Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Medical Mnemonics
Enviado por
Janice MarcoDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Medical Mnemonics
Enviado por
Janice MarcoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MEDICAL MNEMONICS
HYPERNATREMIA F R I E D fever low grade restless increased fluid retention, increased Bp edema (peripheral, pitting) decreased UO, dry mouth
CAUSES M O D E L meds, meals osmotic diuretics diabetes insipidus excessive water loss low water intake
HYPONATERMIA S A L T L O S S stupor/coma anorexia N & V lethargy tendon reflex decreased limp muscle weakness orthostatic hypotension seizures/ headache stomach cramping
HYPERKALEMIA M U R D E R muscle weakness urine: oliguria/anuria respiratory distress decreased cardiac contractility ECG changes reflex: hyper/ are (flaccid) M A C H I N E meds: ACE inhibitors, NSAIDS acidosis: respiratory & meta. cellular destruction hypoaldosteronism/hemolysis intake: excessive nephrons: renal failure excretion impaired
HYPOKALEMIA
HYPOCALCEMIA C - Convulsions A - Arrhythmias T - Tetany S - Spasms and stridor
RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION inducing drugs STOP breathing
STOP breathing S - Sedatives and hypnotics T - Trimethoprim O - Opiates P Polymyxins P-THORAX P - Pleuretic pain T - Trachea deviation H - Hyperresonance O - Onset sudden R - Reduced breath sounds (& dypsnea) A - Absent fremitus X - X-ray shows collapse INSPIRATION I - Immunosuppression N - Neoplasia S - Secretion retention P - Pulmonary oedema I - Impaired alveolar macrophages R - RTI (prior) A - Antibiotics & cytotoxics T - Tracheal instrumentation I - IV dug abuse O - Other (general debility, immobility) N - Neurologic impairment of cough reflex, (eg NMJ disorders) AAAAPPPP A - Airway obstruction A - Angina A - Anxiety A - Asthma P - Pneumonia P - Pneumothorax P - Pulmonary Edema P - Pulmonary Embolus THE ATRIAL FIBS: T-hyroid H-ypothermia E-mbolism (P.E.) A-lcohol T-rauma (cardiac contusion) R-ecent surgery (post CABG) I-schemia A-trial enlargement L-one or idiopathic F-ever, anemia, high-output states
PNEUMOTHORAX - S/Sx PTHORAX
PNEUMONIA -risk factors INSPIRATION
SHORTNESS OF BREATH Causes AAAAPPPP
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: CAUSES OF NEW ONSET THE ATRIAL FIBS:
I-nfarct B-ad valves (mitral stenosis) S-timulants (cocaine, theo, amphet, caffeine) DOGASH: D-iamorphine O-xygen G-TN spray A-sprin 300mg S-treptokinase H-eparin MONA M-orphine O-xygen N-itrates A-sprin TV SPARC CUBE: T-hirst V-omiting S-weating P-ulse weak A-nxious R-espirations shallow/rapid C-ool C-yanotic U-nconscious BP- low E-yes blank BATS: B-erry aneurysm A-rteriovenous malformation/ Adult polycystic kidney disease T-rauma (eg being struck with baseball bat) S-troke "Shock, Shock, Shock, Everybody Shock, Little Shock, Big Shock, Momma Shock, Poppa Shock": Shock= Defibrillate Everybody= Epinephine Little= Lidocaine Big= Bretylium Momma= MgSO4 Poppa= Pocainamide "Every Little Boy Must Pray": E-pinephrine L-idocaine B-retylium
MI: IMMEDIATE TREATMENT DOGASH:
SHOCK: SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS TV SPARC CUBE:
SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE (SAH) CAUSES BATS
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION: TREATMENT "Shock, Shock, Shock, Everybody Shock, Little Shock, Big Shock, Momma Shock, Poppa Shock":
VFIB/VTACH DRUGS USED ACCORDING TO ACLS "Every Little Boy Must Pray":
M-agsulfate P-rocainamide KING UFC: K-+ (potassium) I-nsulin (5u/hour. Note: sliding scale no longer recommended in the UK) N-asogastic tube (if patient comatose) G-lucose (once serum levels drop to 12) U-rea (check it) F-luids (crytalloids) C-reatinine (check it)/ Catheterize "Some Hot Dude Better Give Iced Fluids Fast!" (Hot dude = hypothermia): Stop triggering agents H-yperventilate/ Hundred percent oxygen D-antrolene (2.5mg/kg) B-icarbonate G-lucose and insulin I-V Fluids and cooling blanket F-luid output monitoring/ Furosemide/ Fast heart [tachycardia] ABCDE: A-irway B-reathing C-irculation D-rugs E-nvironment "ROME" (Respiratory Opposite, Metabolic Equal) Acidosis Respiratory (opposite): pH Pco2 Metabolic(equal): pH HCO3 Alkalosis Respiratory (opposite): pH Pco2 Metabolic(equal): pH HCO3 clinical features"HITS" H-allucinations (visual, tactile) I-ncreased vital signs and insomnia T-remens delirium tremens (potentially lethal) S-hakes/ Sweats/ Seizures/ Stomach pains (nausea, vomiting) precipitating factors"4E's" E-ating E-motion E-xertion (Exercise) E-xtreme Temperatures (Hot or Cold weather)
DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS MANAGEMENT KING UFC:
MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA TREATMENT"Some Hot Dude Better Give Iced Fluids Fast!" (Hot dude = hypothermia):
RESUSCITATION: BASIC STEPS ABCDE:
Acid-base"ROME" (Respiratory Opposite, Metabolic Equal)
Alcohol withdrawal: clinical features"HITS"
Angina: precipitating factors"4E's"
Anorexia nervosa: clinical features "ANOREXIC"
clinical features"ANOREXIC" A-dolescent women/ Amenorrhea N-GT alimentation (most severe cases) O-bsession with losing weight/ becoming fat though underweight R-efusal to eat (5% die) E-lectrolyte abnormalities (e.g., K+, cardiac arrhythmia) X - ercise I-ntelligence often above average/ Induced vomiting C-athartic use (and diuretic abuse) assessment"PAINS" P-ain (RLQ) A-norexia I-ncreased temperature, WBC (15,000-20,000) N-ausea S-igns (McBurney's, Psoas) Symptom Implication C-old and clammy . . . give hard candy H-ot and dry . . . glucose is high F-emale F-at F-orty F-ertile F-air "CLEFT LIP" C-rying, minimize L-ogan bow E-lbow restraints F-eed with Brecht feeder T-each feeding techniques; two months of age (average age at repair) L-iquid (sterile water), rinse after feeding I-mpaired feeding (no sucking) P-ositionnever on abdomen "JOCAM" J-udgment O-rientation C-onfabulation A-ffect M-emory "A-E-I-O-U TIPS" A-lcohol, acidosis (hyperglycemic coma) E-pilepsy (also electrolyte abnormality, endocrine problem)
Appendicitis: assessment"PAINS"
Blood glucose (rhyme)Symptom Implication
Cholecystitis: risk factors"5F's"
Cleft lip: nursing care plan (postoperative)"CLEFT LIP"
Cognitive disorders: assessment of difficultiesJOCAM
Coma: causes"A-E-I-O-U TIPS"
I-nsulin (hypoglycemic shock) O-verdose (or poisoning) U-remia and other renal problems T-rauma; temperature abnormalities (hypothermia, heat stroke) Infection (e.g., meningitis) P-sychogenic ("hysterical coma") S-troke or space-occupying lesions in the cranium "HELLP" H- emolysis E- levated L- iver function tests L- ow P- latelet count "3S's" S-ugar (hyperglycemia) S-alt (hypernatremia) S-ex (excess androgens) "3P's," Polydipsia (very thirsty) Polyphagia (very hungry) Polyuria (urinary frequency) avoid the "3C's" C-ake C-ookies C-ream (dairy, e.g., milk, ice cream) "REEDA" R-edness E-dema E-cchymosis D-ischarge A-pproximation of skin M-ydriatic = dilated pupils M-iotic = tiny (constricted) pupils "4 C's" CAD (coronary artery disease) CHF (congestive heart failure) CRF (chronic renal failure) CVA (cardiovascular accident; now called brain attack or stroke) "I-TIRED" I-ntake and output (urine) T-ake blood pressure I-schemia attack, transient (watch for TIAs) R-espiration, pulse
Complication of severe preeclampsia"HELLP" syndrome
Cushing's syndrome: symptoms "3S's"
Diabetes: signs and symptoms "3P's,"
Diet: low cholesterolavoid the "3C's"
Episiotomy assessment"REEDA"
Eye medications
Hypertension: complications"4 C's"
Hypertension: nursing care plan "ITIRED"
E-lectrolytes D-aily weight "DIRE" D-iaphoresis I-ncreased pulse R-estless E-xtra hungry "TORCH" T-oxoplasmosis O-ther (hepatitis B, syphilis, group B beta strep) R-ubella C-ytomegalovirus H-erpes simplex virus "PAINS" P-eriod (menstrual: late, spotting, bleeding) A-bdominal pain, dyspareunia I-nfection (abnormal vaginal discharge) N-ot feeling well, fever or chills S-tring missing "3C's" C-ooperation C-ompromise C-ollaboration "3R's" R-egularity (provide routine and structure) R-eward (positive reinforcement) R-edundancy (repeat) "MONA" M-onitor/ Morphine O-xygen N-itroglycerin A-spirin "APGAR" A-ppearance P-ulse G-rimace A-ctivity R-espiratory effort "GTPAL" Gravida Term Preterm Abortions (SAB, TAB) Living children
Hypoglycemia: signs and symptoms "DIRE"
Infections during pregnancy "TORCH"
IUD: potential problems with use "PAINS"
Manipulation: nursing planpromote the "3C's"
Mental retardation: nursing care plan"3R's"
Myocardial infarction: treatment "MONA"
Newborn assessment components "APGAR"
Obstetric (maternity) history "GTPAL"
Oral contraceptives: signs of potential problems"ACHES"
"ACHES" A-bdominal pain (possible liver or gallbladder problem) C-hest pain or shortness of breath (possible pulmonary embolus) H-eadache (possible hypertension, brain attack) E-ye problems (possible hypertension or vascular accident) S-evere leg pain (possible thromboembolic process) "PQRST" What Provokes the pain? What is the Quality of the pain? Does the pain Radiate? What is the Severity of the pain? What is the Timing of the pain? "ABCs" A-sk about the pain B-elieve when clients say they have pain C-hoiceslet clients know their choices D-eliver what you can, when you said you would E-mpower/Enable clients' control over pain "4W's" Wind (pulmonary) Wound Water (urinary tract infection) Walk (thrombophlebitis) "TRIES" T-emperature regulation (poor) R-esistance to infections (poor) I-mmature liver E-limination problems (necrotizing enterocolitis [NEC]) S-ensory-perceptual functions (retinopathy of prematurity [ROP]) "VENT" V-ivactil E-lavil N-orpramin T-ofranil "4A's" Affect Ambivalence Associative looseness Autism
Pain: assessment"PQRST"
Pain: management"ABCs"
Postoperative complications: order "4W's"
Preterm infant: anticipated problems"TRIES"
Psychotropic medications: common antidepressives (tricyclics) "VENT"
Schizophrenia: primary symptoms "4A's"
Sprain: nursing care plan"RICE"
"RICE" R-est I-ce C-ompression E-levation "ACCT" A-mount C-olor C-onsistency T-iming "3Cs" Coughing Choking Cyanosis "TRACTION" T-rapeze bar overhead to raise and lower upper body R-equires free-hanging weights; body alignment A-nalgesia for pain, prn C-irculation (check color and pulse) T-emperature (check extremity) I-nfection prevention O-utput (monitor) N-utrition (alteration related to immobility) "3Ts" Temporary unilateral visual impairment Transient paralysis (one-sided) Tinnitus = vertigo "TRAUMA" T-hromboembolism; Tissue perfusion, altered R-espiration, altered A-nxiety related to pain and prognosis U-rinary elimination, altered M-obility impaired A-lterations in sensory-perceptual functions and skin integrity (infections) "COAT RACK" W-ernicke's encephalopathy (acute phase) clinical features: C-onfusion O-phthalmoplegia A-taxia Thiamine is an important aspect of Tx K-orsakoff's psychosis (chronic phase)characteristic findings: R-etrograde amnesia (recall of some old
Stool assessment"ACCT"
Tracheoesophageal fistula: assessment"3Cs"
Traction: nursing care plan "TRACTION"
Transient ischemic attacks: assessment"3Ts"
Trauma care: complications "TRAUMA"
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (alcohol-associated neurological disorder)"COAT RACK"
memories) A-nterograde amnesia (ability to form new memories) C-onfabulation K-orsakoff's psychosis "BOOMAR" B-ed rest O-xygen O-piate M-onitoring A-nticoagulation R-educe clot size "A Permanently Temperamental Man" A-ortic P-ulmonary T-ricuspid M-itral The 3rd, 4th and 5th cervical spinal nerves innervate the diaphragm. "Oh Ohh Ohhh To Try And Fit A Gold Velvet So Heavenly" Olfactory CN I Optic CN II Occulomotor CN III Trochlear CN IV Trigeminal CN V Abducens CN VI Facial CN VII Auditory CN VIII Glasopharyngeal CN IX Vagus CN X Spinal/Accessory CN XI Hypoglossal CN XII "RED LIP" R-heumatoid arthritis E-xtra intestinal amoebiasis D-iscoid lupus erythematosus L-epra reaction I-nfectious mononucleosis P-hotogenic reactions "TO A SIS" T-erbutaline O-rciprenaline A-drenaline S-albutamol I-soprenaline
Basic MI management - "BOOMAR"
Location of the heart valve from right to left - "A Permanently Temperamental Man"
"Cut C4, breathe no more"
Cranial Nerves - "Oh Ohh Ohhh To Try And Fit A Gold Velvet So Heavenly"
Uses of Chloroquine (other than malaria) - "RED LIP"
Bronchodilators - "TO A SIS"
S-almeterol "Please Read His Text" P-eripheral edema R-aised JVP H-epatomegaly T-ricuspid incompetence "ABCDE" A-scites B-leeding (hematemesis, piles) C-aput medusae D-iminished liver E-nlarged spleen Allergies Medication Past medical history Last meal Events and environment related to injury "Laging Panalo Kung Taga Bulacan" Lung Prostat Kidney Thyroid Breast Streptococci causal organism Sorethroat Swollen tonsils Strawberry tongue Sandpaper rash miliarySudamina vesicles over hands, feet, abdomen "SLUD" S-alivation L-acrimation U-rination D-efecation "3M's Myelofibrosis Malaria Myelogenous leukemia "TRAP" T-remor R-igidity A-kinesia and bradykinesia P-ostural Instability
Signs of cor pulmonale - "Please Read His Text"
Portal hypertension features "ABCDE"
Key questions needed in an emergency history taking situation "AMPLE"
Malignancies that metastisize to bone - "Laging Panalo Kung Taga Bulacan"
Six "S" in Scarlet Fever
Signs of anti-cholinergic crisis "SLUD"
Causes of huge spleen - "3M's"
Cardinal Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease - "TRAP"
Days of appearance of rashesVaricella(chickenpox) - "Very Sick Patients Must Take Double Exercise"
"Very Sick Patients Must Take Double Exercise" 1st dayScarlet fever 2nd dayPox(smallpox) 3rd dayMumps 4th dayTyphus 5th dayDengue 6th dayEnteric fever(typhoid) HYPOTENSION TACHYPNEA TACHYCARDIA CUSHINGS TRIAD: HYPERTENSION (WIDE PULSE PRESSURE) BRADYCARDIA BRADYPNEA TREMORS, TACHYCARDIA IRRITABILITY RESTLESSNESS EXTREME DIAPHORESIS RESTLESSNESS AGITATION TACHYCARDIA BRADYCARDIA EXTREME RESTLESSNESS DYSPNEA CYANOSIS DIGOXIN MORPHINE AMINOPHYLLINE DOPAMINE DIURETICS O2 GASSES - MONITOR (ABG) B-P DECREASE U-RINE OUTPUT DECREASE R-ESPIRATORY RATE DECREASE P-ATELLAR REFLEX ABSENT H-YDRATION O-XYGENATION P-AIN I-NFECTION A-VOID HIGH PLACES H-EMOLYSIS E-LEVATED LIVER ENZYMES
SHOCK - HYPOTACHYTACHY
INCREASE ICP HYPERBRADYBRADY
HYPOGLYCEMIA
EARLY SIGNS OF HYPOXIA
LATE SIGNS OF HYPOXIA
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
MG SO4 TOXICITY
SICKLE CELL DISEASE
PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION
L-OW PLATELETS V-OMITING A-NOREXIA N-AUSEA D-IARRHEA A-BDOMINAL PAIN P-RESSURE R-EST I-CE C-OMPRESSION E-LEVATION S-KELETAL MUSCLE WEAKNESS U--WAVE ON ECG C-ONSTIPATION T-OXICITY TO DIGOXIN I-RREGULAR WEAK PULSE O-TOSTASIS N-UMBNESS PARESTHESIA HYPOKALEMIA Signs and Symptoms 6 L's Lethargy Leg cramps Limp muscles Low, shallow respirations Lethal cardiac dysrhythmias Lots of urine (polyuria) P-AIN P-ULSELESSNESS P-ARESTHESIA P-ARALYSIS P-ALLOR ASSYMPTOMATIC ABDOMINAL MASS ABDOMINAL PULSE ACHES LOW BACK RIFAMPICIN - RED-ORANGE URINE ISONIAZID - PERIPHERAL NEURITIS PYRAZINAMIDE - INCREASE URIC ACID ETHAMBUTOL - EYE PROBLEMS STREPTOMYCIN - OTOTOXIC Use a star as these drugs stain the teeth H-eat I-nduration
GI SYMPTOMS AND TOXICITY TO DIGOXIN
FRACTURE
NEUROVASCULAR CHECK
ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURISM (4A)
ANTI TB DRUGS AND SIDE EFFECTS
Inflammation (HIPER)
P-ain E-dema R-edness Adrenal Gland Hormones (SSS) S-ugar (Glucocorticoids) S-alt (Mineralcorticoids) S-ex (Androgens) M-Morphine A-Aminophylline D- Digitalis Pulmonary Edema (MAD DOG) D-Diuretics (Lasix) O- Oxygen G- ases (Blood Gases ABG's) D-aily Weight I- ntake and Output (I & O) U- rine Output R-esponse of BP E-lectrolytes T-ake Pulses I-schemic Episodes (TIA) C-omplications: 4C's C- Coronary Artery Disease C- Coronary Rheumatic Fever C- Congestive Heart Failurehttp://quizlet.com/create_set/#remove-row C- Cardio Vascular Accident T-issue Perfusion Problems R-espiratory Problems A-nxiety U-nstable Clotting Factors M-alnutrition A-ltered Body Image T-hromboembolism I-nfection C-oping Problems N - Non-reactive N - Non- Stress is N - Not good A- Amniocentesis L- L/S Ratio O - Oxytocin Test N - Non-Stress Test E - Estriol Level R- Redness E- Edema
Hypertension Nursing Care (DIURETIC)
4 C's of Hypertension (Complications)
Complications of Trauma Client (TRAUMATIC)
OB Non-Stress Test (NNN) 3 negatives in a row to interpret results of Non-Stress Test
Assessment Tests for Fetal WellBeing (ALONE)
Evalution of Episiotomy Healing (REEDA)
E - Ecchymosis D - Discharge, Drainage A - Approximation B-reasts U-terus B-owels B-ladder L-ochia E-pisiotomy/lateration/C-section incision R- Razor Electric/ Blades A- Aspirin N- No needles (esp. in small gauge) D- Do decrease in needle sticks) I - Injury (Protect from) C- Cane O- Opposite A- Affected L- Leg W- Walker W- With A- Affected L - Leg D-elirium I-nfection A-trophic Urethra P-harmaceuticals P-sychologic E-xcess Urine Output R-estricted Mobility S-tool Impaction P-osition O-utput O-ffer Fluids P-rivacy E-xercise R-eport Results S-ize (Amount) C-onsistency O-ccult Blood O-dor P-eristalsis Emergency Trauma Assessment (ABCDEFGHI) A-irway B-reathing C-irculation
Post-Partum Assessment (BUBBLE)
Bleeding Precautions (RANDI)
Canes and Walkers (COAL & WWAL)
Common Causes of Transient Incontinence (DIAPPERS)
Promotion of Normal Elimination (POOPER SCOOP)
D-isability E-xamine F-ahrenheit G-et Vitals H-ead to Toe Assessment I-ntervention A-llergies M-edications P-ast Medical History L-ast Meal E-vents Surrounding Injury S-lurred Speech A-ltered Central Nervous System M-uscle Twitching S-eizures T - Theophyline D - Dilantin C - Coumadin I - losone (Erythromycin) A- Abdominal Pain C - Chest Pain H - Headache E - Eye Problems S - Severe Leg Pain L- Lidocaine E - Epinephrine A- Atropine Sulfate N - Narcan I - Isoproterenol D - Dopamine E - Epinephrine A - Atropine Sulfate S-leep Disturbances I-nterest Decreased G-uilty Feelings C-oncentration decreased A-ppetite P-sychomotor function decreased S-uicidal Ideations A-mnesia A-nomia A-praxia A-gnosia A-phasia
Trauma Surgery (AMPLE) after initial assessment
Lidocaine Toxicity (SAMS)
TDCI (These Drugs Can Interact)
Serious Complications of Oral Birth Control Pills (ACHES)
Emergency Drugs to LEAN on
Drugs for Bradycardia & low BP (IDEA)
Depression Assessment (SIG)
Energy Decreased (CAPS)
5 A's to Alzheimer Diagnosis
D- Distractibility I - Indiscretion G - Grandiosity Major Symptoms of a Manic Attack (DIG FAST) F- Flight of Ideas A- Activity Increase S- Sleep Deficit T - Talkative A- Anemia N- Neutropenia T- Thrombocytopenia F - Frequency (3x per week) I - Intensity (60-80% of Maximal Heart Rate) T- Time (Aerobic Activity) F-eeding difficulty I-nspiratory Stridor N-ares Flares E-xpiratory Grunting S-ternal Retractions A-irway Closed I-ncreased Pulse R-estlessness Epiglottitis (AIR RAID) R-etractions A-nxiety Increased I-nspiratory Stridor D-rooling U-pright Position N-itrates (in low dose) L-asix O-xygen A-minophylline D-igoxin F-luids (decrease) A-fterload (decrease) S-odium restriction T-est (Dig level, ABGs, K level) Make sure they don't have problems with: D-rug and alcohol E-yes and ears M-etabolic and endocrine disorders E-motional disorders N-eurologic disorders T-umors and trauma
Symptoms of Leukemia (ANT)
Exercise Guide for Diabetic Fitness (FIT)
Symptoms of Hypoxia (in Pediatrics) FINES
Treating CHF (UNLOAD FAST)
DEMENTIA
I-nfection A-rteriovascular disease A-lcohol Use C-orticosteroid Use C-alcium low E-strogen low S-moking S-edentary lifestyle/s ACCESS leads to OSTEOPOROSIS A- Acid-Base Problems E- Electrolyte Problems I- Intoxications O- Overload of fluids U - Uremic Symptoms F- Frequency U- Urgency N- Nocturia B- Banana R- Rice A- Apple T- Toasted Bread R- Rye O- Oats W- Wheat J- Judgment A- Affect M- Memory C- Cognition O- Orientation P- Polyuria (excessive urination) P- Polydypsia (excessive thirst) P- Polyphagia (excessive hunger) H- Hepatomegaly E- Edema (Bipedal) A- Ascites D- Distended Neck Vein C- Cough H- Hemoptysis O- Orthopnea P- Pulmonary Congestion (crackles/ rales) K- Kayexalate (orally/ enema) I- Insulin
Osteoporosis Risk Factors (ACCESS)
Who needs dialysis? (Check the vowels: AEIOU)
Prostate Problems are no... FUN
BRAT Diet (for severe dehydration)
Gluten Free Diet (ROW)
Assess Changes in Senile Dementia (JAMCO)
3 P's of Diabetes Mellitus - Type 1 Signs & Symptoms
Right-Sided Heart Failure (HEAD)
Left-Sided Heart Failure (CHOP)
Hyperkalemia Management (KIND)
N- Na HCO3 D- Diuretics (Furosemide & Thiazides) M- Morphine O- Oxygen N- Nitrates (Nitroglycerin) A- Aspirin (ASA) T- Thormbolytics A- Anti-Coagulants S- Stool Softeners P- Potassium I- Inside S- Sodium O- Outside A-menorrhea delayed N-o organic factors accounts for weight loss O-bviously thin but feels FAT R-efusal to maintain normal body weight E-pigastric discomfort is common X-symptoms (peculiar symptoms) I-ntense fears of gaining weight A-lways thinking of foods B-inge eating U-nder strict dieting L-acks control over-eating I-nduced vomiting M-inimum of to binge eating episodes I-ncrease/Persistent concern of body size/shape A-buse of diuretics & laxatives W-eight loss of 15% of original body weight A-menorrhea S-ocial withdrawal H-istory of high activity & achievement E-lectrolyte Imbalance D-epression/ Distorted Body Image B- Brain Damage A- Alcoholic Hallucinosis D- Death D- Denial D- Dependency D- Demanding D- Destructive D- Domineering R- Ruthless A- Abusive P- Personal
Management of Myocardial Infarction (MONATAS)
Electrolytes - PISO
Eating Disorder: ANOREXIA
Eating Disorder: BULIMIA
Findings of a Bulimia client: WASHED
Outcome of Alcoholism: BAD
5 D's of Behavioral Problems of Alcoholism
Situations requiring Crisis Situation: RAPE
E- Experience C-hild's excessive knowledge on sex & abusive words H-air growth in various lengths I-nconsistent stories from the child & parent/s L-ow self-esteem D-epression A-pathy, no emotion B-ruised U-nusual injuries S-erious injuries E-vidence of old injuries not reported S tupor/coma A norexia, N&V L ethargy T endon reflexes decreased S/S of Hyponatremia L imp muscles (weakness) O rthostatic hypotension S eizures/headache S tomach cramping Beta Blockers B1 Blocks the heart (you have only one heart) B2 Blocks the lungs (you have two lungs) B- Breasts U- Uterus B- Bladder B- Bowel function L- Lochia E- Episiotomy H- Homan's sign E- Emotional Status R- Respiratory System A-Amantadine L- Levodopa B- Bromocriptine M-MAO inhibitors SALT Stupor/coma Anorexia Lethargy Tendon reflexes decreased LOSS Limp muscles Orthostatic hypotension
Warning Signs of a Child Abuse/ Neglect: CHILD ABUSE
Nine-point Postpartum Assessment. BUBBLEHER
Parkinson's Medications: "Ali Loves Boxing Matches"
Hyponatremia: Signs and Symptoms
Seizures/headache Stomach cramps Signs and Symptoms I remember by the rhyme: Groans, Moans, Bones, Stones, and Overtones Hypercalcemia Groans: constipation Moans: pain - joint aches Bones: loss of calcium from bones, bone metastasis Stones: kidney stones Overtones: psychiatric overtones - depression, confusion Right = Right C=oronary A=Artery M=Marginal Artery P=Posterior Interventricular Artery Left=Left A=Anterior Interventricular Artery C=Circumflex Artery
Coronary Arteries
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Neocortex Size As A Constraint On Group Size in Primates (Dunbar)Documento25 páginasNeocortex Size As A Constraint On Group Size in Primates (Dunbar)David HeAinda não há avaliações
- HypoxiaDocumento21 páginasHypoxiaJojo RyelciusAinda não há avaliações
- Microorganisms Important in Food MicrobiologyDocumento39 páginasMicroorganisms Important in Food MicrobiologyKumkum CRAinda não há avaliações
- Naturally Unique For WeeblyDocumento9 páginasNaturally Unique For Weeblyapi-272676615Ainda não há avaliações
- Bio Chapter 5Documento10 páginasBio Chapter 5Rosfaizzati MarnunAinda não há avaliações
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento58 páginasCyanotic Congenital Heart Diseasegolden37Ainda não há avaliações
- An Estimation of The Number of Cells in The Human BodyDocumento11 páginasAn Estimation of The Number of Cells in The Human BodysedilotAinda não há avaliações
- The Inorganic Side of Chemical Biology: CommentaryDocumento4 páginasThe Inorganic Side of Chemical Biology: CommentarySilloAntonioAinda não há avaliações
- Individual Assignment - SwimmingDocumento9 páginasIndividual Assignment - Swimminghaafiz5arisAinda não há avaliações
- Nephrotic Syndrome Msn-3Documento12 páginasNephrotic Syndrome Msn-3Bibi Renu100% (3)
- BTE-308 L4 Tissue Culture Part III Tissue Culture MethodologyDocumento51 páginasBTE-308 L4 Tissue Culture Part III Tissue Culture MethodologyPURSUIT OF GROWTHAinda não há avaliações
- Training Effects of Long Versus Short Bouts of Exercise in Healthy Subjects.Documento4 páginasTraining Effects of Long Versus Short Bouts of Exercise in Healthy Subjects.HosseinAinda não há avaliações
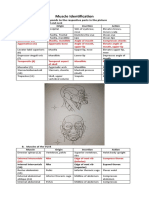
- Muscle IdentificationDocumento7 páginasMuscle Identificationhakdog hakdogAinda não há avaliações
- The Structure and Function of Proteins Chapter 5 (Continued)Documento27 páginasThe Structure and Function of Proteins Chapter 5 (Continued)Rabi MehrAinda não há avaliações
- Per Dev Lesson For 1 WeekDocumento2 páginasPer Dev Lesson For 1 WeekEjay Balils IIAinda não há avaliações
- Sphygmomanometer FileDocumento12 páginasSphygmomanometer FileKye GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Organophosphorus PoisoningDocumento15 páginasOrganophosphorus PoisoningtaufiAmaneeAinda não há avaliações
- Observations During Fundus ExaminationDocumento3 páginasObservations During Fundus ExaminationAn'umillah Arini ZidnaAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System Anatomy PhysiologyDocumento20 páginasDigestive System Anatomy PhysiologyKids JangAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical and Physical Properties of Nucleic AcidsDocumento6 páginasChemical and Physical Properties of Nucleic AcidsSherlock Wesley ConanAinda não há avaliações
- Vedio 3Documento20 páginasVedio 3أحمد الكنديAinda não há avaliações
- Lumbar Traction Review2Documento9 páginasLumbar Traction Review2Phooi Yee LauAinda não há avaliações
- Sankalp Proton NEET: Human ReproductionDocumento4 páginasSankalp Proton NEET: Human ReproductionComics WorldAinda não há avaliações
- Acupuncture in India:: As Defined by The National Institutes of HealthDocumento3 páginasAcupuncture in India:: As Defined by The National Institutes of Healthmanikandan16Ainda não há avaliações
- Cansuje National High School: Quarter 3 Summative Test No. 1 in Science 10Documento3 páginasCansuje National High School: Quarter 3 Summative Test No. 1 in Science 10Jannet FuentesAinda não há avaliações
- Medtronic Physio Control Lifepak 10 DefibrillatorDocumento2 páginasMedtronic Physio Control Lifepak 10 DefibrillatorCarlos RomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Brain Imaging Techniques and HemisphereDocumento4 páginasBrain Imaging Techniques and HemisphereYour MaterialsAinda não há avaliações
- Aits Neet Grand Test - 23 Paper Key (04-05-2023)Documento10 páginasAits Neet Grand Test - 23 Paper Key (04-05-2023)vulurakashsharma2005Ainda não há avaliações
- A Multi-Dimensional Model of Dysfunctional BreathiDocumento4 páginasA Multi-Dimensional Model of Dysfunctional Breathimari_kundera19Ainda não há avaliações
- 083 41 Final Biologi T4 DLP-30-60Documento31 páginas083 41 Final Biologi T4 DLP-30-60Farhan DarwisyAinda não há avaliações