Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
3 CaCO3
Enviado por
Yesid CepedaDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
3 CaCO3
Enviado por
Yesid CepedaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
3CaCO3 + 2C6H8O7 = Ca3(C6H5O7)2 + 3CO2 + 3H2O MgCO3 + C6H8O7 = C6H6O7Mg + CO2 + H2O 3 NaHCO3 + C6H8O7 = Na3C6H5O7 + 3 H2O + 3 CO2
Identification Name Zinc citrate
Molecular Structure
Molecular Formula Molecular Weight CAS Registry Number EINECS
Zn3(C6H5O7)2 574.37 546-46-3 208-901-2
ZINC CITRATE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION CAS NO. 546-46-3 (Anhydrous) 5990-32-9 (Dihydrate) EINECS NO. 208-901-2 FORMULA [OOCCH2C(OH)(COO)CH2COO]2Zn3 MOL WT. 574.37 H.S. CODE 2918.16 TOXICITY Oral rat LD50: > 5,000 mg/kg SYNONYMS 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, zinc salt; DERIVATION CLASSIFICATION PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES PHYSICAL STATE White to yellow powder MELTING POINT 334 C BOILING POINT SPECIFIC GRAVITY SOLUBILITY IN WATER100 g/l pH VAPOR DENSITY AUTOIGNITION NFPA RATINGS REFRACTIVE INDEX FLASH POINT STABILITY Stable under ordinary conditions APPLICATIONS Zinc is an essential mineral having a role in the maintenance of the body's nervous and immune systems (T-cell function). This mineral is involved in the biochemical reactions as an antioxidant in the healing process and develops normal tissues Zinc is a cofactor in enzymatic reactions such as protein synthesis polymerases and in carbonic acid anhydrase. Zinc maintains the body's alkaline balance. Zinc finger, a structural domain found in many gene-regulatory proteins, is a component of hydrophobic hormones acting stabilizing the biomembrane structures and cell membrane metabolism. Zinc deficiencies may result in prolonged wound healing, delayed sexual maturation, mental lethargy, skin changes, and susceptibility to infections. Gluconate and citrate forms are mainly used as zinc supplements. They are easily absorbed by the body. Zinc citrate can be formulated in pharmaceuticals, and foods as a zinc supplement. Zinc citrate is used as an ingredient to treat common cold and various hygienic products. Zinc inhibits the growth of
bacteria in the throat and can be used in toothpaste. SALES SPECIFICATION APPEARANCE White to yellow powder CONTENT 96.0% min IDENTIFICATION Positive (Test A, B) ZINC CONTENT 31.0% (Dihydrate) - 34.0% (Anhydrate)( SULFATE 0.05% max LOSS ON DRYING 3.0% max CADMIUM 5ppm max CHLORIDE 0.05% max LEAD 10ppm max ARSENIC 3ppm max TRANSPORTATION PACKING 25kgs in fiber drum HAZARD CLASS not regulated UN NO. GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CITRIC ACID Citric Acid (2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid, in IUPAC naming) is a colourless crystalline organic compound belong to carboxylic acid family. It exists in all plants (especially in lemons and limes) and in many animal tissues and fluids. In biochemistry, it is involved in important metabolism of almost all living things; the Krebs cycle (also called citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle), a part of the process by which animals convert food to energy. Citric acid works as a preservative ( or as an antioxidant) and cleaning agent in nature. It is commercially obtained by fermentation process of glucose with the aid of the mold Aspergillus niger and can be obtained synthetically from acetone or glycerol. It can be used as an sour taste enhancer in foods and soft drinks. The three carboxy groups lose protons in solution; resulting in the excellent pH control as a buffer in acidic solutions. It is used as a flavouring, stabilizing agent and acidulant (to control acidity) in food industry, in metal-cleaning compositions as it chelates metals. Citric acid is available in forms of anhydrous primarily and in monohydrate, the crystallized form from water. The hydrated form will be converted to the anhydrous form above 74 C. Citrate is a salt or ester of citric acid. Citrates are formed by replacing the acidic one, two, or all three of the carboxylic hydrogens in citric acid by metals or organic radicals to produce an extensive series of salts, esters, and mixed (double) salts. Cirrates are used in food, cosmetics, pharmaceutical and medicine industries as well as in plastic industry; nutrient or food additives having functions of acidity regulator, sequestering and stabilizing agent, antioxidants synergist, firming agent; anticoagulant for stored whole blood and red cells and also for blood specimens as citrates chelate metal ions and saline cathartics, effervescent medicines; high boiling solvent, plasticizer and resin for food contact plastics.
Você também pode gostar
- Processing Contaminants in Edible Oils: MCPD and Glycidyl EstersNo EverandProcessing Contaminants in Edible Oils: MCPD and Glycidyl EstersNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (2)
- Citric AcidDocumento3 páginasCitric AcidFoxies 2020Ainda não há avaliações
- Sorbic AcidDocumento6 páginasSorbic AcidIoana IlutiaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-5, POC-1, SEM-2Documento53 páginasUnit-5, POC-1, SEM-2Avinash rajAinda não há avaliações
- Production of Citric Acid as Antioxidant, Preservative & AcidulantDocumento4 páginasProduction of Citric Acid as Antioxidant, Preservative & AcidulantSubrata ParaiAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamin C in Food ProcessingDocumento4 páginasVitamin C in Food ProcessingKishor Parihar100% (1)
- Vitamin C in Food ProcessingDocumento5 páginasVitamin C in Food ProcessingKishor PariharAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Tissue Culture Basal Salts and Media FormulationsDocumento18 páginasPlant Tissue Culture Basal Salts and Media Formulationspetri_jvAinda não há avaliações
- Citric 032012 FRDocumento37 páginasCitric 032012 FRAlbin JolyAinda não há avaliações
- Jublient Training ReportDocumento33 páginasJublient Training ReportsumitAinda não há avaliações
- Citric AcidDocumento5 páginasCitric AcidSarah JeanAinda não há avaliações
- BIOCHEM - LipidDocumento323 páginasBIOCHEM - LipidPrincess Jeyan PagatpatanAinda não há avaliações
- Lactic Acid Production ReviewDocumento20 páginasLactic Acid Production ReviewPaola MurgaAinda não há avaliações
- 5.Applied-Acid Tolerant - KenjiTanakaDocumento8 páginas5.Applied-Acid Tolerant - KenjiTanakaImpact JournalsAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Project ANTACIDDocumento17 páginasChemistry Project ANTACIDMAX MusicAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry F5 (Chp.5)Documento12 páginasChemistry F5 (Chp.5)Nurul DiyanaAinda não há avaliações
- Sodium bicarbonate: versatile chemical raising agent and disinfectantDocumento63 páginasSodium bicarbonate: versatile chemical raising agent and disinfectantSridhar RaparthiAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Compound: Wikipedia Formula Melting Point Molar Mass Iupac Id Density Soluble in WaterDocumento1 páginaChemical Compound: Wikipedia Formula Melting Point Molar Mass Iupac Id Density Soluble in WaterSantanuAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Compound: Wikipedia Formula Melting Point Molar Mass Iupac Id Density Soluble in WaterDocumento1 páginaChemical Compound: Wikipedia Formula Melting Point Molar Mass Iupac Id Density Soluble in WaterSantanuAinda não há avaliações
- Additive INS NumberDocumento11 páginasAdditive INS NumberKin KwanAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of Vitamin C Lab ReportDocumento3 páginasDetermination of Vitamin C Lab ReportMuhammadHasanAnsariAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2Documento15 páginasUnit 2Parmod KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Natural Antioxidants For Food UseDocumento73 páginasNatural Antioxidants For Food UseEgaSulsitiyoNingrumAinda não há avaliações
- Instant powder drink ZukoDocumento3 páginasInstant powder drink ZukoKaren RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- CitratoDocumento2 páginasCitratoJob Garcia RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Certificate of AnalysisDocumento4 páginasCertificate of Analysisbetahita_80174Ainda não há avaliações
- Analyses FOOD AdetivetDocumento162 páginasAnalyses FOOD AdetivetMatrixi GashiAinda não há avaliações
- Glycerol: Glycerine (Song)Documento17 páginasGlycerol: Glycerine (Song)Chaeyoung SonAinda não há avaliações
- Protein, Dan LemakDocumento70 páginasProtein, Dan LemakAlief MoulanaAinda não há avaliações
- Process For Preparation of Vitamin C and Method For Determination of Vitamin CDocumento84 páginasProcess For Preparation of Vitamin C and Method For Determination of Vitamin CSozdar ArgoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Food AdditivesDocumento5 páginasFood AdditiveszezethuAinda não há avaliações
- Sweeteners Teaching 2013Documento9 páginasSweeteners Teaching 2013Karen_suzzyAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Project To To Determine Which Antacid Neutralizes Stomach Acid Most To Determine Which Antacid Could Neutralize The Most Stomach AcidDocumento8 páginasChemistry Project To To Determine Which Antacid Neutralizes Stomach Acid Most To Determine Which Antacid Could Neutralize The Most Stomach AcidAnkur GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- European Council ReportDocumento41 páginasEuropean Council ReportSushitha NairAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry Lab Report 5Documento4 páginasBiochemistry Lab Report 5Lih XuanAinda não há avaliações
- Potassium Nitrite E250 Sodium Nitrite SourcesDocumento3 páginasPotassium Nitrite E250 Sodium Nitrite SourcesbhaleshAinda não há avaliações
- Microbial Production of Citric AcidDocumento15 páginasMicrobial Production of Citric AcidNizar MousaAinda não há avaliações
- Fermentation Technology For ProductionDocumento218 páginasFermentation Technology For Productionsb.21p20133Ainda não há avaliações
- Isothiazolinone ChlorideDocumento2 páginasIsothiazolinone ChlorideAndiAinda não há avaliações
- Food Additives: Antioxidants and SweetnersDocumento53 páginasFood Additives: Antioxidants and SweetnersR FAinda não há avaliações
- Lactic Acid TR 2015Documento27 páginasLactic Acid TR 2015Huỳnh Thị Thu HiềnAinda não há avaliações
- Tripalmitin Names: Formula Molecular WeightDocumento4 páginasTripalmitin Names: Formula Molecular WeightShereen AlobinayAinda não há avaliações
- Components of Food: Chemistry Project 2005-2006Documento69 páginasComponents of Food: Chemistry Project 2005-2006Ann Deocampo DuayAinda não há avaliações
- JBL FO Product Range 2015Documento16 páginasJBL FO Product Range 2015Victor CastrejonAinda não há avaliações
- Laundry Wastewater CharacterizationDocumento3 páginasLaundry Wastewater CharacterizationNicole Anne BorromeoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapt. V Gastrointestinal Agents: Inorganic Agents Used To Treat Gastro-Intestinal Tract DisordersDocumento9 páginasChapt. V Gastrointestinal Agents: Inorganic Agents Used To Treat Gastro-Intestinal Tract DisordersJoy VergaraAinda não há avaliações
- Trichloroacetic Acid: 1.1 Chemical and Physical DataDocumento38 páginasTrichloroacetic Acid: 1.1 Chemical and Physical Datalencute_2809Ainda não há avaliações
- Cyclamates: 1.1 Chemical and Physical Data Cyclamic AcidDocumento28 páginasCyclamates: 1.1 Chemical and Physical Data Cyclamic AcidHerdianAinda não há avaliações
- Inorganic Compounds With Economic, Industrial, Environmental and Social ImpactDocumento4 páginasInorganic Compounds With Economic, Industrial, Environmental and Social ImpactScribdTranslationsAinda não há avaliações
- Odev 1. Acids & BasesDocumento37 páginasOdev 1. Acids & BasesIlayda AltayAinda não há avaliações
- Produce Succinic Acid PlantDocumento102 páginasProduce Succinic Acid PlantHafiidz MalekAinda não há avaliações
- Standards For Pesticide Residue Analysis of WakoDocumento1 páginaStandards For Pesticide Residue Analysis of WakotoanvmpetrologxAinda não há avaliações
- L (+) Lactic Acid Fermentation and Its Product PolymerizationDocumento10 páginasL (+) Lactic Acid Fermentation and Its Product PolymerizationRyan MichaelAinda não há avaliações
- ABC CompoundDocumento164 páginasABC CompoundcabangonjasselAinda não há avaliações
- Bab Ii Tinjauan Pustaka 2.1. PanganDocumento4 páginasBab Ii Tinjauan Pustaka 2.1. PanganekoAinda não há avaliações
- Biomarkers for Antioxidant Defense and Oxidative Damage: Principles and Practical ApplicationsNo EverandBiomarkers for Antioxidant Defense and Oxidative Damage: Principles and Practical ApplicationsGiancarlo AldiniAinda não há avaliações
- Guide to Trivial Names, Trade Names and Synonyms for Substances Used in Analytical Nomenclature: International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Analytical Chemistry DivisionNo EverandGuide to Trivial Names, Trade Names and Synonyms for Substances Used in Analytical Nomenclature: International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Analytical Chemistry DivisionAinda não há avaliações
- Profile of IrbesartanDocumento11 páginasProfile of IrbesartanYesid Cepeda100% (1)
- Irbesartan JaperDocumento8 páginasIrbesartan JaperCecília RodriguesAinda não há avaliações
- WC 500036108Documento15 páginasWC 500036108wikka94Ainda não há avaliações
- Application of Thermal Analysis To Study The CompatibilityDocumento12 páginasApplication of Thermal Analysis To Study The CompatibilityYesid CepedaAinda não há avaliações
- Vademecum For Vitamin FormulationsDocumento144 páginasVademecum For Vitamin FormulationsSergio M Junior0% (1)
- Belt Road Capital Management: Method Statement For Installation Pipe Sleeve BRCM-CFU-ET&S-GENERAL-MS-1003Documento8 páginasBelt Road Capital Management: Method Statement For Installation Pipe Sleeve BRCM-CFU-ET&S-GENERAL-MS-1003Dong Vanra100% (1)
- Alkali-Activated Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers With Zeolite or BentoniteDocumento7 páginasAlkali-Activated Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers With Zeolite or BentoniteSo Thu DaiAinda não há avaliações
- 2017 H1 Chemistry Prelim SA2 Raffles InstitutionDocumento32 páginas2017 H1 Chemistry Prelim SA2 Raffles InstitutionSasha AnandAinda não há avaliações
- Mech Vi Non Traditional Machining (10me665) NotesDocumento45 páginasMech Vi Non Traditional Machining (10me665) Notesnikhil0% (1)
- Vigneshwara Raja CV Feb 2022Documento4 páginasVigneshwara Raja CV Feb 2022kamarajme2006Ainda não há avaliações
- (Vol VI), 2019 Rules For Welding, 2019 PDFDocumento348 páginas(Vol VI), 2019 Rules For Welding, 2019 PDFMuhammad BaqiAinda não há avaliações
- Drainage Pump 50HzDocumento20 páginasDrainage Pump 50HzashishkkrAinda não há avaliações
- Problemario1-Diseã o Mecanico1Documento4 páginasProblemario1-Diseã o Mecanico1Gerardo BocanegraAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Process Calculations - Anna UnivDocumento10 páginasChemical Process Calculations - Anna UnivGoutham R100% (1)
- Checklist NOM-251-SSA1-2009Documento14 páginasChecklist NOM-251-SSA1-2009ScribdTranslationsAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental I AssDocumento15 páginasEnvironmental I AssAbel TayeAinda não há avaliações
- Staircase AssignmentDocumento10 páginasStaircase AssignmentNabila Faiqah Zayn100% (1)
- Mortar Mixes and Earthwork ItemsDocumento841 páginasMortar Mixes and Earthwork ItemsShashank SAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 1 Food TestDocumento5 páginasLab 1 Food TestMichael Timson83% (6)
- Petrochemistry and Manganese MineralizatDocumento25 páginasPetrochemistry and Manganese Mineralizatนายช่างคมสัน นักธรณีวิทยาAinda não há avaliações
- Loctite 577™: Technical Data SheetDocumento5 páginasLoctite 577™: Technical Data SheetAditya DarmawanAinda não há avaliações
- 2023宣传册最终版 修改3Documento16 páginas2023宣传册最终版 修改3CAMILA ESTAY TORRESAinda não há avaliações
- Isocure: Concrete Curing AgentDocumento1 páginaIsocure: Concrete Curing AgentshafiullahAinda não há avaliações
- Curriculum Vitae: I Personal DataDocumento10 páginasCurriculum Vitae: I Personal DataRachmat SirojudinAinda não há avaliações
- Options and Accessories: Complete Wear Part ListDocumento1 páginaOptions and Accessories: Complete Wear Part ListIvánAinda não há avaliações
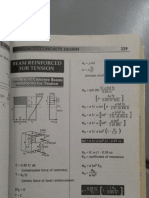
- RCD Beam Analysis and DesignDocumento33 páginasRCD Beam Analysis and DesignJayChristian Quimson50% (12)
- Wrb-Air Barrier - Parex Usa Weatherseal Spray and Roll OnDocumento3 páginasWrb-Air Barrier - Parex Usa Weatherseal Spray and Roll Onsaffronbuilders9Ainda não há avaliações
- Pow Template Project 2020Documento7 páginasPow Template Project 2020EdgarAinda não há avaliações
- Filtration Method Using Activated Charcoal, Zeolite and Silica Sand Media to Reduce Total Ammonia (N-NH3) and Sulfide (S2-) in Leather Tanning Industry Wastewater OutletDocumento14 páginasFiltration Method Using Activated Charcoal, Zeolite and Silica Sand Media to Reduce Total Ammonia (N-NH3) and Sulfide (S2-) in Leather Tanning Industry Wastewater OutletmarlianiAinda não há avaliações
- Superfrac BrochureDocumento16 páginasSuperfrac Brochureunknownx_XAinda não há avaliações
- Smart, Eco-Friendly, Money-Saving Home Tips by Kevin ReganDocumento1 páginaSmart, Eco-Friendly, Money-Saving Home Tips by Kevin ReganKathy Irene ReganAinda não há avaliações
- Physics and Technology For Engineers... 2023Documento546 páginasPhysics and Technology For Engineers... 2023david floresAinda não há avaliações
- Hints & Solutions: NSEJS - STAGE-I (2016-17) Paper Code: Js-530Documento11 páginasHints & Solutions: NSEJS - STAGE-I (2016-17) Paper Code: Js-530Bhuvnesh MathurAinda não há avaliações
- Basement Column Design Analysis and Capacity CheckDocumento3 páginasBasement Column Design Analysis and Capacity CheckPhanithAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Destructive Testing: Laboratory ManualDocumento65 páginasNon-Destructive Testing: Laboratory ManuallokendraAinda não há avaliações