Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Antacids
Enviado por
Ma Corazon MelecioDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Antacids
Enviado por
Ma Corazon MelecioDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Itopride HCl Indications Treatment of GI symptoms of functional, non ulcer dyspepsia (chronic gastritis) ie, feeling of abdominal bloatedness,
upper abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea and vomiting. Dosage Adults: Recommended Dose: 150 mg daily (50-mg tab taken orally 3 times a day before meals). Overdosage There have been no reported cases of overdose in humans. In case of excessive overdose, the usual measures of gastric lavage and symptomatic therapy should be applied. Administration Should be taken on an empty stomach (Take before meals.). Contraindications Known hypersensitivity to itopride HCl or any of the excipients. Patients in whom an increase in GI motility could be harmful eg, GI hemorrhage, mechanical obstruction or perforation. Special Precautions Itopride HCl enhances the action of acetylcholine and may produce cholinergic side effects. Data on long-term use are not available. Use in pregnancy: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Therefore, itopride HCl should not be used during pregnancy unless the benefits outweigh the potential risks. Labor and Delivery: There are no known effects of itopride HCl on labor or delivery. Use in lactation: Because itopride is excreted in milk and because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. Use in children: Safety of itopride in children <16 years has not been established. Use in the elderly: In general, appropriate caution should be exercised in the administration and monitoring of itopride HCl in elderly patients reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Adverse Drug Reactions The following adverse events have been reported in patients receiving itopride HCl. Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Leukopenia and thrombocytopenia. Immune System Disorders: Anaphylactoid reaction. Endocrine Disorders: Increased prolactin level and gynecomastia. Nervous System Disorders: Dizziness, headache, tremor. Gastrointestinal Disorders: Diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, increased saliva, and nausea. Hepatobiliary Disorder: Jaundice. Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Rash, redness, itching. Investigations: Increased AST (SGOT), increased ALT (SGPT), increased -GTP, increased alkaline phosphatase and increased bilirubin. Drug Interactions Metabolic interactions are not expected since itopride is primarily metabolized by flavine monooxygenase and not by CYP450. No changes in protein-binding have been seen with co-administration of warfarin, diazepam, diclofenac sodium, ticlopidine HCl, nifedipine and nicardipine HCl. Since itopride has gastrokinetic effects it could influence the absorption of concomitantly orally administered drugs. Particular caution should be taken with drugs with a narrow therapeutic index, sustained-release or enteric-coated formulations. Antiulcer drugs eg, cimetidine, ranitidine, teprenone and cetraxate do not affect the prokinetic action of itopride. Anticholinergic drugs may reduce the action of itopride. Storage Store at temperatures not exceeding 30C. Description Each tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: Lactose, corn starch, carmellose, light
anhydrous silicic acid, magnesium stearate, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose 2910 2 (6 mm /s), macrogol 6000, titanium oxide and carnauba wax. The tablet is formulated to provide immediate-release. Itopride HCl is N-(4-(2(dimethylamino)ethoxy)benzyl)-3,4-dimethoxybenzamide HCl. Itopride HCl is a substituted benzamide. It has an empirical formula of C20H26N2O4HCl and a molecular weight of 394.89 g/mol. Mechanism of Action Pharmacology: Mechanism of Action: Itopride HCl activates GI propulsive motility due to its dopamine D2 antagonizing activity and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. Itopride activates acetylcholine release and inhibits degradation. Pharmacodynamics: Itopride HCl also has antiemetic action through interaction with D2 receptors located in the chemoreceptor trigger zone. Itopride HCl has been shown to accelerate gastric emptying in humans. The action of itopride HCl is highly specific for the upper GIT. It does not affect serum gastrin levels. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Itopride HCl is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the GIT. Relative bioavailability is calculated to be 60% due to liver first-pass metabolism. There is no effect of food on bioavailability. Peak plasma levels (Cmax 0.28 mcg/mL) are reached after 30-45 min after 50 mg of itopride HCl. Following multiple oral doses ranging from 50-200 mg 3 times daily, itopride HCl and its metabolites showed linear pharmacokinetics over a treatment period of 7 days, with minimal accumulation. Distribution: Approximately 96% of itopride HCl is bound to plasma proteins. Albumin accounts for most of the binding. 1-acid glycoprotein accounts for <15% of binding. Metabolism: Itopride undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism in humans. Three metabolites have been identified, of which only 1 exerts minor activity without pharmacological relevance (approximately 2-3% of that of itopride). The primary metabolite in humans is the N-oxide generated by oxidation of the tertiary amine N-dimethyl group. Itopride is metabolized by a flavin-dependent monooxygenase (FMO3). The abundance and efficiency of the human FMO-isozymes can be subject to genetic polymorphisms, which can lead to a rare autosomal recessive condition known as trimethylaminuria (fish odor syndrome). The t of itopride may therefore be longer in trimethylaminuria patients. In vivo pharmacokinetic studies on CYP-mediated reactions revealed that itopride showed neither inhibitory nor inductory effect on CYP2C19 and CYP2E1, CYP content and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase activity were not altered with the administration of itopride. Excretion: Itopride HCl and its metabolites are primarily excreted in the urine. The urinary excretions of itopride and its N-oxide were 3.7% and 75.4%, respectively, in healthy subjects after oral administration of a single therapeutic dose. The terminal phase t of itopride HCl was approximately 6 hrs. Toxicology: Itopride has undergone extensive toxicological testing in various experimental models. The results of these studies are summarized in the table. Acute Toxicity Studies: Itopride was administered by the oral route in various experimental models. The LD50 values were high in all the groups, indicating that itopride has a wide range of safety. Subacute Toxicity Studies: Subacute toxicity studies were undertaken in rats, dogs and monkeys for a period of up to 3 months. No changes of toxicological significance were observed in these animals. Chronic Toxicity Studies: Itopride was administered orally to rats and dogs for 6 months and its effect on animals were observed. No treatment-related changes
of toxicological significance were seen. Studies in rats and rhesus monkeys indicated that itopride was not associated with physical dependence. Preclinical Safety Data: Itopride has been extensively evaluated for its clinical efficacy and tolerability in Japan and India. In Japan, the drug was evaluated in 572 patients. In India, the studies were undertaken in 6 centers with 179 patients. These studies enrolled patients suffering from gastric motility disorders like chronic gastritis, non-ulcer dyspepsia, reflux esophagitis and diabetic gastroparesis. The result of these clinical studies indicated that: Itopride was effective in providing moderate to complete relief of symptoms in 73-100% of the patients. Itopride effectively improved GI symptoms caused by reduced gastric motility like gastric fullness, upper abdominal pain, anorexia, heartburn, nausea and vomiting. Treatment with Ganaton (itopride) was consistently shown to be safe and well tolerated and did not cause prolongation of QT interval on ECG in these patients. Teratogenicity: Sub-acute toxicity studies were taken in rats, dogs and monkeys for a period of up to 3 months. No changes of toxicological significance were observed in these animals. Itopride was administered orally to rats and dogs for 6 months and its effect on animals were observed. No treatment-related changes of toxicological significance were seen. Studies in rats and rhesus monkeys indicated that itopride was not associated with physical dependence. Reverse mutations tests (Ames test), chromosomal aberration test and micronucleus test indicated that itopride was devoid of mutagenic potential. Studies in guinea pigs and mice revealed that itopride had no antigenic potential. Following oral administration of itopride 30, 100 and 300 mg/kg/day to rats and rabbits, no abnormalities in organogenesis and fetal developments were observed. MIMS Class GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories
Pantoprazole Generic Name: Pantoprazole sodium Dosage Form: tablet, delayed release Indications and Usage for Pantoprazole Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets are indicated for: Short-Term Treatment of Erosive Esophagitis Associated with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets are indicated in adults for the short-term treatment (up to 8 weeks) in the healing and symptomatic relief of erosive esophagitis. For those adult patients who have not healed after 8 weeks of treatment, an additional 8-week course of Pantoprazole sodium delayedrelease tablets may be considered. Safety of treatment beyond 8 weeks in pediatric patients has not been established. Pediatric indication and usage information in pediatric patients ages 5 years and older with erosive esophagitis associated with GERD is approved for Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. s Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets. However, due to Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information. Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets are indicated for maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis and reduction in relapse rates of daytime and nighttime heartburn symptoms in adult patients with GERD. Controlled studies did not extend beyond 12 months. Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions Including Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets are indicated for the long-term treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions, including Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Pantoprazole Dosage and Administration Recommended Dosing Schedule Pantoprazole sodium is supplied as delayed-release tablets. The recommended dosages are outlined in Table 1.
delayed-release tablets may be considered.
GELTAZINE
Dosage regimens should be adjusted to individual patient needs and should continue for as long as clinically indicated. Doses up to 240 mg daily have been administered. Generic : Aluminum hydroxide, Magnesium hydroxide, Oxethacaine Indication Dose Frequency Short-Term Treatment of Erosive Esophagitis Associated with GERD Adults Adults Adults 40 mg 40 mg 40 mg Once daily for up to 8 weeks* Once daily Twice daily Recommended Dosage: Pediatric dosing information in pediatric patients ages 5 years and older with erosive esophagitis associated with GERD is approved for Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. s Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets. However, due to Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information. Administration Instructions Directions for method of administration for the tablet dosage form are presented in Table 2. Table 2: Administration Instructions * Formulation Delayed-Release Tablets Route Oral Instructions* Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions Including Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome PPD Drug Class: Needs a Prescription: Indications: Gastro/ Acid-Peptic Disease Agents/ Antacids No Symptomatic relief of peptic ulcers (gastric & duodenal), acute/chronic gastritis, esophagitis & heartburn associated w/ hiatus hernia, pregnancy, post-radiation or other conditions. 1-2 caps thrice daily 30 mins before meals & at bedtime or as recommended by a physician.
Contents Al(OH)3 (dried gel) 400 mg, Mg(OH)2 97.5 mg, oxethazaine 10 mg Indications Symptomatic relief of peptic ulcer, acute & chronic gastritis, esophagitis & heartburn associated w/ hiatus hernia, pregnancy & postradiation. Dosage 1 cap tid. Administration May be taken with or without food Special Precautions Renal insufficiency. Adverse Drug Reactions Constipation; CNS depressions. Drug Interactions Reduces absorption of chlordiazepoxide, Fe compd, digoxin, indomethacin, tetracyclines, chlormazine, propranolol.
Patients should be cautioned that Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets should not be Antacids, Antireflux Agents & Antiulcerants ATC MIMS Class split, chewed, or crushed. Classification A02AX - Antacids, other combinations ; [?] Poison Schedule Non-Rx Swallowed whole, with or without food
Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets should be swallowed whole, with or without food in the stomach. If patients are unable to swallow a 40 mg tablet, two 20 mg tablets may be taken. Concomitant administration of antacids does not affect the absorption of Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets.
Table 1: Recommended Dosing Schedule for Pantoprazole Sodium Delayed-release Tablets * For adult patients who have not healed after 8 weeks of treatment, an additional 8-week course of Pantoprazole sodium
Você também pode gostar
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesNo EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- Ganaton SPCDocumento8 páginasGanaton SPCNguyen Manh TuanAinda não há avaliações
- A, A-Diphenyl-1-Piperidinebutyramide Monohydrochloride, Is A Synthetic Antidiarrheal ForDocumento10 páginasA, A-Diphenyl-1-Piperidinebutyramide Monohydrochloride, Is A Synthetic Antidiarrheal ForDevi SaputriAinda não há avaliações
- Itopride HCL Pynetic 50mg TabDocumento2 páginasItopride HCL Pynetic 50mg TabAusaf AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Cleveland Clinic Skugor Oral Antidiabetic MedicationsDocumento76 páginasCleveland Clinic Skugor Oral Antidiabetic MedicationstmdgusAinda não há avaliações
- 13.drugs For GI - Part IDocumento38 páginas13.drugs For GI - Part ILee BoborasAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacologic Agents For Chronic DiarrheaDocumento7 páginasPharmacologic Agents For Chronic DiarrheaAriAinda não há avaliações
- The Antihyperlipidaemic and Hepatoprotective Effect of Ipomoea Batatas L. Leaves Extract in High-Fat Diet RatsDocumento7 páginasThe Antihyperlipidaemic and Hepatoprotective Effect of Ipomoea Batatas L. Leaves Extract in High-Fat Diet RatsIJPHSAinda não há avaliações
- CyclosporineDocumento25 páginasCyclosporineraki9999Ainda não há avaliações
- Sambiloto PDFDocumento7 páginasSambiloto PDFMarselina SattuAinda não há avaliações
- Hypoglycemic effects of herbal formulations and gliclazide on diabetesDocumento7 páginasHypoglycemic effects of herbal formulations and gliclazide on diabetesNova RosalinaAinda não há avaliações
- Pharma - Drugs Affecting Git MotilityDocumento6 páginasPharma - Drugs Affecting Git MotilityBobet ReñaAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Acting On Gastro Intestinal TractDocumento20 páginasDrugs Acting On Gastro Intestinal TractManikanta GupthaAinda não há avaliações
- Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia and Elevated Liver Enzymes Associated With Thyroid Hormone Deficiency in NeonatesDocumento4 páginasNeonatal Hyperbilirubinemia and Elevated Liver Enzymes Associated With Thyroid Hormone Deficiency in NeonatesOlfiany Laurenzia PongohAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Acting on the Gastrointestinal SystemDocumento41 páginasDrugs Acting on the Gastrointestinal SystemDivya JoyAinda não há avaliações
- Furosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites EliminationDocumento4 páginasFurosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites Eliminationmole_fkAinda não há avaliações
- ItoprideDocumento2 páginasItoprideLesValenzuelaAinda não há avaliações
- Myoril Capsules PIDocumento6 páginasMyoril Capsules PIHaris MusakhelAinda não há avaliações
- Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant effects of naringeninDocumento12 páginasAntihyperglycemic and antioxidant effects of naringeninNyayu Fitriani MuttaqienAinda não há avaliações
- Leaflet - ProsoganDocumento7 páginasLeaflet - ProsoganurmymelodyAinda não há avaliações
- Antidiabetic Activity of Ruellia Tuberosa L Role oDocumento9 páginasAntidiabetic Activity of Ruellia Tuberosa L Role orandy hidayatAinda não há avaliações
- Onion Peel Extracts Ameliorate Hyperglycemia and Insulin Resistance in High Fat Diet/ Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic RatsDocumento8 páginasOnion Peel Extracts Ameliorate Hyperglycemia and Insulin Resistance in High Fat Diet/ Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic RatsRizky Agustian HadiAinda não há avaliações
- M3 - Lesson 1bDocumento20 páginasM3 - Lesson 1bLhara MañoAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Use of Drugs: Pharmacotherapy GI DisordersDocumento52 páginasClinical Use of Drugs: Pharmacotherapy GI DisordersalfamiftahulkhoirAinda não há avaliações
- MkpperiaDocumento10 páginasMkpperiaIlham Akbar Helmy KurniawanAinda não há avaliações
- Hormones & antagonists: Pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, gonadalDocumento27 páginasHormones & antagonists: Pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, gonadalVarsha Shende KhobragadeAinda não há avaliações
- Fitoterapia: Jianfeng Xue, Wenjun Ding, Yan LiuDocumento5 páginasFitoterapia: Jianfeng Xue, Wenjun Ding, Yan LiuAamir SohailAinda não há avaliações
- Fitoterapia: Jianfeng Xue, Wenjun Ding, Yan LiuDocumento5 páginasFitoterapia: Jianfeng Xue, Wenjun Ding, Yan LiuAamir SohailAinda não há avaliações
- Pioglitazone (Actos, Lilly) : May Be Confused With Actidose, ActonelDocumento3 páginasPioglitazone (Actos, Lilly) : May Be Confused With Actidose, Actonelshidyakg100% (1)
- ImotilDocumento2 páginasImotilMeraz AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- LM, KLDocumento5 páginasLM, KLVictor CondeAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Olanzapine and Haloperidol On The Metabolic Status of Healthy MenDocumento8 páginasEffects of Olanzapine and Haloperidol On The Metabolic Status of Healthy MenBenjamin paulAinda não há avaliações
- Antidiarrhoeal DrugsDocumento15 páginasAntidiarrhoeal DrugsJyoti SidhuAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Preparations: Erdosteine ZertinDocumento4 páginasOral Preparations: Erdosteine ZertinmagreaAinda não há avaliações
- Module 3.4 - EndocrineDocumento5 páginasModule 3.4 - EndocrineCatherine Sinen ObinqueAinda não há avaliações
- Antinauseants and AntiemeticsDocumento8 páginasAntinauseants and AntiemeticsHamad AlshabiAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasDrug StudyMarielle Denise Tagtag BugtongAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Kelompok 8Documento6 páginasJurnal Kelompok 8Bertha YunitaAinda não há avaliações
- The Endocrine System: Hypothalamus Pituitary GlandDocumento58 páginasThe Endocrine System: Hypothalamus Pituitary GlandMirumbi Kefa MomanyiAinda não há avaliações
- C - VVV VV VVVV VVV - VVV VV - VVVV VV VVDocumento3 páginasC - VVV VV VVVV VVV - VVV VV - VVVV VV VVBea Angela Bithao AnonoyAinda não há avaliações
- Uniuyo Physiology Final Project (CHAPTER 1&2)Documento41 páginasUniuyo Physiology Final Project (CHAPTER 1&2)Itoro UdohAinda não há avaliações
- DrugsDocumento8 páginasDrugsShizuka Marycris AmaneAinda não há avaliações
- Insulin and Anti Diabetic DrugsDocumento38 páginasInsulin and Anti Diabetic DrugsDharun Ranganathan100% (1)
- Endocrine Pharmacology GuideDocumento17 páginasEndocrine Pharmacology GuideUsmanAinda não há avaliações
- Laporan Kasus GastroenteritisDocumento7 páginasLaporan Kasus GastroenteritisinaAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of growth hormone treatment on obese NIDDM patientsDocumento1 páginaEffects of growth hormone treatment on obese NIDDM patientsamritaryaaligarghAinda não há avaliações
- 5th Draft DrugsDocumento7 páginas5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 9 Endocrine HormonesDocumento18 páginasLecture 9 Endocrine HormonesKC PalattaoAinda não há avaliações
- Research Article: The Extract of Herbal Medicines Activates AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in Diet-Induced Obese RatsDocumento9 páginasResearch Article: The Extract of Herbal Medicines Activates AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in Diet-Induced Obese RatsJoshAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs Classification Mechanisms Clinical Uses Side EffectsDocumento48 páginasOral Hypoglycemic Drugs Classification Mechanisms Clinical Uses Side EffectsUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Diabetes That The Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor May Act Effectively and SafelyDocumento5 páginasTypes of Diabetes That The Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor May Act Effectively and SafelyRidha Surya NugrahaAinda não há avaliações
- Cloxacillin Classification, Mechanism, IndicationsDocumento3 páginasCloxacillin Classification, Mechanism, IndicationsKrizzia CarlosAinda não há avaliações
- DILIDocumento28 páginasDILIsepti nurhidayatiAinda não há avaliações
- Sialogogues & Anti SailogoguesDocumento43 páginasSialogogues & Anti SailogoguesTavleen KaurAinda não há avaliações
- FIXINGPLENDocumento7 páginasFIXINGPLENNur Aini BudiyantiAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperuricemia Case DiscussionDocumento7 páginasHyperuricemia Case DiscussionVineth MartinAinda não há avaliações
- Treatments For Diabetes MellitusDocumento21 páginasTreatments For Diabetes MellitusValeria OboroceanuAinda não há avaliações
- Insuficiencia Pancreática Exocrina Canina Tratada Con Extracto Pancreático PorcinoDocumento4 páginasInsuficiencia Pancreática Exocrina Canina Tratada Con Extracto Pancreático PorcinoAndreaAinda não há avaliações
- Protective Effect of Thymoquinone Against Antitubercular Drug Induced Hepatic Toxicity in RatsDocumento8 páginasProtective Effect of Thymoquinone Against Antitubercular Drug Induced Hepatic Toxicity in RatsDiga AlbrianAinda não há avaliações
- Phani Jun 18Documento12 páginasPhani Jun 18Geetangli PanwarAinda não há avaliações
- KCCLDocumento18 páginasKCCLAnonymous v6pZ9s9MNAinda não há avaliações
- MRTZ Bestel GB PDFDocumento8 páginasMRTZ Bestel GB PDFmilanmcaAinda não há avaliações
- Fatal Side Effects: Medicine Patents Under The MicroscopeDocumento61 páginasFatal Side Effects: Medicine Patents Under The MicroscopeOxfamAinda não há avaliações
- Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Diazepam (Valium) : Nicholas E. Calcaterra and James C. BarrowDocumento8 páginasClassics in Chemical Neuroscience: Diazepam (Valium) : Nicholas E. Calcaterra and James C. BarrowEga Trikuntianti100% (1)
- Cefotaxime Drug Class, Uses, Side EffectsDocumento3 páginasCefotaxime Drug Class, Uses, Side EffectsKristi WrayAinda não há avaliações
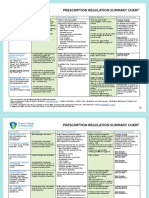
- PRESCRIPTION REGULATION SUMMARYDocumento2 páginasPRESCRIPTION REGULATION SUMMARYroxiemannAinda não há avaliações
- Bayes Therom Practice ProblemsDocumento2 páginasBayes Therom Practice ProblemsPadam Shrestha100% (2)
- Vincristine (OncovinDocumento4 páginasVincristine (Oncovin9959101161Ainda não há avaliações
- DPRI 2017 Edition Guide for Government Procurement of Essential MedicinesDocumento23 páginasDPRI 2017 Edition Guide for Government Procurement of Essential MedicineskrisconradAinda não há avaliações
- I Hi Trigger Tool For Measuring Adverse Drug EventsDocumento16 páginasI Hi Trigger Tool For Measuring Adverse Drug EventsGaby ValenzuelaAinda não há avaliações
- Hyoscine ButylbromideDocumento2 páginasHyoscine ButylbromideKepslock StahpAinda não há avaliações
- Final - Hikma Injectable 2020 CatalogDocumento80 páginasFinal - Hikma Injectable 2020 CatalogjayjayshrigokuleshAinda não há avaliações
- First Sem Pharma NotesDocumento75 páginasFirst Sem Pharma NotesLindsay LunodAinda não há avaliações
- Micro EmulsionDocumento39 páginasMicro Emulsionnazeer hasanAinda não há avaliações
- Medicinal and Aromatic Crops PDFDocumento194 páginasMedicinal and Aromatic Crops PDFAshutosh LandeAinda não há avaliações
- Antibacterial ChemotherapyDocumento47 páginasAntibacterial ChemotherapyPawan PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Document (12) 1Documento7 páginasDocument (12) 1Fazal JalalAinda não há avaliações
- Philhealth Cf4 2017-2018Documento8 páginasPhilhealth Cf4 2017-2018Julius Yves Dulfo BagacayAinda não há avaliações
- WHO Pharm 2-2023Documento19 páginasWHO Pharm 2-2023Paola Cristini Gama SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Guideline For Registration of Medical Devices in Sri LankaDocumento14 páginasGuideline For Registration of Medical Devices in Sri LankaVladimir Arguirov100% (1)
- JURISPRUDENCE Unit-1 Bachlor of PharmacyDocumento17 páginasJURISPRUDENCE Unit-1 Bachlor of PharmacySachin NagarAinda não há avaliações
- January 2009 Room Assignments For Pharmacy Licensure ExaminationDocumento35 páginasJanuary 2009 Room Assignments For Pharmacy Licensure ExaminationdericAinda não há avaliações
- مذكرة فارماكولوجي روعةDocumento56 páginasمذكرة فارماكولوجي روعةKomang Gede Suwija Negara100% (1)
- 1 BDDSDocumento27 páginas1 BDDSVatsal PandyaAinda não há avaliações
- Ayurvedic medicine for renal stonesDocumento3 páginasAyurvedic medicine for renal stoneshk_scribdAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento43 páginasDrug StudyMamot MotAinda não há avaliações
- Biocad Interim Report Group 6 1Documento15 páginasBiocad Interim Report Group 6 1MonikaSarkisyanAinda não há avaliações
- OsteoporosisDocumento15 páginasOsteoporosisWil LesterAinda não há avaliações
- Restrictions in Use and Availability of PharmaceuticalsDocumento328 páginasRestrictions in Use and Availability of PharmaceuticalsinfooncoAinda não há avaliações
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNo EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (402)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (78)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNo EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (13)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeAinda não há avaliações
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNo EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementNo EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (40)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNo EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (169)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNo EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesNo EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNo EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNo EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsAinda não há avaliações
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (8)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNo EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (33)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.No EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingNo EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeNo EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (253)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsAinda não há avaliações
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossNo EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (4)