Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Power Plant
Enviado por
Numair AshrafDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Power Plant
Enviado por
Numair AshrafDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
M.
NUMAIR ASHRAF
EXPERIMENT # 5
STEAM (THERMAL) POWER PLANT
BE-CHEM-15
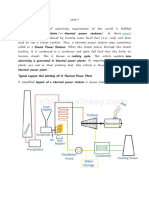
A Steam power station is a power plant in which the prime mover is steam driven. Water is heated, turns into steam and spins a steam turbine which drives an electrical generator. After it passes through the turbine, the steam is condensed in a condenserand recycled to where it was heated; this is known as a Rankine cycle. The greatest variation in the design of thermal power stations is due to the different fuel sources. Some prefer to use the term energy centerbecause such facilities convert forms of heat energyinto electricity. Some thermal power plants also deliver heat energy for industrial purposes, for district heating, or for desalination of water as well as delivering electrical power. A large part of human CO2emissions comes from fossil fueled thermal power plants; efforts to reduce these outputs are various and widespread.
Boiler And Steam Cycle:In fossil-fueled power plants, steam generator refers to a furnace that burns the fossil fuel to boil water to generate steam. In the nuclear plant field, steam generator refers to a specific type of large heat exchanger used in apressurized water reactor (PWR) to thermally connect the primary (reactor plant) and secondary (steam plant) systems, which generates steam. In a nuclear reactor called a boiling water reactor(BWR), water is boiled to generate steam directly in the reactor itself and there are no units called steam generators.
Feed Water Heating And Deaeration:The feed water used in the steam boiler is a means of transferring heat energy from the burning fuel to the mechanical energy of the spinning steam turbine. The total feed water consists of recirculatedcondensate water and purified makeup water. Because the metallic materials it contacts are subject to corrosion at high temperatures and pressures, the makeup water is highly purified before use. A system of water softeners and ion exchange demineralizers produces water so pure that it coincidentally becomes an electrical insulator, with conductivity in the range of 0.31.0 microsiemensper centimeter. The makeup water in a 500 MWe plant amounts to perhaps 20 US gallons per minute (1.25 L/s) to offset the small losses from steam leaks in the system.
Boiler Operation:The boiler is a rectangular furnace about 50 feet (15 m) on a side and 130 feet (40 m) tall. Its walls are made of a web of high pressure steel tubes about 2.3 inches (58 mm) in diameter. Pulverized coal is air-blown into the furnace from fuel nozzles at the four corners and it rapidly burns, forming a large fireball at the center. The thermal radiation of the fireball heats the water that circulates through the boiler tubes near the boiler perimeter. The water circulation rate in the boiler is three to four times the throughput and is typically driven by pumps. As the water in the boiler circulates it absorbs heat and changes into steam at 700 F (371 C) and 3,200 psi (Template:Convert/MP). It is separated from the water inside a drum at the top of the furnace. The saturated steam is introduced intosuperheat pendant
M.NUMAIR ASHRAF
EXPERIMENT # 5
BE-CHEM-15
tubes that hang in the hottest part of the combustion gases as they exit the furnace. Here the steam is superheated to 1,000 F (500 C) to prepare it for the turbine.
Boiler Furnace And Steam Drum:Once water inside the boiler or steam generator, the process of adding the latent heat of vaporizationor enthalpy is underway. The boiler transfers energy to the water by the chemical reaction of burning some type of fuel.
Superheater:Fossil fuel power plants can have a superheater and/or re-heater section in the steam generating furnace. In a fossil fuel plant, after the steam is conditioned by the drying equipment inside the steam drum, it is piped from the upper drum area into tubes inside an area of the furnace known as the superheater, which has an elaborate set up of tubing where the steam vapor picks up more energy from hot flue gases outside the tubing and its temperature is now superheated above the saturation temperature. The superheated steam is then piped through the main steam lines to the valves before the high pressure turbine.
Steam Condensing:The condenser condenses the steam from the exhaust of the turbine into liquid to allow it to be pumped. If the condenser can be made cooler, the pressure of the exhaust steam is reduced and efficiency of the cycle increases.
Reheater:Power plant furnaces may have a reheater section containing tubes heated by hot flue gases outside the tubes. Exhaust steam from the high pressure turbine is passed through these heated tubes to collect more energy before driving the intermediate and then low pressure turbines.
Steam turbine generator
The turbine generator consists of a series of steamturbines interconnected to each other and a generator on a common shaft. There is a high pressure turbine at one end, followed by an intermediate pressure turbine, two low pressure turbines, and the generator. As steam moves through the system and loses pressure and thermal energy it expands in volume, requiring increasing diameter and longer blades at each succeeding stage to extract the remaining energy
M.NUMAIR ASHRAF
EXPERIMENT # 5
BE-CHEM-15
Advantages Of Thermal Power Plant:y y Low initial cost. Since located near the load centre, the cost of transmission and the losses due to transmission are considerably reduced. The construction and commissioning of thermal power plant takes lesser period.
Disadvantages Of Thermal Power Plant:y y y y y Fuel is a non-renewable source of energy. Efficiency decreases with decreasing load. Cost of power generation is high. Smoke produced by burning the fuel causes air pollution. Life of thermal power plant is 25 years. The efficiency decreases to less than 10% after its life period. Turbines have a high running speed of 3000 to 4000 rpm.
M.NUMAIR ASHRAF
EXPERIMENT # 5
BE-CHEM-15
Você também pode gostar
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento35 páginasThermal Power PlantAngelaa DassAinda não há avaliações
- Essentials of Steam Power Plant EquipmentDocumento102 páginasEssentials of Steam Power Plant EquipmentPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- 2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTDocumento101 páginas2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTKishore KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento9 páginasThermal Power Plantmuneeb rafiqAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento11 páginasThermal Power PlantAnand Kalani100% (1)
- Thermal Power PlantsDocumento24 páginasThermal Power Plantslakshmigsr6610100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About ItDocumento7 páginasThermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About Itngoc hoangAinda não há avaliações
- Jagan Steam Power PlantDocumento101 páginasJagan Steam Power PlantMahender VangalaAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Equipment of Steam Power PlantsDocumento101 páginasEssential Equipment of Steam Power Plantsjamunaa83100% (1)
- DVC Mejia ReportDocumento37 páginasDVC Mejia ReportRahul RoyAinda não há avaliações
- Power Plant FamiliarisationDocumento110 páginasPower Plant FamiliarisationmrdipakwaghAinda não há avaliações
- Steam Power Plant Components & ProcessesDocumento37 páginasSteam Power Plant Components & ProcessessureshlalAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On KSTPSDocumento28 páginasPresentation On KSTPSatul mishra100% (1)
- Construction and Working of Thermal Power PlantDocumento5 páginasConstruction and Working of Thermal Power PlantdibyenindusAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Engineering Project - Thermal Power Plant Study - WWW - Amie.nbcafe - inDocumento24 páginasMechanical Engineering Project - Thermal Power Plant Study - WWW - Amie.nbcafe - inbtdoss72100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringDocumento34 páginasThermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringMos MohAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Power Plant - EeDocumento20 páginasThermal Power Plant - EePrabhat Chandra100% (1)
- Layout of Thermal Power PlantDocumento21 páginasLayout of Thermal Power PlantRaj_Jai03100% (1)
- Abhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliDocumento21 páginasAbhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliSuphi YükselAinda não há avaliações
- Cfakepathlayoutofthermalpowerplant 091031114144 Phpapp01Documento21 páginasCfakepathlayoutofthermalpowerplant 091031114144 Phpapp01Shruti GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Power Plant Rankine CycleDocumento27 páginasThermal Power Plant Rankine Cyclevenki249100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant: Gaini Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus (Bathinda)Documento30 páginasThermal Power Plant: Gaini Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus (Bathinda)Sriram ramsAinda não há avaliações
- Power Plant Engineering BasicsDocumento21 páginasPower Plant Engineering BasicsSiman NapstervkkAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - I Steam Power PlantsDocumento32 páginasUnit - I Steam Power Plantsrsankarganesh MECH-HICET100% (1)
- Power Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineDocumento7 páginasPower Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineMonglafru MogAinda não há avaliações
- Ennore Thermal Power StationDocumento14 páginasEnnore Thermal Power StationRajesh Kumar100% (2)
- Title of Project-: Preliminary Study On Thermal Power Plant and Detail Study On Coal Handling PlantDocumento98 páginasTitle of Project-: Preliminary Study On Thermal Power Plant and Detail Study On Coal Handling PlantAbir MukherjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Me Lab 3Documento27 páginasMe Lab 3Jerome Vega AndesAinda não há avaliações
- Generation of Electric PowerDocumento108 páginasGeneration of Electric Powermausam sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Site Selection For Thermal Power PlantDocumento3 páginasSite Selection For Thermal Power PlantNehaKashyapAinda não há avaliações
- Brief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical LocationDocumento22 páginasBrief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical Locationcoolvipin1988Ainda não há avaliações
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento36 páginasThermal Power PlantAshvani Shukla100% (1)
- Ukai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3Documento13 páginasUkai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3eman.refai13lcsAinda não há avaliações
- Power Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineDocumento7 páginasPower Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineMonglafru MogAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Power StationDocumento6 páginasThermal Power StationAnkit RajAinda não há avaliações
- 8 Steam Power PlantsDocumento57 páginas8 Steam Power PlantsSaif Younus100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant Project ReportDocumento63 páginasThermal Power Plant Project Reportasutoshjena28174% (23)
- Gajendra KumarDocumento23 páginasGajendra KumarGAJENDRA KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento29 páginasThermal Power PlantSiri VenniAinda não há avaliações
- Ppe NotesDocumento51 páginasPpe NotesCharan PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- تقرير محطات الطاقهDocumento45 páginasتقرير محطات الطاقهعبد الرحمن إبراهيمAinda não há avaliações
- EXP-1 Steam Power PlantDocumento7 páginasEXP-1 Steam Power PlantsejalAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Training AT: Submitted By: Rishikesh (11-1-6-002) NIT, SilcharDocumento26 páginasIndustrial Training AT: Submitted By: Rishikesh (11-1-6-002) NIT, SilcharRakesh Roshan KeshriAinda não há avaliações
- Jaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyDocumento29 páginasJaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyAnonymous ytZsBOVAinda não há avaliações
- Jaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyDocumento29 páginasJaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyAashish SangwanAinda não há avaliações
- Lab ReportDocumento12 páginasLab ReportFaisal ArslanAinda não há avaliações
- Hydroelectric Power Plants Convert Power PlantDocumento4 páginasHydroelectric Power Plants Convert Power Plantuikeshekhar610Ainda não há avaliações
- Thermal Power Plant: Feed Water Heating and DeaerationDocumento4 páginasThermal Power Plant: Feed Water Heating and DeaerationVenkatachalam AnnamalaiAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Power Plant ExplainedDocumento10 páginasThermal Power Plant Explainedmusu MukeshAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas Util (Boiler)Documento4 páginasTugas Util (Boiler)AkhmadSumarnoAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 1Documento7 páginasExp 1HR HabibAinda não há avaliações
- Power Plant Engineering MTPP-1Documento13 páginasPower Plant Engineering MTPP-1devendra pratapAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal EngineeringDocumento10 páginasThermal Engineeringlokeshdhangar842Ainda não há avaliações
- Thermal Power Plants: Key Components and Working PrincipleDocumento157 páginasThermal Power Plants: Key Components and Working Principlegteklay100% (1)
- Common Engineering GlossaryDocumento2 páginasCommon Engineering Glossarykicchu001Ainda não há avaliações
- Report #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantDocumento41 páginasReport #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantKian TecsonAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 4.Documento5 páginasPhysics 4.SOLAIMANAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningNo EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Pakistan Engineering Council: Sample Mcqs Chemical Engineering (Process Synthesis, Design and Optimization)Documento18 páginasPakistan Engineering Council: Sample Mcqs Chemical Engineering (Process Synthesis, Design and Optimization)Numair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- SOP Attestation Verification NUSTDocumento1 páginaSOP Attestation Verification NUSTNumair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Maintenance Process Overview: Steps, Benefits & Best PracticesDocumento48 páginasPlant Maintenance Process Overview: Steps, Benefits & Best PracticesYeldoReyesCórdova100% (1)
- Accountancy Finance Keywords PDFDocumento2 páginasAccountancy Finance Keywords PDFNumair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- ERPDocumento7 páginasERPHasan BukhariAinda não há avaliações
- List of SAP T-CodesDocumento18 páginasList of SAP T-CodesastinetAinda não há avaliações
- Fiverr Holidays Marketing GuideDocumento16 páginasFiverr Holidays Marketing Guideprince stephenAinda não há avaliações
- Daleel E PDFDocumento44 páginasDaleel E PDFNumair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Contacts:: Siemens Learning Center Digital Factory DivisionDocumento34 páginasContacts:: Siemens Learning Center Digital Factory DivisionBadarMoonAinda não há avaliações
- SAP PM T - CodesDocumento4 páginasSAP PM T - CodesBujjibabu Katta0% (1)
- Wi-Tribe Modem Configure in 5 MinutesDocumento23 páginasWi-Tribe Modem Configure in 5 MinutesSyed Azeem AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 YrDocumento71 páginas2013 YrNumair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Resumes and Cover Letters Technical MajorsDocumento53 páginasSample Resumes and Cover Letters Technical MajorsDeepak SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Nebosh International General CertificateDocumento4 páginasNebosh International General Certificatescribblers18Ainda não há avaliações
- Traveler GuidDocumento15 páginasTraveler GuidNumair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- List of Documents To Be Attached With The Application Form For Registration As Professional Engineer (Pe)Documento6 páginasList of Documents To Be Attached With The Application Form For Registration As Professional Engineer (Pe)Yasir Ali KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental, Health & Safety TrainingDocumento54 páginasEnvironmental, Health & Safety Trainingvijay2bhagyaAinda não há avaliações
- GRP Engineers/consultantsDocumento2 páginasGRP Engineers/consultantsNumair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Cost Estimate Comparison Spreadsheet 7-15-10Documento3 páginasCost Estimate Comparison Spreadsheet 7-15-10Numair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- NUST at A Glance (2014)Documento48 páginasNUST at A Glance (2014)Numair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Recommendation 1Documento1 páginaRecommendation 1Numair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Steve Jobs ArticleDocumento14 páginasSteve Jobs ArticleAshvin M GuttiAinda não há avaliações
- Film Evaporation TechnologyDocumento12 páginasFilm Evaporation TechnologyAditya Bayu SalaksaAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio ControlDocumento1 páginaRatio ControlNumair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- My WorkDocumento1 páginaMy WorkNumair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Power PlantDocumento4 páginasPower PlantNumair AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- ATUM (Rhamnosa E.coli)Documento4 páginasATUM (Rhamnosa E.coli)Ruth MichelleeAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1.5 - Stress and Strain in Lifting EquipmentDocumento14 páginasUnit 1.5 - Stress and Strain in Lifting EquipmentnitharsunAinda não há avaliações
- Niosh SHO Exam Notes - Module 3 Question and Answer PDFDocumento19 páginasNiosh SHO Exam Notes - Module 3 Question and Answer PDFExcellentdeals4all94% (51)
- Process Analysis of Refinery Crude Charge HeaterDocumento21 páginasProcess Analysis of Refinery Crude Charge HeaterNicholas RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- Carbobond 3028 1Documento1 páginaCarbobond 3028 1Yan TengAinda não há avaliações
- Greener One-Pot Synthesis of Chromeno Oxazin and Oxazin Quinoline Derivatives and Their Antibacterial ActivityDocumento5 páginasGreener One-Pot Synthesis of Chromeno Oxazin and Oxazin Quinoline Derivatives and Their Antibacterial ActivityIJAERS JOURNALAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy & Physiology Made Incredibly Visual!Documento412 páginasAnatomy & Physiology Made Incredibly Visual!Cereal KillerAinda não há avaliações
- By Niranjan S. L.N College of Engineering, Raichur.Documento29 páginasBy Niranjan S. L.N College of Engineering, Raichur.alistuguiAinda não há avaliações
- Task No. 1 (Written Work) Direction: Problem Solving. Show Your Solution and Follow Proper Significant FiguresDocumento2 páginasTask No. 1 (Written Work) Direction: Problem Solving. Show Your Solution and Follow Proper Significant FiguresMonica TanglaoAinda não há avaliações
- RMS 6th 2019Documento14 páginasRMS 6th 2019angelgupta2303Ainda não há avaliações
- CH 7 ObjDocumento4 páginasCH 7 ObjchongpeisiAinda não há avaliações
- Reinforcing Low-Grade Glulam Beams with GFRP RodsDocumento12 páginasReinforcing Low-Grade Glulam Beams with GFRP RodsCălin MartonAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 10: Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA)Documento13 páginasLecture 10: Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA)Binoni Laja EndongAinda não há avaliações
- Kate Coleen D. Galera BS in Chemistry II May 4, 2017 Experiment 11 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and DetergentsDocumento5 páginasKate Coleen D. Galera BS in Chemistry II May 4, 2017 Experiment 11 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and DetergentsKateAinda não há avaliações
- Nuclear ReactorDocumento13 páginasNuclear ReactorMouth with No teethAinda não há avaliações
- Api Melafix Safety Data Sheet PDFDocumento10 páginasApi Melafix Safety Data Sheet PDFumaAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of geotextiles on low plastic sandy clayDocumento9 páginasEffect of geotextiles on low plastic sandy clayRajesh Prasad ShuklaAinda não há avaliações
- Expressing Concentration of Solutions in Different UnitsDocumento4 páginasExpressing Concentration of Solutions in Different UnitsKunal Kishor100% (5)
- Glucose Solution ViscosityDocumento13 páginasGlucose Solution ViscosityThomas Teh Qian Hua100% (1)
- Important Aspect of Viscosity in Gravure Printing ProcessDocumento18 páginasImportant Aspect of Viscosity in Gravure Printing ProcessMakarand Dole100% (1)
- Die-Materials classEDITDocumento45 páginasDie-Materials classEDITSatya AsatyaAinda não há avaliações
- Applying Cold Plasma in Food IndustryDocumento18 páginasApplying Cold Plasma in Food Industryprachi mahajanAinda não há avaliações
- Determine Xenon's Ionization PotentialDocumento3 páginasDetermine Xenon's Ionization PotentialAbhi Rami50% (2)
- Pyrocrete 241Documento2 páginasPyrocrete 241Carboline2013Ainda não há avaliações
- CR8047 Sulzer CompaX Short Report1Documento20 páginasCR8047 Sulzer CompaX Short Report1DucVikingAinda não há avaliações
- Essay 2Documento3 páginasEssay 2Norhaida NdAinda não há avaliações
- Pre-Cal - Exponential Equations and Functions, and Logarithms WorksheetDocumento5 páginasPre-Cal - Exponential Equations and Functions, and Logarithms WorksheetFons Roxas-ChuaAinda não há avaliações
- In-Line Pulsation Dampeners For Bredel 25-100, APEX 28 and APEX 35 PumpsDocumento2 páginasIn-Line Pulsation Dampeners For Bredel 25-100, APEX 28 and APEX 35 PumpsVruno Velasquez LAinda não há avaliações
- PhosphatingDocumento9 páginasPhosphatingnirai101259Ainda não há avaliações
- OzonolysisDocumento1 páginaOzonolysisThu NguyenAinda não há avaliações