Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
United Nations Brundtland Report: Venn Diagram of Economic Sustainability
Enviado por
Mousumi MajumdarDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
United Nations Brundtland Report: Venn Diagram of Economic Sustainability
Enviado por
Mousumi MajumdarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
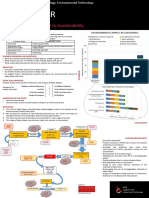
In 1987, the United Nations released the Brundtland Report, which included what is now one of the most
widely recognised definitions: "Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." It contains within it two key concepts:
the concept of 'needs', in particular the essential needs of the world's poor, to which overriding priority should be given; and
the idea of limitations imposed by the state of technology and social organization on the environment's ability to meet present and future needs." Venn diagram of Economic Sustainability
The sustainability entails that the local economies are economically viable, environmentally sound and socially responsible. To achieve this it requires intra-sectoral participation to determine community needs and to implement innovative and appropriate solutions. There are variety of sources, approaches and techniques to successfully develop key aspects of their local economies on a sustainable basis. In this paper we will be discussing about financial inclusion being one of the key approach towards economic sustainability.
Agriculture and Food Systems Community efforts can preserve agricultural land, encourage sustainable agricultural practices, support local food producers, and facilitate the production and distribution of locally produced food through farmer's markets and cooperative food buying programs. This section presents examples of whole systems approaches to sustainable agriculture. Fisheries Aquatic wildlife play a major role in sustaining healthy marine and freshwater ecosystems. It is therefore important that communities associated with fisheries and aquatic ecosystems responsibly manage these resources. Community participation can provide support for sound management practices and remedial programs, as well as for persons and industries engaged in commercial and recreational fishing. Forestry and Wood Products Trees are important for both urban and rural ecosystems. Mature trees maintain desirable microclimates and shelter wildlife. Trees also have economic value as a raw material used in producing paper, buildings, furniture, and other wood products. Examples of communities balancing these environmental and economic considerations are in this section. Manufacturing and Industry Economically healthy businesses and industries with minimal environmental impact on communities should be encouraged. Communities should work to attract and support such industries and to reduce or eliminate negative impacts from existing industries. New approaches are explored in this section. Small Business Small businesses are sources of employment and providers and consumers of goods and services that sustain the local economy. Their operation should support the local ecology, minimize energy use and waste, and utilize recycled products and materials. Examples are in this section. Technology Technological advances in business, health, education, and the environment provide new opportunities for communities. More information products are available, and some may have environmental implications. Communities must be current and guide their economies accordingly. This section provides examples. Economics and Finance Residents from all segments of the community can play a role in the future of their local economy. Working together, business and government leaders, local non-profit organizations, and citizen groups can analyze needs and resources and guide the economy. Local financial institutions can invest in sustainable community initiatives. Examples of innovative approaches are in this section. Urban/Rural Economic Ties It is in the interest of urban and rural residents to work together in mutually supportive ways. In this section are examples of cooperative efforts in land preservation, sustainable agriculture, growth management, appropriate development of rural resources, improved trading and tourism, and development of low-impact regional planning and transportation systems.
Reference: World Commission on Environment and Development. "Our Common Future, Chapter 2: Towards Sustainable Development". Un-documents.net. Retrieved 2011-09-28.
Economic sustainability is the term used to identify various strategies that make it possible to utilize available resources to best advantage. The idea is to promote usage of those resources that is both efficient and responsible, and likely to provide long-term benefits. In the case of a business operation, economic sustainability calls for using resources so that the business continues to function over a number of years, while consistently returning a profit. In most scenarios, the measure of economic sustainability is presented in monetary terms.
Você também pode gostar
- Proposal For School Feeding ProgramDocumento3 páginasProposal For School Feeding Programremyuntalan86% (73)
- Philippines Pathway to SustainabilityDocumento2 páginasPhilippines Pathway to SustainabilityJo Traven AzueloAinda não há avaliações
- Education in A Multilingual WorldDocumento5 páginasEducation in A Multilingual WorldSandro JonesAinda não há avaliações
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Working in GroupsDocumento7 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of Working in GroupsAnastancius Ariel MacuacuaAinda não há avaliações
- Jiamini Community ReportDocumento20 páginasJiamini Community Reportlex tecAinda não há avaliações
- Capability StatementDocumento9 páginasCapability StatementacolrainAinda não há avaliações
- Building A More Complete Theory of Sustainable Supple Chain Management Using Case Studies of 10 Exemplars PDFDocumento20 páginasBuilding A More Complete Theory of Sustainable Supple Chain Management Using Case Studies of 10 Exemplars PDFjoannakamAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER I KyleDocumento13 páginasCHAPTER I KyleCresiel Pontijon100% (1)
- Pelayo ManuscriptDocumento26 páginasPelayo ManuscriptqwertyAinda não há avaliações
- Gawad KalingaDocumento7 páginasGawad Kalingaeya_iAinda não há avaliações
- Batho PrinciplesDocumento3 páginasBatho PrinciplesKebadabing100% (2)
- Urban Governance, Voice and Poverty in The Developing WorldDocumento240 páginasUrban Governance, Voice and Poverty in The Developing WorldV. L.Ainda não há avaliações
- MBA - Total Quality ManagementDocumento40 páginasMBA - Total Quality ManagementJignesh PatelAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Economic DevelopmentDocumento2 páginasWhat Is Economic DevelopmentNna Yd UJAinda não há avaliações
- A Study of Housing Conditions, Public Health Regulations On Housing and Their Health Implications in Lagos NigeriaDocumento34 páginasA Study of Housing Conditions, Public Health Regulations On Housing and Their Health Implications in Lagos NigeriaFavour Chukwuelesie100% (1)
- Media and CorruptionDocumento20 páginasMedia and CorruptionPankaj AdhagaleAinda não há avaliações
- Dialogue ReportDocumento17 páginasDialogue ReportFrancisco SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Mainstreaming Ethics and Professionalism in The Civil Service Week 6 SlidesDocumento50 páginasMainstreaming Ethics and Professionalism in The Civil Service Week 6 Slidestilahunthm100% (1)
- Social Policy in A Development Context (2004)Documento42 páginasSocial Policy in A Development Context (2004)Camille Mangay-ayamAinda não há avaliações
- Role of local gov't in tourismDocumento27 páginasRole of local gov't in tourismCharles DeanAinda não há avaliações
- The Effectiveness of The Local Governance Performance Management System (LGPMS) in Improving Governance in The Municipality of San RafaelDocumento10 páginasThe Effectiveness of The Local Governance Performance Management System (LGPMS) in Improving Governance in The Municipality of San RafaelapjeasAinda não há avaliações
- Minnow Brook IIIDocumento1 páginaMinnow Brook IIIsunishsugunan100% (5)
- Chapter One: 1.1 Background of The StudyDocumento14 páginasChapter One: 1.1 Background of The Studypercepshan100% (1)
- Government - NGO (GO-NGO) Collaboration: Regional Focus - BenefitDocumento6 páginasGovernment - NGO (GO-NGO) Collaboration: Regional Focus - Benefittasfaan100% (1)
- Leadership and GovernanceDocumento26 páginasLeadership and GovernanceyousafAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Point Socio Economic AgendaDocumento1 página10 Point Socio Economic AgendaCharlene Lyra SaacAinda não há avaliações
- From Dependency to Sustainability: A Case Study on the Economic Capacity Development of the Ok Tedi Mine-area CommunityNo EverandFrom Dependency to Sustainability: A Case Study on the Economic Capacity Development of the Ok Tedi Mine-area CommunityAinda não há avaliações
- General Management - Managing in A Global EnvironmentDocumento22 páginasGeneral Management - Managing in A Global EnvironmentDr Rushen SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Coomer - Three Modes of InquiryDocumento4 páginasCoomer - Three Modes of InquiryNina NaguyevskayaAinda não há avaliações
- Sustainable Development PPT by Sagar 10CDocumento12 páginasSustainable Development PPT by Sagar 10CSeema DayalAinda não há avaliações
- Poverty DriversDocumento48 páginasPoverty DriversvjAinda não há avaliações
- Research Methodology of NokiaDocumento3 páginasResearch Methodology of NokiaRAJ0% (1)
- Government Regulation and DeregulationDocumento9 páginasGovernment Regulation and DeregulationIan Jasper P. MongoteAinda não há avaliações
- Ethics and Social ResponsibilityDocumento7 páginasEthics and Social ResponsibilitysamrulezzzAinda não há avaliações
- Wastewater Report 2017Documento198 páginasWastewater Report 2017mirzaAinda não há avaliações
- How Covid-19 Changed Consumer HabitsDocumento1 páginaHow Covid-19 Changed Consumer HabitsApril MacmuffinAinda não há avaliações
- Quality Service in Tourism and HospitalityDocumento7 páginasQuality Service in Tourism and HospitalityGelo MamitagAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Civil Society in RTI LAWDocumento56 páginasRole of Civil Society in RTI LAWlalitdadwal100% (1)
- Four Ethical Issues of The Information AgeDocumento7 páginasFour Ethical Issues of The Information AgeMithinga NarzaryAinda não há avaliações
- Batho PeleDocumento26 páginasBatho PeleNundkishor100% (1)
- The Human Development ParadigmDocumento9 páginasThe Human Development ParadigmZia Mahmud Khan RatulAinda não há avaliações
- Public Sector EthicsDocumento15 páginasPublic Sector EthicsJones Lyndon Crumb DamoAinda não há avaliações
- Human DevelopmentDocumento15 páginasHuman DevelopmentKhurram MallAinda não há avaliações
- War On DrugsDocumento5 páginasWar On DrugsBE ALAinda não há avaliações
- Business and Society Stakeholders Ethics Public Policy 14th Edition Lawrence Test Bank PDFDocumento10 páginasBusiness and Society Stakeholders Ethics Public Policy 14th Edition Lawrence Test Bank PDFkhera5654100% (1)
- Using The StrategiesDocumento18 páginasUsing The StrategiesLukMan DoangAinda não há avaliações
- Capabilities ApproachDocumento22 páginasCapabilities ApproachShahriar SayeedAinda não há avaliações
- Article of Ethics and ValuesDocumento15 páginasArticle of Ethics and Valuesapi-300198447Ainda não há avaliações
- Eportfolio Reflection PaperDocumento2 páginasEportfolio Reflection Paperapi-298236337Ainda não há avaliações
- SALE Research ProposalDocumento65 páginasSALE Research ProposalLouise Joseph PeraltaAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of Globalization On National SecurityDocumento7 páginasImpact of Globalization On National SecurityDit Sap MarjAinda não há avaliações
- Ethical ConflictDocumento8 páginasEthical ConflictFouzia Kamal SarkerAinda não há avaliações
- Managing Software Projects: Stakeholders AnalysisDocumento38 páginasManaging Software Projects: Stakeholders AnalysisVarundeep SinghalAinda não há avaliações
- Organization CultureDocumento4 páginasOrganization CultureUmesh AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento26 páginasChapter 1Baby KhorAinda não há avaliações
- A Conceptual Model of Corporate Moral DevelopmentDocumento12 páginasA Conceptual Model of Corporate Moral DevelopmentmirianalbertpiresAinda não há avaliações
- A Study On Employee Attrition With Special Reference To Software Company in Bangalore CityDocumento27 páginasA Study On Employee Attrition With Special Reference To Software Company in Bangalore CityCHEIF EDITORAinda não há avaliações
- CSR Essay FinalDocumento6 páginasCSR Essay FinalGiuliana Triviño100% (1)
- Management as Atheoretical: Exploring Superstitious PracticesDocumento5 páginasManagement as Atheoretical: Exploring Superstitious PracticesAlex Corporal100% (1)
- Electronic Government - Concepts, Tools, Methodologies, and Applications - Introductory ChapterDocumento35 páginasElectronic Government - Concepts, Tools, Methodologies, and Applications - Introductory ChapterСтаменић МаринаAinda não há avaliações
- CSR in Global ContextDocumento24 páginasCSR in Global ContextJulie Ann PiliAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of Small and Medium Enterprises On Economic Growth and DevelopmentDocumento5 páginasImpact of Small and Medium Enterprises On Economic Growth and DevelopmentBabak HedayatiAinda não há avaliações
- Om4 c01 StudentDocumento37 páginasOm4 c01 StudentTammy Yah0% (1)
- Imagine A Better World PDFDocumento278 páginasImagine A Better World PDFNILSCRIBAinda não há avaliações
- AGRI INSTITUTE FEASABILITY REPORT - DRAFT Nyasha's InputDocumento101 páginasAGRI INSTITUTE FEASABILITY REPORT - DRAFT Nyasha's InputAntony MalungaAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges in ForestryDocumento4 páginasChallenges in ForestryTushar JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- B.Sc. Final Project Report (Md. Nazmul Haque, Roll-1295)Documento96 páginasB.Sc. Final Project Report (Md. Nazmul Haque, Roll-1295)nazmul_juAinda não há avaliações
- Annual Report 2016: Aturmaju Resources BerhadDocumento138 páginasAnnual Report 2016: Aturmaju Resources BerhadRichbull TraderAinda não há avaliações
- Modelling of A CHP SOFC System Fed With Biogas From Anaerobic Digestion of Municipal Waste Integrated With Solar Collectors and Storage UnitDocumento8 páginasModelling of A CHP SOFC System Fed With Biogas From Anaerobic Digestion of Municipal Waste Integrated With Solar Collectors and Storage UnitsergiovelasquezgAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Paper1Documento38 páginasConcept Paper1rico lopezAinda não há avaliações
- Poster New FileDocumento1 páginaPoster New FileAntonio de JesusAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Transition Model 2030 - Impact of Sustainable Lifestyle Without Usage of Natural GasDocumento7 páginasEnergy Transition Model 2030 - Impact of Sustainable Lifestyle Without Usage of Natural GasStefan BruinsAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Sustainable Development?: Tweet With Us !!Documento28 páginasWhat Is Sustainable Development?: Tweet With Us !!clara dupitasAinda não há avaliações
- Five Year Strategic Plan For A Hospital ExampleDocumento40 páginasFive Year Strategic Plan For A Hospital ExampleEsteban R. Langlois100% (1)
- ENVIRONMENTAL LAW IN TANZANIA: A REVIEW OF PROGRESS AND CHALLENGESDocumento18 páginasENVIRONMENTAL LAW IN TANZANIA: A REVIEW OF PROGRESS AND CHALLENGESEchannel khpAinda não há avaliações
- MATATO Report 2022-23 Tourism and FinanceDocumento21 páginasMATATO Report 2022-23 Tourism and FinanceMATATOAinda não há avaliações
- Pos Malaysia 2016 PDFDocumento195 páginasPos Malaysia 2016 PDFMohd Razmir Abdul RashitAinda não há avaliações
- A Multidimensional Tourism Carrying Capacity Model - An Empirical ApproachDocumento16 páginasA Multidimensional Tourism Carrying Capacity Model - An Empirical Approachita faristaAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences: Publication Details, Including Instructions For Authors and Subscription InformationDocumento25 páginasCritical Reviews in Plant Sciences: Publication Details, Including Instructions For Authors and Subscription InformationkhajeeAinda não há avaliações
- Mena Regional Water OutlookDocumento529 páginasMena Regional Water OutlookMabrouk AdouaneAinda não há avaliações
- IIML - PGP-SM - Final - PlsBro - 2020-22 - 5th DraftDocumento22 páginasIIML - PGP-SM - Final - PlsBro - 2020-22 - 5th DraftPriyanka MishraAinda não há avaliações
- How Energy Production Affects Populations GrowthDocumento2 páginasHow Energy Production Affects Populations GrowthNJAinda não há avaliações
- Ethics, CSR and Sustainability in International ManagementDocumento29 páginasEthics, CSR and Sustainability in International ManagementAaryaman PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Pratik RM Project ReportDocumento66 páginasPratik RM Project ReportNayan patelAinda não há avaliações
- Seaorbiter en PDFDocumento8 páginasSeaorbiter en PDFowiswellAinda não há avaliações
- Determinants of Sustainability Reporting A Review of Results, TrendsDocumento17 páginasDeterminants of Sustainability Reporting A Review of Results, TrendsramiraliAinda não há avaliações
- Manchester School of Architecture Year Book 2012Documento63 páginasManchester School of Architecture Year Book 2012Khairul AfifAinda não há avaliações
- Readings List and Links PDFDocumento3 páginasReadings List and Links PDFrajendran rAinda não há avaliações
- Canteen Food Waste Disposal - CSRDocumento16 páginasCanteen Food Waste Disposal - CSRVishwanath KrAinda não há avaliações