Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Engineering Mechanics
Enviado por
Ugender SingarapuDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Engineering Mechanics
Enviado por
Ugender SingarapuDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ENGINEERING MECHANICS KAKATIYA UNIVERSITY WARANGAL
1 (a) What is cone friction (b) Explain polar moment of inertia with few examples. (c) State and prove parrallegram of forces. (d) State and discuss Newtons laws of gravitation (e) Explain the law of conservation of momentum with examples. (f) Differentiate between coeffient of restitution and period of restitution.
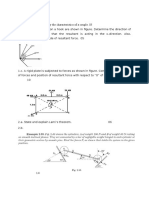
1. A strut AB attached to the face of a vertical wall at A by a spherical hinge stands Perpendicular to the wall and is supported by two guy wires, as shown in Figure1. At B, in a plane parallel to the wall, two forces P and Q acts as shown, Q being horizontal and P, vertical. Find the axial forces produced in the members if P = 500 N and Q = 1000 N.
Figure 1: 2. (a) Find the least horizontal force P to start motion of any part of the system of three blocks resting upon one another as shown in figure2. The weights of the blocks are A = 3000N, B = 1000N, C = 2000N. Between A and B, = 0.3, between B and C, = 0.2 and between C and the ground = 0.1.
Figure 2:
(b) A block overlying a 100 wedge on a horizontal floor and leaning against a vertical wall and weighing 1500N is to be raised by applying a horizontal force to the wedge. Assuming the coefficient of friction to be 0.3, determine the minimum horizontal force to be applied to raise the block. {As shown in the Figure3}
Figure 3: 4. (a) Differentiate between polar moment of inertia and product of inertia (b) Find the moment of inertia and radius of gyration about the horizontal centroidal axis. {As shown in the Figure4}
Figure 4:
5. Determine the mass moment of inertia of a thin equilateral triangular plate of mass m and thickness t about the axis perpendicular to the plane of the plate and passing through the mass center. Base width= b and height of vertex above base= h. Density of material is w.
7. If Wa:Wb:Wc is in the ratio of 3:2:1 , find the accelerations of the blocks A, B, and C. Assume that the pulleys are weightless. {As shown in the Figure5}
Figure 5:
8. A weight of 10N attached to a spring oscillates at a frequency of 60 oscillations per minute. If the maximum amplitude is 30mm, find the tension induced in the spring. Also find the spring constant and the maximum velocity in the spring.
PAPER-2 2. (a) Explain the principles of operation of a screw-jack with a neat sketch.
(b) Outside diameter of a square threaded spindle of a screw Jack is 40mm. The screw pitch is 10mm. If the coefficient of friction between the screw and the nut is 0.15, neglecting friction between the nut and collar, determine i. Force required to be applied at the screw to raise a load of 2000N ii. The efficiency of screw jack iii. Force required to be applied at pitch radius to lower the same load of 2000N and
iv. Efficiency while lowering the load v. What should be the pitch for the maximum efficiency of the screw and what should be the value of the maximum efficiency. 4. (a) Deduce an equation for moment of inertia of right circular solid cone about its generating axes of base radius R and altitude h (b) Locate the centroid of a shaded area as shown in figure4b.
5. (a) Show that the moment of inertia of a thin circular ring of mass M and mean radius R with respect to its geometric axis is MR2. (b) Find out the mass moment of inertia of a right circular cone of base radius R and mass M about the axis of the cone. 6. (a) Ram and Rahim are sitting in cars A and B respectively. The cars are 300m apart and at rest. Ram starts the car and moves towards B with an acceleration of 0.5m/s2. After three seconds , Rahim starts his car towards A with an acceleration of 1m/s2. Calculate the time and point at which two cars meet with respect to A.
(b) A projectile is fired at a speed of 800 m/s at an angle of elevation of 500 from the horizontal. Neglecting the resistance of air, calculate the distance of the point along the inclined surface at which the projectile will strike the inclined surface which makes an angle of 150 with the horizontal.
7. (a) A homogeneous sphere of radius of a=100mm and weight W=100N can rotate freely about a diameter. If it starts from rest and gains, with constant angular acceleration, an angular speed n=180rpm, in 12 revolutions, find the acting moment. .
(b) A block starts from rest fromA . If the coefficient of friction between all surfaces of contact is 0.3, find the distance at which the block stop on the horizontal plane. Assume the magnitude of velocity at the end of slope is same as that at the beginning of the horizontal plane. {As shown in the Figure7b}
Figure 7b 8. A clock with a seconds pendulum is running correct time at a place where the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81m/s2. Find the length of the pendulum. This clock is taken at a place where the acceleration due to gravity is 9.80m/s2. Find how much the clock will loose or gain in a day at this place?
PAPER-3
1. (a) A system of forces consists of i. Force P1 = 3i + 5j 6k acting through point (2,1,-3) ii. Force P2 = 5i 4j + 3k acting through point (1,4,2) and a moment M = 20i 35j + 60k. The forces are in Newton (N) units, distances in m units and the moment in N-m units. Calculate i. The component of the resultant forces and its magnitude ii. The total moment of the system about the origin O. iii. The moment of the system about the line through O drawn in the 1stoctant which makes angles of 650 and 750 with X and Y axes respectively. (b) Write the Equilibrium equations for concurrent force system in space.
2. The three flat blocks are positioned on the 300 incline as shown in Figure2, and a force P parallel to the incline is applied to the middle block. The upper block is prevented from moving by a wire which attaches it to the fixed support. The coefficient of static friction for each of the three pairs of mating surfaces is shown.Determine the maximum value which P may have before any slipping takes place.
Figure 2 4. (a) Explain the terms: i. Moment of inertia ii. Polar moment of inertia iii. Product of inertia. (b) Locate the centroid of the shaded area as shown in the Figure4b.
5. The area shown in figure5 is revolved about x axis to form a homogeneous solid of revolution of mass m. Determine the mass moment of inertia of the solid about x-axis. 6. (a) A small grinding wheel is attached to the shaft of an electric motor which has
a rated speed of 3000r.p.m . When the power is turned on, the unit reaches its rated speed in 5secs and when the power is turned off, the unit comes to rest in 60secs. Assuming the acceleration to be uniform, find the number of revolutions that the motor executes i. in reaching its rated speed and ii. to come to rest. (b) A cord is wrapped around a wheel which is initially at rest as shown in (figure6b) Force is applied to the cord and is gives an acceleration a=6t m/s2where t is in seconds. Determine i. The angular velocities of the wheel ii. The angular position of radial line OP as a function of time.
7. (a) A homogeneous solid cylinder of weight 100 N whose axis is horizontal rotates about its axis, in frictionless bearings under the action of the weight of a 10N block which is carried by a rope wrapped around the cylinder. What will be angular velocity of cylinder two seconds after the motion starts? Assume the diameter of cylinder as 100cm.
(b) A block of mass 5Kg resting on a 300 inclined plane is released. The block after travelling a distance of 0.5m along the inclined plane hits a spring of stiffness 15N/cm. Find the maximum compression of spring. Assume coefficient of friction between the block and the inclined plane is 0.2. As shown in the Figure 7b
8. A pendulum having a time period of 1 sec. is installed in a lift. Determine its time period when (a) the lift is moving upwards with an acceleration of g/10 (b) the lift is moving downwards with an acceleration of g/20
Você também pode gostar
- Engineering MechanicsDocumento18 páginasEngineering MechanicsSiva ChidambaramAinda não há avaliações
- I B.Tech Regular Examinations Engineering MechanicsDocumento12 páginasI B.Tech Regular Examinations Engineering MechanicsGanesh YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment Questions For All UnitsDocumento10 páginasAssignment Questions For All UnitsPiyush BhandariAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering MechanicsDocumento37 páginasEngineering Mechanicser_paramjeetgillAinda não há avaliações
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- nov/dec 2005 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂Documento14 páginasnov/dec 2005 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂badboy_rockssAinda não há avaliações
- R05010105-APPLIED-MECHANICS apr/may 2007 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂™Documento12 páginasR05010105-APPLIED-MECHANICS apr/may 2007 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂™badboy_rockssAinda não há avaliações
- r05010302 Engineering MechanicsDocumento11 páginasr05010302 Engineering MechanicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTAAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics EquationsDocumento16 páginasEngineering Mechanics Equationsgovind4ever5Ainda não há avaliações
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Nota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Engineering Mechanics Question BankDocumento15 páginasEngineering Mechanics Question BankKrishna MurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Steam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70No EverandSteam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Ainda não há avaliações
- 1429r05210804 Engineering MechanicsDocumento11 páginas1429r05210804 Engineering MechanicsSaivenkat PenuguduruAinda não há avaliações
- Applied MechanicsDocumento13 páginasApplied Mechanicsapi-26349602100% (1)
- Explain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorNo EverandExplain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorAinda não há avaliações
- Part B question BankDocumento9 páginasPart B question BankSriram SrinivasanAinda não há avaliações
- GE6253-Engineering Mechanics Qustion BankDocumento20 páginasGE6253-Engineering Mechanics Qustion Banknanthakumar91100% (1)
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsNo EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- 1Documento5 páginas1reddiAinda não há avaliações
- C Nsa192004 Pages:4Documento4 páginasC Nsa192004 Pages:4TMX PoketooAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics Question PaperDocumento0 páginaEngineering Mechanics Question PaperBala SubramanianAinda não há avaliações
- Em QPDocumento3 páginasEm QPkb210538Ainda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics Question BankDocumento15 páginasEngineering Mechanics Question BankSatyanarayanaAinda não há avaliações
- rr10105 Applied MechanicsDocumento13 páginasrr10105 Applied MechanicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTAAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering MechanicsDocumento15 páginasEngineering Mechanicsapi-26349602100% (1)
- r5100105 Applied MechanicsDocumento2 páginasr5100105 Applied MechanicssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Rr10105 Applied MechanicsDocumento13 páginasRr10105 Applied MechanicsSrinivasa Rao GAinda não há avaliações
- Ge8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFDocumento8 páginasGe8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFThamizh gomathiAinda não há avaliações
- 152AH052019Documento4 páginas152AH052019చిమ్ముల సందీప్ రెడ్డిAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet F Ch6Documento3 páginasWorksheet F Ch6PeewoopAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics DADocumento5 páginasMechanics DAMihir AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Questions in Engineering MechanicsDocumento4 páginasQuestions in Engineering MechanicsprashmceAinda não há avaliações
- TSM101 (SS2019) - Set ADocumento9 páginasTSM101 (SS2019) - Set ANgeedup DhojeeAinda não há avaliações
- Model-EM-29 5 13Documento2 páginasModel-EM-29 5 13rkumaravelanAinda não há avaliações
- EM Coaching QBDocumento10 páginasEM Coaching QBsaravananAinda não há avaliações
- KTU Engineering Mechanics Exam QuestionsDocumento4 páginasKTU Engineering Mechanics Exam QuestionsBalmukund KumarAinda não há avaliações
- NR 10105 Engineering MechanicsDocumento13 páginasNR 10105 Engineering MechanicsVijay PrakashAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment I: Statics of Particles and Rigid BodiesDocumento8 páginasAssignment I: Statics of Particles and Rigid BodiesmAinda não há avaliações
- rr100105 Applied MechanicsDocumento1 páginarr100105 Applied MechanicssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank & Bit BankDocumento20 páginasQuestion Bank & Bit BankKomma HemaAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics March 2014r13Documento14 páginasEngineering Mechanics March 2014r13api-248483124Ainda não há avaliações
- r5100105 Applied MechanicsDocumento2 páginasr5100105 Applied MechanicssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Infant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Documento4 páginasInfant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Robinston Jeyasingh KAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento5 páginasAssignment 1Mansimran Singh-iit GuwahatiAinda não há avaliações
- 07a1ec09 Engineering MechanicsDocumento4 páginas07a1ec09 Engineering Mechanicsأشرف عليAinda não há avaliações
- 07a10101 Applied MechanicsDocumento11 páginas07a10101 Applied MechanicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTAAinda não há avaliações
- T1403 Mom Ii 24.6.14Documento2 páginasT1403 Mom Ii 24.6.14STUDENTS OF DOE CUSATAinda não há avaliações
- April 2011 2008Documento7 páginasApril 2011 2008Piyush BhandariAinda não há avaliações
- Engg Mechanics Question Bank UNIT-1Documento10 páginasEngg Mechanics Question Bank UNIT-1Thiyagarajan GurusamyAinda não há avaliações
- Model QSTN Paper 1-Be100Documento5 páginasModel QSTN Paper 1-Be100nanduAinda não há avaliações
- Btes103 203 em QBDocumento10 páginasBtes103 203 em QBSurajAinda não há avaliações
- Vedantu Atomic StructureDocumento306 páginasVedantu Atomic StructureD. JAYA100% (1)
- Current Sensing Techniques and Pulse Current Transformer Design for DC-DC ConvertersDocumento9 páginasCurrent Sensing Techniques and Pulse Current Transformer Design for DC-DC ConvertersKathir VelAinda não há avaliações
- Laser Light Controlling SystemDocumento121 páginasLaser Light Controlling SystemJanvi Mayank JainAinda não há avaliações
- Nikola Tesla's 1890 Patent for a Pyromagneto-Electric GeneratorDocumento3 páginasNikola Tesla's 1890 Patent for a Pyromagneto-Electric GeneratorbcampbellAinda não há avaliações
- BLDC MotorsDocumento45 páginasBLDC Motorswicked_not_meAinda não há avaliações
- 11KV Capacitor Bank - SPECDocumento7 páginas11KV Capacitor Bank - SPECNasaii RayAinda não há avaliações
- Cable Systems - ETAPDocumento10 páginasCable Systems - ETAPJoeDabidAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 9: Electronics: 9. 1: Uses of The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) 9.1.1: Thermionic EmissionDocumento35 páginasChapter 9: Electronics: 9. 1: Uses of The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) 9.1.1: Thermionic Emissionfizbro100% (2)
- Voltage Disturbances: Standard EN 50160Documento16 páginasVoltage Disturbances: Standard EN 50160tatacpsAinda não há avaliações
- Elevator Commissioning Guide: Quickly Complete Installation & TestingDocumento30 páginasElevator Commissioning Guide: Quickly Complete Installation & TestingtoufikAinda não há avaliações
- Eee 205-W2Documento9 páginasEee 205-W2mahamudul hasanAinda não há avaliações
- History-Triumph of AC. 2. The Battle of The Currents PDFDocumento4 páginasHistory-Triumph of AC. 2. The Battle of The Currents PDFAshish MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- Vectors and Equilibrium: Key ConceptsDocumento2 páginasVectors and Equilibrium: Key ConceptshassanAinda não há avaliações
- Emb 2 NTN PDFDocumento9 páginasEmb 2 NTN PDFRicky SitorusAinda não há avaliações
- System Earthing Methods and TechniquesDocumento70 páginasSystem Earthing Methods and TechniquesBasudev PatraAinda não há avaliações
- Application of A Matrix Converter For The Power Control of A Variable-Speed Wind-Turbine Driving A Doubly-Fed Induction GeneratorDocumento6 páginasApplication of A Matrix Converter For The Power Control of A Variable-Speed Wind-Turbine Driving A Doubly-Fed Induction GeneratorchetanAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Specifications For Door Trim Panel Assembly: PDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionDocumento15 páginasTechnical Specifications For Door Trim Panel Assembly: PDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionDiego CamargoAinda não há avaliações
- Shindengen: (F8F60VX2)Documento13 páginasShindengen: (F8F60VX2)VictorManuelBernalBlancoAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Fundamentals Module BreakdownDocumento665 páginasElectrical Fundamentals Module BreakdownJimmy CheungAinda não há avaliações
- 1-5/8" CELLFLEX Lite Low-Loss Foam-Dielectric Coaxial Cable: LCF158-50JLDocumento2 páginas1-5/8" CELLFLEX Lite Low-Loss Foam-Dielectric Coaxial Cable: LCF158-50JLPaulo AzevedoAinda não há avaliações
- Transmission QbankDocumento20 páginasTransmission QbankjascnjAinda não há avaliações
- 6n1 SPK Prot Rev 1.2B - With Basic Function How It WorksDocumento34 páginas6n1 SPK Prot Rev 1.2B - With Basic Function How It Worksអំភ្លី សំលេងAinda não há avaliações
- Control Ratio CalculationDocumento15 páginasControl Ratio CalculationJayanth KolliAinda não há avaliações
- Review of Primary Voltage and FrequencyDocumento11 páginasReview of Primary Voltage and FrequencyDeepak GehlotAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple-Choice Questions on Waves and Wave PropertiesDocumento3 páginasMultiple-Choice Questions on Waves and Wave PropertiesGaurav SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Irrigation Engineering and Hydraulic Structure Santosh Kumar GargDocumento165 páginasIrrigation Engineering and Hydraulic Structure Santosh Kumar GargAnand RatnaAinda não há avaliações
- Communicating Measurement Centre Type M230Documento8 páginasCommunicating Measurement Centre Type M230javed shaikh chaandAinda não há avaliações
- 3.three Ph. Circuits PDocumento22 páginas3.three Ph. Circuits Parchanabelge1Ainda não há avaliações
- CH2 Describing Motion, Kinematics in One DimensionDocumento38 páginasCH2 Describing Motion, Kinematics in One DimensionEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- AP World History: Modern Premium, 2024: Comprehensive Review with 5 Practice Tests + an Online Timed Test OptionNo EverandAP World History: Modern Premium, 2024: Comprehensive Review with 5 Practice Tests + an Online Timed Test OptionNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- MCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsNo EverandMCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementAinda não há avaliações
- Digital SAT Reading and Writing Practice Questions: Test Prep SeriesNo EverandDigital SAT Reading and Writing Practice Questions: Test Prep SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- GMAT Foundations of Verbal: Practice Problems in Book and OnlineNo EverandGMAT Foundations of Verbal: Practice Problems in Book and OnlineAinda não há avaliações
- AP Computer Science A Premium, 2024: 6 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo EverandAP Computer Science A Premium, 2024: 6 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeAinda não há avaliações
- Medical English Dialogues: Clear & Simple Medical English Vocabulary for ESL/EFL LearnersNo EverandMedical English Dialogues: Clear & Simple Medical English Vocabulary for ESL/EFL LearnersAinda não há avaliações
- GMAT Prep 2024/2025 For Dummies with Online Practice (GMAT Focus Edition)No EverandGMAT Prep 2024/2025 For Dummies with Online Practice (GMAT Focus Edition)Ainda não há avaliações
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- The LSAT Law School Admission Test Study Guide Volume I - Reading Comprehension, Logical Reasoning, Writing Sample, and Analytical Reasoning Review Proven Methods for Passing the LSAT Exam With ConfidenceNo EverandThe LSAT Law School Admission Test Study Guide Volume I - Reading Comprehension, Logical Reasoning, Writing Sample, and Analytical Reasoning Review Proven Methods for Passing the LSAT Exam With ConfidenceAinda não há avaliações
- AP English Language and Composition Premium, 2024: 8 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo EverandAP English Language and Composition Premium, 2024: 8 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeAinda não há avaliações
- Digital SAT Prep 2024 For Dummies: Book + 4 Practice Tests Online, Updated for the NEW Digital FormatNo EverandDigital SAT Prep 2024 For Dummies: Book + 4 Practice Tests Online, Updated for the NEW Digital FormatAinda não há avaliações
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationAinda não há avaliações
- Finish What You Start: The Art of Following Through, Taking Action, Executing, & Self-DisciplineNo EverandFinish What You Start: The Art of Following Through, Taking Action, Executing, & Self-DisciplineNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (94)
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesNo EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Digital SAT Preview: What to Expect + Tips and StrategiesNo EverandDigital SAT Preview: What to Expect + Tips and StrategiesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyNo EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyAinda não há avaliações
- AP Q&A Psychology, Second Edition: 600 Questions and AnswersNo EverandAP Q&A Psychology, Second Edition: 600 Questions and AnswersAinda não há avaliações
- The Ultimate UCAT Collection: 3 Books In One, 2,650 Practice Questions, Fully Worked Solutions, Includes 6 Mock Papers, 2019 Edition, UniAdmissions Aptitude Test, UniAdmissionsNo EverandThe Ultimate UCAT Collection: 3 Books In One, 2,650 Practice Questions, Fully Worked Solutions, Includes 6 Mock Papers, 2019 Edition, UniAdmissions Aptitude Test, UniAdmissionsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesNo EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (14)
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryNo EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryAinda não há avaliações
- 50 Successful Harvard Medical School EssaysNo Everand50 Successful Harvard Medical School EssaysAinda não há avaliações
- AP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo EverandAP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeAinda não há avaliações
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersNo EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (12)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisNo EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)