastamonien are successful Multipath Error : The reception of a signal along a direct path and along one or more reflected paths. The classical example of multipath is the ghosting that appears on TV when an a plane passes overhead
Signal reaches antenna via two or more paths Effect can be reduced in the antenna design process Can also be reduced in the signal processing step Higher chip rate greater multipath immunity Pseudorange measurements 1- 5m Carrier phase measurements 1- 5 cms
Você também pode gostar
- Simulation of Soliton Propagation in Directional CouplersDocumento97 páginasSimulation of Soliton Propagation in Directional Couplersr2b2mAinda não há avaliações
- Plugin-Plasma 4th State of MatterDocumento42 páginasPlugin-Plasma 4th State of Matterr2b2mAinda não há avaliações
- My PlasmaDocumento1 páginaMy Plasmar2b2mAinda não há avaliações
- 105Documento3 páginas105r2b2mAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Clase Transformaciones TrigonometricasDocumento12 páginasClase Transformaciones TrigonometricasDiego Ventura VicentAinda não há avaliações
- Dragon Warrior - ManualDocumento36 páginasDragon Warrior - ManualguyAinda não há avaliações
- RF Plans, Symbols and Device Description: Attachment 014 666 A01Documento49 páginasRF Plans, Symbols and Device Description: Attachment 014 666 A01asohaibk_45197431100% (1)
- Service Manual: NSX-TR99Documento85 páginasService Manual: NSX-TR99Vidal VelasquezAinda não há avaliações
- JAA ATPL Aircraft Knowledge 4Documento738 páginasJAA ATPL Aircraft Knowledge 4abbasAinda não há avaliações
- Microwave Engineering - Complete Handwritten Lecture Notes (Lectures 1 Till 11)Documento49 páginasMicrowave Engineering - Complete Handwritten Lecture Notes (Lectures 1 Till 11)Chandra Mohanty92% (51)
- Broadcast Speech Radio and TelevisionDocumento15 páginasBroadcast Speech Radio and Televisionjaidy morgadezAinda não há avaliações
- Locking of Hene Laser Modes Induced by Synchronous Intracavity ModulationDocumento3 páginasLocking of Hene Laser Modes Induced by Synchronous Intracavity ModulationMohamad paidarAinda não há avaliações
- Adrf5020: 100 MHZ To 30 GHZ, Silicon SPDT SwitchDocumento12 páginasAdrf5020: 100 MHZ To 30 GHZ, Silicon SPDT SwitchMuhammad ArslanAinda não há avaliações
- CommunicationDocumento107 páginasCommunicationJose Rigoberto Corleto BerganzaAinda não há avaliações
- ZTE UMTS RAN Perfomance Monitor Feature GuideDocumento23 páginasZTE UMTS RAN Perfomance Monitor Feature GuideThiagu Manikandan100% (1)
- EU-type Examination Certificate UK/0126/0012 Revision 15Documento24 páginasEU-type Examination Certificate UK/0126/0012 Revision 15MjeriteljXAinda não há avaliações
- WLAN Topologies: Andrew CrouthamelDocumento30 páginasWLAN Topologies: Andrew CrouthamelMark BAinda não há avaliações
- USART Synchronous Mode - MCQs With AnswersDocumento2 páginasUSART Synchronous Mode - MCQs With AnswersRohit PendseAinda não há avaliações
- External Processing For Controlled Envelope Single Sideband Hershberger - QEX - 1 - 16Documento4 páginasExternal Processing For Controlled Envelope Single Sideband Hershberger - QEX - 1 - 16stanpjames2309Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab Manual - 801Documento28 páginasLab Manual - 801Shivratan GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- "Determination of Parameters in The Universal Induction Motor Model" Anand KumarDocumento19 páginas"Determination of Parameters in The Universal Induction Motor Model" Anand KumarAmit VermaAinda não há avaliações
- A TV Pattern Generator Part1Documento4 páginasA TV Pattern Generator Part1riverajluizAinda não há avaliações
- ZXSDR - Base Station Structure and Principles - ZTEDocumento59 páginasZXSDR - Base Station Structure and Principles - ZTEJacob ObboAinda não há avaliações
- Architectural Emi ShieldingDocumento229 páginasArchitectural Emi Shieldingrodrigoct88100% (1)
- Service Publications: Number SubjectDocumento60 páginasService Publications: Number SubjectJamesAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics World 1960-09Documento142 páginasElectronics World 1960-09Washington RibeiroAinda não há avaliações
- Puncher 2 Manual GuideDocumento2 páginasPuncher 2 Manual GuidejizzmoAinda não há avaliações
- Space Engineering: Multipaction Design and TestDocumento88 páginasSpace Engineering: Multipaction Design and TestRamiro ArtazaAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Custom Autosound USA-630Documento8 páginasManual Custom Autosound USA-630Jesus TAinda não há avaliações
- Baby Girl Proposal - For MergeDocumento20 páginasBaby Girl Proposal - For MergeKenji JasperAinda não há avaliações
- Unmatched Performance Marine Satellite TV Antenna System: IntellianDocumento2 páginasUnmatched Performance Marine Satellite TV Antenna System: IntellianManikanta Sai KumarAinda não há avaliações
- DataSheet Equipo Nokia PDFDocumento53 páginasDataSheet Equipo Nokia PDFJhordan FelipeAinda não há avaliações
- 真藍牙耳機晶片與系統 設計 Data Converters: Su-Hao Wu (吳書豪)Documento48 páginas真藍牙耳機晶片與系統 設計 Data Converters: Su-Hao Wu (吳書豪)黃良初100% (1)
- 119A2032 Krishnaveni Doki MCS Exp5Documento8 páginas119A2032 Krishnaveni Doki MCS Exp5Ishika DokiAinda não há avaliações