Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Sheet Number - 1 R 09 Previous Questions From Ellipse - 2010 1
Enviado por
durga323Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sheet Number - 1 R 09 Previous Questions From Ellipse - 2010 1
Enviado por
durga323Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
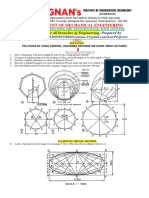
CMR TECHNICAL CAMPUS ENGINEERING DRAWING CSE-A SHEET NUMBER -1 R 09 PREVIOUS QUESTIONS FROM ELLIPSE -2010 1.
Two fixed points A and B are 100mm apart. Trace the complete path of
a point P moving in the same plane as that of A and B in such a way that, the sum of its distances from A and B is always the same and equal to 125 mm. 2. The major axis of an ellipse is 100mm and the foci are at a distance of 15 mm from its ends. Find the minor axis. Draw the ellipse by arc of circles method. 3. Draw an ellipse in a parallelogram having sides 15cm and 9 cm long and an included angle of 60 degrees. 4. The major axis of the ellipse is 100 mm and the minor axis is 55 mm. Find the foci and construct the ellipse by Arc of circles method. Also draw a pair of tangents from any point, P outside the ellipse.
SHEET NUMBER- 2 R 09 PREVIOUS QUESTIONS FROM PARABOLA -2010 1. Draw a parabola when the distance between focus and directrix is
50mm. Draw a tangent and normal at a point distant 70mm from the directrix. 2. A ball thrown up in the air maches a maximum height of 45 meters and travels a horizontal distance of 75 meters. Trace the path of the ball assuming it to be parabolic. 3. The ordinate of a point P on the curve is 50 mm and is at a distance of 25 mm from the vertex. Draw the parabola.
SHEET NUMBER- 3 R 09 PREVIOUS QUESTIONS FROM HYPERBOLA -2010 1. The vertex of a hyperbola is 5cms from directrix. Draw the curve if the
eccentrics is 3/2. Draw the normal and tangent at a point 50mm from axis. 2. Two straight lines, OA and OB make an angle of 750 between them. P is a point 40 mm from OA and 50 mm from OB. Draw a hyperbola through P, with OA and OB as asymptotes. 3. A point P is 30mm and 50mm respectively from two straight lines which are at right angles to each other. Draw a rectangular hyperbola from p with in 10mm distance from each line. Note: All students should submit above the sheets after
completing the above topics immediately by next class for day to day assessment of internal marks.
N.CHANDRA SEKAHAR REDDY Associate Professor
SHEET NUMBER -4 1.
2.
3.
4.
CYCLOIDS A circle of 50 mm diameter rolls on a straight line without slipping. Draw the locus of a point on the circumference of the circle for one complete revolution. Draw tangent and normal to the curve 15 mm above the axis. [JUNE2010] A circle of 50 mm diameter rolls on a straight line, without slipping. Draw the locus of a point on the circumference of the circle for one revolution. Name the Curve. Draw the tangent & normal to the curve at a point 2 cm below the axis. [JUNE2010] A coin of 40mm diameter rolls over a horizontal table without slipping. A point on the circumference of the coin in contact with the table surface in the beginning and after one complete revolution. Draw the path traced by the point. Draw a tangent and normal at a point 25 mm from the table. [JUNE2010] A circle of 50 mm diameter rolls on a horizontal line for half a revolution. For the remaining half revolution it rolls on a line perpendicular to the first. Draw the curve traced by a point on the circumference of the circle. [JUNE2010]
SHEET NUMBER -5
HYPO CYCLOID
1. Draw a hypo cycloid of a circle of 40 mm. diameter which rolls inside
another circle of 160 mm diameter for one complete revolution.
[JUNE2010]
2. A circle of 30mm diameter rolls on the concave side of generating
circle of radius 30mm. Draw the path traced by a point on the generating circle for one complete revolution. [JUNE2010] 3. Construct a hypocycloid with rolling circle of 50 mm diameter and directing circle of 175 mm diameter. Draw a tangent to it at a point 50 mm from the centre of the directing circle. [JUNE2010] 4. A circus man rides on a motor cycle, inside a globe of 4 m diameter. The motor cycle wheel is 1 m in diameter. Draw the locus of a point on the circumference of the wheel of motor cycle for its one complete turn on the maximum circular path and name the curve. [JUNE2010]
SHEET NUMBER -6
EPI CYCLOID
1. Draw an epi-cycloid of circle of 40 mm diameter which rolls outside
another circle of 120 mm diameter for one revolution. [JUNE2010] 2. Draw an epi cycloid generated by a rolling circle of 60 mm diameter for one complete revolution. The radius of directing circle is 100mm.Draw a tangent and a normal to the curve at 150mm from the center of the directing circle. [JUNE2010]
should submit above the sheets after completing the above topics immediately by next class for day to day assessment of internal marks.
Note: N.CHANDRA SEKAHAR REDDY Associate Professor
SHEET NUMBER -7
INVOLUTE
All students
1. Draw in volute of a pentagon side 30 mm. Draw its tangent and normal 2. Draw an involute of a circle of 35 mm diameter. Draw also a normal and tangent to it
at a point 75 mm away from the centre of the circle. [JUNE 2010] SHEET NUMBER -8 PLAINSCALE / PLAIN COMPARITIVE SCALE 1. A room of 1728 cu.m. in volume is shown by a cube of 216 cu.cm. Volume. Find R.F. construct a plain scale to measure up to 40 m. Mark on it a distance of 28 m. .[JUNE
2010]
fit at 70 mm of the centre of pentagon. [JUNE 2010]
2. A train is running at a speed of 40 km/hr. Construct a plane scale to read up to a km
and a minute. The scale should measure up to 50 km. The RF of the scale is 1:25000. On the scale show the distance covered by the train in 39 minutes. [JUNE 2010] 3. Construct a plain scale to compute time in minutes and distance covered by a train in km., when the train passes between two stations 250 km apart in five hours. The scale should have R.F. 1/500000. Show the distance covered in 45 minutes on the scale. [JUNE 2010] SHEET NUMBER -9 DIAOGONAL SCALE / DIAOGONAL COMPARITIVE SCALE 1. Construct a diagonal scale of R F = 1/2000 to show meters and long enough to measure up to 300 m. Mark on it a distance of 257 m. [JUNE 2010] 2. An area of 144 sq.cm on the map represents an area of 36 sq.km on the field. Find R.F and draw a diagonal scale to show kilometers, hectometers & decameters and to measure up to 10 km. indicate on this scale 7.58 km. [JUNE 2010] 3. Construct a diagonal scale to read up to 1/100 of kilometers having given the value of R.F. = 1/50,000 and to measure up to 8 kilometers. Indicate on the scale, a distance of 6.76 kilometers. [JUNE 2010]
4. A small length of 1 mm is to be enlarged to 20 times and a diagonal scale is to be
constructed to represent this such that the LC is 0.01 mm. Construct this scale and mark on it a distance of 0.73 mm and 0.29 mm. What is the RF of this scale? [JUNE
2010]
1. 2. 3. 4.
SHEET NUMBER -10 VERNIEAR SCALE Construct a vernier scale of 1:2 to show decimeters, centimeters, millimeters an long enough to read up to 4 decimeters. Mark on it a distance of 2.38 decimeters on the scale. [JUNE 2010] The actual length of 500m is represented by a line of 15 cm on a drawing. Construct a vernier scale to read upto 600 m. Mark on the scale a length of 549 m. [JUNE 2010] Draw a vernier scale of R.F=5 to read 1/5cm and 1/25cm and to measure upto 5cm.Mark on the scale distances of 2.12cm. [JUNE 2010] Draw a Vernier scale of RF = 1/24 to read yards, feet and inches, and to measure up to 4 yards. Show on it lengths representing) 2 yards 2 feet 10 inches ii) 1 foot 3 inches. [JUNE 2010]
Note: All students should submit above the sheets after completing the above topics immediately by next class for day to day assessment of internal marks.
N.CHANDRA SEKHAR REDDY ate Professor Associ
Você também pode gostar
- Decision Model Using ExcelDocumento236 páginasDecision Model Using Excelসামিউল ইসলাম রাজু100% (3)
- AP Calculus BC Study GuideDocumento4 páginasAP Calculus BC Study GuideHarshil SahaiAinda não há avaliações
- THPS DegradationDocumento5 páginasTHPS DegradationAhmad Naim KhairudinAinda não há avaliações
- Measurement of SubstructureDocumento24 páginasMeasurement of SubstructureAamaniVeeranam80% (10)
- What Is XRF ?: Prepared by Lusi Mustika SariDocumento34 páginasWhat Is XRF ?: Prepared by Lusi Mustika SariBayuAinda não há avaliações
- VeEX OTN Quick Reference GuideDocumento12 páginasVeEX OTN Quick Reference GuideDewan H S SalehinAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Worksheet Answer Grade 12Documento6 páginasAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Worksheet Answer Grade 12sethu100% (1)
- Ed Most Important Questions With Answers by SsraoDocumento16 páginasEd Most Important Questions With Answers by SsraoSANYASIRAO SURADAAinda não há avaliações
- B Tech I Year - Previous Year Questions Engineering Drawing Unit - IDocumento4 páginasB Tech I Year - Previous Year Questions Engineering Drawing Unit - ISavantAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - 1Documento6 páginasUnit - 1anjaiah_19945Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit I Conics N Free Hand SketchingDocumento24 páginasUnit I Conics N Free Hand SketchingVenkata Sitarami Reddy KoppulaAinda não há avaliações
- ED Question BankDocumento19 páginasED Question BankSandeep MatetiAinda não há avaliações
- EG Assignment-2Documento1 páginaEG Assignment-2Syed Mushtaq AliAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Graphics Plane Curves ProblemsDocumento1 páginaEngineering Graphics Plane Curves Problemsmuthupecmec4908Ainda não há avaliações
- Sheet No 1Documento3 páginasSheet No 1sikandarAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Graphics ProblemsDocumento3 páginasEngineering Graphics ProblemsBALAMUGUNDAN50% (2)
- Handout 1Documento3 páginasHandout 1sunil varma0% (1)
- Engineering Graphics Assignment Long Questions Unit-IDocumento2 páginasEngineering Graphics Assignment Long Questions Unit-Ishaikamaan10jgs18080006Ainda não há avaliações
- Psna College of Engineering and Technology, Dindigul Department of Mechanical Engineering Assignment - I Class - Cse - D ConicsDocumento1 páginaPsna College of Engineering and Technology, Dindigul Department of Mechanical Engineering Assignment - I Class - Cse - D Conicsbalusharma1212Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment No 1 Unit 1Documento1 páginaAssignment No 1 Unit 1AravamudhanAinda não há avaliações
- AVC College Engineering Graphics Course Drawing Curves Tangents NormalsDocumento1 páginaAVC College Engineering Graphics Course Drawing Curves Tangents Normalsalertaru29Ainda não há avaliações
- Sheet01 Engineering CurvesDocumento4 páginasSheet01 Engineering Curvesneo4895651Ainda não há avaliações
- (Common To All Branches of Engineering) : (20A03101T) Engineering DrawingDocumento2 páginas(Common To All Branches of Engineering) : (20A03101T) Engineering Drawingramu vasaAinda não há avaliações
- Ex-3 & 4. Manual PagesDocumento4 páginasEx-3 & 4. Manual PagesViren ModiyaniAinda não há avaliações
- ED Lecture NotesDocumento27 páginasED Lecture NotesHaritha ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Pages - Engg. CurvesDocumento2 páginasManual Pages - Engg. Curvesviral chauhanAinda não há avaliações
- New Drawing ManualDocumento16 páginasNew Drawing ManualcbarajAinda não há avaliações
- Ge 6152 Engineering Graphics Anna University Question Bank - I Plane Curves & Freehand SketchingDocumento14 páginasGe 6152 Engineering Graphics Anna University Question Bank - I Plane Curves & Freehand SketchingArul JothiAinda não há avaliações
- ECE - AssignmentDocumento17 páginasECE - AssignmentsimalaraviAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics and MachineryNovDec2014R2013Documento3 páginasFluid Mechanics and MachineryNovDec2014R2013Mohanraj SubramaniAinda não há avaliações
- ENGINEERING CURVES GUIDEDocumento4 páginasENGINEERING CURVES GUIDErkadiraj7011Ainda não há avaliações
- CAEG Question Bank With SolutionsDocumento24 páginasCAEG Question Bank With SolutionssksnjgamingAinda não há avaliações
- Question BankDocumento12 páginasQuestion BankBalaChandarAinda não há avaliações
- EDRG 101 Engineering Drawing Course HandoutDocumento8 páginasEDRG 101 Engineering Drawing Course Handouttonmoyahmed06Ainda não há avaliações
- AssignmentDocumento14 páginasAssignmentAdel AwadAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing Notes PDFDocumento35 páginasEngineering Drawing Notes PDFSoubha ChakrabortyAinda não há avaliações
- EG All Problems Tutorials TW 06-07Documento19 páginasEG All Problems Tutorials TW 06-07Chirag Patel100% (2)
- Engineering Graphics: (Common To All Branches of Engineering)Documento32 páginasEngineering Graphics: (Common To All Branches of Engineering)bhavanamsambireddyofficialAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Wise CAEGDocumento1 páginaUnit Wise CAEGy.sudha madhuriAinda não há avaliações
- ENGINEERING GRAPHICS TITLEDocumento39 páginasENGINEERING GRAPHICS TITLEsugunay123Ainda não há avaliações
- I Mid Examination dec2010CSEDocumento3 páginasI Mid Examination dec2010CSEAraveeti C S ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Ellipses Parabolas Hyperbolas ProblemsDocumento5 páginasEllipses Parabolas Hyperbolas ProblemsayachandraAinda não há avaliações
- Edited AssignmentDocumento1 páginaEdited AssignmentPreethi SharmiAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Questions - I - EGDocumento2 páginasPractice Questions - I - EGDhanus DhanuAinda não há avaliações
- First Semester Engineering Graphics Two Marks With Answers Regulation 2013Documento26 páginasFirst Semester Engineering Graphics Two Marks With Answers Regulation 2013PRIYA RAJIAinda não há avaliações
- Ge 6152 Eng G Graphics 16 MarkDocumento13 páginasGe 6152 Eng G Graphics 16 MarkNatarajan AgoramAinda não há avaliações
- 1st B.tech Engineering Graphics Question BankDocumento9 páginas1st B.tech Engineering Graphics Question BankDrkumar SwamyAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering DrawingDocumento16 páginasEngineering DrawingDhaya VAinda não há avaliações
- Conic CurvesDocumento2 páginasConic CurvesanandandmeenaAinda não há avaliações
- MEE101 Engineering Graphics Tutorial BookDocumento23 páginasMEE101 Engineering Graphics Tutorial Bookk4r7hyAinda não há avaliações
- 3110013_EGD MANUAL-2023-24Documento16 páginas3110013_EGD MANUAL-2023-24devambanugariya2803Ainda não há avaliações
- Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College VIJAYAWADA-520007 Sectional-1Documento2 páginasVelagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College VIJAYAWADA-520007 Sectional-1Srikant PotluriAinda não há avaliações
- Conics NotesDocumento12 páginasConics NotesyogeshwaranAinda não há avaliações
- Ed Mid-1 Question Bank With Answers Viit 2022-23 by SsraoDocumento14 páginasEd Mid-1 Question Bank With Answers Viit 2022-23 by SsraoSANYASIRAO SURADAAinda não há avaliações
- Conic SectionsDocumento1 páginaConic SectionsHarish MugutkarAinda não há avaliações
- Engg. Graphics Lab Manual For BEDocumento34 páginasEngg. Graphics Lab Manual For BEalokvyas008Ainda não há avaliações
- Total Marks - 20 Min. Marks - 10 SET - A 1.) 2.)Documento3 páginasTotal Marks - 20 Min. Marks - 10 SET - A 1.) 2.)rizwan_862002Ainda não há avaliações
- Eg AssignmentDocumento2 páginasEg AssignmentPreethi Sharmi100% (1)
- SELVAM COLLEGE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GRAPHICS DOCUMENTDocumento13 páginasSELVAM COLLEGE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GRAPHICS DOCUMENTRichard S DavidsonAinda não há avaliações
- CurvesDocumento2 páginasCurvesVivek VijayakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Engg. Drawing QuestionsDocumento9 páginasEngg. Drawing QuestionsdearsaswatAinda não há avaliações
- 637Documento8 páginas637Bhavsar HardikAinda não há avaliações
- SET-1 R09: Code No: 09A10291Documento8 páginasSET-1 R09: Code No: 09A10291Joel WallerAinda não há avaliações
- r5100106 Engineering GraphicsDocumento4 páginasr5100106 Engineering GraphicssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Computational Intelligence in Communications and Business AnalyticsDocumento369 páginasComputational Intelligence in Communications and Business AnalyticsSourasish NathAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 8 Diagnostic Test 2022-2023Documento2 páginasGrade 8 Diagnostic Test 2022-2023JennyAinda não há avaliações
- Homework1 PDFDocumento3 páginasHomework1 PDFYuanhao LiuAinda não há avaliações
- AC axial compact fan technical specificationsDocumento5 páginasAC axial compact fan technical specificationsdhanasekhar27Ainda não há avaliações
- Cisco Certified Network Associate - CCNA (200-301) : Building Blocks of NetworkingDocumento5 páginasCisco Certified Network Associate - CCNA (200-301) : Building Blocks of NetworkingShahnawaz SiddiqueAinda não há avaliações
- Composition, Thermal and Rheological Behaviour of Selected Greek HoneysDocumento13 páginasComposition, Thermal and Rheological Behaviour of Selected Greek HoneyssyazaqilahAinda não há avaliações
- Treatment of Electroplating Wastewater Containing Cu2+, ZN 2+ and CR (VI) by ElectrocoagulationDocumento8 páginasTreatment of Electroplating Wastewater Containing Cu2+, ZN 2+ and CR (VI) by ElectrocoagulationAnonymous ZAr1RKAinda não há avaliações
- Ductile deformation finite strain analysisDocumento27 páginasDuctile deformation finite strain analysisJorgeBarriosMurielAinda não há avaliações
- A RANS-based Analysis Ool For Ducted Propeller Systems in Open Water ConditionDocumento23 páginasA RANS-based Analysis Ool For Ducted Propeller Systems in Open Water ConditionLeonardo Duarte MilfontAinda não há avaliações
- Cross Taping - A Practical Guide 12Documento2 páginasCross Taping - A Practical Guide 12jfjjfjfjjfjfAinda não há avaliações
- Martillo Hyd Atlas Copco SB 150Documento12 páginasMartillo Hyd Atlas Copco SB 150Nain murilloAinda não há avaliações
- CC5291-Design For Manufacture Assembly and Environments QBDocumento11 páginasCC5291-Design For Manufacture Assembly and Environments QBYuvaraj Yuvi0% (1)
- Z 80 HelptopicsDocumento5 páginasZ 80 HelptopicsEverly NAinda não há avaliações
- Thinsat®300 Installation and User'S Manual: Thinkom Solutions, IncDocumento39 páginasThinsat®300 Installation and User'S Manual: Thinkom Solutions, IncHiep Mai Van100% (1)
- Smart Card/Proximity Based Vehicle Identification & Access Control SystemDocumento4 páginasSmart Card/Proximity Based Vehicle Identification & Access Control SystemkarunamoorthiAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle® Fusion Middleware: Administrator's Guide For Oracle Business Intelligence Applications 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.7)Documento76 páginasOracle® Fusion Middleware: Administrator's Guide For Oracle Business Intelligence Applications 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.7)Nicholas JohnAinda não há avaliações
- GSM Modem XM1510S-B00-103 ManualDocumento19 páginasGSM Modem XM1510S-B00-103 ManualPaul MaposaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 17: Lightning Accidents: Grade 9-Science-Sussex College - WennappuwaDocumento5 páginasLesson 17: Lightning Accidents: Grade 9-Science-Sussex College - WennappuwaSwarnapaliliyanageAinda não há avaliações
- TP 03: Technique D'optimisation PSODocumento3 páginasTP 03: Technique D'optimisation PSOCEM Yelle N centreAinda não há avaliações
- IMME19 Schedule PDFDocumento39 páginasIMME19 Schedule PDFVikram JainAinda não há avaliações
- Tools - For - Problem - Solving (Appendix B), R.K. Malik's Newton Classes PDFDocumento48 páginasTools - For - Problem - Solving (Appendix B), R.K. Malik's Newton Classes PDFMoindavis DavisAinda não há avaliações
- Design of RivetsDocumento20 páginasDesign of RivetsRavishanker BaligaAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On Power Grid InertiaDocumento47 páginasPresentation On Power Grid InertiajorjijonAinda não há avaliações