Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Congenital Anomalies
Enviado por
Led Teoderick LuaDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Congenital Anomalies
Enviado por
Led Teoderick LuaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
TCVS CONGENITAL CARDIAC ANOMALIES Acyanotic heart diseases: Left to right shunts Patent ductus arteriosus Atrial septal
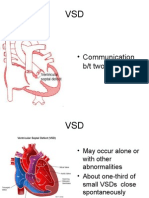
defect Ventricular septal defect
Pulmonary valve atresia with intact septum Hypoplastic left heart syndrome Double outlet ventricle Truncus arteriosus Tetralogy of fallot Components
Aortopulmonary window Combination (ASD & PDA, VSD &
PDA)
RV hypertrophy Infundibulovalvar stenosis Overriding of the aorta VSD Indications for total correction Pulmonary artery size: 2D older
Clinical manifestations Depends on the volume of the shunt Failure to thrive Heart murmur
Echo or Angiogram
age group Infective endocarditis Diagnostic work up Non invasive
Right ventricular failure in older
Age: 6 months or (Younger: Risk of destroying pulmonary valves Cyanotic spells Nakata: 330 surface????
mm2/body
ECG Chest X Ray
2D Echo with Doppler Cine CT Scan Invasive Hemodynamic studies Angiogram Hemodynamic studies angiogram: Gold standard Electrophysiology study Management Medical mangement
McGun Criteria ?? Size of right + left pulmonary = or 2x aorta Level of diaphragm
Palliative Procedures: When young, pulmonary artery not yet developed Increase flow to the lungs PA growth Blalock Taussig Shunt: Subclavian artery connect to pulmonary artery (Modified Blalock Taussig Shunt: Graft which will connect subclavian artery to pulmonary artery)
&
Treatment for heart failure
Lower pulmonary hypertension: Milrinone, nitric oxide Treatment for infective endocarditis Prepare patient for surgery (Identify other problems like neurological or bleeding) Catheter base treatment
Waterston Shunt: Connect right pulmonary artery to ascending aorta Mortality <5 % in total correction >10% in palliative operation Transposition of the Great arteries Aorta arises from the right ventricle, pulmonary artery arises from the left ventricle TGA intact septum with PDA TGA VSD,ASD and PDA TGA VSD with Coarctation of Aorta Other combinations Natural Course 5 % will reach 1year old
years Surgical treatment
Coil closure of PDA: 2-3 Umbrella closure of ASD Umbrella closure of VSD Umbrella closure under trial PDA ligation/ transaction:
95 % will die before the reach the age of one year 65% will die within the 1st 6
may develop aneurysm
Open heart surgery ASD closure: 0 1% mortality rate VSD closure: <3% mortality rate AP window patching
Common complex cardiac anomalies (Cyanotic) Tetralogy of fallot Transposition of great arteries Total anomalous pulmonary venous return CHRABI Page 1 of 2
months of life Indication for Arterial Switch operation Age 5 - 15 days old: ASO >21 days: BAS 30 days: 60 days for TGA with VSD LV Mass - 70 grams
With other anomalies: Stage procedure or other types of repair
Other Procedures physiologic operation
Mustard operation Senings operation Both are atrial switch or
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return Intracardiac or coronary sinus drainage Supracardiac type Infracardiac type Mixed type [mixture of any anomalous drainage] Indications for Surgery
Upon diagnosis: correction if venous drainage are obstructed
Urgent
Pulmonary Valve Atresia Intact Septum Usually associates with obligatory shunts [PFO or PDA] Types Membranous valve atresia Muscular type Tripartite RV Bipartite RV Monopartite RV Types of Correction Biventricular repair Membranous types Tripartite RV Univentricular repair [Fontan operation} Bipartite RV Monopartite RV Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Underdeveloped LV Hypoplastic aortic arc Mitral valve atresia VSD PDA Norwood Operation
school: Glen Shunt
Stage I: 1 month Stage II - 6 months to pre Stage III school age:
Fontan operation Result 30 %
Stage I - 8 % - 40 % Stage II - 8% - 20 % Over all survival usually 20CHRABI
CHRABI Page 2 of 2
Você também pode gostar
- 100 Case Histories in Clinical Medicine For MRCP by Jypee (PART 1) PDFDocumento352 páginas100 Case Histories in Clinical Medicine For MRCP by Jypee (PART 1) PDFmuntaser67% (3)
- ACC SAP 8 Exam1&2ACC SAP 8 Exam1&2Documento115 páginasACC SAP 8 Exam1&2ACC SAP 8 Exam1&2Yahya Hassan Hussein El-tamaly100% (3)
- Peds Shelf NotesDocumento88 páginasPeds Shelf Notesγιαννης παπαςAinda não há avaliações
- Acynotic Heart DiseasesDocumento13 páginasAcynotic Heart DiseasesSimran JosanAinda não há avaliações
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocumento10 páginasValvular Heart DiseaseEzyan SyaminAinda não há avaliações
- Valvular Heart Disease: Presented by DR Mirjana Milutinovic Professor, SJSMDocumento69 páginasValvular Heart Disease: Presented by DR Mirjana Milutinovic Professor, SJSMAbanoub AwadallaAinda não há avaliações
- CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION LABORATORY AN INTRODUCTORY MANUAL, University of TennesseeDocumento29 páginasCARDIAC CATHETERIZATION LABORATORY AN INTRODUCTORY MANUAL, University of TennesseeNavojit ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular System: by DR - Nuha Abdel GhaffarDocumento41 páginasCardiovascular System: by DR - Nuha Abdel GhaffarMohammed Alaa EldeanAinda não há avaliações
- Peran Perawat Di CathlabDocumento71 páginasPeran Perawat Di CathlabMabro CahyoAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento77 páginasCongenital Heart DiseaseMalueth Angui100% (1)
- VSDDocumento29 páginasVSDVaibhav Krishna100% (2)
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento51 páginasCongenital Heart Diseaseelsa prima putri100% (2)
- PracticeExam 3 AnsDocumento52 páginasPracticeExam 3 AnsBehrouz YariAinda não há avaliações
- Transposition of The Great ArteriesDocumento29 páginasTransposition of The Great ArteriesbookwormMD100% (1)
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento6 páginasCongenital Heart DiseaseSamah KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Anthony Alexander University of The West Indies at MonaDocumento40 páginasUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Anthony Alexander University of The West Indies at MonaAy Alex0% (1)
- Non-Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease-UpDate 4-22-53Documento136 páginasNon-Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease-UpDate 4-22-53getnusAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac CTDocumento7 páginasCardiac CTdaniel7pintiliiAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento38 páginasCongenital Heart DiseaseSnIP StandredAinda não há avaliações
- Achd Ug OriginalDocumento43 páginasAchd Ug OriginalchristyAinda não há avaliações
- Approach Cyanosis FinalDocumento31 páginasApproach Cyanosis Finalsuheena.CAinda não há avaliações
- PedsnotesDocumento18 páginasPedsnoteskp13oyAinda não há avaliações
- Arrhythmias PDFDocumento29 páginasArrhythmias PDFbencleeseAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart DeseasesDocumento54 páginasCongenital Heart DeseasesAntony100% (1)
- TCVS Congenital Cardiac AnomaliesDocumento49 páginasTCVS Congenital Cardiac Anomaliesapi-3704562Ainda não há avaliações
- GuchDocumento42 páginasGuchMaretha Dyah AnggrainiAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Ika Prasetya W, SPPD: Divisi Kardiologi Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FKUI/RSCM JakartaDocumento39 páginasDr. Ika Prasetya W, SPPD: Divisi Kardiologi Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FKUI/RSCM JakartaStefani Astari Dewi AryaniAinda não há avaliações
- 7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraDocumento57 páginas7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraSurya Ashri Rahman HAinda não há avaliações
- 7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraDocumento57 páginas7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraSurya ArhAinda não há avaliações
- Tricuspid AtresiaDocumento44 páginasTricuspid Atresiadoctorsaty7539Ainda não há avaliações
- Curs de Chirurgie Cardiaca PT StudentiDocumento86 páginasCurs de Chirurgie Cardiaca PT StudentiLozan GabrielaAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart Disease: Kevin Jones Senior Chief Technician Alder Hey Childrens HospitalDocumento32 páginasCongenital Heart Disease: Kevin Jones Senior Chief Technician Alder Hey Childrens HospitalVaibhav KaroliyaAinda não há avaliações
- Transposition of Great ArteriesDocumento21 páginasTransposition of Great ArteriesAlusio Navosailagi VUNIIVI100% (1)
- Penyakit Vaskular PeriverDocumento84 páginasPenyakit Vaskular PeriverFreandhy PutraAinda não há avaliações
- CHD - Med IIDocumento70 páginasCHD - Med IISanskruthi KurniAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento57 páginasCongenital Heart DiseaseAparna RawatAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento124 páginasCongenital Heart DiseasemulkanmustafaAinda não há avaliações
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus - Most Common Congenital Heart Defect Symptoms DependDocumento5 páginasPatent Ductus Arteriosus - Most Common Congenital Heart Defect Symptoms DependANNEAinda não há avaliações
- Duct Dependent Lesions - PPSXDocumento41 páginasDuct Dependent Lesions - PPSXSindujaAinda não há avaliações
- Aortic Stenosis: Changing Disease Concepts: ReviewDocumento11 páginasAortic Stenosis: Changing Disease Concepts: ReviewdiogoAinda não há avaliações
- 1 - VSD (Part 2) - Hatem HosnyDocumento28 páginas1 - VSD (Part 2) - Hatem Hosnyrami ibrahiemAinda não há avaliações
- DR - Azad A Haleem AL - Brefkani: University of Duhok Faculty of Medical Science School of Medicine Pediatrics DepartmentDocumento58 páginasDR - Azad A Haleem AL - Brefkani: University of Duhok Faculty of Medical Science School of Medicine Pediatrics DepartmentGomathi ShankarAinda não há avaliações
- Transposition of The Great Arteries: Eric Osborn January 27, 2010Documento35 páginasTransposition of The Great Arteries: Eric Osborn January 27, 2010Soad ShedeedAinda não há avaliações
- VSD 180207074930Documento33 páginasVSD 180207074930widyaAinda não há avaliações
- 14.1 The Hole Inside The Heart ABSTRAKDocumento11 páginas14.1 The Hole Inside The Heart ABSTRAKYudhistira AdiAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical Intervention in Management of Heart Failure: DR Royman Simanjuntak Sp. BTKVDocumento118 páginasSurgical Intervention in Management of Heart Failure: DR Royman Simanjuntak Sp. BTKVEmily RumiaAinda não há avaliações
- Achd LectureDocumento48 páginasAchd LecturedrmdsaeedAinda não há avaliações
- Valvular Heart Disease IM 8-12 NewDocumento80 páginasValvular Heart Disease IM 8-12 NewRachilla Arandita SaraswatiAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiology FMDocumento25 páginasCardiology FMtrushaAinda não há avaliações
- Pulmonary Thromboembolism: DR Olubunmi Ogunlade Consultant PulmonologistDocumento34 páginasPulmonary Thromboembolism: DR Olubunmi Ogunlade Consultant PulmonologistEmeka Chinedu Precious PetrousAinda não há avaliações
- Rosenberg Circulatory Assist DevicesDocumento61 páginasRosenberg Circulatory Assist DevicesMilisha Albro100% (1)
- Valvular Heart Disease: Bekele T. (MD)Documento47 páginasValvular Heart Disease: Bekele T. (MD)alehegn beleteAinda não há avaliações
- Penyakit Katup Jantung: Dr. Tjatur Winarsanto SPPD Rs CiremaiDocumento59 páginasPenyakit Katup Jantung: Dr. Tjatur Winarsanto SPPD Rs CiremaianisamayaAinda não há avaliações
- Usm UvodDocumento12 páginasUsm UvodMicija CucuAinda não há avaliações
- CVD 10 (١) PDFDocumento23 páginasCVD 10 (١) PDFHmhm HmhmAinda não há avaliações
- PDA Case StudyDocumento5 páginasPDA Case StudyDiana Andrea AyongaoAinda não há avaliações
- Penyakit Katup Jantung-Kuliah DR ErlinaDocumento70 páginasPenyakit Katup Jantung-Kuliah DR ErlinaAdhiatma DotAinda não há avaliações
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocumento32 páginasValvular Heart DiseasefallenczarAinda não há avaliações
- 78 - Endocarditis, ValvedzDocumento15 páginas78 - Endocarditis, ValvedzStefani SihombingAinda não há avaliações
- (I..) KMU Peads CardicDocumento88 páginas(I..) KMU Peads CardicMuhammadAinda não há avaliações
- Timing of Intervention For Common Congenital Heart Diseases-IapDocumento26 páginasTiming of Intervention For Common Congenital Heart Diseases-IapADAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular Disorders IIDocumento13 páginasCardiovascular Disorders IIAngel Joy CatalanAinda não há avaliações
- Peds CH 46 Cardiovascular DisordersDocumento14 páginasPeds CH 46 Cardiovascular DisordersLeanne Therese L. Malapitan100% (1)
- Acyanotic CHDDocumento83 páginasAcyanotic CHDmrinmayee deshmukhAinda não há avaliações
- 9 - Acynotic Congenital HeartDiseasesDocumento49 páginas9 - Acynotic Congenital HeartDiseasessamar yousif mohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Arterial Septal Defect (Asd)Documento38 páginasArterial Septal Defect (Asd)Rhahima SyafrilAinda não há avaliações
- VSDDocumento4 páginasVSDtikabdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Tony Cross CDU Low Risk ACS Proforma - V3.212 Review Due June 2014Documento4 páginasTony Cross CDU Low Risk ACS Proforma - V3.212 Review Due June 2014ED@HEFTAinda não há avaliações
- 216A ABSTRACTS - Cardiac Function and Heart Failure Jacc March 3, 2004Documento1 página216A ABSTRACTS - Cardiac Function and Heart Failure Jacc March 3, 2004vikram.vAinda não há avaliações
- Heart DiseaseDocumento11 páginasHeart Diseaseapi-529065933Ainda não há avaliações
- BMI Priory Edgbaston Hospitals Consultant DirectoryDocumento28 páginasBMI Priory Edgbaston Hospitals Consultant DirectorypsdsportsdocAinda não há avaliações
- How Caffeine Causes TachycardiaDocumento30 páginasHow Caffeine Causes TachycardiaMadelleine PaduaAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Criterias For Ventricular Hypertrophy by DR PRASANTH SDocumento13 páginasECG Criterias For Ventricular Hypertrophy by DR PRASANTH SnadineAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Q1 Function by The IntensivistDocumento10 páginasEvaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Q1 Function by The IntensivistMartha Isabel BurgosAinda não há avaliações
- Denktas 2016Documento7 páginasDenktas 2016Sinisa RisticAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Management: Medical and Surgical Management of Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocumento4 páginasMedical Management: Medical and Surgical Management of Acute Myocardial InfarctionLouie ParillaAinda não há avaliações
- Magdy El-Masry Prof. of Cardiology Tanta UniversityDocumento55 páginasMagdy El-Masry Prof. of Cardiology Tanta UniversityPrabJot SinGhAinda não há avaliações
- BASIC ECG CKKDocumento79 páginasBASIC ECG CKKAlexzander BrendonAinda não há avaliações
- 101161@circinterventions119008487 230823 233136Documento13 páginas101161@circinterventions119008487 230823 233136Nasru llahAinda não há avaliações
- Sgarbossa CriteriaDocumento5 páginasSgarbossa Criteriajacknaim7090Ainda não há avaliações
- Soyombo Emmanuel Oluwabunmi PimDocumento1 páginaSoyombo Emmanuel Oluwabunmi PimVasilAinda não há avaliações
- 15-Lead ECG PowerpointDocumento20 páginas15-Lead ECG Powerpointgillian102290Ainda não há avaliações
- Olewinski 2016Documento15 páginasOlewinski 2016Nazihan Safitri AlkatiriAinda não há avaliações
- FacksheetDocumento21 páginasFacksheetFernandaAinda não há avaliações
- Cardio Quizlet Questions Medsurg MidtermsDocumento27 páginasCardio Quizlet Questions Medsurg Midtermsnuguitnorelyn30Ainda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Versus Bioprosthetic Aortic Valve ReplacementDocumento13 páginasMechanical Versus Bioprosthetic Aortic Valve ReplacementAndrea OrtizAinda não há avaliações
- Radiology Packet 7 Congenital Cardiac DiseaseDocumento27 páginasRadiology Packet 7 Congenital Cardiac Diseaseludiegues752Ainda não há avaliações
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Joisy Aloor Leonard Shaju Smit Bhaisare Shawn RyneDocumento36 páginasHypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Joisy Aloor Leonard Shaju Smit Bhaisare Shawn RyneJoisy Aloor100% (1)
- Coronary Circulation FDocumento36 páginasCoronary Circulation FjefferyAinda não há avaliações