Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Nasogastric Feeding
Enviado por
Shella LaguatanDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Nasogastric Feeding
Enviado por
Shella LaguatanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
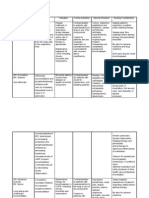
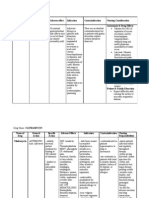
Nasogastric Tube Feeding It is a type of enteral feeding which is used as an alternative feeding method to ensure adequate nutrition and
it is also used for gastric decompression through the use of a nasogastric tube. Purposes of NGT 1. To provide feeding (gastric gavage). 2. To irrigate stomach (gastric gavage). 3. For decompression (drainage of gastric content). 4. To administer medications. 5. To administer supplemental fluids. Indication of NGT 1. To clients who are unable to eat by mouth or swallow a sufficient diet without aspirating food or fluids into the lungs. 2. Those who can not tolerate sufficient amount of fluids needed for their care. 3. Those that need gastric drainage. Nursing Responsibilities Before and During Insertion 1. Check the doctors order. To be safe or out of any legal issues. 2. Inform the patient and explain the procedure. To allay anxiety. 3. Wash hands. To prevent infection. 4. Assess the clients nares. To check which nares is the best for insertion. 5. Prepare equipment. 6. Place in high-fowlers position. To facilitate insertion of NGT. 7. Measure the length of NGT to be inserted (tip of the nose to the tip of the ear lobe to the xiphoid process=50cm.) NEX technique. This length approximates the distance from the nares to the stomach. 8. Lubricate tip of the tube with water-soluble lubricant. To reduce friction. Do not use oil because it may cause lipoid pneumonia. 9. Hyperextend the neck, gently advance the tube toward the nasopharynx. For easier passage of the tube.
10.Tilt the patients head forward once the tube reaches the throat and ask to swallow, as the tube is advanced. To facilitate or to help in the insertion of the tube. 11.Secure the tube. To prevent the tube from being dislodge or pulled out. 12.Document the procedure. To inform the other members of the health care team. Nursing Responsibilities During Administering Tube Feeding 1. Assist client to a semi-Fowlers position in bed or sitting position in a chair, or slightly elevated right side lying position. For more efficient feeding. 2. Assess tube placement and patency. To ensure that tube is placed in the right place. Auscultate abdomen Aspirate gastric content and check for pH Immerse tip of tube in water X-ray
3. Assess residual feeding contents. To assess absorption of the last feeding. 4. Introduce feeding slowly. To prevent flatulence, crampy pain and or reflex vomiting. 5. Height of feeding should be 12 inches above the tubes point of insertion into the client. This allows slow introduction of feeding. 6. Instill 60 mL of water into the NGT after feeding. To cleanse the lumen of the tube thus, preventing microorganism from thriving. 7. Clamp the NGT before all the water is instilled. To prevent entry of air in the stomach. 8. Instruct client to remain in fowlers position or in slightly elevated right lateral position for at least 30 minutes. To prevent regurgitation of feeding. 9. Document. To prevent repetition of the procedure.
Você também pode gostar
- Nasogastric Tube FeedingDocumento4 páginasNasogastric Tube FeedingAru VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Ainda não há avaliações
- Tranexamic AcidDocumento18 páginasTranexamic AcidFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasAinda não há avaliações
- A Simple Guide to Pseudohypoparathyroidism, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo EverandA Simple Guide to Pseudohypoparathyroidism, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Nasogastric Tube Feeding ML4763 PDFDocumento7 páginasNasogastric Tube Feeding ML4763 PDFStereo PodAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study LCPDocumento3 páginasDrug Study LCPalleen_viaAinda não há avaliações
- Resurrection University Medication CardDocumento2 páginasResurrection University Medication CardBohung ConAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasDrug StudyGena Manimtim100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento8 páginasDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition and Malnutrition Resource UnitDocumento22 páginasNutrition and Malnutrition Resource UnitMitch GatdulaAinda não há avaliações
- Alteration in Fluid and Electrolyte Status Lecture NotesDocumento11 páginasAlteration in Fluid and Electrolyte Status Lecture Notes0912247251Ainda não há avaliações
- Loxapine PDFDocumento2 páginasLoxapine PDFDavid AdamsAinda não há avaliações
- PEDIADRUGDocumento6 páginasPEDIADRUGPatrice LimAinda não há avaliações
- DiazepamDocumento3 páginasDiazepamGwyn RosalesAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd) : By: Therese Jane TimbalopezDocumento14 páginasGastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd) : By: Therese Jane Timbalopezjoyrena ochondraAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumonia Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasPneumonia Drug Studyatienza02Ainda não há avaliações
- Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences Dhulikhel, Kavre 2018Documento5 páginasKathmandu University School of Medical Sciences Dhulikhel, Kavre 2018Archana MaharjanAinda não há avaliações
- Health Teaching of Patients With Tuberculosis TreatmentDocumento34 páginasHealth Teaching of Patients With Tuberculosis TreatmentFarhanaRahimAinda não há avaliações
- Anorexia NervosaDocumento11 páginasAnorexia NervosaSashMalikAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - PiptazDocumento1 páginaDrug Study - PiptazMutya XDAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasDrug StudyStephannie MirandaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Set Mosquito Kelly Curves Allis Babcock Needle Holder Tissue Forcep Thumb Forcep Army Navy Kidney Basin Towel Clips Straight Clamp MixterDocumento14 páginasBasic Set Mosquito Kelly Curves Allis Babcock Needle Holder Tissue Forcep Thumb Forcep Army Navy Kidney Basin Towel Clips Straight Clamp MixterZeng SolomonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study 1Documento15 páginasDrug Study 1Czarina Isabela TuazonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDrug StudySytrose MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - AmoxicillinDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - AmoxicillinVANESSA PAULA ALGADORAinda não há avaliações
- Nasogastric Feeding ProcedureDocumento20 páginasNasogastric Feeding ProcedureKrishna Sonu SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Kabiven: (Amino Acids, Electrolytes, Dextrose and Lipid Injectable Emulsion), For Intravenous UseDocumento24 páginasKabiven: (Amino Acids, Electrolytes, Dextrose and Lipid Injectable Emulsion), For Intravenous UseDivine Mercy De JulianAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study NurseryDocumento2 páginasDrug Study Nurseryjulesubayubay54280% (1)
- CHN Drug StudyDocumento10 páginasCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study of FluoxetineDocumento2 páginasDrug Study of FluoxetineLance De GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Dela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Documento2 páginasDela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Atsu MiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Post Cesarean Section DeliveryDocumento5 páginasPost Cesarean Section Deliveryᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩAinda não há avaliações
- PediculosisDocumento28 páginasPediculosisLucy PalmaAinda não há avaliações
- HemodialysisDocumento2 páginasHemodialysisjustin_saneAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study ColestipolDocumento3 páginasDrug Study ColestipolAbby AngAinda não há avaliações
- Antimalarial DrugsDocumento7 páginasAntimalarial DrugsHilmanAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento9 páginasDrug Studyjanelee2824Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDocumento6 páginasDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeJaymark LambinoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramDocumento3 páginasDrug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramJear RomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Lrti Case Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasLrti Case Drug Studyn_I_K_K_I02Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasDrug StudyemmanuelmyagokayeAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Study and Discharge Plan Arnold and SelwynDocumento17 páginasDrugs Study and Discharge Plan Arnold and SelwynArnold ZamoroAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento21 páginasDrug StudyLeya ThaobunyuenAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocumento23 páginasNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationyusivileidyAinda não há avaliações
- Piperacillin Tazobactam (Zosynpiperacillin)Documento1 páginaPiperacillin Tazobactam (Zosynpiperacillin)EAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study For Cefuroxime, Tramadol, Paracetamol and NCP For Post ThoracostomyDocumento6 páginasDrug Study For Cefuroxime, Tramadol, Paracetamol and NCP For Post Thoracostomynursejr24100% (2)
- Drug Study East AveDocumento15 páginasDrug Study East AveSean Philippe CabralAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Risk InfectionDocumento1 páginaNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Mission-Vision: Care Using Knowledge and CompassionDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan: Mission-Vision: Care Using Knowledge and CompassionBen Jeremy del MarAinda não há avaliações
- Ethical Schools of Thought - Part TwoDocumento56 páginasEthical Schools of Thought - Part TwoFille_Anne_Lay_1019100% (1)
- Self-Care Deficit Related To Inability To Perceive Body Part (Bathing)Documento2 páginasSelf-Care Deficit Related To Inability To Perceive Body Part (Bathing)lilpeabea100% (1)
- Oral Rehydration TherapyDocumento7 páginasOral Rehydration TherapyBala MuruganAinda não há avaliações
- VancomycinDocumento2 páginasVancomycinxoxo318Ainda não há avaliações
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) : Group A Beta Hemolytic StretococcusDocumento3 páginasAcute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) : Group A Beta Hemolytic StretococcusKristine Danielle DejeloAinda não há avaliações
- ENT Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasENT Drug StudyMcmac YangoAinda não há avaliações
- Gastric Gavage and LavageDocumento5 páginasGastric Gavage and LavageEgielyn PainandosAinda não há avaliações
- Tube FeedingDocumento50 páginasTube FeedingHari Priya TangiralaAinda não há avaliações
- Nagogastric Tube FeedingDocumento8 páginasNagogastric Tube FeedingSiwani raiAinda não há avaliações
- Administration of Nasogastric Tube FeedingDocumento3 páginasAdministration of Nasogastric Tube FeedingAmy Lalringhluani Chhakchhuak100% (1)
- Architecture For AutismDocumento16 páginasArchitecture For AutismSivaRamanAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Manual: RTS Automatic Transfer SwitchDocumento28 páginasTechnical Manual: RTS Automatic Transfer SwitchKrīztīän TörrësAinda não há avaliações
- Case Write Up 3Documento4 páginasCase Write Up 3E learningAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Contoh Analytical Exposition Pendek Bahasa InggrisDocumento6 páginas7 Contoh Analytical Exposition Pendek Bahasa InggrisDarsi YujiwatiAinda não há avaliações
- 04fc75de986c12 Pharmaceutics-I AROMATIC WATERSDocumento14 páginas04fc75de986c12 Pharmaceutics-I AROMATIC WATERSsultanAinda não há avaliações
- Risk Assessment - TemplateDocumento10 páginasRisk Assessment - TemplateJohn KalvinAinda não há avaliações
- People Vs Campuhan, 329 SCRA 270Documento2 páginasPeople Vs Campuhan, 329 SCRA 270Name ToomAinda não há avaliações
- Interview Marsha SarverDocumento3 páginasInterview Marsha Sarverapi-326930615Ainda não há avaliações
- Antibiotic SolutionDocumento1 páginaAntibiotic SolutionBodhi DharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Cancer Genetics-Genetic InstabilityDocumento60 páginasCancer Genetics-Genetic InstabilityMadhu MithaAinda não há avaliações
- Iligan Medical Center College Research PaperDocumento9 páginasIligan Medical Center College Research PaperRyan Sulog PangantingAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Paper 1Documento36 páginasSample Paper 1Annshai Jam MetanteAinda não há avaliações
- Adoption LawsDocumento10 páginasAdoption LawsAneesh PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- India's #1 Nroute Daily Whey Protein Powder Online 2022Documento3 páginasIndia's #1 Nroute Daily Whey Protein Powder Online 2022NRoute ProteinAinda não há avaliações
- MSDS Baybl T65 901510Documento8 páginasMSDS Baybl T65 901510gnavarroAinda não há avaliações
- h2s Hand BookDocumento34 páginash2s Hand BookJorge Eliecer Ferro Cotes100% (4)
- 15.meat and Meat ProductsDocumento19 páginas15.meat and Meat ProductsMahesh DevasigamaniAinda não há avaliações
- Citations Issued Due To COVID-19Documento726 páginasCitations Issued Due To COVID-19Maritza NunezAinda não há avaliações
- Story of ChangeDocumento3 páginasStory of ChangeSend Sierra LeoneAinda não há avaliações
- Dental Juris and Practice MGT Board 2008Documento14 páginasDental Juris and Practice MGT Board 2008Anonymous FwwfR650% (2)
- TinnitusDocumento34 páginasTinnitusHnia UsmanAinda não há avaliações
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocumento3 páginasCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJasleen KaurAinda não há avaliações
- Aferisis Transfuncional Teromuco BCTDocumento310 páginasAferisis Transfuncional Teromuco BCTNorma RamosAinda não há avaliações
- LlageriDocumento8 páginasLlageriBlodin ZylfiuAinda não há avaliações
- Anoplastia Percutanea 2022Documento11 páginasAnoplastia Percutanea 2022Sandra Cárdenas HilasacaAinda não há avaliações
- Rules Related Statutes All CodesDocumento150 páginasRules Related Statutes All CodesRod SatreAinda não há avaliações
- DLM JOY Bread Maker Recipe BookDocumento35 páginasDLM JOY Bread Maker Recipe BookmimaAinda não há avaliações
- Real-Time Health Care Monitoring System Using Iot: International Journal of Engineering & TechnologyDocumento5 páginasReal-Time Health Care Monitoring System Using Iot: International Journal of Engineering & TechnologyShaik JunaidAinda não há avaliações
- CFPC SampsDocumento39 páginasCFPC SampsSumer Chauhan100% (9)
- Human Factors and Safety Culture in Maritime Safety (Revised)Documento10 páginasHuman Factors and Safety Culture in Maritime Safety (Revised)Al-aayan D. IsmaelAinda não há avaliações
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)No EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Nota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (82)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNo EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (32)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNo EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNo EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsAinda não há avaliações
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNo EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (42)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.No EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (110)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeNo EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (254)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNo EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (170)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesNo EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (1412)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNo EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceNo EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (51)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNo EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryNo EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (46)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlNo EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (60)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNo EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (328)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingNo EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)