Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Pa Tho Physiology of Acute Pyelonephritis
Enviado por
Crystal Diane Cardona0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
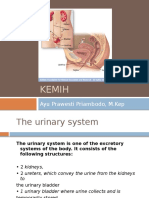
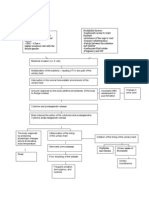
332 visualizações2 páginasThe document summarizes the pathophysiology of acute pyelonephritis. It involves the invasion of bacteria, usually E. coli, from the bladder into the kidneys up the ureters. This causes destruction of nephrons, injury to cells and inflammation in the kidneys. Symptoms include decreased urine output, increased ability to concentrate urine, pain, and increased blood flow and white blood cells at the infected site. Risk factors include instrumentation, urinary tract infections, renal stones, catheter insertion, poor hygiene, trauma from intercourse, and anatomical issues.
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThe document summarizes the pathophysiology of acute pyelonephritis. It involves the invasion of bacteria, usually E. coli, from the bladder into the kidneys up the ureters. This causes destruction of nephrons, injury to cells and inflammation in the kidneys. Symptoms include decreased urine output, increased ability to concentrate urine, pain, and increased blood flow and white blood cells at the infected site. Risk factors include instrumentation, urinary tract infections, renal stones, catheter insertion, poor hygiene, trauma from intercourse, and anatomical issues.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
332 visualizações2 páginasPa Tho Physiology of Acute Pyelonephritis
Enviado por
Crystal Diane CardonaThe document summarizes the pathophysiology of acute pyelonephritis. It involves the invasion of bacteria, usually E. coli, from the bladder into the kidneys up the ureters. This causes destruction of nephrons, injury to cells and inflammation in the kidneys. Symptoms include decreased urine output, increased ability to concentrate urine, pain, and increased blood flow and white blood cells at the infected site. Risk factors include instrumentation, urinary tract infections, renal stones, catheter insertion, poor hygiene, trauma from intercourse, and anatomical issues.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
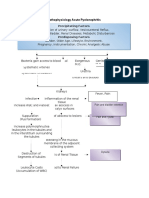
Invasion of CA to the surrounding tissues (renal papilla, medulla, cortex)
Destruction of nephrons
Injury to the cells and lining
Passage of large molecules
Decreased GFR
Inflammation Release of chemicals (Kinins, Prostaglandins, Histamins)
+2 CHON +1 Bilirubin +3 Urobilinogen +2 Leukotrase
Decreased urine output
Increased ability to concentrate urine (Specific gravity of 1.075)
Chemotaxis
Pain
Increased blood flow to the injured site
Increased WBC
Increased neutrophils
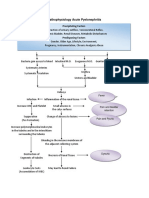
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS
Instrumentation Hygiene Current UTI Sexually Active
Gender
Presence of Renal Stones
Insertion of catheter & other birth contraception
Poor personal Hygiene
Urethral trauma upon intercourse
Female
Male
Shorter urethra
Prostatic Hypertrophy Calculi in the bladder Compression to the urethra
Calculi in the nephrons
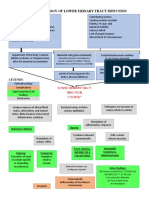
Entrance of the CA (E.coli) Bacterial Infection of the bladder
S/S: frequency; urgency, dysuria
Colonization
Obstruction
Obstruction in urine flow
Incompetence of vesiculoureter orifice
Bladder dysfunction Urinary Stasis
Increased pressure in the kidney
S/S: flank pain
Ascending of bacteria to the ureter and kidney
Increased residual volume
Colonization in the renal pelvis & parenchyma
Hydronephrosis
Bacterial Infection S/S: fever (38.7C), malaise, anorexia
Você também pode gostar
- 1 Infeksi Saluran Kemih New-1Documento61 páginas1 Infeksi Saluran Kemih New-1Dezttie IdEss NdessAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionSTORAGE FILEAinda não há avaliações
- Infeksi Saluran KemihDocumento35 páginasInfeksi Saluran KemihLestari Amelia AdmAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisAnonymous 75TDy2y100% (1)
- Patho UtiDocumento1 páginaPatho UtiCarl Mayrina de Jesus100% (1)
- 2106 UtiDocumento2 páginas2106 UtishimiAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephriti1Documento2 páginasPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephriti1Stephanie Joy EscalaAinda não há avaliações
- C09 Urinary Tract Infections 2009Documento47 páginasC09 Urinary Tract Infections 2009Andy XiaoAinda não há avaliações
- Uti Urinary Tract InfectionDocumento17 páginasUti Urinary Tract InfectionlulukhasniAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocumento71 páginasUrinary Tract Infectionsdayibon499Ainda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888Ainda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENADocumento2 páginasUrinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENASheena Arnoco ToraynoAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract Infections: Dr. Shweta Naik Assistant ProfessorDocumento62 páginasUrinary Tract Infections: Dr. Shweta Naik Assistant ProfessorMeenakshisundaram CAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocumento44 páginasUrinary Tract InfectiongunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Infections of The Urinary Genirouty TractDocumento4 páginasInfections of The Urinary Genirouty Tractfifa nasrul ummahAinda não há avaliações
- ESRD PathophyDocumento1 páginaESRD PathophyPamü BaltazarAinda não há avaliações
- Acute PyelonephritisDocumento12 páginasAcute PyelonephritisHaziq AnuarAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Colon CancerDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Colon CancerArt Christian Ramos67% (15)
- INFEKSI SALURAN KEMIH (ISK) PADA ANAK Blok 14Documento26 páginasINFEKSI SALURAN KEMIH (ISK) PADA ANAK Blok 14Siti Shaihany YustikawariAinda não há avaliações
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocumento4 páginasPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factorselfera09Ainda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract Infection: Akhyar Albaar Haerani RasyidDocumento49 páginasUrinary Tract Infection: Akhyar Albaar Haerani Rasyidrolly riksantoAinda não há avaliações
- KIDNEY AND URINARY TRACT PROBLEMS Edited (Autosaved)Documento29 páginasKIDNEY AND URINARY TRACT PROBLEMS Edited (Autosaved)Jane Ann AlolodAinda não há avaliações
- Bedah Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocumento27 páginasBedah Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaRs93Ainda não há avaliações
- 313 - Disorders of Renal and Urinary SystemsDocumento8 páginas313 - Disorders of Renal and Urinary SystemsChrissy Mendoza100% (2)
- Renal Concept MapDocumento8 páginasRenal Concept MapXtine CajiAinda não há avaliações
- Infectious and Inflammatory Disorders of The Urinary SystemDocumento16 páginasInfectious and Inflammatory Disorders of The Urinary SystemBibi Renu100% (1)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocumento24 páginasUrinary Tract InfectionraddagAinda não há avaliações
- UTI LectureDocumento62 páginasUTI LectureHaidar ShiddiqAinda não há avaliações
- General Anatomu UrologyDocumento60 páginasGeneral Anatomu UrologyAllan ManiAinda não há avaliações
- Obstruksi Uropati IrfanDocumento43 páginasObstruksi Uropati IrfanirfanAinda não há avaliações
- Seminar On: Urinary Tract Infections and NephritisDocumento34 páginasSeminar On: Urinary Tract Infections and NephritisGargi MPAinda não há avaliações
- Grand Case StudyDocumento13 páginasGrand Case StudyLaica A. LunetaAinda não há avaliações
- PathophyDocumento1 páginaPathophyMaria MargarethAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Concept MapDocumento8 páginasRenal Concept MapDavis KallanAinda não há avaliações
- Patho Intussusception RevisedDocumento8 páginasPatho Intussusception RevisedPj Gabano60% (5)
- Educational Module For Nursing Assistants in Long-Term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic BacteriuriaDocumento35 páginasEducational Module For Nursing Assistants in Long-Term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic BacteriuriaPH Ph GnsoAinda não há avaliações
- Ginjal PatofisiologiDocumento49 páginasGinjal PatofisiologiJonovSelfAinda não há avaliações
- Small Bowel Obstruction Vs IleusDocumento63 páginasSmall Bowel Obstruction Vs IleusKamalesh MurariAinda não há avaliações
- 8.urinary Tract Infections-1Documento82 páginas8.urinary Tract Infections-1fikirjohn8Ainda não há avaliações
- Renal Concept MapDocumento8 páginasRenal Concept MapRob DavilaAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary System (Complaints, Disorders, First Aid Measures)Documento61 páginasUrinary System (Complaints, Disorders, First Aid Measures)David Badaru100% (1)
- Urinary Elimination: Lesson 5eDocumento33 páginasUrinary Elimination: Lesson 5eMikhaela Andree MarianoAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Track Infections . .1Documento40 páginasUrinary Track Infections . .1ayesha sagheerAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)Documento25 páginasUrinary Tract Infections (UTI)microperadeniya0% (1)
- 17-Laboratory Evaluation of Urinary TR Act Infection v1 - 3Documento33 páginas17-Laboratory Evaluation of Urinary TR Act Infection v1 - 3Shaoran AuliaAinda não há avaliações
- Bartter Syndrom-WPS OfficeDocumento29 páginasBartter Syndrom-WPS OfficeMuhammad SaqlainAinda não há avaliações
- PielonefritisDocumento7 páginasPielonefritisAhmad FathanAinda não há avaliações
- Alterations of Renal Function-1Documento44 páginasAlterations of Renal Function-1Meqdad HyariAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Genitourinary Dise 2020 Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectioDocumento8 páginas6 Genitourinary Dise 2020 Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectioThaiz P.SAinda não há avaliações
- UTI Childhood Tadulako2015Documento38 páginasUTI Childhood Tadulako2015ani bandasoAinda não há avaliações
- Infeksi Saluran KemihDocumento44 páginasInfeksi Saluran KemihAyunda Henna PelalawanAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)Documento58 páginasUrinary Tract Infections (UTI)afdaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Pyelonephritis PathoDocumento1 páginaAcute Pyelonephritis PathoGlenn Asuncion PagaduanAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocumento9 páginasUrinary Tract InfectionsGeethika GummadiAinda não há avaliações
- Acute and Chronic PyelonephritisDocumento7 páginasAcute and Chronic PyelonephritisMatthew Ryan100% (1)
- Overview of Urinary Incontinence (UI) in The Long Term Care FacilityDocumento81 páginasOverview of Urinary Incontinence (UI) in The Long Term Care Facilityالغزال الذهبيAinda não há avaliações
- Cystitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition Treatment And Urinary DiseasesNo EverandCystitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition Treatment And Urinary DiseasesAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children - Classification, Diagnosis and TreatmentNo EverandUrinary Tract Infection in Children - Classification, Diagnosis and TreatmentAinda não há avaliações