Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
ANAT 215 Lecture Notes
Enviado por
jchyeung20Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ANAT 215 Lecture Notes
Enviado por
jchyeung20Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lecture 6 Cartilage and Bone Cartilage: Supportive Connective Tissue provide flexibility + support, plastic materials, no blood vessels,
, no nerve, diffusion from adjacent tissues into cartilage, perichondrium is full of water Hyaline Cartilage (breast bone in chicken): cells, fibers, ground substance, most common cartilage, o found at the articular surface of moveable joints, walls of the nose, larynx, trachea, bronchi, ribs o collagen fiber (type II), avascular, o Chondromucoid jelly like substance give resilency + strength o Lacunae contains cartilage cells o Chondrocytes cartilage cells o Perichondrium cellular and fibrous layer, dense irregular CT, covers everywhere but articular surface o matrix appear homogenous in fresh collagen b/c same refractive index as ground substance Fibrous Cartilage: lots of collagen fibers (type I), little ground substance, very tough, no perichondrium but bonds with dense reulgar CT and hyline waste removal is continuous, dense regular blood merges with dense regular CT in cartilage o Found in intervertebral discs, symphysis pubis, some joints and tendons Elastic Cartilage: presence of elastic fibers similar to hyaline, flexible, found in excternal ear, epiglottis, larynx
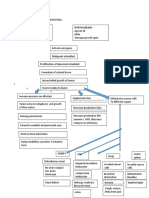
Bone: Protection, support, movement, mineral storage, blood production 2 Components o Organic 35% - cells, fibers, ground substance o Inorganic 65% - mineralized salts, hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate, calcium hydroxide), calcium carbonate, sodium, magnesium, fluoride Concentric cylindrical layers around longitudinal canal Microscopic structures: o Osteon basic structural of bone lamella outer interior space of bone lacune capsules containing osteocytes Canaliculi links up lacunae and eventually to Haversian canal Haversion Canal (central canal) contains blood vessels o Volkmans cana (perforating canal) connects osteon together o Intertistial lamellae bones that fill gaps between osteon o Cement lines the white lines, separate intertistial lamella and osteon o Circumferential Lamellae duct tape around the bone, holds everything together
Macroscopic structure: o 2 Forms: Compact Bone dense, long, continuous, seemingly solid Spongy bone made up of narrow bars join with the compact bone, find bone marrow here o Long Bones: Bones in arm and leg (humerous) Diaphysis long cylindrical compact bone lined with spongy bone, where we find marrow Epiphysis Rounded end of a long bone, joint area covered with articular cartilage 5
Epiphyseal line - a plane or plate on a long bone, visible as a line, marking the junction of the epiphysis and diaphysis, made of hyaline cartilage, use for growth Articular cartilage white hyaline tissue that covers the surface of a joint Periosteum Lines the outer layer of bones. It is connected to the circumferential lamellae by Sharpeys Fibers Endosteum - lines the medullary cavity, covers spongy bone and lines the inner surfaces of the central canals. Active during growth of bone and repair Medullary (marrow cavity) - the central cavity of bone shafts where red bone marrow and/or yellow bone marrow (adipose tissue) is stored o Short Bone wrist bone + ankle bone o Flat Bone skull A sandwich of Spongy bones o Irregular Vertebrae Bone Cells o Osteoblast responsible for bone formation o Osteoclast Removes bone tissues by dissolving matrix to return phosphate and calcium in the blood o Osteocytes mature bone cells that maintain and monitors the protein and mineral in the matrix
Você também pode gostar
- Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Skeletal StructureDocumento70 páginasChapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Skeletal StructureStefanie Henry100% (1)
- Bone Tissues 1Documento38 páginasBone Tissues 1ms_pianist100% (1)
- MODULE 4 Skeletal SystemDocumento16 páginasMODULE 4 Skeletal SystemKate Andrea PanizalesAinda não há avaliações
- Histology of BoneDocumento20 páginasHistology of Boneyudha anantha khaerul putraAinda não há avaliações
- How Many Bones Are in The BodyDocumento3 páginasHow Many Bones Are in The BodycanAinda não há avaliações
- Notes From Dental Articles ANATOMYDocumento6 páginasNotes From Dental Articles ANATOMYpatelpurvivAinda não há avaliações
- Connective TissuesDocumento45 páginasConnective TissuesAbrar osmanAinda não há avaliações
- Sesamoid Bone: Jump ToDocumento8 páginasSesamoid Bone: Jump ToBet Mustafa EltayepAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy 1Documento69 páginasAnatomy 1ravinder malwalAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 - OsteologyDocumento66 páginasLecture 2 - OsteologyRubia Iftikhar100% (1)
- Archs of The Foot - May 023Documento33 páginasArchs of The Foot - May 023mrizvi334Ainda não há avaliações
- Connective Tissues 2Documento71 páginasConnective Tissues 2Asma Aijaz100% (1)
- L9 Blood VesselsDocumento2 páginasL9 Blood VesselsalihusseinAinda não há avaliações
- ORGAN OF VISION. Clinical Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture by M. Bezugly MD, PH.D.)Documento9 páginasORGAN OF VISION. Clinical Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture by M. Bezugly MD, PH.D.)Azra AzmunaAinda não há avaliações
- Orbital and Ocular Anatomy: Abdulrahman Al-Muammar, MD, FRCSC King Saud UniversityDocumento45 páginasOrbital and Ocular Anatomy: Abdulrahman Al-Muammar, MD, FRCSC King Saud UniversityAriyanie NurtaniaAinda não há avaliações
- Intrdoduction Gis 2 (Associated Organs) : Maya Tejasari Histology DepartmentDocumento24 páginasIntrdoduction Gis 2 (Associated Organs) : Maya Tejasari Histology DepartmentIpan YustiartaAinda não há avaliações
- 03 Connective TissueDocumento60 páginas03 Connective TissueMuhammad Khaled TaubehAinda não há avaliações
- Parts of The Horse: 4-H Horse Project Manual-PartsofthehorseDocumento20 páginasParts of The Horse: 4-H Horse Project Manual-Partsofthehorsenikhil3831Ainda não há avaliações
- ZOO3731 chptr.6-8Documento55 páginasZOO3731 chptr.6-8Raylax2sik24Ainda não há avaliações
- Histo Slides Volume IDocumento67 páginasHisto Slides Volume IKristian CadaAinda não há avaliações
- Bone HistologyDocumento30 páginasBone HistologyVicAinda não há avaliações
- Histology of The Circulatory SystemDocumento24 páginasHistology of The Circulatory SystemFatima Zehra YusefAinda não há avaliações
- XX Popliteal Fossa and Knee JointDocumento43 páginasXX Popliteal Fossa and Knee JointAlistair WalkerAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy PDFDocumento63 páginasAnatomy PDFPranavAinda não há avaliações
- Cells: USC Messed Up The Following QuestionsDocumento119 páginasCells: USC Messed Up The Following Questionsopeyemi idaeworAinda não há avaliações
- Skeletal SystemDocumento14 páginasSkeletal SystemCharlize PalmaAinda não há avaliações
- Fetal Pig AnatomyDocumento43 páginasFetal Pig Anatomymihai2242Ainda não há avaliações
- Posterior Compartment of ForearmDocumento60 páginasPosterior Compartment of Forearmnickmirad2Ainda não há avaliações
- BIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyDocumento7 páginasBIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyCloie Anne Rabinetas100% (1)
- Upper Limb 1Documento14 páginasUpper Limb 1faraAinda não há avaliações
- Bones Ossification.Documento9 páginasBones Ossification.Shimmering MoonAinda não há avaliações
- Temporo Mandibular JointDocumento146 páginasTemporo Mandibular Jointdentistpro.orgAinda não há avaliações
- The Skin NotesDocumento7 páginasThe Skin NotesSafeer SefiAinda não há avaliações
- ANP 300 Exam 3 ReviewDocumento15 páginasANP 300 Exam 3 ReviewNerdy Notes Inc.Ainda não há avaliações
- Histology SummaryDocumento24 páginasHistology SummaryaelsehamyAinda não há avaliações
- Histology of BreastDocumento2 páginasHistology of BreastIbrahim SugiyonoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Skeletal 1Documento196 páginasIntroduction To Skeletal 1Earl TrinidadAinda não há avaliações
- Histo Slides Volume IIDocumento21 páginasHisto Slides Volume IIKristian CadaAinda não há avaliações
- Histology Practical Manual Part 1 2021Documento124 páginasHistology Practical Manual Part 1 2021khushikumari1407Ainda não há avaliações
- Development of TeethDocumento25 páginasDevelopment of TeethDrShweta Saini100% (1)
- Skull, Bones, AnatomyDocumento54 páginasSkull, Bones, AnatomyYasemen KAinda não há avaliações
- Popliteal Fossa and LegDocumento40 páginasPopliteal Fossa and LegRaj Shekhar SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Connective TissueDocumento14 páginasConnective TissueDr NehaAinda não há avaliações
- FIU - Eye AnatomyDocumento23 páginasFIU - Eye AnatomyKira23406Ainda não há avaliações
- Sistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)Documento38 páginasSistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaAinda não há avaliações
- Animal TissueDocumento47 páginasAnimal TissueJoshua Verzosa PalconitAinda não há avaliações
- Histology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTDocumento108 páginasHistology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTVernadel ApolloAinda não há avaliações
- Cheat Sheet Integumentary SystemDocumento4 páginasCheat Sheet Integumentary SystemLisa RetbergAinda não há avaliações
- I.T.S Dental College, Greater Noida: FacultyDocumento70 páginasI.T.S Dental College, Greater Noida: FacultyAMIT GUPTAAinda não há avaliações
- Scope Biochemistry 2015Documento31 páginasScope Biochemistry 2015prima octafiaAinda não há avaliações
- Osteogenesis & Osteolysis of Alveolar Bone in Health & Disease 18-11-09Documento65 páginasOsteogenesis & Osteolysis of Alveolar Bone in Health & Disease 18-11-09sandipladaniAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Dental Anatomy Central Insicor Lec 3Documento20 páginas3 Dental Anatomy Central Insicor Lec 3Somansh GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- 2.histologi DarahDocumento38 páginas2.histologi DarahIrfanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocumento11 páginasChapter 4 Tissues, Glands, and MembranesMaria Angela Del Gallego100% (2)
- Lecture 3 AnatomyDocumento14 páginasLecture 3 AnatomyZA IDAinda não há avaliações
- CT Anatomy of OrbitDocumento31 páginasCT Anatomy of OrbitMaajid Mohi Ud Din MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory SystemDocumento54 páginasRespiratory SystemHannah YsaBelle LeguroAinda não há avaliações
- A Respiratory System Histology 16-12-14Documento33 páginasA Respiratory System Histology 16-12-14Suhas KapseAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 Cartilage and BoneDocumento5 páginasChapter 6 Cartilage and BoneSuperjunior8Ainda não há avaliações
- Bone Physiology: By: Sandesh. A. PDocumento75 páginasBone Physiology: By: Sandesh. A. PAnalhaq ShaikhAinda não há avaliações
- Muscle: Duchenne Muscular DystrophyDocumento13 páginasMuscle: Duchenne Muscular DystrophyMicke RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Congenital Anomalies?: Anomalies That Occur During Intrauterine Life. Also Called Birth DefectsDocumento17 páginasWhat Is Congenital Anomalies?: Anomalies That Occur During Intrauterine Life. Also Called Birth DefectsSantosh OjhaAinda não há avaliações
- Unilateral Mandibular Swelling in A Young Female Patient A Case ReportDocumento4 páginasUnilateral Mandibular Swelling in A Young Female Patient A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- Decalcification ReviewerDocumento4 páginasDecalcification ReviewerKD Nudo0% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMaDocumento1 páginaPATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMakyawAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs in Orthodontics: G.Shekar Subramanian Ist Year PGDocumento69 páginasDrugs in Orthodontics: G.Shekar Subramanian Ist Year PGShekar SubramanianAinda não há avaliações
- Biology M10 Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocumento25 páginasBiology M10 Musculo-Skeletal SystemMark Nathaniel100% (2)
- Brown Tumors of The Oral Cavity: Presentation of 4 New Cases and A Systematic Literature ReviewDocumento14 páginasBrown Tumors of The Oral Cavity: Presentation of 4 New Cases and A Systematic Literature Reviewisma wahyuniAinda não há avaliações
- FracturesDocumento18 páginasFracturesNicole Anne ValerioAinda não há avaliações
- 1.introduction, The General Description of OsteologyDocumento47 páginas1.introduction, The General Description of OsteologyRioAinda não há avaliações
- LECTURE 3 - Body Cells and TissuesDocumento11 páginasLECTURE 3 - Body Cells and TissuesGGonzales KarlaAinda não há avaliações
- Boron CaMgMetabDocumento7 páginasBoron CaMgMetabChintan PatelAinda não há avaliações
- M3 L1 Part 2 Check-In Activity - Specialized Connective TissueDocumento2 páginasM3 L1 Part 2 Check-In Activity - Specialized Connective TissueSam QuilangAinda não há avaliações
- FT - 116 A1 - Clinicals-Week 12 - Gen Task 1Documento79 páginasFT - 116 A1 - Clinicals-Week 12 - Gen Task 1Megan BarreraAinda não há avaliações
- Biomechanical Properties of BoneDocumento28 páginasBiomechanical Properties of BoneUsama RafiqAinda não há avaliações
- Osteoporosis and OsteopeniaDocumento29 páginasOsteoporosis and OsteopeniaShruti Maroo - RathiAinda não há avaliações
- 100per Science cl9 Ed ch6Documento6 páginas100per Science cl9 Ed ch6Manthan JajuAinda não há avaliações
- PRP What Is PRP and What Is NotDocumento4 páginasPRP What Is PRP and What Is NotAyu Nur A'IniAinda não há avaliações
- Course Information 2013Documento12 páginasCourse Information 2013Osama AldahamshehAinda não há avaliações
- All About BonesDocumento2 páginasAll About Bonesantonia putriAinda não há avaliações
- NachamkinDocumento425 páginasNachamkinapi-532187335Ainda não há avaliações
- Medical Physics QuestionsDocumento110 páginasMedical Physics QuestionsmodadadAinda não há avaliações
- The Role Of Prostaglandin D2 Reseptor Dp And Pparγγγγγ In Bone Metastasis Of Breast CancerDocumento1 páginaThe Role Of Prostaglandin D2 Reseptor Dp And Pparγγγγγ In Bone Metastasis Of Breast Cancerlinda ayuAinda não há avaliações
- (1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) ENDOCRINOLOGY and ADOLESCENCE - Osteoporosis in Children - Diagnosis and ManagementDocumento13 páginas(1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) ENDOCRINOLOGY and ADOLESCENCE - Osteoporosis in Children - Diagnosis and Managementtamaz takidzeAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To HematologyDocumento10 páginasIntroduction To HematologyClaire Nicole100% (1)
- PDF - Concussion in Professional Football - Brain Responses by Finite Element Analysis - Part 9Documento27 páginasPDF - Concussion in Professional Football - Brain Responses by Finite Element Analysis - Part 9protectthebrainAinda não há avaliações
- Injectable Hydrogels For Cartilage and Bone TissueDocumento20 páginasInjectable Hydrogels For Cartilage and Bone Tissue9147. 5125'321199316Ainda não há avaliações
- AP1 Lab4 Intro To Skeleton FA2021Documento15 páginasAP1 Lab4 Intro To Skeleton FA2021Kim VenturaAinda não há avaliações
- 11-Metabolic &genetic Bone DiseasesDocumento12 páginas11-Metabolic &genetic Bone Diseasesفراس الموسويAinda não há avaliações
- 448 FullDocumento21 páginas448 FullSonnymon A. SobrevillaAinda não há avaliações