Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Vlsi Lab
Enviado por
ASDFGHJNDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Vlsi Lab
Enviado por
ASDFGHJNDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CMOS INVERTER
AIM: To perform the functional verification of the CMOS Inverter through schematic entry.
APPARATUS REQUIRED: S-Edit using Tanner Tool. THEORY: CMOS Inverter consist of nMOS and pMOS transistor in series connected between VDD and GND. The gate of the two transistors are shorted and connected to the input. When the input to the inverter A = 0, nMOS transistor is OFF and pMOS transistor is ON. The output is pull-up to VDD. When the input A = 1, nMOS transistor is ON and pMOS transistor is OFF. The Output is Pull-down to GND.
PROCEDURE 1. Draw the schematic of CMOS Inverter using S-edit. 2. Perform Transient Analysis of the CMOS Inverter. 3. Obtain the output waveform from W-edit. 4. Obtain the spice code using T-edit. RESULT: The functionality of the CMOS Inverter was verified using transient analysis.
Powered By www.technoscriptz.com
Powered By www.technoscriptz.com
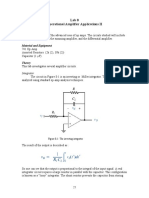
DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER AIM: To calculate the gain, bandwidth and CMRR of a differential amplifier through schematic entry. APPARATUS REQUIRED: S-Edit using Tanner Tool. Theory : A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that multiplies the difference between two inputs by some constant factor (the differential gain). Many electronic devices use differential amplifiers internally. The output of an ideal differential amplifier is given by:
Where
and
are
the
input
voltages
and Ad is
the
differential
gain.
In practice, however, the gain is not quite equal for the two inputs. This means that if and are equal, the output will not be zero, as it would be in the ideal case. A more realistic expression for the output of a differential amplifier thus includes a second term.
Ac is called the common-mode gain of the amplifier. As differential amplifiers are often used when it is desired to null out noise or bias-voltages that appear at both inputs, a low common-mode gain is usually considered good. The common-mode rejection ratio, usually defined as the ratio between differential-mode gain and common-mode gain, indicates the ability of the amplifier to accurately cancel voltages that are common to both inputs. Common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR):
PROCEDURE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Draw the schematic of differential amplifier using S-edit and generate the symbol Draw the schematic of differential amplifier circuit using the generated symbol. Perform AC Analysis of the differential amplifier. Obtain the frequency response from W-edit. Obtain the spice code using T-edit.
RESULT: The gain, bandwidth of the differential amplifier was obtained using AC analysis.
Powered By www.technoscriptz.com
Powered By www.technoscriptz.com
Powered By www.technoscriptz.com
LAYOUT OF CMOS INVERTER
AIM: To draw the layout of CMOS Inverter using L-Edit and extract the SPICE code.
APPARATUS REQUIRED: L-Edit & T-SPICE - Tanner Tool. PROCEDURE 1. Draw the CMOS Inverter layout by obeying the Lamda Rules using L-edit. i. Poly - 2 ii. Active contact - 2 iii. Active Contact Metal - 1 iv. Active Contact Active region - 2 v. Active Region Pselect - 3 vi. Pselect nWell - 3 2. Check DRC to verify whether any region violate the lamda rule. 3. Setup the extraction and extract the spice code using T-spice. RESULT: The layout of CMOS Inverter was drawn and generated the SPICE Code.
Powered By www.technoscriptz.com
Powered By www.technoscriptz.com
Powered By www.technoscriptz.com
Você também pode gostar
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Ainda não há avaliações
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Nota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (3)
- EDN Design Ideas 2006Documento142 páginasEDN Design Ideas 2006chag1956100% (1)
- Articolo SWR EngDocumento4 páginasArticolo SWR EngLuis Enrique Castillejo GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Signal Conditioning Operations GuideDocumento34 páginasSignal Conditioning Operations GuidemathewosAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Testing of Instrumentation AmplifierDocumento76 páginasDesign and Testing of Instrumentation Amplifierarun93921100% (1)
- Integrated Analog Electronics Design of Two-Stage Opamp Project ReportDocumento24 páginasIntegrated Analog Electronics Design of Two-Stage Opamp Project ReportGülçin Köse50% (2)
- Measuring Total Power of AM TransmitterDocumento44 páginasMeasuring Total Power of AM TransmitterNikhil KolheAinda não há avaliações
- Two Stage RC Amplifier CircuitDocumento3 páginasTwo Stage RC Amplifier Circuitfarzana kousar100% (1)
- Wein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2Documento11 páginasWein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2krishna goggiAinda não há avaliações
- Simulation of rectifier, amplifier and sensor circuitsDocumento12 páginasSimulation of rectifier, amplifier and sensor circuitsShashiAinda não há avaliações
- Design and DSP Implementation of 3.3-kW Resonant LLC On-Board Charger (AN005)Documento23 páginasDesign and DSP Implementation of 3.3-kW Resonant LLC On-Board Charger (AN005)uzair aminAinda não há avaliações
- AN005-Design and DSP Implementation of 3.3-kW Resonant LLC On-Board ChargerDocumento23 páginasAN005-Design and DSP Implementation of 3.3-kW Resonant LLC On-Board ChargerRudhi KurniawanAinda não há avaliações
- DCLabDocumento31 páginasDCLabani rohiraAinda não há avaliações
- ADIC ExperimentsDocumento41 páginasADIC ExperimentsTushar PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Amplitude & Frequency Modulation Lab ExperimentsDocumento35 páginasAmplitude & Frequency Modulation Lab ExperimentsSharmila KrishnaswamyAinda não há avaliações
- VCO Produces Positive and Negative Output Frequencies PDFDocumento4 páginasVCO Produces Positive and Negative Output Frequencies PDFagmnm1962100% (1)
- 06 Wireless ReportDocumento17 páginas06 Wireless ReportshastryAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Circuits - II Lab ManualDocumento26 páginasElectronic Circuits - II Lab Manualbalabasker100% (1)
- 2-15-1381147174-25 .Design of 1 V.FULL PDFDocumento10 páginas2-15-1381147174-25 .Design of 1 V.FULL PDFABHILASH RAIAinda não há avaliações
- Communication Systems Lab Manual ExperimentsDocumento37 páginasCommunication Systems Lab Manual Experimentsnidheeshlal10Ainda não há avaliações
- Tidu 174Documento16 páginasTidu 174AmyAinda não há avaliações
- Lab3!Documento4 páginasLab3!SharvilAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Amplitude Modulation (AM) :-: Generation of AM Signal For Radio ReceiverDocumento5 páginasIntroduction To Amplitude Modulation (AM) :-: Generation of AM Signal For Radio ReceiverRavi TeliAinda não há avaliações
- Resonant&Buck ChopperDocumento18 páginasResonant&Buck ChopperKata Naresh BabuAinda não há avaliações
- Analog and Digital Ic'S Short Questions With AnswersDocumento41 páginasAnalog and Digital Ic'S Short Questions With Answerspriya adhavanAinda não há avaliações
- WIRE LESS Land Mine Detection Robo-VehicleDocumento35 páginasWIRE LESS Land Mine Detection Robo-VehicleDebashish BeheraAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristics and Compensation of ServomotorsDocumento46 páginasCharacteristics and Compensation of Servomotorsabixek100% (2)
- Unit 4 NotesDocumento9 páginasUnit 4 NotesPrathamesh BhavsarAinda não há avaliações
- Silicon Wafer (Substrate) Preparation 2. Epitaxial Growth 3. Oxidation 4. Photolithography 5. Diffusion 6. Ion Implantation 7. Isolation Techniques 8. MetallizationDocumento21 páginasSilicon Wafer (Substrate) Preparation 2. Epitaxial Growth 3. Oxidation 4. Photolithography 5. Diffusion 6. Ion Implantation 7. Isolation Techniques 8. MetallizationMangaiyarkarasi VengatachalamAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 9Documento13 páginasLab 9Abu BakarAinda não há avaliações
- IC Report Group4Documento11 páginasIC Report Group4pablo orellanaAinda não há avaliações
- Signal Processing Circuits: An Overview of Key ConceptsDocumento47 páginasSignal Processing Circuits: An Overview of Key ConceptsAthira rcAinda não há avaliações
- Maths OperationDocumento27 páginasMaths OperationTurkish GatxyAinda não há avaliações
- Op Amp Lab - Integrator, Summing Amp, Diff AmpDocumento4 páginasOp Amp Lab - Integrator, Summing Amp, Diff AmpAlexandreAinda não há avaliações
- ManualDocumento61 páginasManualprembalanAinda não há avaliações
- A High Performance CMOS Band - Gap Reference Circuit DesignDocumento6 páginasA High Performance CMOS Band - Gap Reference Circuit DesignKhaja Mujeebuddin QuadryAinda não há avaliações
- Biomedical Engineering Unit - I Two Mark QuestionsDocumento7 páginasBiomedical Engineering Unit - I Two Mark QuestionsMATHANKUMAR.SAinda não há avaliações
- ASE Dual Channel Bell 202 and V.23 Modem 1.1Documento7 páginasASE Dual Channel Bell 202 and V.23 Modem 1.1periAinda não há avaliações
- Applicatoin Note - Phil Zanotti (AD Converter)Documento4 páginasApplicatoin Note - Phil Zanotti (AD Converter)arturovinnAinda não há avaliações
- Eca Lab Manual PDFDocumento56 páginasEca Lab Manual PDFrppvch100% (5)
- DLC Lab ManualDocumento59 páginasDLC Lab ManualkulamangalamAinda não há avaliações
- ANALOG AND DIGITAL IC Short Question With AnswerDocumento46 páginasANALOG AND DIGITAL IC Short Question With AnswerMATHANKUMAR.S100% (1)
- A Manual To A LabDocumento6 páginasA Manual To A Lab1d22Ainda não há avaliações
- High Accuracy Impedance Measurements Using 12-Bit Impedance ConvertersDocumento6 páginasHigh Accuracy Impedance Measurements Using 12-Bit Impedance Converterschristobal_huntaAinda não há avaliações
- Digital StethoscopeDocumento4 páginasDigital StethoscopeDhaval ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No. 4 ADC PDFDocumento16 páginasExperiment No. 4 ADC PDFRia Cordova0% (1)
- Op-Amp Basics ExplainedDocumento40 páginasOp-Amp Basics ExplainedBhalchandra ChandakkarAinda não há avaliações
- EE21 Design of Closed Loop Controlled Ac Voltage Regulator Using TRIACDocumento3 páginasEE21 Design of Closed Loop Controlled Ac Voltage Regulator Using TRIACSatishkumar KundrapuAinda não há avaliações
- Digital To Analog Converter: Raghu Tumati May 11, 2006Documento30 páginasDigital To Analog Converter: Raghu Tumati May 11, 2006সাদ ইবনে মাজAinda não há avaliações
- Integrator Circuits: 7.0.1 ReadingDocumento5 páginasIntegrator Circuits: 7.0.1 Readingnaveenkv10_105528408Ainda não há avaliações
- Aic FL MergedDocumento14 páginasAic FL Mergedshashank.pg23Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter One Controlling The Operation of Wind-Solar Hybrid Power System Using Arduino-Based Hybrid MPPT ControllerDocumento48 páginasChapter One Controlling The Operation of Wind-Solar Hybrid Power System Using Arduino-Based Hybrid MPPT ControllerOdebunmi NathanielAinda não há avaliações
- Flyback Converter Design ThesisDocumento8 páginasFlyback Converter Design Thesisleanneuhlsterlingheights100% (2)
- DC Manual FinalDocumento42 páginasDC Manual FinalsrvsbondAinda não há avaliações
- ES442 Lab 6 Frequency Modulation and Demodulation: ObjectiveDocumento6 páginasES442 Lab 6 Frequency Modulation and Demodulation: Objectiveحماد حسينAinda não há avaliações
- ES442 Lab 6 Frequency Modulation and Demodulation: ObjectiveDocumento6 páginasES442 Lab 6 Frequency Modulation and Demodulation: ObjectivekidusAinda não há avaliações
- AES VLSI ArchitectureDocumento11 páginasAES VLSI ArchitectureAbhishek JainAinda não há avaliações
- Spe184t PDFDocumento7 páginasSpe184t PDFaarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações
- Aes Instructions Set - WP PDFDocumento35 páginasAes Instructions Set - WP PDFaarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações
- VLSI Company ListDocumento2 páginasVLSI Company Listaarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações
- Safe Driving Using Mobile PhonesDocumento3 páginasSafe Driving Using Mobile Phonesaarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações
- Alu 8Documento2 páginasAlu 8aarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações
- Mosfet ModelingDocumento3 páginasMosfet Modelingaarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações
- Matlab Code For FiltersDocumento1 páginaMatlab Code For Filtersaarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações
- Alu 8Documento2 páginasAlu 8aarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações
- Matlab Code For FiltersDocumento1 páginaMatlab Code For Filtersaarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações
- Matlab Code For FiltersDocumento1 páginaMatlab Code For Filtersaarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações
- Matlab Code For FiltersDocumento1 páginaMatlab Code For Filtersaarunece10_866905186Ainda não há avaliações