Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Unit 1 Terms
Enviado por
Jeffrey WangDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Unit 1 Terms
Enviado por
Jeffrey WangDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Unit 1: Nature and Perspectives of Geography
Cartography: The art and science of making maps, including data compilation, layout, and design. Also concerned with the interpretation of mapped patterns Connections: Relationships among people and objects across the barrier of space Contagious diffusion: A type of expansion diffusion in which cultural innovation spreads by person-to person contact, moving wavelike through an area and population without regard to social status Cultural ecology: Broadly defined, the study of the relationships between the physical environment and culture; narrowly (and more commonly) defined, the study of culture as an adaptive system that facilitates human adaptation to nature and environmental change Culture: The sum total of the knowledge, attitudes, and habitual behavior patterns shared and transmitted by the members of a society Density: The quantity of anything (people, buildings, animals, traffic, etc.) per unit area Diffusion: The process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time Distance-Decay: The effects of distance on interaction, generally the greater the distance the less interaction Distribution: The arrangement of something across Earths surface Environmental determinism: The belief that cultures are directly or indirectly shaped by the physical environment Environmental possiblism: the idea that although the environment may be limiting in some aspects, humans have the ultimate power to adjust to their environment Equator: An imaginary east-west line that encircles the globe halfway between the North and South Poles Expansion diffusion: The spread of a feature or trend among people from one area to another in a snowballing process. Formal region: An area in which everyone shares in one or more distinctive characteristics Function region: A region defined by the particular set of activities or interactions that occur within it GIS: Integrated computer programs for handling, processing, and analyzing data specifically referenced to the surface of the earth
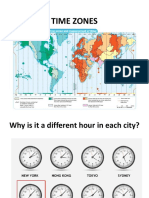
GPS: A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers Hierarchical diffusion: A type of expansion diffusion in which innovations spread from one important person to another or from one urban center to another, temporarily bypassing other persons or rural areas Hearth: The region from which innovative ideas originate International Date Line: An arc that for the most part follows 180 longitude, although it deviates in several places to avoid dividing land areas. When you cross the International Date Line heading east (toward America), the clock moves back 24 hours, or one entire day. When you go west (toward Asia), the calendar moves ahead one day. Latitude: An imaginary line running parallel to the equator that is used to measure distance in degrees north or south from the equator. Longitude: An imaginary line circling the Earth and running through the poles. Used to determine the location of things by measurement of the angular distance, in degrees east or west, from the Prime Meridian Mercator projection: A true conformal cylindrical projection first published in I569, useful for navigation Prime Meridian: An imaginary north-south line of longitude on the Earth grid, passing through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich in London, defined as having a longitude of 0 Projection: The system used to transfer locations from Earths surface to a flat map Relocation diffusion: The spread of a feature or trend through bodily movement of people from one place to another. Remote sensing: The acquisition of data about Earths surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods. Robinson projection: a compromise map projection showing the poles as lines rather than points and more accurately portraying high latitude lands and water to land ratio Scale: Generally, the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole, specifically the relationship between the size of an object on a map and the size of the actual feature on Earths surface Site: The internal physical attributes of a place, including its absolute location, its spatial character and physical setting Situation: The location of a place relative to other places Space-time compression: The reduction in the time it takes to diffuse something to a distant place, as a result of improved communications and transportation systems
Spatial perspective: Observing variations in geographic phenomena across space Stimulus diffusion: A type of expansion diffusion in which a specific trait fails to spread but the underlying idea or concept is accepted Time zones: regions on Earth that have uniform, legally mandated standard times Toponym: The name given to a portion of Earths surface Uneven development: The increasing gap in economic conditions between core and peripheral regions as a result of the globalization of the economy Vernacular region: An area that people believe exists as part of their cultural identity
Você também pode gostar
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Building Geography SkillsDocumento238 páginasBuilding Geography Skillsseyka4100% (9)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- AP Human Geography Chapter 1 NotesDocumento25 páginasAP Human Geography Chapter 1 NotesTeddy Sadowski67% (9)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Sepharial - The Silver KeyDocumento72 páginasSepharial - The Silver KeyVincent Sampieri95% (19)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Nautical Almanac 2022 PDFDocumento386 páginasNautical Almanac 2022 PDFtonyAinda não há avaliações
- Destination Geography English 19 July PDFDocumento92 páginasDestination Geography English 19 July PDFVintonius Raffaele PRIMUSAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Geography EdtDocumento73 páginasIntroduction To Geography EdtJv PeridoAinda não há avaliações
- Science 7 Quarter 4 Module 1Documento15 páginasScience 7 Quarter 4 Module 1Daisy Soriano PrestozaAinda não há avaliações
- Geography NotesDocumento20 páginasGeography NotesBnb Times100% (1)
- Basic Principles of Geological and Thematic MappingDocumento109 páginasBasic Principles of Geological and Thematic MappingSouvik ChakrabortyAinda não há avaliações
- Navigation I: STCW Table A-II/1Documento205 páginasNavigation I: STCW Table A-II/1Bernard Barrita100% (2)
- Science 7 Q4 SLM1Documento15 páginasScience 7 Q4 SLM1Melanie Tagudin Trinidad100% (1)
- Science - Grade 7Documento10 páginasScience - Grade 7kris hicomAinda não há avaliações
- Et02340001 PDC 3928Documento60 páginasEt02340001 PDC 3928Patricia Pato77% (13)
- Time ZoneDocumento16 páginasTime ZoneJobins KjAinda não há avaliações
- John Rennie Short-Global Dimensions - Space, Place and The Contemporary World (2004)Documento192 páginasJohn Rennie Short-Global Dimensions - Space, Place and The Contemporary World (2004)desain jalAinda não há avaliações
- Locating the Philippines Using Latitude and LongitudeDocumento9 páginasLocating the Philippines Using Latitude and LongitudeLianne Marie CabanginAinda não há avaliações
- Our Nation Our World - WPS OfficeDocumento14 páginasOur Nation Our World - WPS OfficeAlla Marie SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Navi112 ReviewerDocumento3 páginasNavi112 ReviewerXander Rubia jr100% (1)
- International Boundary StudyDocumento11 páginasInternational Boundary Studyinbox9999Ainda não há avaliações
- Dwnload Full International-Financial-Management-13th-Edition-Madura-Test-Bank PDFDocumento35 páginasDwnload Full International-Financial-Management-13th-Edition-Madura-Test-Bank PDFlucaehplee100% (9)
- EarthDocumento24 páginasEarthAmilinda Amsar100% (1)
- GEO Handout W5 U2 L1-4Documento6 páginasGEO Handout W5 U2 L1-4Choy DanAinda não há avaliações
- ViewpointsDocumento4 páginasViewpointsMg BhoneAinda não há avaliações
- Bennis Desrivieres: Pearson 7-8 Connected For SuccessDocumento66 páginasBennis Desrivieres: Pearson 7-8 Connected For SuccessRex Lemuel AndesAinda não há avaliações
- Topic I - Im - Intro To GeoDocumento8 páginasTopic I - Im - Intro To GeoHobiAinda não há avaliações
- Cu31924030898344 PDFDocumento582 páginasCu31924030898344 PDFVictor R Satriani0% (1)
- Vi Cbse Worksheet KeyDocumento35 páginasVi Cbse Worksheet KeyPuthiya ElangoAinda não há avaliações
- Presidential Decree No. 1596Documento2 páginasPresidential Decree No. 1596Rommel Mancenido LagumenAinda não há avaliações
- Latitudes and Longitudes: Earth's Coordinate System ExplainedDocumento10 páginasLatitudes and Longitudes: Earth's Coordinate System ExplainedshivanAinda não há avaliações
- Navigation Course PDFDocumento45 páginasNavigation Course PDFSeamen 777Ainda não há avaliações