Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NCP - Hmole
Enviado por
Chloe OpiñaDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NCP - Hmole
Enviado por
Chloe OpiñaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
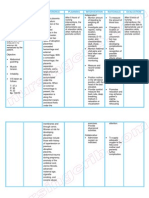
Gestational trophoblastic disease or Hydatidiform Mole Nursing Care Plan to Mrs. Smith Assessment: S> Mrs.
Smith, a 35 year old,married Chief complaint: Vaginal bleeding that varies from dark brown spotting for 1 day duration. 3 days PTA, Mrs. Smith experienced excessive vomiting that occurs in the morning. O> Urinalysis test for hCG revealed positive, UTZ revealed multiple small cystic structures, negative for fetal parts and fetal heart beat. Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Interventions: Independent: - Assess skin turgor and moisture of mucous membranes
Indicators of hydration status/ degree of deficit
Fluid volume deficit r/t elevated levels of human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) from the proliferating trophoblasts
- Monitor Vital signs. Evaluate peripheral pulses, capillary refill
to have a baseline data, reflects adequacy of circulating volume
- Monitor I&O; include all output sources (e.g., emesis, diarrhea
Decreasing renal output and concentration of urine suggest developing dehydration and need for fluid replacement.
- Weigh daily
Sensitive measurement of fluctuations in fluid balance
- Observe for bleeding tendencies; Note the amount, lochia/color of the vaginal discharge
Early identification of problems (which may occur as a result of cancer), allows for prompt intervention.
-Encourage increase fluid intake as tolerated
To compensate with the fluid volume deficit problem
-Encourage ice chips on mouth
For the vomiting episodes
-Encourage rest
Prevent unnecessary energy expenditure related to vomiting (as may trigger) and bleeding (loss of blood/RBC)
Dependent:
1. Blood Transfusion for Anemia Monitor VS Monitor signs of allergy Check blood package Monitor IV line and regulate drops
2. Correction of Coagulopathy
Assist
3. Hypertension Treatment Monitor VS Give meds as ordered Health teaching: diet and exercise Promote exercise
4. Dilation and Curettage for Evacuation of the Uterus Medication-Drug: Assist
5. Intravenous Oxytocin
to be started with the dilation of the cervix and continued postoperatively to reduce likelihood of hemorrhage. Consideration of using other uterotonic formulations such as Methergine or Hemabate is also accepted.
Monitor IV line and regulate drops
6. Assisted Ventilation and Monitoring for Respiratory
Distress
during surgery, this can happen due to trophoblastic embolization, high-output congestive heart failure caused by anemia, or iatrogenic fluid overload. Ventilation and monitoring should be done during such situation.
Assist
7. Monitor HCG for 1year
Increased HCG results to Choriocarcinoma (malignant)
8. Drug of Choice: Methotrexate (drug analysis on last
page)
(chemo-therapeutic drug)
9. Anitemetics
Diagnostic Procedure: o
For the vomiting episodes
Pretest
>Urine test for hCG
positive up to 100th day of pregnancy 1 2 million IU compared with a normal pregnancy level of 400,000 IU)
>Ultrasound >Laboratory test of vaginal discharge o After mole extraction to r/o tumor
> Pelvic examination > Chest x-ray > Serum test for the beta subunit of hCG
2 weeks until levels are normal, thereafter, levels are assessed every 4 weeks for 6 12 months. Increased levels after this suggest that malignant transformation has occurred.
Nursing Responsibility
- explain the procedure to client - ask client to void before the procedure - label and preserve specimen Collaborative: Dietary Department protein, folic acid, B12-rich food
To help patient develop new mature red blood cells to prevent further anemia due to blood loss for further evaluation and proper treatment
OB-Gyne Department
Patient Health Teaching:
- Encourage to have a high protein, folic acid and carotene diet R: Avoid use of OTC drugs and aspirin, gastric irritants
Affect clotting mechanism and potentiate to bleeding.
Patient Outcome:
Client will display adequate fluid balance as evidenced by stable vital signs , moist mucous membranes, skin turgor less than 1 sec, capillary refill of less than 2 secs. and adequate urine output
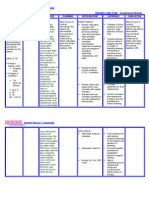
Medical Management 1. Patient Stabilization 2. Blood Transfusion for Anemia 3. Correction of Coagulopathy 4. Hypertension Treatment 5. Dilation and Curettage for Evacuation of the Uterus 6. Intravenous Oxytocin to be started with the dilation of the cervix and continued postoperatively to reduce likelihood of hemorrhage. Consideration of using other uterotonic formulations such as Methergine or Hemabate is also accepted. 7. Assisted Ventilation and Monitoring for Respiratory Distress During surgery, this can happen due to trophoblastic embolization, high-output congestive heart failure caused by anemia, or iatrogenic fluid overload. Ventilation and monitoring should be done during such situation. 8. Monitor HCG x 1year= Increased HCG results to Choriocarcinoma (malignant)
Nursing Management 1. Asses for signs and symptoms of h mole such as vaginal bleeding, nausea and vomiting, abnormal growth in the size of uterus for the stage of pregnancy and symptoms of hyperthyroidism 2. Explain the importanceof adequate nutrition in order to reduce the risk of h mole 3. Explain the risk factors such as women under 20 or over 40; other risk factors include a diet low in protein folic acid and carotene 4. Enumerate the possible potential causes such as defect in the egg, abnormality within the uterus, or nutritional deficiency. 5. Instruct the patient to plan the next conception after 12 months to prevent false result of pregnancy 6. Instruct to use a reliable contraceptive method such as an oral contraceptive for 12 months so that a (+) pregnancy test resulting from a new pregnancy will not be confused with increasing levels and devloping malignancy. 7. Explain the importance of oral contraceptives 8. Monitor HCG levels 9. Encourage to verbalize feelings about the loss of a possible child
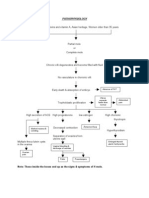
Gestational trophoblastic disease or Hydatidiform Mole
(Reproductive System)
IV- B12
Aguirre, Maria Felicidad Alabastro, Robin Niceno Arancon, Dominique Baula, Maria Feliza De Leon, Adriane Jerel Gomintong, Aura Mae Lim, Giselle Marie Osorio, Maria Christiana Reyes, Ana Katrina Simon, Stephanie Lou Tiburcio, Maria Victoria
Methotrexate Mechanism of Action: Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase, preventing reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate, subsequently resulting to decreased synthesis of purines and consequently DNA. Its activity is cell cycle specific. Indication: Patients with Hydatidiform mole. Nursing Responsibilities: Assess patients condition before therapy and reassess regularly thereafter to monitor drug effectiveness. Monitor for severe allergic reaction: rash, pruritus, urticaria, itching and flushing. Avoid contact with skin, since this drug is very irritating. Give in the morning so drug can be eliminated at bedtime. Take medication on an empty stomach. Encourage diligent mouth care to reduce risk for oral infections. Avoid use of aspirin or NSAIDS, sharp objects to reduce risk for bleeding. Instruct patient to report signs of anemia such as faintness, shortness of breathe. Contraceptive measures may be advised. Hair may be lost during treatment. Advise patient not to use sunblock or protective clothing to avoid burns.
Hydatidiform Mole / Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)
a developmental anomaly of the placenta, resulting in the proliferation & degeneration of chorionic villi w/c develops into a grape like clusters of vesicles. Incidence of H-mole most common lesion anteceding choriocarcinoma.
Diagnostics
Ultrasound reveals no fetal skeleton High HCG level in urine or blood
Risk Factors: Can predispose but not really cause
Taiwanese & Mexicans - protein diet (noodles) Familial Tendency buntis pero di bata ang laman , buwa incidence w/ advanced maternal age; assoc. w/ induction of ovulation by Clomiphine Therapy (hormone) 35 & 18 yr. old In women w/ socio-economic status
Clinical Manifestations ADEA
Anemia due to loss of blood Discharge of brownish red fluid (like prune juice) from vagina, around the 12th wk. w/c may contain clear fluid filled grape sized vesicles. Exaggerated symptoms of pregnancy Uterus too large for pregnancy Excessive Nausea & vomiting Early signs of PIH (before 24 weeks.) Absence of Fetal Heart sound
Complications DICT
DIC Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Infection Choriocarcinoma is possible Trophoblastic embolization after evacuation of molar pregnancy can cause Cardio-pulmonary arrest
Management
D & C to empty the uterus
Medical mgmt after D & C Follow-up supervision (1 yr.) monitor HCG level every wk., on 3-4 mos. every other wk., then every month until 1 year is completed. If there is rising titer of HCG, indicates pathology of choriocarcinoma. Drug of choice: Methotrexate (chemo-therapeutic drug) Pregnancy shld. be avoided for at least 1 yr. can use contraceptives but not pills (alters HCG levels)
Você também pode gostar
- Nursing Process For A Client With Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)Documento24 páginasNursing Process For A Client With Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)api-370148995% (19)
- Incomplete AbortionDocumento22 páginasIncomplete AbortionAJ Dalawampu100% (2)
- H-Mole (Case Study)Documento28 páginasH-Mole (Case Study)Mary Ann Lumbay Paye50% (4)
- NCP Pain (H Mole)Documento3 páginasNCP Pain (H Mole)Khat Quimen Mayo86% (7)
- NCP H-MoleDocumento6 páginasNCP H-MoleJaysonPangilinanAban100% (3)
- Case Study H MOLEDocumento11 páginasCase Study H MOLEmaori_martinez82% (11)
- Incompetent NCPDocumento1 páginaIncompetent NCPJohn Francis Velasco100% (6)
- Hydatidiform MoleDocumento2 páginasHydatidiform MoleDaniele Katrina Pimentel100% (3)
- NCP: Premature Dilation of The CervixDocumento6 páginasNCP: Premature Dilation of The CervixJavie80% (5)
- Hydatidiform MoleDocumento23 páginasHydatidiform MoleKristel Rivamonte100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY HmoleDocumento4 páginasPATHOPHYSIOLOGY HmoleMonica Lyka Bancale100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeWann WannAinda não há avaliações
- Precipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryDocumento7 páginasPrecipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryLei Ortega100% (1)
- NSVD Case StudyDocumento11 páginasNSVD Case StudyMichael UrrutiaAinda não há avaliações
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Documento3 páginasSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Milagros FloritaAinda não há avaliações
- Hydatidiform MoleDocumento28 páginasHydatidiform MoleRitamaria100% (7)
- NCP HmoleDocumento5 páginasNCP HmolemeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Molar PregnancyDocumento24 páginasNursing Molar PregnancyLord Pozak Miller100% (1)
- H Mole PathoDocumento1 páginaH Mole PathoKyle AlmeroAinda não há avaliações
- CP Hydatidiform MoleDocumento13 páginasCP Hydatidiform Molesweetheart_joannieAinda não há avaliações
- Molar Pregnancy - Case PresentationDocumento7 páginasMolar Pregnancy - Case Presentationアンナドミニク100% (1)
- H-Mole NCPsDocumento7 páginasH-Mole NCPsJoevence Gazo CuaresmaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Diagnosis: May Be Related To: Fluid Volume Deficit (Isotonic)Documento26 páginasNursing Diagnosis: May Be Related To: Fluid Volume Deficit (Isotonic)Ric Nacional75% (4)
- OB JC Case of Hydatidiform MoleDocumento37 páginasOB JC Case of Hydatidiform MoleBlykeBantugan100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan AbortionDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan Abortionnengsk84% (19)
- Nursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDocumento2 páginasNursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionJustin PasaronAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction HmoleDocumento32 páginasIntroduction HmoleBrian Montales BaggayanAinda não há avaliações
- Incomplete Abortion MINI CASE STUDY Group 3Documento23 páginasIncomplete Abortion MINI CASE STUDY Group 3Katrina TinapianAinda não há avaliações
- Incompetent CervixDocumento4 páginasIncompetent CervixCharm Arroyo100% (1)
- OxytocinDocumento1 páginaOxytocinAudrey Martin RañisesAinda não há avaliações
- ABORTIONDocumento10 páginasABORTIONSivi Joseph100% (1)
- H Mole Case StudyDocumento7 páginasH Mole Case StudyReznak0% (1)
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Documento6 páginasPlacenta Previa NCP 1Faye Nervanna Alecha Alferez83% (18)
- Case Study Castillo H MoleDocumento52 páginasCase Study Castillo H MoleGodfrey Bag-ao100% (1)
- NCP Placenta PreviaDocumento2 páginasNCP Placenta PreviaCathy CnlsAinda não há avaliações
- NCP: Labor Stage 1 Latent PhaseDocumento9 páginasNCP: Labor Stage 1 Latent PhaseJavieAinda não há avaliações
- H Mole Case PresentationDocumento12 páginasH Mole Case PresentationjisooAinda não há avaliações
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Documento6 páginasPlacenta Previa NCP 1Nicole ArandingAinda não há avaliações
- Recitation in MaternalDocumento6 páginasRecitation in MaternalVictoria Eugelio BungalsoAinda não há avaliações
- Pre Gestational ConditionsDocumento68 páginasPre Gestational ConditionsQuinonez Anna MarieAinda não há avaliações
- Hyper Emesis GravidarumDocumento22 páginasHyper Emesis Gravidarumchandu ranaAinda não há avaliações
- H MoleDocumento27 páginasH MoleAnjela Fae Jintalan Amador100% (1)
- ANTERPARTAL COMPLICATIONS Women With Preexisting Illness 1Documento85 páginasANTERPARTAL COMPLICATIONS Women With Preexisting Illness 1justinekaye diongsonAinda não há avaliações
- CholestasisDocumento15 páginasCholestasisMohamed Na3eemAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Mrs - Jagadeesw Ari.j M.SC NursingDocumento28 páginasHyperemesis Gravidarum: Mrs - Jagadeesw Ari.j M.SC NursingErika Anne Mercado CadawanAinda não há avaliações
- Psych Review NotesDocumento9 páginasPsych Review Notesslg233Ainda não há avaliações
- NURS325 05 Antepartum ComplicationDocumento81 páginasNURS325 05 Antepartum ComplicationaliAinda não há avaliações
- Liver Cirrhosis Case PresDocumento77 páginasLiver Cirrhosis Case Presmarlx580% (5)
- Abruptio Placenta Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasAbruptio Placenta Nursing Care PlanJharene Basbaño100% (5)
- Ectopic PregnancyDocumento36 páginasEctopic PregnancyLorenz BreezAinda não há avaliações
- PPH Care PlanDocumento4 páginasPPH Care PlanGCAinda não há avaliações
- Placenta Abruptio: Maneja, Jan Michael B. BSN 223Documento6 páginasPlacenta Abruptio: Maneja, Jan Michael B. BSN 223JiraGonzales100% (1)
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocumento32 páginasHyperemesis GravidarumBharat ThapaAinda não há avaliações
- Liverdiseaseinpregnancy 2Documento40 páginasLiverdiseaseinpregnancy 2Fadil HidayatAinda não há avaliações
- Hydatidiform MoleDocumento15 páginasHydatidiform MoleRegine Mae Morales EncinadaAinda não há avaliações
- Patient'S Profile: GROUP 1: Camposano, Cielo, Edem, Ibalin, RodriguezDocumento3 páginasPatient'S Profile: GROUP 1: Camposano, Cielo, Edem, Ibalin, RodriguezDivina Gracia Vibal CieloAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd Lecture Substance Abuse & Gestational Conditions (NCM102)Documento14 páginas3rd Lecture Substance Abuse & Gestational Conditions (NCM102)Charmaine MativoAinda não há avaliações
- GNM 3rd YearDocumento53 páginasGNM 3rd Yearrαj rαuѕhαnAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Pregnancy - 094218Documento67 páginasNormal Pregnancy - 094218Beatrice habukuwie BaahAinda não há avaliações
- Gestational Conditions 1Documento19 páginasGestational Conditions 1MrLarry Dolor100% (1)
- District Level Functionaries NHMDocumento56 páginasDistrict Level Functionaries NHMAADITYESHWAR SINGH DEOAinda não há avaliações
- Reproduction System NotesDocumento18 páginasReproduction System NotesmorganicalAinda não há avaliações
- Miscarriage (Spontaneous Abortion) : Abnormal PregnancyDocumento4 páginasMiscarriage (Spontaneous Abortion) : Abnormal PregnancyKyjoy Flores CstrAinda não há avaliações
- The Ultimate Guide To FertilityDocumento32 páginasThe Ultimate Guide To FertilityMirjana14Ainda não há avaliações
- Economic Development Essay On PopulationDocumento7 páginasEconomic Development Essay On PopulationHenry LatourAinda não há avaliações
- Flashcards - Topic 16 Reproduction - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocumento191 páginasFlashcards - Topic 16 Reproduction - CAIE Biology IGCSEHuda BilalAinda não há avaliações
- Panduan KomunikasiDocumento8 páginasPanduan KomunikasiDewi KartilaAinda não há avaliações
- Blocked Fallopian TubesDocumento2 páginasBlocked Fallopian TubesPreethi JoseAinda não há avaliações
- Persuasive SpeechDocumento7 páginasPersuasive SpeechRod LustreAinda não há avaliações
- SOGC Guideline No. 292 - AUB in Pre-Menopausal WomenDocumento25 páginasSOGC Guideline No. 292 - AUB in Pre-Menopausal WomendubblewalkerAinda não há avaliações
- Prescribing HRTDocumento10 páginasPrescribing HRTAnaAinda não há avaliações
- Abortion, GRP 3Documento49 páginasAbortion, GRP 3Brahmmadandi RuchikaAinda não há avaliações
- Notes-Maternal Health NursingDocumento22 páginasNotes-Maternal Health NursingRachael Crossgrove100% (4)
- Endometriosis: DR OMBAKU Kingsley Sama DR SakinatouDocumento99 páginasEndometriosis: DR OMBAKU Kingsley Sama DR SakinatouOmbaku KingsleyAinda não há avaliações
- Unwanted PregnanciesDocumento3 páginasUnwanted PregnanciesElmeraine EstrellaAinda não há avaliações
- Contraception For Women With Psychiatric DisordersDocumento14 páginasContraception For Women With Psychiatric DisordersFourtiy mayu sariAinda não há avaliações
- Gestational HypertensionDocumento5 páginasGestational HypertensionJason Jimmy Lee PillayAinda não há avaliações
- The Effect of Family Planning On Household Welfare in Nabweru Sub-County, Wakiso DistrictDocumento54 páginasThe Effect of Family Planning On Household Welfare in Nabweru Sub-County, Wakiso Districtsolomon kyagabaAinda não há avaliações
- 11.21 - Maternal Health Status in The PhilippinesDocumento7 páginas11.21 - Maternal Health Status in The PhilippinesJøshua CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Regional Office Xiii: Department of HealthDocumento7 páginasRegional Office Xiii: Department of HealthSDN HelplineAinda não há avaliações
- MENSTRUAL CYCLE - QuizDocumento13 páginasMENSTRUAL CYCLE - QuizMaria Germamae ResosoAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs in PregnancyDocumento14 páginasDrugs in Pregnancyhenry_poirotAinda não há avaliações
- ContraceptieDocumento20 páginasContraceptieBindar AdrianAinda não há avaliações
- LHV 2022 TestDocumento1 páginaLHV 2022 TestMuhammad AliAinda não há avaliações
- Sex EducationDocumento20 páginasSex Educationapi-302539618Ainda não há avaliações
- Quantification of Health Commodities - RMNCH SupplementDocumento173 páginasQuantification of Health Commodities - RMNCH Supplementv_ratAinda não há avaliações
- B1 2 Coordination & Control Questions and AnswersDocumento36 páginasB1 2 Coordination & Control Questions and AnswersBioScMentor-1Ainda não há avaliações
- Asimov, Isaac - On The Marching MoronsDocumento6 páginasAsimov, Isaac - On The Marching MoronsJohannHBasson0% (1)
- Creighton MethodDocumento2 páginasCreighton MethodPooja YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Family Nursing Care Plan: "Hindi Kasi Uso Sa Kanila Yung Family Planning Eh "Documento2 páginasFamily Nursing Care Plan: "Hindi Kasi Uso Sa Kanila Yung Family Planning Eh "Jonver David0% (1)