Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
EETC 1042 AC Electricity Final Exam PRACTICE
Enviado por
rynotexas2705Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
EETC 1042 AC Electricity Final Exam PRACTICE
Enviado por
rynotexas2705Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
EETC 1042
AC Electricity
Final Exam PRACTICE [Show all your work!]
Name___________________________________
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. [t1-1] The maximum current that the d'Arsonval movement can read independently is equal to the current sensitivity of the movement. [t1-2] An ideal capacitor looks like an open circuit to dc current once it has charged to its final value. [t3-1] The superposition theorem is applicable to power effects in ac circuits, since it is dealing with a nonlinear relationship. [t3-2] In order to remove a voltage source from a circuit for superposition analysis, we must replace it with an open circuit. [f] A power gain of 3 dB is equivalent to an output power that is twice the power of the input. [f] Decibels are used to provide a comparison between power levels and voltage levels. ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______
PROBLEMS. Work the problems and write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Show all work! If simple calculations are done in calculator, identify with by calc.
Meter 1 Ratings: Current Sensitivity = 10 mA, Resistance = 500 RSHUNT = 0.77 Figure 7.3 7. [t1-3] See Figure 7.3. What voltage V must be applied to the circuit to result in full-scale meter deflection?
Voltage Source VS1 = 12V R1 = 22k C1 = 4.7 F
ac final exam practice.docx Page 1 of 10
Figure 10.1 8. 9. [t1-4] See Figure 10.1. What is the time constant t for this circuit? [t1-5] See Figure 10.1. If the initial voltage of the capacitor = 0V, after the closing of the switch, when will the voltage vC reach 5.0 V?
10. [t1-6] See Figure 10.1. If the initial voltage of the capacitor = 0V, what is the maximum instantaneous current that will flow through the capacitor after the closing of the switch?
Voltage Source VS1 = 90V C1 = 4.7 F C2 = 4.7 F C3 = 4.7 F C4 = 4.7 F
Figure 10.3
11. [t1-7] See Figure 10.3. What is the total capacitance CT?
Voltage Source VS1 = 4.5V R1 = 2.2 K L1 = 100 mH Figure 12.1 12. [t1-8] See Figure 12.1. What is the time constant in this circuit?
ac final exam practice.docx
Page 2 of 10
Voltage Source VS1 = 3.3V R1 = 47 K R2 = 470 K L1 = 50 mH Figure 12.3 13. [t1-9] See Figure 12.3. After the closing of the switch, what will the current through the inductor be after the circuit voltages and currents have reached steady-state values? Assume that the inductor is an ideal (lossless) device. 14. [t1-10] See Figure 12.3. After the current has reached a steady-state value, the switch opens. What will the voltage across the inductor be the instant that the switch opens? 15. [t1-11] What is the period of a 50 kHz sine wave? 16. [t1-12] What is the angular velocity of a 50 kHz sine wave? 17. [f] A 10 mV input to an amplifier produces a 5 V output. What is the voltage gain in dB?
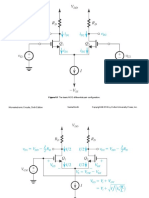
Figure 22.2 18. See Figure 22.2. If the mutual inductance M12 = 1 H, what is the total inductance LT of this circuit?
Primary turns = 120
/ Secondary turns = 48,000 Figure 22.3
Page 3 of 10
ac final exam practice.docx
19. [f] See Figure 22.3. What is the transformation ratio, a, for this transformer? 20. [f] See Figure 22.3. What is the voltage ES across the load, assuming ideal components? 21. [f] See Figure 22.3. What is the current IS through the load, assuming ideal components? 22. [f] See Figure 22.3. What is the volt-amp rating of this transformer if the transformer is operating at its rated capacity? 23. [f] See Figure 22.3. If this transformer is an ideal device and the load is a resistor, how much power is transferred to the load?
Figure 22.4 24. [f] See Figure 22.4. A resistive load, RL, is connected to the transformer secondary as shown. What is the primary impedance Zp if the primary has 1600 turns and the secondary has 100 turns? 25. [t2-1] What is the amplitude in the equation v = 186 sin(7700t) V? 26. [t2-2] At what frequency does a 10 F capacitor have a reactance of 77?
27. [t2-3] What is the frequency in the equation v = 186 sin(7700t)?
28. [t2-4] Determine the frequency at which the reactance of a 0.47 :F capacitor equals that of a 3.3 H coil. 29. [t2-5] The current i = 125sin 377t mA passes through a 0.22 F capacitor. Find the sinusoidal expression for the voltage across the capacitor. 30. [t2-6] If i = 7.7 sin , what is i at = 30?
ac final exam practice.docx
Page 4 of 10
t1 = 1 mS, t2 = 2 mS, t3 = 3 mS, t4 = 4 mS Figure 13.2 31. [t2-7] See Figure 13.2. What is the average value of this waveform?
XC = 990, R = 220, XL = 770 Figure 15.5 32. [t2-8] See Figure 15.5. Assume the source frequency is 60 Hz. What component, when placed in parallel with the existing components, would make the total impedance ZT purely resistive? Specify actual component value in Farads or Henries, not just inductive reactance or capacitive reactance. 33. [t2-9] Express the impedance of a 220 pF capacitor at 60 Hz in rectangular form.
ac final exam practice.docx
Page 5 of 10
Vs = 120 V < 60, R = 560 , XL = 237 , XC = 150 Figure 15.3 34. [t2-10] See Figure 15.3. What is ZT in polar form? 35. [t2-11] Ignoring any effects of DC resistance, what is the total reactance of a 250 mH coil in series with a 4.7 microfarad capacitor at a signal frequency of 1000 Hz?
XL1 = 70, XC1 = 77 Figure 2 36. [t3-3] See Figure 2. What is the total impedance ZT for this circuit?
Figure 3 37. [t3-4] See Figure 3. Write one equation to describe the total impedance ZT for this circuit in terms of the impedances Z1, 2, and 3.
ac final exam practice.docx Page 6 of 10
Figure 5 38. [t3-5] See Figure 5. The voltage source (a) consists of VS = 500 V <20 and Z = 100 m <30. If this voltage source is converted to a current source (b), what is the value of the current IS?
Figure 6 39. [t3-6] See Figure 6. Consider the mesh analysis solution method for this circuit. Write an equation describing the loop on the left.
Figure 7 40. [t3-7] See Figure 7. Assume that the bridge is balanced. If Z1 = 1 <10, Z2 = 2 <33, Z3 = 40 <-10, what must Z4 be?
ac final exam practice.docx
Page 7 of 10
VS1 = 150,000 V < 33, VS2 = 75,000 V < -33, R1 = 100, XL1 = 60, XC1 = 40 Figure 8 41. [t3-8] See Figure 8. Use the superposition theorem to calculate the portion of the current through the capacitor caused by the VS1 voltage source.
XL1 = 77, XC1 = 77 Figure 1 42. [t4-1] See Figure 1. What is the total impedance ZT for this circuit, assuming ideal components? 43. [t4-2] Given Zload = Zth* for maximum power transfer, where * designates complex conjugate, if Zth = 10 - j30 , what must the load impedance be for maximum power transfer to occur? 44. [t4-3] How is the amount of heat dissipated in an ideal inductor calculated? 45. [t4-4] What are the units of apparent power? 46. [t4-5] What are the units of reactive power? 47. [t4-6] What are the units of real power? 48. [t4-6] As what form of energy will the total power delivered to a resistor typically be dissipated? 49. [t4-7] What is the net flow of power to a pure (ideal) capacitor over a full cycle?
ac final exam practice.docx
Page 8 of 10
Figure 19.1 50. [t4-8] See Figure 19.1. What is the total real power (PT) delivered to this circuit? 51. [t4-9] See Figure 19.1. What is the total apparent power delivered to this circuit?
Figure 19.3 52. [t4-10] See Figure 19.3. The power triangle shown represents the characteristics of a 230 V 60 Hz ac motor. What is the power factor of this motor? 53. [t4-11] How does the total impedance of a series RLC circuit at resonance as compare to the resistance of the circuit? 54. [t4-12] What is the phase relationship between current and voltage in series resonant circuits? 55. [t4-13] How does current in a series RLC circuit at resonance compare to the current at a higher frequency?
ac final exam practice.docx
Page 9 of 10
Figure 20.2 56. [t4-14] See Figure 20.2. What is the source current at resonance? 57. [t4-15] What is the resonant frequency of a series circuit consisting of a 100 pf capacitor, a 10 k resistor, and a 1 mH inductor?
Figure 20.6 58. [t4-16] What is the resonant frequency of the circuit shown in Figure 20.6? 59. [t4-17] In a parallel resonant circuit, how does impedance at resonance compare to that of a series resonant circuit at the same resonant frequency?
Figure 20.5 60. [t4-18] See Figure 20.5. These curves describe three series resonant circuits. Which response curve represents the circuit with the highest Q?
ac final exam practice.docx
Page 10 of 10
Você também pode gostar
- Maxwell BridgeDocumento4 páginasMaxwell BridgeRohit Birnale0% (1)
- Analysis and Design of Linear Circuits SolutionsDocumento49 páginasAnalysis and Design of Linear Circuits SolutionsSherifAinda não há avaliações
- AMPLIFIERSDocumento4 páginasAMPLIFIERStinAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Chemical CleaningDocumento28 páginasIntroduction To Chemical Cleaningmordidomi0% (1)
- 1.1 Ohm's Law: Unit Quantity I.EDocumento53 páginas1.1 Ohm's Law: Unit Quantity I.EMithun MahtoAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Computer Aided Electrical Drawing (17EE651)Documento29 páginasDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Computer Aided Electrical Drawing (17EE651)Wasim NidgundiAinda não há avaliações
- UAC Clipper and Clamper Homework CircuitsDocumento21 páginasUAC Clipper and Clamper Homework CircuitsgadisureshkumarAinda não há avaliações
- BJT Biasing-2spDocumento30 páginasBJT Biasing-2spHazal0% (1)
- Bifpcl Question Solve - 2015: R 5+3+2 10 V 20+20 40 Sor 10 P 40 / (4 X 10)Documento7 páginasBifpcl Question Solve - 2015: R 5+3+2 10 V 20+20 40 Sor 10 P 40 / (4 X 10)Mazharul HaqueAinda não há avaliações
- Sedra Cap8Documento79 páginasSedra Cap8Gustavo Omar Mesones MálagaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 - FET BiasingDocumento10 páginasChapter 7 - FET BiasingEliaquim RomanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit1 EDCDocumento24 páginasUnit1 EDCKarthick Sivakumar ChellamuthuAinda não há avaliações
- Four-Way Traffic LightDocumento3 páginasFour-Way Traffic LightjoshuaAinda não há avaliações
- PLC Objective Questions Answers - PLC SCADA ACADEMYDocumento5 páginasPLC Objective Questions Answers - PLC SCADA ACADEMYRinalyn-Oscar Gamboa MagtibayAinda não há avaliações
- BJT and JFET Frequency ResponseDocumento16 páginasBJT and JFET Frequency ResponseVert WheelerAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5 - Climper and Clamper CircuitDocumento22 páginasLecture 5 - Climper and Clamper CircuitArifah HamidunAinda não há avaliações
- Electric Machinery Fundamentals-1Documento28 páginasElectric Machinery Fundamentals-1AmaniDarwishAinda não há avaliações
- Matlab Simulations For Power Factor Correction of Switching PowerDocumento20 páginasMatlab Simulations For Power Factor Correction of Switching PowerPhil Lei0% (3)
- Verify Thevenin's TheoremDocumento10 páginasVerify Thevenin's TheoremJay SathvaraAinda não há avaliações
- Exp-No6 Multiplication of 8 Bit and 16-Bit NumbersDocumento2 páginasExp-No6 Multiplication of 8 Bit and 16-Bit NumbersMohammed Dyhia Ali0% (1)
- Concordia University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ELEC 6411 - Power Electronics I Course Outline Fall 2015 Course InstructorDocumento30 páginasConcordia University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ELEC 6411 - Power Electronics I Course Outline Fall 2015 Course InstructorAndrewJohnsonJenssonAinda não há avaliações
- THREE PHASE POWER FACTOR CORRECTIONDocumento9 páginasTHREE PHASE POWER FACTOR CORRECTIONuama87Ainda não há avaliações
- Electronic System Design LabDocumento25 páginasElectronic System Design Labsramiz_1987Ainda não há avaliações
- Electronic Devices Used in Power Electronics Characteristics ComparisonDocumento12 páginasElectronic Devices Used in Power Electronics Characteristics ComparisonEysha qureshiAinda não há avaliações
- Filters QCMDocumento15 páginasFilters QCMMary-Joe SemaaniAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics 2 Lab ManualDocumento75 páginasElectronics 2 Lab ManualLuisa Marie Bernardo Rañada100% (1)
- How Does Microprocessor Differentiate Between Data and InstructionDocumento60 páginasHow Does Microprocessor Differentiate Between Data and InstructionUbaid Saudagar100% (1)
- Viper 12s Buck Boost ConverterDocumento14 páginasViper 12s Buck Boost ConverterelkillyAinda não há avaliações
- I DT DT DT DT: Class Notes On Electrical Measurements & InstrumentationDocumento71 páginasI DT DT DT DT: Class Notes On Electrical Measurements & InstrumentationTia Nur AmaliahAinda não há avaliações
- Boost DesignDocumento4 páginasBoost DesignmuthukumartharaniAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Wave GuidesDocumento150 páginasChapter 2 Wave GuidesMohdIhsanAinda não há avaliações
- Transmission Lines and Waveguides Notes PDFDocumento134 páginasTransmission Lines and Waveguides Notes PDFSubbu NithyaAinda não há avaliações
- Power ElectronicsDocumento90 páginasPower ElectronicsPalanisamy NagappanAinda não há avaliações
- ARDUINO SPWM SINE INVERTER PROJECT GUIDEDocumento5 páginasARDUINO SPWM SINE INVERTER PROJECT GUIDEmaurilioctbaAinda não há avaliações
- Induction Motor Drive Control MethodsDocumento8 páginasInduction Motor Drive Control MethodsRudra Kumar MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Power Electronics ChapterDocumento9 páginasIntroduction to Power Electronics ChapterSouvik GanguliAinda não há avaliações
- 9 Way Clap Switch!!Documento8 páginas9 Way Clap Switch!!Trilok Sawant100% (1)
- Ee105 Fet LectDocumento61 páginasEe105 Fet LectKahMun LimAinda não há avaliações
- Intrinsic SemiconductorDocumento2 páginasIntrinsic SemiconductorGilberto ManhattanAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of The Transient Response of A DC MotorDocumento6 páginasEvaluation of The Transient Response of A DC MotorNesuh MalangAinda não há avaliações
- EE5251 Unit 1Documento129 páginasEE5251 Unit 1SathyaAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transform C4 - StudentsDocumento21 páginasLaplace Transform C4 - StudentsJing ZeAinda não há avaliações
- EE321 Lab 1Documento16 páginasEE321 Lab 1Alvish NaiduAinda não há avaliações
- EE113 Course Notes Electronic CircuitsDocumento268 páginasEE113 Course Notes Electronic Circuitspowerdeadlifter100% (1)
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsAinda não há avaliações
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsNo EverandHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Overstress (EOS): Devices, Circuits and SystemsNo EverandElectrical Overstress (EOS): Devices, Circuits and SystemsAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsNo EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsAinda não há avaliações
- Modeling of Digital Communication Systems Using SIMULINKNo EverandModeling of Digital Communication Systems Using SIMULINKAinda não há avaliações
- Real-Time Simulation Technology for Modern Power ElectronicsNo EverandReal-Time Simulation Technology for Modern Power ElectronicsAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Engineering Applications of Two–Port Networks: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo EverandElectronic Engineering Applications of Two–Port Networks: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionAinda não há avaliações
- Variable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersNo EverandVariable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Techniques for Electromagnetics: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringNo EverandComputer Techniques for Electromagnetics: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringR. MittraNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Partition Coefficient Determination MethodsDocumento24 páginasPartition Coefficient Determination MethodsdeshmukhgeolAinda não há avaliações
- NY Regents Chemistry Exam Scoring KeyDocumento12 páginasNY Regents Chemistry Exam Scoring KeyAAVANIAinda não há avaliações
- Production Drawings & Process ModelsDocumento15 páginasProduction Drawings & Process ModelsnotonectalAinda não há avaliações
- 13thPMO Area Ver5Documento3 páginas13thPMO Area Ver5Yinkci Heart Entertainment StudioAinda não há avaliações
- 2-Mark Questions Anna University Signals and SystemsDocumento11 páginas2-Mark Questions Anna University Signals and SystemsSonu100% (2)
- Ultrasonic FlowmetersDocumento30 páginasUltrasonic Flowmetersvcharles0% (1)
- Muhammad Imran YousufDocumento1 páginaMuhammad Imran YousufMuhammad Irfan YousufAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Benzoic Acid Kinetics Using Temperature vs Time GraphsDocumento3 páginasAnalysis of Benzoic Acid Kinetics Using Temperature vs Time GraphssnowinceptionAinda não há avaliações
- G-Snack Evolution Rev05Documento2 páginasG-Snack Evolution Rev05whaleAinda não há avaliações
- Upem Ch-22Documento9 páginasUpem Ch-22siddharthsrathor04Ainda não há avaliações
- Design and Analysis of Single Plate Friction ClutchDocumento29 páginasDesign and Analysis of Single Plate Friction ClutchSagar BhoiteAinda não há avaliações
- C 0024 - TLZ THLZ - 04 08Documento46 páginasC 0024 - TLZ THLZ - 04 08Oscar Alvitez DominguezAinda não há avaliações
- Hibernia Study (Flare)Documento178 páginasHibernia Study (Flare)bmgarisAinda não há avaliações
- Vernacular ArchitectureDocumento33 páginasVernacular ArchitectureShyam Sekhar MenonAinda não há avaliações
- TP PDFDocumento1 páginaTP PDFRîkèñ PâtélAinda não há avaliações
- Bulk and Suspenshion Polynerization of MMA Into PMMADocumento5 páginasBulk and Suspenshion Polynerization of MMA Into PMMADavid Meza CarbajalAinda não há avaliações
- TentDocumento24 páginasTenthanyassawy50% (2)
- Gases Tutorial 2Documento4 páginasGases Tutorial 2Idil WarsameAinda não há avaliações
- Coal Carbonization: Current and Future ApplicationsDocumento9 páginasCoal Carbonization: Current and Future ApplicationsVenkata Krishnan RamanujamAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring Elastic Potential EnergyDocumento2 páginasMeasuring Elastic Potential EnergyKerem TuranAinda não há avaliações
- Wind Loading of Industrial, Mining and Petrochemical StructuresDocumento16 páginasWind Loading of Industrial, Mining and Petrochemical StructuresapirakqAinda não há avaliações
- Soundness TestDocumento4 páginasSoundness TestC-one Goncalves100% (2)
- 01 11 20-Cta5Documento36 páginas01 11 20-Cta5Goury ShankarAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 8.1 - Energy SourcesDocumento92 páginasTopic 8.1 - Energy SourcesAnshulAinda não há avaliações
- 2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerDocumento6 páginas2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerSiti Nursahidah0% (1)
- Aits 2223 FT Vi Jeem OfflineDocumento15 páginasAits 2223 FT Vi Jeem OfflineSuvrajyoti TaraphdarAinda não há avaliações
- Universal temperature transmitter for HART protocolDocumento16 páginasUniversal temperature transmitter for HART protocolALI5034Ainda não há avaliações
- Control Strategies For Water Level Control of Two Tank System 11 AugDocumento7 páginasControl Strategies For Water Level Control of Two Tank System 11 AugGJESRAinda não há avaliações
- Polarization Index TestDocumento3 páginasPolarization Index TestShahriar AhmedAinda não há avaliações