Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Symbols Used in ECON 3240
Enviado por
Santosh Kumar GautamDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Symbols Used in ECON 3240
Enviado por
Santosh Kumar GautamDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Basic symbols used in ECON 3240 (also useful for ECON 4290)
Prof. Xavier de Vanssay *********************************************************************** * Y Yw Yr Yi Yr Yd y Yd Y* YFE C I G x M T S K Kc Ig = Real National Income/Real NDP (or Real NNP) = Income from wages, salaries. = Income from rentals and royalties = Interest Income = Income from retained business profit = Income from distributed business profit ( = dividend) = Nominal National Income/Nominal GDP (or NNP) = Disposable Income = Equilibrium level of output = Level of output at full employment (FE) = Consumption = Net (Fixed) Investment = Government spending = Exports = Imports = Net Tax revenues (= Taxes - Transfers) = Private (Households) Savings = Capital stock. = Depreciation of Capital Stock = Gross Investment
I dX
= [pronounce small delta] Depreciation rate . 3% is a normal value. = Ig - Kc = X = change in X (where X is a variable)
dX/dt = change in X due to change in time (where change is new old) = [pronounce X bar], when X (= a variable) is parametric, when x is exogenous. X Attention: Do not confuse this notation, used in my economic theory courses, with the one used in statistics, econometrics or forecasting courses, where X means the sample mean of X. X (pronounce X hat) = dlnX= dX/X = percentage change in X. (where X is a variable) Attention: Do not confuse this notation, used in my economic theory courses, with the one used in statistics, econometrics or forecasting courses, where X means the estimated value for X. P L = [When talking about price indices] is the Paasche index. = [When talking about price indices] is the Laspeyres index.
F = [When talking about price indices] is the Fisher index. (used by Statistics Canada: F= L.P ) a b APC APS MPS Sd Sa Id Ia IS LM = Autonomous component of the consumption function = Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) = Average Propensity to Consume = Average Propensity to Save = Marginal Propensity to Save = ex-ante savings (also known as desired savings) = ex-post savings (also known as actual savings) = ex-ante investment (also known as desired investment) = ex-post investment (also known as actual investment) = Investment/Savings (part of IS/LM Model) = Liquidity Market (part of IS/LM Model) 2
AS AD t h ATR r i id
= Aggregate Supply (part of AS/AD Model) = Aggregate Demand (part of AS/AD Model) = marginal tax rate = Autonomous component of the tax function = average tax rate = real interest rate = nominal interest rate (prime rate) = nominal discount rate
MEC = Marginal Efficiency of Capital J J CSR CLR L = level of inventories = changes in inventories = Short-run consumption function = Long-run consumption function = [pronounce small lambda], the Lagrange multiplier = the Lagrangian
MUC0 = Marginal Utility of C0 E(X) RRr DC FX DD CC H = Expected value of X, where X is a variable. = Required Reserve Ratio = Direct Claims = Foreign Exchange Reserves = Demand Deposits = Currency in Circulation = High Powered Money = Monetary Base
Ms Md Cr Rr XRr mm P T
= Nominal Money Supply = Nominal money Demand = Currency Ratio = Reserve Ratio = Excess Reserves Ratio = money multiplier = average price per transaction = number of transactions
M = nominal quantity of money in circulation (e.g. M1) Vt ms md Vc k PV0 PV1 ic in = Transaction velocity of Money = Real Money Supply = Real money Demand = Income velocity of circulation = a constant = present value at t=t0 = present value at t=t1 = [pronounce capital GAMMA], capital loss/gain on consol.] = [pronounce small GAMMA], % capital loss/gain on consol.] = critical interest rate = natural (long term) interest rate
E(W) = Expected Wealth 2 = [pronounce small SIGMA], standard deviation = variance
W w L H TPL
= [pronounce capital OMEGA], percentage of total wealth in non-human form = nominal wage rate = real wage rate = (here) leisure = number of hours worked = Total Labor Productivity
MPPL = Marginal Physical Productivity of Labour X SN DN = Number of workers = Labour Supply = Demand for labour.
(Last updated: September 2008)
Você também pode gostar
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionNo EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (8)
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsAinda não há avaliações
- CFA Level I Formula SheetDocumento27 páginasCFA Level I Formula SheetAnonymous P1xUTHstHT100% (4)
- Corporate Finance Formula SheetDocumento4 páginasCorporate Finance Formula Sheetogsunny100% (3)
- Formula SheetDocumento7 páginasFormula SheetanasfinkileAinda não há avaliações
- Formula SheetDocumento5 páginasFormula SheetherculesAinda não há avaliações
- CheatSheet (Finance)Documento1 páginaCheatSheet (Finance)Guan Yu Lim100% (3)
- MGT201 Financial Management Formulas Lect 1 To 22Documento13 páginasMGT201 Financial Management Formulas Lect 1 To 22Farhan UL HaqAinda não há avaliações
- 2017 Level I Formula SheetDocumento28 páginas2017 Level I Formula SheetVishal GoriAinda não há avaliações
- GSFSD 2 SDocumento32 páginasGSFSD 2 SJay SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Important FormulasDocumento5 páginasImportant FormulasKhalil AkramAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 Level I Formula Sheet 1 PDFDocumento27 páginas2018 Level I Formula Sheet 1 PDFShamima YesminAinda não há avaliações
- Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceDocumento6 páginasFormulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceNaeemAinda não há avaliações
- Corporate Finance - FormulasDocumento3 páginasCorporate Finance - FormulasAbhijit Pandit100% (1)
- Plant Design and EconomicsDocumento3 páginasPlant Design and EconomicsAnonymous NayakAinda não há avaliações
- R) (1 CF ...... R) (1 CF R) (1 CF CF NPV: Invesment Initial NPV 1 Invesments Initial Flows Cash Future of PVDocumento9 páginasR) (1 CF ...... R) (1 CF R) (1 CF CF NPV: Invesment Initial NPV 1 Invesments Initial Flows Cash Future of PVAgnes LoAinda não há avaliações
- CFA Formula Cheat SheetDocumento9 páginasCFA Formula Cheat SheetChingWa ChanAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 1. InvestmentDocumento9 páginasTopic 1. Investment휘슈휘슈Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 Rec Formula ResearchDocumento20 páginas1 Rec Formula Researchbhobot riveraAinda não há avaliações
- Abm FormulasDocumento39 páginasAbm FormulasYogambica Pilladi0% (1)
- Notes On National Accounting: Luciano MAURODocumento15 páginasNotes On National Accounting: Luciano MAUROiamamazerful111Ainda não há avaliações
- MGT201 Formulas From Chapter 1 To 22 (Documento11 páginasMGT201 Formulas From Chapter 1 To 22 (Ali IbrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Introductory DerivativesDocumento2 páginasIntroductory DerivativesnickbuchAinda não há avaliações
- Wealth Management: (Page 1 of 2) (Printed Only On One Side)Documento2 páginasWealth Management: (Page 1 of 2) (Printed Only On One Side)mohakbhutaAinda não há avaliações
- Profitability RatiosDocumento9 páginasProfitability RatiosfasmekbakerAinda não há avaliações
- CA IPCC FM Charts For All Chapters by CA Mayank KothariDocumento4 páginasCA IPCC FM Charts For All Chapters by CA Mayank Kotharishanky63167% (3)
- O o o o o Total Costs Q X V + FC o Accounting Break-Even: Q (FC + D) / (P-V)Documento3 páginasO o o o o Total Costs Q X V + FC o Accounting Break-Even: Q (FC + D) / (P-V)Ana C. RichiezAinda não há avaliações
- Pvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i IDocumento12 páginasPvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i ISyed Abdul Mussaver ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Pvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i IDocumento15 páginasPvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i INadir AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Important FormulasDocumento4 páginasImportant FormulasRakesh Ranjan JhaAinda não há avaliações
- CFA L1 Entire FRA Notes Summary Part 2Documento3 páginasCFA L1 Entire FRA Notes Summary Part 2Nishant SenapatiAinda não há avaliações
- BMS SSF 2009-10Documento46 páginasBMS SSF 2009-10Nitin GoriAinda não há avaliações
- PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocumento1 páginaPMP Formula Pocket Guidejindalyash1234100% (2)
- Numerical Problems PDFDocumento31 páginasNumerical Problems PDFciljokmoncyAinda não há avaliações
- CFM - FormulasDocumento3 páginasCFM - FormulasAbhijit PanditAinda não há avaliações
- Economic AnalysisDocumento3 páginasEconomic Analysismiang.gabriel0928Ainda não há avaliações
- Time Value AnalysisDocumento35 páginasTime Value Analysisrizalito_t7644Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2: Nature of Financial Accounting Principles: 3.8 Matching ConceptsDocumento6 páginasChapter 2: Nature of Financial Accounting Principles: 3.8 Matching ConceptsRavikumar GandhiAinda não há avaliações
- Real Estate Appraisal FormulasDocumento4 páginasReal Estate Appraisal FormulasMichelleOgatis83% (6)
- HW Chapter 11Documento3 páginasHW Chapter 11ndthtbbAinda não há avaliações
- Notes by RK SirDocumento80 páginasNotes by RK SirMriduAinda não há avaliações
- L 2 TIMEV1 - Class NotesDocumento12 páginasL 2 TIMEV1 - Class NotesSEKEETHA DE NOBREGAAinda não há avaliações
- DMSQF - Formula Sheet PDFDocumento1 páginaDMSQF - Formula Sheet PDFJudy PhanomphoneAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Management FormulasDocumento9 páginasFinancial Management FormulasTannao100% (1)
- Caiib-Abm-Important FormulaDocumento3 páginasCaiib-Abm-Important FormulaVasimAinda não há avaliações
- Fnce 100 Final Cheat SheetDocumento2 páginasFnce 100 Final Cheat SheetToby Arriaga100% (2)
- Financial Management: (Formulas From Chapter 1-22)Documento12 páginasFinancial Management: (Formulas From Chapter 1-22)Li Hui FooAinda não há avaliações
- Fin 440 Lecture 4Documento2 páginasFin 440 Lecture 4Sparkïñg KønaAinda não há avaliações
- Macro FinalDocumento198 páginasMacro FinalpitimayAinda não há avaliações
- Go To and Click Sing Up To RegisterDocumento16 páginasGo To and Click Sing Up To RegisterRana AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter4 Risk and ReturnDocumento70 páginasChapter4 Risk and ReturnOctari NabilaAinda não há avaliações
- BEC CPA Formulas - November 2015 - Becker CPA ReviewDocumento20 páginasBEC CPA Formulas - November 2015 - Becker CPA Reviewgavka100% (1)
- BMS FM SDF 2012-13Documento127 páginasBMS FM SDF 2012-13Digvijay KakuleAinda não há avaliações
- Strategic Financial Management Formula and Concept KitDocumento84 páginasStrategic Financial Management Formula and Concept KitNirmal ShresthaAinda não há avaliações
- Appraisal FormulaDocumento13 páginasAppraisal FormulaBangsa Qu Rash100% (2)
- Evaluating The Performance of An Investment CenterDocumento16 páginasEvaluating The Performance of An Investment Centeribrahim toksoyAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionNo EverandAccounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (8)
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionNo EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)No EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (9)
- Economics Sample ProblemDocumento6 páginasEconomics Sample ProblemanthonyAinda não há avaliações
- Business Finance Peirson 11e CH 3Documento24 páginasBusiness Finance Peirson 11e CH 3RitaAinda não há avaliações
- How Many Types of Swaps Are ThereDocumento2 páginasHow Many Types of Swaps Are ThereNagendra GadamSetty VenkataAinda não há avaliações
- S3 10-11paper 2 Half-YearlyDocumento7 páginasS3 10-11paper 2 Half-YearlyTO ChauAinda não há avaliações
- Fixed Income Asset Pricing: Course Objectives and OverviewDocumento10 páginasFixed Income Asset Pricing: Course Objectives and OverviewSiddharth NandaAinda não há avaliações
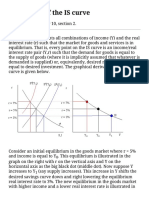
- Derivation of The IS Curve: Reading: AB, Chapter 10, Section 2Documento2 páginasDerivation of The IS Curve: Reading: AB, Chapter 10, Section 2olarshAinda não há avaliações
- Qs Based On W13 LectureDocumento3 páginasQs Based On W13 LectureMark S.PAinda não há avaliações
- p4 Afm BPP - Workbook-2020Documento625 páginasp4 Afm BPP - Workbook-2020david2151997Ainda não há avaliações
- Seminar 2Documento13 páginasSeminar 2Precious Diamond DeeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 21 The Monetary Policy and Aggregate Demand CurvesDocumento7 páginasChapter 21 The Monetary Policy and Aggregate Demand CurvesserbannerAinda não há avaliações
- Spouses Silos v. PNBDocumento2 páginasSpouses Silos v. PNBFrancisco Ashley AcedilloAinda não há avaliações
- 16 Volatility SmilesDocumento15 páginas16 Volatility SmilesGDFGDFererreerAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering EconomicsDocumento7 páginasEngineering EconomicsLynnAinda não há avaliações
- Derivatives AFMDocumento63 páginasDerivatives AFMSamarth SinghAinda não há avaliações
- (VCE Further) 2008 Insight Unit 34 Exam 2 Amended SolutionsDocumento45 páginas(VCE Further) 2008 Insight Unit 34 Exam 2 Amended SolutionsKawsarAinda não há avaliações
- Capital: Microeconomic TheoryDocumento67 páginasCapital: Microeconomic TheoryJennifer Gabrielle IrawanAinda não há avaliações
- Case 2a - Flirting With Risk - SolutionDocumento5 páginasCase 2a - Flirting With Risk - SolutionMahesh Satapathy67% (3)
- Updated Questions NotesDocumento10 páginasUpdated Questions NotesBijesh SahAinda não há avaliações
- Portfolio Theory and Assets Pricing ModelsDocumento67 páginasPortfolio Theory and Assets Pricing ModelsBhakti MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- Trial Version: Bb318 Bank Treasury ManagementDocumento4 páginasTrial Version: Bb318 Bank Treasury ManagementmsanusiAinda não há avaliações
- International Financial Management: Assignment # 1Documento7 páginasInternational Financial Management: Assignment # 1Sadia JavedAinda não há avaliações
- Interest Rate Pass Through: Case Study KBC GroupDocumento18 páginasInterest Rate Pass Through: Case Study KBC GroupMelanie VanAinda não há avaliações
- Synopsis Vasu ProjectDocumento7 páginasSynopsis Vasu ProjectRockyLagishettyAinda não há avaliações
- Excel Functions - Full ListDocumento13 páginasExcel Functions - Full ListKhan MohammadAinda não há avaliações
- Sbi Car LoanDocumento10 páginasSbi Car LoanShweta Yashwant Chalke100% (2)
- CH 06Documento9 páginasCH 06Bairah KamilAinda não há avaliações
- Macsg12: Aggregate Demand in The Money Goods and Current MarketsDocumento30 páginasMacsg12: Aggregate Demand in The Money Goods and Current MarketsJudithAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Compound Interest 1 4Documento17 páginasChapter 2 Compound Interest 1 4Rodin PaspasanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento42 páginasChapter 6Laraib KhanAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Interest Rate Parity TheoryDocumento2 páginas11 Interest Rate Parity TheoryPawan KasatAinda não há avaliações