Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-B
Enviado por
Kenrick Randell IbanaDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-B
Enviado por
Kenrick Randell IbanaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
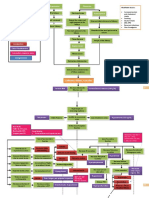
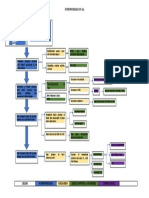
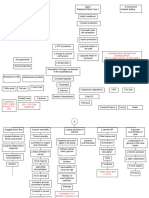
Diabetic Nephropathy
Chronic Glomerulonephritis
Chronic Pyelonephritis
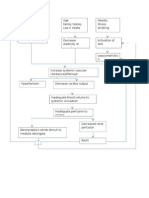
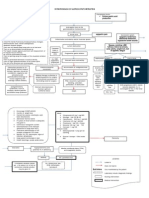
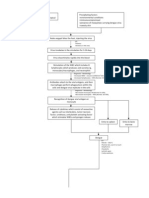
Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure
Non-modifiable Risk Factors: Age Gender Heredity Modifiable Risk Factors: Diet Sedentary Lifestyle Nephrotoxins
Polycystic Kidney Dse.
HPN
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Intracellular Glucose Repeated Inflammation
Multiple Bilateral Cysts
Long Standing HPN leads to further arteriosclerosis
Supports the formation of abnormal glycoprotein in the basement membrane of glomerulus
Ischaemia, Nephron loss, Shrinkage of Kidney Stage
Renal Blood Renal Reserve Damage to Nephrons 50% damage More than 75% damage Renal Insufficiency As nephrons are destroyed, the remaining nephrons undergo changes to compensate for those Remaining nephrons must filter more solute particles from the Hypertrophy of remaining nephrons Nephrons cannot tolerate the work Further damage of nephrons 80-90% damage Renal Failure Impaired kidney function & Uremia GFR 20-50% BUN, Creatinine GFR 50% Normal BUN, Creatinine
As cysts fill, enlarge & multiply, kidneys also enlarge Renal blood vessels & nephrons are compressed & obstructed & functional tse. are destroyed Renal Parenchyma atrophies & become fibrotic & scarred
Production of large variety of auto antibodies against normal body components such as nucleic acids, RBC, platelet, and WBC SLE antibodies react with their corresponding antigen
Glomerulosclerosis impairs the filtering fxn. of the glomerulus thus protein lost in urine
Forms Immune Complexes
Deposited in the connective tse. such as blood volume & kidneys
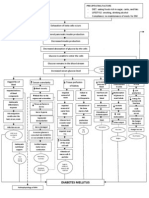
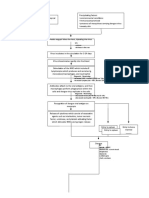
Stage
Trigger an inflammatory response and damage the kidney
Stage
GFR 10-20% Sharp BUN,
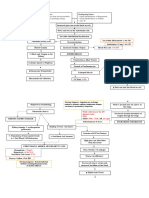
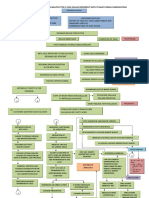
Na & H2O retention
K retention
+
HCO3 production in kidney
H retention
+
Urine Output Oliguria
Blood
Hyperkalemia Metabolic Acidosis Lungs Compensates Kussmauls Respiration
Nitrogenous waste impairs platelets GI stress
Erythropoietin production
Mg retention
+
Vit. D activation
Phosphate retention Hyperphosphatemi Ca+ absorption
Continuous decline in renal fxn. > 90% kidney Reduction in renal capillaries Scarring of Glomeruli Atrophy & Fibrosis of Stage End Stage Renal Dse. (ESRD) Continuous Multisystem Affectation Death
Bleeding tendencies
Hypermagnesemia Anemia
Toxins irritate pericardial sac Pericarditi Cardiac Tamponade
Toxins impair WBCs, humoral & cell mediated immunity; Fever is suppressed; Phagocyte becomes defective
Salivary urea breakdown Uremic Fetor
Deposit of urea on skin Uremic Frost Yellowish hue
Toxins affect the nerve fibers Atrophy & Demyalination Peripheral Neuropath Restless Leg Syndrome
Toxins causes CNS affectation Uremic Encephalopathy Reduction in alertness & awareness Changes in mentation Difficulty of concentrating Fatigue Insomnia Psychiatric symptoms
Retentio n of Cells become resistant to insulin Erratic blood glucose level Because of glucose intracellularly, liver produces tryglycerides & HDL
Malfunction of RAAS
GI bleeding
Blood loss during hemodialysis
Hypocalcemia Parathyroid overworks (Hyperparathyroidism) PTH secretion Ca+ resorption from bone + Ca absorption from GI tract Renal Osteodysthrophy Osteomalacia Osteoporosis Bone tenderness Bone pain Muscle Weakness
Immune System Decline Risk for Superinfection
Irritation of Phrenic Hiccups
Edema
Heart Failure
Anorexia Nausea Vomiting Gastroenteritis Peptic Ulcer
Loss of appetite Fatigue Weakness Pallor
GFR less than 10%
Pulmonary Edema Peripheral Edema
Atherosclerosis
Thrombus & Embolus Formation
By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-B
Você também pode gostar
- End Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocumento2 páginasEnd Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramSharmaine Camille de LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Kidney DiseaseDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Kidney DiseaseSTEPHANIE JOSUE100% (1)
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocumento2 páginasPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Ainda não há avaliações
- Patho Liver Cirrhosis PathoDocumento1 páginaPatho Liver Cirrhosis Pathochelle_asenjoAinda não há avaliações
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocumento3 páginasAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocumento1 páginaPathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocumento3 páginasHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Retention of Ca in kidneys causes kidney stonesDocumento2 páginasRetention of Ca in kidneys causes kidney stonesQueenie Rose ArsenalAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Modifiable, Partially Modifiable, and Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic DiseaseDocumento15 páginasNon-Modifiable, Partially Modifiable, and Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic DiseaseWiljohn de la CruzAinda não há avaliações
- PATHOPHYDocumento3 páginasPATHOPHYArlly Faena AbadAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of ESRD: Organ Dysfunctions & Associated AbnormalitiesDocumento5 páginasPathophysiology of ESRD: Organ Dysfunctions & Associated AbnormalitiesCarl JardelezaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZDocumento8 páginasPathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZAnna Lira Manluyang MungcalAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes PathoDocumento2 páginasDiabetes Pathodrewcel100% (1)
- CeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginasCeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyJjessmar Bolivar FamaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of AllDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of AllBGHMC PEDIAHOAinda não há avaliações
- Predisposing and precipitating factors leading to ESRD, DM, atherosclerosis, and pneumoniaDocumento11 páginasPredisposing and precipitating factors leading to ESRD, DM, atherosclerosis, and pneumoniaJonathan CuaAinda não há avaliações
- CKD - For Concept MappingDocumento7 páginasCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- Nephrotic Syndrome PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaNephrotic Syndrome PathophysiologyKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology HPN CvaDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology HPN Cvatresdos09Ainda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Hypertension, Diabetes, Ubm, BPHDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Hypertension, Diabetes, Ubm, BPHCarly Beth Caparida LangerasAinda não há avaliações
- Addison'sDocumento4 páginasAddison'sKoRnflakesAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)Documento3 páginasDiabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)John Henry ValenciaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisAprille Rose UrbanoAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology CVD InfarctDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology CVD InfarctElisa KerrAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysio CRF2 - RevisedDocumento1 páginaPathophysio CRF2 - Reviseddeborah malnegroAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Kawasaki Disease: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology Diagram of Kawasaki Disease: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsAb Staholic Boii100% (1)
- Predisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento52 páginasPredisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsMoshi MoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type IIEricka Genove100% (1)
- Renal Concept MapDocumento1 páginaRenal Concept MapShaira Ann CalambaAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Documento6 páginasConcept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Ran PioloAinda não há avaliações
- DB13 - Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocumento2 páginasDB13 - Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosisi_vhie03Ainda não há avaliações
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseDocumento3 páginasDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseAngel FiloteoAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map Worksheet Mary Richards Heart Failure Jasgou1752Documento3 páginasConcept Map Worksheet Mary Richards Heart Failure Jasgou1752Jasmyn Rose100% (1)
- Vii. Pathophysiology A. AlgorithmDocumento2 páginasVii. Pathophysiology A. AlgorithmJonna Mae TurquezaAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State - A Diabetic EmergencyDocumento2 páginasHyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State - A Diabetic EmergencyNiken AninditaAinda não há avaliações
- Anal Canal: Fissure in Ano HaemorrhoidsDocumento37 páginasAnal Canal: Fissure in Ano Haemorrhoidsyash shrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyAinda não há avaliações
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginas"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocumento3 páginasSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoAinda não há avaliações
- Precipitating Factors:: Myocardial Cell Death (NecrosisDocumento2 páginasPrecipitating Factors:: Myocardial Cell Death (NecrosisLean Ashly MacarubboAinda não há avaliações
- Pathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDocumento4 páginasPathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseOnyedika EgbujoAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology CKDDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology CKDSugar Capule - ManuelAinda não há avaliações
- Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusDocumento3 páginasPa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusPong's Teodoro SalvadorAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: What is it and What Causes itDocumento12 páginasAcute Glomerulonephritis: What is it and What Causes itSara Sonnya Ayutthaya NapitupuluAinda não há avaliações
- Hypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFDocumento6 páginasHypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFBella TogasAinda não há avaliações
- Path o PhysiologyDocumento9 páginasPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map of CKD Gastrointestinal SymptomsDocumento4 páginasConcept Map of CKD Gastrointestinal SymptomsWendy Escalante0% (1)
- Kidney Function and Chronic Renal FailureDocumento50 páginasKidney Function and Chronic Renal FailureKevin MontoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction PathophysiologyDocumento2 páginasGastric Outlet Obstruction PathophysiologyTania Noviza100% (1)
- DIabetes Mellitus ! Patho (Complete)Documento8 páginasDIabetes Mellitus ! Patho (Complete)freyaAinda não há avaliações
- Osteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Documento34 páginasOsteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Angelic khanAinda não há avaliações
- Heart FailureDocumento10 páginasHeart Failureurmila prajapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology On DementiaDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology On Dementiaiamjulzcurtis50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of DMDocumento5 páginasPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Managing Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with DiabetesDocumento47 páginasManaging Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with DiabetesTamzid Rabby TanmoyAinda não há avaliações
- Presented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureDocumento40 páginasPresented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureRavanshi ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- Alternative NamesDocumento67 páginasAlternative NamespashaAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Renal Failure-7Documento5 páginasChronic Renal Failure-7GERA SUMANTHAinda não há avaliações
- Pa Tho Physiology DengueDocumento2 páginasPa Tho Physiology DengueKenrick Randell IbanaAinda não há avaliações
- Laser Therapy in Cardio DiseasesDocumento1 páginaLaser Therapy in Cardio DiseasesKenrick Randell IbanaAinda não há avaliações
- Diffuse Lewy Body Disease NonameDocumento5 páginasDiffuse Lewy Body Disease NonameKenrick Randell IbanaAinda não há avaliações
- Travel To Belgian BrusselsDocumento3 páginasTravel To Belgian BrusselsKenrick Randell IbanaAinda não há avaliações
- Laser Therapy in Cardio DiseasesDocumento1 páginaLaser Therapy in Cardio DiseasesKenrick Randell IbanaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Fever and Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Dengue Fever and Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverKenrick Randell IbanaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Fever and Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Dengue Fever and Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverKenrick Randell IbanaAinda não há avaliações
- Travel To Belgian BrusselsDocumento3 páginasTravel To Belgian BrusselsKenrick Randell IbanaAinda não há avaliações
- PC Metabolic AcidosisDocumento4 páginasPC Metabolic AcidosisErine Emmanuelle Cawaling Hetrosa50% (2)
- Managing Uremia in a CKD PatientDocumento14 páginasManaging Uremia in a CKD PatientGrape JuiceAinda não há avaliações
- Immune Dysfunction and Risk of Infection in CKD - 2019Documento8 páginasImmune Dysfunction and Risk of Infection in CKD - 2019Lú VillalobosAinda não há avaliações
- Death Benefits CasesDocumento4 páginasDeath Benefits CasesSittie Aina MunderAinda não há avaliações
- Vital Signs ReferenceDocumento177 páginasVital Signs ReferenceQueenie FarrahAinda não há avaliações
- Teaching Plan NutritionDocumento2 páginasTeaching Plan NutritionAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (3)
- Uremic EncephalopathyDocumento12 páginasUremic EncephalopathyRAechelle_Marc_4102Ainda não há avaliações
- Daftar Pustaka-DikonversiDocumento7 páginasDaftar Pustaka-DikonversiRomi MufthiAinda não há avaliações
- NCP: Chronic Renal FailureDocumento14 páginasNCP: Chronic Renal FailureJavie77% (13)
- Nephrology by Prof NegoDocumento9 páginasNephrology by Prof NegoAbedinego MalukaAinda não há avaliações
- Dr.M.Kannan MD DA Professor and HOD of Anaesthesiology Tirunelveli Medical CollegeDocumento26 páginasDr.M.Kannan MD DA Professor and HOD of Anaesthesiology Tirunelveli Medical CollegeAlina CiubotariuAinda não há avaliações
- "Shankha Prakshalana" (Gastrointestinal Lavage) in Health and DiseaseDocumento8 páginas"Shankha Prakshalana" (Gastrointestinal Lavage) in Health and DiseasesoloroloAinda não há avaliações
- Advances in Hemodiafiltration - Ed by Ayman KarkarDocumento158 páginasAdvances in Hemodiafiltration - Ed by Ayman KarkarbeguenineAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges of delayed awakening after anesthesiaDocumento3 páginasChallenges of delayed awakening after anesthesiaaksinuAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiorenal Syndrome in Heart Failure PDFDocumento277 páginasCardiorenal Syndrome in Heart Failure PDFCosmin AndreiAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Encephalopathy and CausesDocumento7 páginasTypes of Encephalopathy and CausesApriansyah Arfandy AzisAinda não há avaliações
- Renal System Examination OSCE GuideDocumento23 páginasRenal System Examination OSCE GuideBasem Fuad MohammadAinda não há avaliações
- Patofisiologi & Penatalaksanaan Gagal Ginjal KronikDocumento34 páginasPatofisiologi & Penatalaksanaan Gagal Ginjal KronikAvenaAthaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Path o CardsDocumento194 páginasNursing Path o CardsDanielle Shull100% (1)
- CKD Pocket GuideDocumento2 páginasCKD Pocket GuideLutfi MalefoAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer Science Grade 9Documento43 páginasReviewer Science Grade 9Earl AndreiAinda não há avaliações
- Kidney Injury: AcuteDocumento14 páginasKidney Injury: AcuteRizkyaFarhanAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Impairment, Management, Types and Challenges - Emaad M. O. Abdel-RahmanDocumento159 páginasFunctional Impairment, Management, Types and Challenges - Emaad M. O. Abdel-RahmanJorge MartinsAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Toxic-Metabolic Encephalopathy in Adults - UpToDateDocumento19 páginasAcute Toxic-Metabolic Encephalopathy in Adults - UpToDateBruno FernandesAinda não há avaliações
- ACUTE AND CHRONIC RENAL FailureDocumento15 páginasACUTE AND CHRONIC RENAL Failuremaggayj11100% (1)
- Renal Diseases ReviewDocumento45 páginasRenal Diseases ReviewRaheelAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatologic Manifestations of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento27 páginasDermatologic Manifestations of Chronic Kidney DiseaseMadusha Lakshan NagasingheAinda não há avaliações
- DIET in Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento3 páginasDIET in Chronic Kidney Diseaseatul_desai_3Ainda não há avaliações
- Articulo Manejo Paciente IrcDocumento8 páginasArticulo Manejo Paciente IrcJUAN FONSECAAinda não há avaliações
- Early Risk Score Predicts Treatment for GI BleedingDocumento4 páginasEarly Risk Score Predicts Treatment for GI BleedingjimotivaAinda não há avaliações