Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Bottom Trunnion (-) 45m - With Shear Plate Extension (0 Deg)
Enviado por
nallay1705Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Bottom Trunnion (-) 45m - With Shear Plate Extension (0 Deg)
Enviado por
nallay1705Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
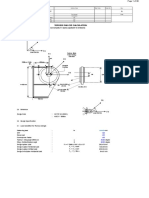
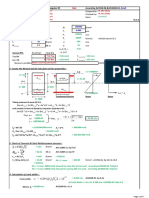
T RUNNION DESIGN @ EL (-)45m Case : 0 degree Lifting Stage
Figure 1 - Trunnion Geometry
Lift angle and Jacket double batter angle 0deg := 14.25 deg :=
Angle between sling line to trunnion pipe := 14.25 deg =
Outer Diameter of jacket leg D
L
2031mm :=
Thickness of jacket leg at node T
L
63 mm :=
Thickness of jacket leg T
n
32 mm :=
Outer diameter of Trunnion Pipe D
T
1219mm :=
Thickness of Trunnion Pipe T
T
50 mm :=
Thickness of stiffner Plate t
st
25mm :=
Thickness of shear plate T
S
72mm :=
Distance between the top of the trunnion
pipe and the shear plate
h
1
200 mm :=
Clearence between the trunnion pipe
and top of the leg
C
c
600 mm :=
Spacing between the ring plate and pipe r
s
1400 mm :=
Height of the External ring d
w
500 mm :=
Thickness of the External ring t
w
50 mm :=
1 of 10 Rev 0
Allowable Stress
E 2 10
5
MPa :=
Young's Modulus
Yield Strength F
y
345MPa :=
Allowable Tensile Stress F
at
0.6 F
y
:=
F
at
207 MPa =
Allowable Bending Stress F
ab
0.66 F
y
:=
F
ab
227.7 MPa =
Allowable Shear Stress F
as
0.4 F
y
:= F
as
138 MPa =
Allowable Von-Mises Stress F
avon
0.75 F
y
:= F
avon
258.8 MPa =
Sling Design Load and Selection
Design Sling load (including DAF = 2.0) P 22975 kN :=
Static Design Load F
STAT
P
2.0
:=
F
STAT
11487.5 kN =
Sling Breaking Safety Factor S
b
4 :=
Calculated Sling Breaking Load F
crbl
F
STAT
S
b
:= F
crbl
45950 kN =
Specification Cable Laid Slings PM20 F
crbl
4686 MTon =
Diameter
s
368 mm :=
Minimum Breaking Strength F
MBS
5049 MTon :=
Weight W
s
400
kgf
m
:=
Sling if F
MBS
F
crbl
> "Ok" , "Not Ok" ,
( )
:= Sling "Ok" =
Force Resolution
Force along trunnion vertical axis P
VI
P cos ( ) := P
VI
22268.1 kN =
Force along perpendicular to trunnion axis P
HI
P sin ( ) := P
HI
5655.4 kN =
Out of Plane force (5% as per design criteria) P
Ho
0.05 P := P
Ho
1148.8 kN =
Trunnion Section Properties
Area of Trunnion Pipe A
1
4
D
T
2
D
T
2 T
T
( )
2
:= A
1
183626 mm
2
=
Moment of inertia of trunnion pipe I
TT
64
D
T
4
D
T
2 T
T
( )
4
:= I
TT
31424m
2
mm
2
=
Stress Checks
Stress checks has been performed at section A-A, section inline with the horizontal force and section along
vertical force. In addition, the load transfer to the jacket leg has been verified. Following load transfer
mechanism is assumed.
a) The local stresses from the sling is transfered to the trunnion pipe and to the shear plate.
(b) The shear plate is transfering the load to the jacket leg through shear.
(c) The axial, bending and shear stresses are check for all possible locations of critical stresses.
2 of 10 Rev 0
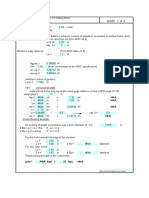
A) Check for Stresses at Section A-A
The plan view of the trunnion at section A-A is shown in figure 2.
Figure 2 - Plan view of trunnion at section A-A
i) Shear Stress
L
1
r
s
D
T
2
+ :=
Width of Shear plate at Section AA L
1
2.01m =
Area of Shear Plate A
2
T
S
L
1
:=
A
2
144684 mm
2
=
Effective Width of Ring Plate r
d
24t
w
:= r
d
1200 mm =
Width of Ring Plate at Section AA r
1
r
d
:=
Area of ring Plate1 @ AA A
3
r
1
t
w
:= A
3
60000 mm
2
=
Inplane Shear Stress at Section AA f
sai
P
HI
0.5 A
1
A
2
+
:=
f
sai
23.9 MPa =
Out-off plane Shear Stress at Section AA f
sao
P
Ho
0.5 A
1
A
3
+
:=
f
sao
7.6 MPa =
Resultant shear stress at section AA f
sa
f
sai
2
f
sao
2
+ ( ) := f
sa
25.08 MPa =
Unity Check Ratio UC
1
f
sa
F
as
:= UC
1
0.18 =
Shear_Stress
aa
"Ok" =
ii) Bending Stress
X
1max
L
1
t
w
2
+
D
T
2
:= X
1max
1425 mm =
Distance of C.G of Pipe from end
Distance of C.G of Shear Plate from end X
2max
L
1
2
t
w
2
+ := X
2max
1029.75 mm =
Distance of C.G of Ring Plate1 from end X
3max
t
w
2
:= X
3max
25 mm =
3 of 10 Rev 0
Distance of C.G of Section from end X
max
A
1
X
1max
A
2
X
2max
+ A
3
X
3max
+
A
1
A
2
+ A
3
+
:=
X
max
1061.41 mm =
Moment of Inertia about XX axis I
xx
64
D
T
4
D
T
2 T
T
( )
4
L
1
T
S
3
12
+
t
w
r
1
3
12
+ :=
I
xx
3.87 10
10
mm
4
=
Y
max
D
T
2
:= Y
max
609.5 mm =
Section Modulus About XX axis Z
xx
I
xx
Y
max
:=
Z
xx
6.35 10
7
mm
3
=
I
yy1
64
D
T
4
D
T
2 T
T
( )
4
A
1
X
1max
X
max
( )
2
+ :=
I
yy2
T
S
L
1
3
12
A
2
X
2max
X
max
( )
2
+ :=
I
yy3
r
1
t
w
3
12
A
3
X
3max
X
max
( )
2
+ :=
Moment of Inertia about YY axis I
yy
I
yy1
I
yy2
+ I
yy3
+ := I
yy
1.69 10
11
mm
4
=
Section Modules About YY axis Z
yy
I
yy
X
max
:=
Z
yy
1.59 10
8
mm
3
=
Eccentricity due to vertical force e
1
L
1
t
w
2
+ X
max
:= e
1
973.09 mm =
Bending Moment at section AA
(Due to Vertical Force)
M
1
P
VI
e
1
:= M
1
21668.9 kN m =
Eccentricity due to horizontal force e
3
C
c
s
2
+ := e
3
784 mm =
In-plane Bending Moment at section AA
(Due to Horizontal Force)
M
2_ip
P
HI
e
3
:=
M
2_ip
4433.8 kN m =
Out of-plane Bending Moment at section AA
(Due to Horizontal Force)
M
2_op
P
Ho
e
3
:=
M
2_op
900.6 kN m =
Total Bending Moment at section AA
(In-Plane)
M
A_ip
M
1
M
2_ip
+ := M
A_ip
17235.1 kN m =
Total Bending Moment at section AA
(Out of-Plane)
M
A_op
M
2_op
:= M
A_op
900.6 kN m =
Bendingg Stress in Section AA(in-plane) f
b_ip
M
A_ip
Z
yy
:= f
b_ip
108.2 MPa =
Bendingg Stress in Section AA(out-plane) f
b_op
M
A_op
Z
xx
:= f
b_op
14.2 MPa =
Combined Bending stress in Section AA f
ba
f
b_ip
2
f
b_op
2
+ ( ) := f
ba
109.2 MPa =
4 of 10 Rev 0
Unity Check Ratio UC
2
f
ba
F
ab
:=
UC
2
0.48 =
Bending_Stress
aa
"Ok" =
iii) Tensile Stress
Tensile Stress at Section AA f
ta
P
VI
A
1
A
2
+
:=
f
ta
67.83 MPa =
UC
3
f
ta
F
at
:= UC
3
0.33 =
Unity Check Ratio
Tensile_Strength
aa
"Ok" =
iv) Combined Von-mises Stress
Von-mises Stress F
vona
f
ta
2
f
ba
2
+ 3 f
sa
( )
2
+ f
ta
f
ba
:= F
vona
104.9 MPa =
Unity Check Ratio UC
4
F
vona
F
avon
:=
UC
4
0.41 =
Von_Mises_Stress
aa
"Ok" =
B) Check for Stresses at Section B-B
Figure 3 - Plan view of trunnion at section B-B
i) Shear Stress
A
1
183626.09 mm
2
=
Area of Trunnion Pipe
Distance between shear plate and pipe
at Section BB
r
o
1212 mm :=
Width of the shear plate at Section BB L
2
r
o
D
T
2
+ := L
2
1.82m =
Area of Shear Plate A
4
T
S
L
2
:=
A
4
131148 mm
2
=
Inplane Shear Stress at Section BB f
sbi
P
HI
0.5 A
1
A
4
+
:=
f
sbi
25.4 MPa =
Out-off plane Shear Stress at Section BB f
sbo
P
Ho
0.5 A
1
:=
f
sbo
12.5 MPa =
5 of 10 Rev 0
Resultant shear stress at section BB f
sb
f
sbi
2
f
sbo
2
+ ( ) := f
sb
28.28 MPa =
Unity Check Ratio UC
5
f
sb
F
as
:= UC
5
0.2 =
Shear_Stress
bb
"Ok" =
ii) Bending Stress
X
4max
L
2
t
w
+
D
T
2
:= X
4max
1262 mm =
Distance of C.G of Pipe from end
Distance of C.G of Shear Plate from end X
5max
L
2
2
t
w
+ := X
5max
960.75 mm =
Distance of C.G of Ring Plate1 from end X
6max
t
w
2
:= X
6max
25 mm =
Distance of C.G of Section from end X
maxb
A
1
X
4max
A
4
X
5max
+ A
3
X
6max
+
A
1
A
4
+ A
3
+
:=
X
maxb
958.54 mm =
Moment of Inertia about XX axis I
xxb
64
D
T
4
D
T
2 T
T
( )
4
L
2
T
S
3
12
+
t
w
r
1
3
12
+ :=
I
xxb
3.87 10
10
mm
4
=
Y
maxb
D
T
2
:= Y
maxb
609.5 mm =
Section Modulus About XX axis Z
xxb
I
xxb
Y
maxb
:=
Z
xxb
6.35 10
7
mm
3
=
I
yy4
64
D
T
4
D
T
2 T
T
( )
4
A
1
X
4max
X
maxb
( )
2
+ :=
I
yy5
T
S
L
2
3
12
A
4
X
5max
X
maxb
( )
2
+ :=
I
yy6
r
1
t
w
3
12
A
3
X
6max
X
maxb
( )
2
+ :=
Moment of Inertia about YY axis I
yyb
I
yy4
I
yy5
+ I
yy6
+ := I
yyb
1.37 10
11
mm
4
=
Section Modules About YY axis Z
yyb
I
yyb
X
maxb
:=
Z
yyb
1.43 10
8
mm
3
=
Eccentricity due to vertical
force
e
4
L
2
t
w
+ X
maxb
:= e
4
913 mm =
Bending moment at Section B-B M
B
P
VI
e
4
:= M
B
20330 kN m =
Bending stress @ B-B f
bb
M
B
Z
yyb
:=
f
bb
142.3 MPa =
6 of 10 Rev 0
Axial stress @ B-B
f
ab
P
VI
A
1
T
S
L
1
+
:=
f
ab
67.83 MPa =
Unity Check Ratio UC
6
f
bb
F
ab
|
\
|
|
.
f
ab
F
at
|
\
|
|
.
+ := UC
6
0.95 =
Bending_Stress
bb
"Ok" =
Axial_Stress
bb
"Ok" =
iii) Combined Von-mises Stress
Von-mises Stress F
vonb
f
ab
2
f
bb
2
+ 3 f
sb
( )
2
+ f
ab
f
bb
:= F
vonb
132.7 MPa =
Unity Check Ratio UC
7
F
vonb
F
avon
:=
UC
7
0.51 =
Von_Mises_Stress
bb
"Ok" =
C) Check for Stresses at Section C-C
Figure 4 - Sectional view of trunnion at C-C
i) Shear Stress
Width of Shear plate at Section CC h
A
D
T
h
1
+ :=
h
A
1419 mm =
Sheat Stress at Section CC f
sc
P
VI
0.5A
1
T
S
h
A
+
:=
f
sc
114.8 MPa =
Unity Check Ratio
UC
8
f
sc
F
as
:=
UC
8
0.83 =
Shear_Stress
cc
"Ok" =
ii) Tensile Stress
f
ac
P
VI
A
1
T
S
L
1
+
:=
Axial stress @ CC f
ac
67.83 MPa =
iii) Bending Stress
Neutral axis distance y
c
0.5A
1
D
T
( )
h
A
h
A
2
T
S
\
|
|
.
+
A
1
h
A
T
S
+
:=
7 of 10 Rev 0
Moment of inertia about XX axis I
XX
I
TT
T
S
h
A
3
12
+ A
1
y
c
D
T
2
\
|
|
.
2
+ y
c
h
A
2
\
|
|
.
2
T
S
h
A
+ :=
Z
XX
I
XX
y
c
:= Z
XX
0.08m
3
=
Section modulus
Eccentricity due to horizontal force e
5
y
c
s
2
+ := e
5
0.83m =
Bending moment at Section CC M
C
P
HI
e
5
:= M
C
4690 kN m =
Bending stress @ C-C f
bc
M
C
Z
XX
:=
f
bc
61.5 MPa =
Unity Check Ratio UC
9
f
bc
F
ab
|
\
|
|
.
f
ac
F
at
|
\
|
|
.
+ := UC
9
0.06 =
Bending_Stress
cc
"Ok" =
Axial_Stress
cc
"Ok" =
iv) Combined Von-mises Stress
Von-mises Stress F
vonc
f
ac
2
f
bc
2
+ 3 f
sc
( )
2
+ f
ac
f
bc
:= F
vonc
228.2 MPa =
Unity Check Ratio UC
10
F
vonc
F
avon
:=
UC
10
0.88 =
Von_Mises_Stress
cc
"Ok" =
D) Check for Punching Shear at Jacket Leg
Width of Effective Tubular Wall B
f
1.1 D
T
T
T
:= B
f
272 mm =
Total Effective area A
eff
B
f
T
T
d
w
t
w
+ :=
Effective Thickness based on
equivalent area
T
eff
min 2 T
L
A
eff
B
f
,
|
\
|
|
.
:=
T
eff
126 mm =
i) Estimation of Qu for axial, inplane and out-off plane bending moment
Since the brace to chord angle is given as 90 degrees, the joint is classified as T joint and appropriate formula
for the computation of Qu shall be selected.
Brace to chord angle 90 deg :=
D
L
2 T
eff
:=
Geometric Parameters
D
T
D
L
:= 0.6 = 8.06 =
Qu Factor for axial load Q
uax
30 :=
Q
uax
18.01 =
Qu for inplane bending moment Q
uip
5 0.7 + ( )
1.2
:= Q
uip
5.77 =
8 of 10 Rev 0
Qu for out-off plane bending moment
Q
uop
2.5 4.5 0.2 + ( )
2.6
+ := Q
uop
4.12 =
ii) Ultimate capacity of chord
C
1ax
0.3 := C
2ax
0.0 := C
3ax
0.8 :=
Chord Coefficients
C
1b
0.20 := C
2b
0.0 := C
3b
0.40 :=
Nominal loads in the chord M
cIP
10756 kN m := M
cOP
5495 kN m := P
c
1929 kN :=
Equivalent Moment
M
c
M
cIP
2
M
cOP
2
+ :=
M
c
12078 kN m =
Yield Axial Capacity of chord
P
y
D
L
T
eff
F
y
:= P
y
277364 kN =
Plastic moment capacity of
chord
M
p
D
L
2
T
eff
F
y
:= M
p
179312 kN m =
Factor of Safety joint capacity FS 1.6 :=
iii) Estimation of Qf for axial, inplane and out-off plane bending moment
Applied Load effect AA FS
P
c
P
y
\
|
|
.
2
FS
M
c
M
p
\
|
|
.
2
+ := AA 0.11 =
Qf for axial load Q
fax
1 C
1ax
FS P
c
P
y
|
\
|
|
.
+ C
2ax
FS M
c
M
p
|
\
|
|
.
C
3ax
AA
2
:=
Q
fax
1 =
Qf for inplane bending moment
Q
fip
1 C
1b
FS P
c
P
y
|
\
|
|
.
+ C
2b
FS M
c
M
p
|
\
|
|
.
C
3b
AA
2
:=
Q
fip
1 =
Qf for out-off plane
bending moment Q
fop
1 C
1b
FS P
c
P
y
|
\
|
|
.
+ C
2b
FS M
c
M
p
|
\
|
|
.
C
3b
AA
2
:=
Q
fop
1 =
iv) Estimation of allowable axial, inplane and out-off plane bending moment capacity
Allowable Axial load P
ac
Q
uax
Q
fax
F
y
T
eff
2
FS sin ( )
:=
P
ac
61265.8 kN =
Effective Total length of can L
c
3 m :=
L
c
3m =
Can length reduction factor r
L
c
2.5 D
L
0.9 s if
4 3 ( ) L
c
1.5 D
L
0.9 > if
:=
r 0.59 =
Actual capacity including the
can length effect
P
a
r 1 r ( )
T
n
T
L
|
\
|
|
.
2
+
(
(
(
P
ac
:= P
a
42666 kN =
9 of 10 Rev 0
Allowable inplane bending
moment
M
aIP
Q
uip
Q
fip
F
y
T
eff
2
D
T
FS sin ( )
:=
M
aIP
24007 kN m =
Allowable out-off plane
bending moment
M
aOP
Q
uop
Q
fop
F
y
T
eff
2
D
T
1.6 sin ( )
:=
M
aOP
17154 kN m =
v) Interaction between axial, inplane and out-off plane bending moment
Axial Capacity of shear plate P
S
0.6 F
y
r
s
0.5 D
T
+
( )
T
S
:= P
S
29950 kN =
Combined interaction ratio of
axial and bending effects
UC
P
VI
P
a
P
S
+
( )
M
A_op
M
aOP
|
\
|
|
.
+
M
A_ip
M
aIP
|
\
|
|
.
2
+ :=
UC 0.87 =
10 of 10 Rev 0
Você também pode gostar
- Calculation Sheet: Padeye Calculations LoadsDocumento15 páginasCalculation Sheet: Padeye Calculations Loadsshani5573Ainda não há avaliações
- TQ-0305-R00 - Calculo Estrutura PDFDocumento4 páginasTQ-0305-R00 - Calculo Estrutura PDFPeterson MagroAinda não há avaliações
- Padeye DolphinDocumento38 páginasPadeye DolphinMuhammad FadelAinda não há avaliações
- Padeye Design CheekDocumento1 páginaPadeye Design CheekPawan ShettyAinda não há avaliações
- Eff - RD V.eff V.eff V.eff V, Eff V.eff: OK!!! OK!!! 1.0 OK!!!Documento2 páginasEff - RD V.eff V.eff V.eff V, Eff V.eff: OK!!! OK!!! 1.0 OK!!!ChangHangWingAinda não há avaliações
- Padeye Design AnalysisDocumento8 páginasPadeye Design AnalysisMyatmyat SwewinAinda não há avaliações
- 2L5x3x1/2LLBB: #N/A #N/A #N/ADocumento1 página2L5x3x1/2LLBB: #N/A #N/A #N/ARaza AidanAinda não há avaliações
- PT Gunanusa Utama Fabricators: Calculation SheetDocumento27 páginasPT Gunanusa Utama Fabricators: Calculation SheetriandiAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Analysis of 67m3 Above Ground Storage TankDocumento16 páginasStructural Analysis of 67m3 Above Ground Storage TankTech DesignAinda não há avaliações
- BOX Sec-Beam-Column-AiscDocumento6 páginasBOX Sec-Beam-Column-AiscWintun73Ainda não há avaliações
- Design Lifting Hook Plate LiftingDocumento3 páginasDesign Lifting Hook Plate LiftingSaravan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Cargo acceleration calculation sheetDocumento2 páginasCargo acceleration calculation sheetiw2fualAinda não há avaliações
- Wind Pressure Calculation As per SP-1275Documento7 páginasWind Pressure Calculation As per SP-1275Siva baalanAinda não há avaliações
- Padeye Check SttandardDocumento36 páginasPadeye Check SttandardRiandi HartartoAinda não há avaliações
- Padeye .5MT CHKDocumento12 páginasPadeye .5MT CHKDhanraj VasanthAinda não há avaliações
- Lifting LugDocumento5 páginasLifting LugFarid Tata100% (1)
- Lashing Lug Round Bar Design: 1. GeneralDocumento3 páginasLashing Lug Round Bar Design: 1. GeneralinnovativekarthiAinda não há avaliações
- Section Properties: Design of Padeye As Per Aisc 360-2005Documento5 páginasSection Properties: Design of Padeye As Per Aisc 360-2005Fadil WimalaAinda não há avaliações
- Lifting Lug Load Capacity Vs Crack Length CalculationDocumento26 páginasLifting Lug Load Capacity Vs Crack Length CalculationMohamed NkAinda não há avaliações
- Pin Base ModuleDocumento16 páginasPin Base ModuleMd Ahsanul KabirAinda não há avaliações
- 8" (200A) SCH.80: A 106 Gr.B/EQ A 36 / EQDocumento3 páginas8" (200A) SCH.80: A 106 Gr.B/EQ A 36 / EQRakeshAinda não há avaliações
- Trunnion 6 TonDocumento3 páginasTrunnion 6 TonEngr Khurram Jaan RamayAinda não há avaliações
- Corbel and NibDocumento17 páginasCorbel and NibCatherine Mohanji GeraAinda não há avaliações
- #754 v-3103 Spreader & Lifting 60 DegreeDocumento12 páginas#754 v-3103 Spreader & Lifting 60 DegreeHafizi HZnumismatic100% (1)
- Sfex Pad Eyes Calculations 35T - 32MMDocumento1 páginaSfex Pad Eyes Calculations 35T - 32MMJohn Rom CabadonggaAinda não há avaliações
- 10T SWL Spreader Bar R2-Fos2.0Documento8 páginas10T SWL Spreader Bar R2-Fos2.0Snr Designer JayaAinda não há avaliações
- Calculation Note Stabbing Guide Design Design Code Check:Api RP 2A Check For Tubular Ø 323.9 X 12.70 Due To Boatlanding InstallationDocumento8 páginasCalculation Note Stabbing Guide Design Design Code Check:Api RP 2A Check For Tubular Ø 323.9 X 12.70 Due To Boatlanding InstallationSai SushankAinda não há avaliações
- Pad Eye Connected To Bottom PieceDocumento7 páginasPad Eye Connected To Bottom PieceAsaru Deen0% (1)
- Spreader Bar3 - L.9 M-CertificationDocumento10 páginasSpreader Bar3 - L.9 M-CertificationsiagiandobahAinda não há avaliações
- API WSD Punch CodeCheckDocumento7 páginasAPI WSD Punch CodeCheckKhải TrươngAinda não há avaliações
- AISC 13th Slip Critical Bolt Capacity ASDDocumento1 páginaAISC 13th Slip Critical Bolt Capacity ASDdantevariasAinda não há avaliações
- Section A: 2.1. Sling Design Load and SelectionDocumento30 páginasSection A: 2.1. Sling Design Load and SelectionThomas StephenAinda não há avaliações
- Round Bar Suppot Plate Design CalculationDocumento3 páginasRound Bar Suppot Plate Design CalculationinnovativekarthiAinda não há avaliações
- PadeyeDocumento14 páginasPadeyeMarshall Minggat AmpiAinda não há avaliações
- API 650 Pipe Column DesignDocumento4 páginasAPI 650 Pipe Column DesignJoselito CalagosAinda não há avaliações
- Slam Force Checks for Jacket Walkway MembersDocumento7 páginasSlam Force Checks for Jacket Walkway MembersSai SushankAinda não há avaliações
- EMBEDMENT CALCULATIONDocumento5 páginasEMBEDMENT CALCULATIONMWKELIOLAAinda não há avaliações
- R D H W FW: Design of Tailing LugDocumento2 páginasR D H W FW: Design of Tailing LugvpjagannaathAinda não há avaliações
- Padeye PATIDocumento43 páginasPadeye PATIbayu_23RAinda não há avaliações
- Design Base Plate For I Beam - Bottom BracketDocumento1 páginaDesign Base Plate For I Beam - Bottom BracketCon CanAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Stage Lifting & Transportation AX 010915Documento95 páginas1st Stage Lifting & Transportation AX 010915Fauzan Rusmayadi ReharderAinda não há avaliações
- MB 400 Base PlateDocumento3 páginasMB 400 Base PlatePeace Rain100% (1)
- Beams in bending: Tension cracks and stress diagramsDocumento23 páginasBeams in bending: Tension cracks and stress diagramsHarold Jackson MtyanaAinda não há avaliações
- Lifting Analysis Report - Mahadi KurniawanDocumento31 páginasLifting Analysis Report - Mahadi KurniawanDian SasAinda não há avaliações
- Wing Plate BucklingDocumento2 páginasWing Plate BucklingSai SushankAinda não há avaliações
- Padeye - 01Documento9 páginasPadeye - 01ramAinda não há avaliações
- DANA-Technical Note (TN)Documento8 páginasDANA-Technical Note (TN)Samsul Imran BahromAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Section Modulas CalculationDocumento18 páginasSample Section Modulas CalculationShamik ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- 21.65 Kips/bolt Shear Strength Controls: Section at ADocumento3 páginas21.65 Kips/bolt Shear Strength Controls: Section at ASuneesh PAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Pad Eye 10T SWL-modifDocumento8 páginasStandard Pad Eye 10T SWL-modifrustamriyadiAinda não há avaliações
- Dog Plate & Tubular Support Subsea Template DesignDocumento4 páginasDog Plate & Tubular Support Subsea Template DesignAkhmad Syahroni100% (1)
- WE-5-2 Fin Plate ConnectionDocumento10 páginasWE-5-2 Fin Plate ConnectionPedro AlmeidaAinda não há avaliações
- RC Slab Crack Width Calculation According to ACI350-06 & ACI224R-01Documento6 páginasRC Slab Crack Width Calculation According to ACI350-06 & ACI224R-01Sureshbabu NarayanasamyAinda não há avaliações
- Bab Iii: Re-Design Dan Hasil Perhitungan Horizontal Pressure VesselDocumento36 páginasBab Iii: Re-Design Dan Hasil Perhitungan Horizontal Pressure VesselTri AgungAinda não há avaliações
- Beam Column Web ConnectionsDocumento9 páginasBeam Column Web Connectionsmsiddiq1Ainda não há avaliações
- Calc Sheet Design PadeyeDocumento8 páginasCalc Sheet Design PadeyeFernando Humberto100% (1)
- Deck Plate Timoshenko TheoreyDocumento4 páginasDeck Plate Timoshenko TheoreyPradeep ChitluriAinda não há avaliações
- Pad-Eye MainDocumento8 páginasPad-Eye MainPradeep ChitluriAinda não há avaliações
- Column SpliceDocumento6 páginasColumn SplicedudoodooAinda não há avaliações
- ENGI 8673 Subsea Pipeline Engineering Lecture 17 ExampleDocumento3 páginasENGI 8673 Subsea Pipeline Engineering Lecture 17 ExampleThyago de LellysAinda não há avaliações
- Submarine DesignDocumento5 páginasSubmarine Designnallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment - 3 & 4Documento2 páginasAssignment - 3 & 4nallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- Submarine DesignDocumento5 páginasSubmarine Designnallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- Submarine DesignDocumento5 páginasSubmarine Designnallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- Submarine DesignDocumento5 páginasSubmarine Designnallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- Submarine DesignDocumento5 páginasSubmarine Designnallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment 5 - Y-Joint FatigueDocumento5 páginasAssignment 5 - Y-Joint Fatiguenallay17050% (1)
- Module 2 - Pile Group Effect (Compatibility Mode)Documento46 páginasModule 2 - Pile Group Effect (Compatibility Mode)nallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- Drilling and Well ConstructionDocumento36 páginasDrilling and Well ConstructionMarcio Nascimento BezerraAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Offshore Structures for EngineersDocumento20 páginasDesign of Offshore Structures for Engineersnallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- VanifestDocumento8 páginasVanifestnallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- Marginal Field Development Concepts (Compatibility Mode)Documento17 páginasMarginal Field Development Concepts (Compatibility Mode)nallay1705100% (1)
- Wednesday, April 26, 2006, 03:08 PM: Page 1 of 17 F:/Angola/New/OUT PUT/Breasting Dolphin/BD Final - AnlDocumento17 páginasWednesday, April 26, 2006, 03:08 PM: Page 1 of 17 F:/Angola/New/OUT PUT/Breasting Dolphin/BD Final - Anlnallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- College RankDocumento6 páginasCollege RankThirumalai TrendchaserAinda não há avaliações
- Pile Soil InteractionDocumento250 páginasPile Soil Interactionnallay1705100% (3)
- Wind LoadsDocumento4 páginasWind Loadsnallay17050% (1)
- Clay Skin FrictionDocumento5 páginasClay Skin Frictionnallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- Presentation 1Documento2 páginasPresentation 1nallay1705Ainda não há avaliações
- Testbanks ch24Documento12 páginasTestbanks ch24Hassan ArafatAinda não há avaliações
- SEMICONDUCTORS AssignmentDocumento8 páginasSEMICONDUCTORS AssignmentMaryam MuneebAinda não há avaliações
- Employee Engagement A Case Study at IVRCL-1Documento7 páginasEmployee Engagement A Case Study at IVRCL-1Anonymous dozzql7znKAinda não há avaliações
- Sieve Shaker: Instruction ManualDocumento4 páginasSieve Shaker: Instruction ManualinstrutechAinda não há avaliações
- Postnatal Assessment: Name Date: Age: D.O.A: Sex: Hospital: Marital Status: IP .NoDocumento11 páginasPostnatal Assessment: Name Date: Age: D.O.A: Sex: Hospital: Marital Status: IP .NoRadha SriAinda não há avaliações
- Cinema 4D ShortcutsDocumento8 páginasCinema 4D ShortcutsAnonymous 0lRguGAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Deviation IntroductionDocumento3 páginasStandard Deviation IntroductionShyam ShresthaAinda não há avaliações
- Modul-Document Control Training - Agus F - 12 Juli 2023 Rev1Documento34 páginasModul-Document Control Training - Agus F - 12 Juli 2023 Rev1vanesaAinda não há avaliações
- National Advisory Committee For AeronauticsDocumento36 páginasNational Advisory Committee For AeronauticsSamuel ChristioAinda não há avaliações
- Benjie Reyes SbarDocumento6 páginasBenjie Reyes Sbarnoronisa talusobAinda não há avaliações
- WhatsoldDocumento141 páginasWhatsoldLuciana KarajalloAinda não há avaliações
- 2019-10 Best Practices For Ovirt Backup and Recovery PDFDocumento33 páginas2019-10 Best Practices For Ovirt Backup and Recovery PDFAntonius SonyAinda não há avaliações
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The DronesDocumento43 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of The DronesVysual ScapeAinda não há avaliações
- Trading Course DetailsDocumento9 páginasTrading Course DetailsAnonymous O6q0dCOW6Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 Writing. Exercise 1Documento316 páginasUnit 1 Writing. Exercise 1Hoài Thương NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- ULN2001, ULN2002 ULN2003, ULN2004: DescriptionDocumento21 páginasULN2001, ULN2002 ULN2003, ULN2004: Descriptionjulio montenegroAinda não há avaliações
- Cianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogDocumento1 páginaCianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogMaier MariaAinda não há avaliações
- Ca. Rajani Mathur: 09718286332, EmailDocumento2 páginasCa. Rajani Mathur: 09718286332, EmailSanket KohliAinda não há avaliações
- Username: Password:: 4193 Votes 9 Days OldDocumento6 páginasUsername: Password:: 4193 Votes 9 Days OldΘώμηΜπουμπαρηAinda não há avaliações
- IELTS Vocabulary ExpectationDocumento3 páginasIELTS Vocabulary ExpectationPham Ba DatAinda não há avaliações
- Imaging Approach in Acute Abdomen: DR - Parvathy S NairDocumento44 páginasImaging Approach in Acute Abdomen: DR - Parvathy S Nairabidin9Ainda não há avaliações
- Ana White - PLANS - A Murphy Bed YOU Can Build, and Afford To Build - 2011-03-03Documento20 páginasAna White - PLANS - A Murphy Bed YOU Can Build, and Afford To Build - 2011-03-03Ahmad KamilAinda não há avaliações
- Bandung Colonial City Revisited Diversity in Housing NeighborhoodDocumento6 páginasBandung Colonial City Revisited Diversity in Housing NeighborhoodJimmy IllustratorAinda não há avaliações
- Chicago Electric Inverter Plasma Cutter - 35A Model 45949Documento12 páginasChicago Electric Inverter Plasma Cutter - 35A Model 45949trollforgeAinda não há avaliações
- Single-Phase Induction Generators PDFDocumento11 páginasSingle-Phase Induction Generators PDFalokinxx100% (1)
- Obiafatimajane Chapter 3 Lesson 7Documento17 páginasObiafatimajane Chapter 3 Lesson 7Ayela Kim PiliAinda não há avaliações
- TransistorDocumento1 páginaTransistorXhaAinda não há avaliações
- USA V BRACKLEY Jan6th Criminal ComplaintDocumento11 páginasUSA V BRACKLEY Jan6th Criminal ComplaintFile 411Ainda não há avaliações
- Childrens Ideas Science0Documento7 páginasChildrens Ideas Science0Kurtis HarperAinda não há avaliações
- ROM Flashing Tutorial For MTK Chipset PhonesDocumento5 páginasROM Flashing Tutorial For MTK Chipset PhonesAriel RodriguezAinda não há avaliações