Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Analysis of Beams and Compound Beams
Enviado por
Mangesh kevadkarDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Analysis of Beams and Compound Beams
Enviado por
Mangesh kevadkarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Engineering Mechanics (Statics) Ex. 7.
6 :
7-1
Analysis of Beams & Compound Beams
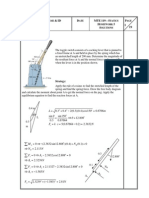
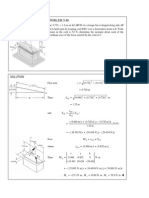
A weight W rests on beam AB of negligible weight. The string connecting the load is passing over a smooth pulley. Show that reaction at A is W (l a) (l + a) . (Refer Fig. Ex. 7.6).
Fig. Ex. 7.6 Soln. : Draw F.B.D of block and beam. (Refer Fig. Ex. 7.6(a)). For block : For beam :
Fy = 0 Fy = 0
T W + RC = 0 (1) T RC + Ay = 0
RC = (W T) Substituting value of RC We get, Ay = RC T = (W T) T Ay = W 2T (2)
MA = 0
RC a T l = 0 RC a = T l (W T) a = T l Wa = T (a + l) Wa T = a+l (3)
Substituting this value in Equation (2) Wa Ay = W 2 a + l
[ ]
= Ay Reaction at A RA
W(a + l) 2 Wa Wa + Wl = a+l a+l W (l a ) = l+a W (l a ) = proved. l+a
Fig. Ex. 7.6(a)
Ex.7.8 : A beam 10 m long is loaded as shown in Fig. Ex.7.8. Find reactions at supports.
Fig. Ex.7.8 Soln. : Here given loading is a varying load so to find out total load and its point of application (centroid) using integration method.
Engineering Mechanics (Statics)
7-2
Analysis of Beams & Compound Beams
Fig. Ex.7.8(a)
Fig. Ex.7.8(b)
Select an elementary strip of thickness dx as shown in Fig. Ex.7.8(a). The area of strip dA = y dx 10 10 x4 Total area bounded = y dx = (100 + 0.3 x3 ) dx = 100 x + 0.3 (4) 0 0 The distance of centroid is given by, Ax
10 0
= 100 (10) +
0.3 (10)4 = 1750 N 4
10 10 = e1 dA = x y dx = (100 x + 0.3 x4) dx x
[100 x2 + 0.3 x5 ]
2 5
10 0
= 100
(10)2 (10)5 2 + 0.3 5
Ax = 11000 m3 11000 x = 1750 = 6.285 m from y-axis Conditions of equilibrium, [Refer Fig. Ex.7.8(b)].
MA = 0 Fy = 0
RB 10 1750 6.285 = 0 RB = 1100 N RA = 650 N Ans. RA + RB = 1750
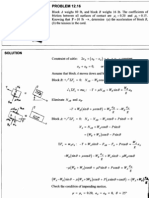
Ex.7.13 : Determine the reaction components at A, B, D, E and F. Also find value of load W if reaction at support G is found to be 25 kN. Refer Fig. Ex.7.13.
Fig. Ex.7.13
Engineering Mechanics (Statics) Soln. : F.B.D. of beams
7-3
Analysis of Beams & Compound Beams
Fig. Ex.7.13(a) Since beam does not carry any horizontal force, all horizontal components are equal to zero. Ax = Dx = 0 Consider beam GF Use,
MF = 0
(RE 3) + (6 4) (25 5) = 0 RE = 33.67 kN 25 + RF 6 RE = 0 RF = 6 + 33.67 25 RF = 14.67 kN
Fy = 0
Consider beam ED, Use,
MD = 0 RE 7 + (7.5 5) + RB 1 = 0
( 33.67 7) + (7.5 5) + RB = 0 RB = 198.19 kN
Fy = 0
RE + Dy 7.5 RB = 0 33.67 + Dy 7.5 198.19 = 0 Dy = 172.02 kN
Consider beam CA, Use,
MA = 0 (36 2) 12 (RB 4) + W (6) = 0
72 12 198.19 4 + 6W = 0 W = 122.13 kN W 36 + RB + Ay = 0 122.13 36 + 198.19 + Ay = 0 Ay = 40.06 kN Ay = 40.06 kN
Fy = 0
Engineering Mechanics (Statics)
7-4
Analysis of Beams & Compound Beams
Ex.7.17 : When closed vertical sluice gate is supported along the lines AA and BB normal to the plane of Fig. Ex.7.17. It is subjected to water pressure from sides. If w = 1000 kg/m3 for water find reaction at A and B. Soln. : Water pressure 1 2 1 P1 = 2 wh1 = 2 1000 9.81 42 = 78480 N = 78.48 kN acting at 4/3 m from B 1 2 1 P2 = 2 wh2 = 2 1000 9.81 (6)2 = 176580 N = 176.58 kN acting at 6/3 = 2 m from B Apply conditions of equilibrium Fig. Ex.7.17
MB = 0
P1 (4/3) + P2 (2) RA (6) = 0 78.48
(4) + 176.58 (2) = 6 R 3
RA = 41.46 kN
Ans.
Fx = 0
RA + P1 + RB P2 = 0 RB = P2 P1 RA = 176.58 78.48 41.46 RB = 56.64 kN Ans. Fig. Ex.7.17(a)
Analysis of Beams & Compound Beams Ends.
Você também pode gostar
- Data Mininig ProjectDocumento28 páginasData Mininig ProjectKarthikeyan Manimaran67% (3)
- Geh 6676 Power System Stabilizer For EX2100 Excitation ControlDocumento48 páginasGeh 6676 Power System Stabilizer For EX2100 Excitation ControlSupolAinda não há avaliações
- Column Interaction Diagram Lecture21Documento58 páginasColumn Interaction Diagram Lecture21kzlondon50% (2)
- MTE119 - Solutions Hw5Documento19 páginasMTE119 - Solutions Hw5Amy TrevinoAinda não há avaliações
- Solution To Problems On Design of Machine Elements 4th Edition - Virgil M Faires, Roy M Wingren (Problem Book)Documento962 páginasSolution To Problems On Design of Machine Elements 4th Edition - Virgil M Faires, Roy M Wingren (Problem Book)Ahmed Zawad Shovon89% (66)
- Examples - PhysicsDocumento8 páginasExamples - Physicslaila1001Ainda não há avaliações
- Diseño de Elementos de Máquinas - V. M. Faires (4ta Edición) SolucionDocumento641 páginasDiseño de Elementos de Máquinas - V. M. Faires (4ta Edición) SolucionCristian Lizaraso Pérez100% (1)
- Math 10 Week 2Documento10 páginasMath 10 Week 2Myla MillapreAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1-Nota Fizik MatrikulasiDocumento13 páginasChapter 1-Nota Fizik MatrikulasiSyahmi Abdullah100% (9)
- Equilibrium of A Particle Equilibrium of A ParticleDocumento4 páginasEquilibrium of A Particle Equilibrium of A ParticleAloysius AlipioAinda não há avaliações
- KAK ME 2 1 EM Set 3Documento15 páginasKAK ME 2 1 EM Set 3Srinu Arnuri100% (1)
- PROBLEM 2.56: SolutionDocumento5 páginasPROBLEM 2.56: SolutionKeilly CasanovaAinda não há avaliações
- Nov-Dec - 2014Documento20 páginasNov-Dec - 2014rkumaravelan4137100% (1)
- Type I: Examples Based On Components in SpaceDocumento13 páginasType I: Examples Based On Components in SpaceAmeya1823100% (1)
- R (Ax) 30 KipsDocumento9 páginasR (Ax) 30 KipsRey Kevin OrtuosteAinda não há avaliações
- Example For Ch.4Documento14 páginasExample For Ch.4Weaven YauAinda não há avaliações
- Equilibrium in 3D NewDocumento32 páginasEquilibrium in 3D NewTuhafeni HailekaAinda não há avaliações
- Review Problems Chapter 4Documento13 páginasReview Problems Chapter 4Alberto RamirezAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 55555Documento25 páginasChap 55555Jean Zyrelle AuronAinda não há avaliações
- HW3 SolutionDocumento5 páginasHW3 SolutiondcasaliAinda não há avaliações
- Statics of Particles.Documento24 páginasStatics of Particles.Nagendran NatarajanAinda não há avaliações
- 114 119Documento9 páginas114 119Carlos Moran CepedaAinda não há avaliações
- Forces in SpaceDocumento64 páginasForces in SpaceKellie BrownAinda não há avaliações
- Phys245 Notes PDFDocumento117 páginasPhys245 Notes PDFfuckitAinda não há avaliações
- ENGR-1100 Introduction To Engineering AnalysisDocumento34 páginasENGR-1100 Introduction To Engineering AnalysisHappy Formidable SmileAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetics of Rectilinear MotionDocumento12 páginasKinetics of Rectilinear MotionAyon SenguptaAinda não há avaliações
- Homework DDS Exo CorrigéDocumento60 páginasHomework DDS Exo CorrigéYacine OAAinda não há avaliações
- Be First Year Engineering Semester 1 2019 December Engineering Mechanics Emrev 2019'c' SchemeDocumento43 páginasBe First Year Engineering Semester 1 2019 December Engineering Mechanics Emrev 2019'c' Schemesinghsitturaj78Ainda não há avaliações
- CH 12 AaDocumento9 páginasCH 12 Aafastidious_5Ainda não há avaliações
- Statics Assignment IIIDocumento5 páginasStatics Assignment IIISaud AlnaderAinda não há avaliações
- ch2 116 118Documento10 páginasch2 116 118Gonçalo CruzeiroAinda não há avaliações
- Design For Simple StressesDocumento131 páginasDesign For Simple Stresseskhudhayer1970Ainda não há avaliações
- 46 55Documento10 páginas46 55Carlos Moran CepedaAinda não há avaliações
- Concurrent Force Systems (II) : ENGR 221 January 22, 2003Documento45 páginasConcurrent Force Systems (II) : ENGR 221 January 22, 2003tolgaenesAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Exam: Topic VII: StaticsDocumento6 páginasDiagnostic Exam: Topic VII: StaticsAnonymous dntnvrKO2100% (1)
- Physics: Work Practice ProblemsDocumento21 páginasPhysics: Work Practice Problemsekdp224Ainda não há avaliações
- QB-em-1 - Mem202Documento19 páginasQB-em-1 - Mem202rahuljaiswal1931Ainda não há avaliações
- ACEDILLA LEVY - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesDocumento10 páginasACEDILLA LEVY - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesKennyAinda não há avaliações
- p11 AnsDocumento8 páginasp11 AnsAnonymous ncBe0B9bAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 22Documento62 páginasLecture 22adilafzalkhan4264Ainda não há avaliações
- Analisis Struktur C2Documento18 páginasAnalisis Struktur C2Hazyema HarunAinda não há avaliações
- Short Columns Subject To Axial Load and BendingDocumento13 páginasShort Columns Subject To Axial Load and BendingHerbert PalacioAinda não há avaliações
- 325 - 12-07 - Elasticity - 43-51Documento7 páginas325 - 12-07 - Elasticity - 43-51Bradley NartowtAinda não há avaliações
- TANAREKEMberly - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesDocumento10 páginasTANAREKEMberly - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesjonathanAinda não há avaliações
- Solution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Documento18 páginasSolution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Gulshan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiNo EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiAinda não há avaliações
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesAinda não há avaliações
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyAinda não há avaliações
- Difference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsNo EverandDifference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsAinda não há avaliações
- An Extension of Casson's Invariant. (AM-126), Volume 126No EverandAn Extension of Casson's Invariant. (AM-126), Volume 126Ainda não há avaliações
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesAinda não há avaliações
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Management - IDocumento7 páginasEngineering Management - IMangesh kevadkarAinda não há avaliações
- EM-I University QP PDFDocumento26 páginasEM-I University QP PDFMangesh kevadkarAinda não há avaliações
- Em-I (MCQ) PDFDocumento12 páginasEm-I (MCQ) PDFMangesh kevadkarAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 6 - SA 1 PDFDocumento18 páginasUnit 6 - SA 1 PDFMangesh kevadkarAinda não há avaliações
- SM-III University QP PDFDocumento29 páginasSM-III University QP PDFMangesh kevadkarAinda não há avaliações
- Sm-Iii (MCQ) PDFDocumento12 páginasSm-Iii (MCQ) PDFMangesh kevadkar100% (1)
- Engineering Management Solapur University - SyllabusDocumento6 páginasEngineering Management Solapur University - SyllabusMangesh kevadkarAinda não há avaliações
- Strasky 2004 CBCDocumento17 páginasStrasky 2004 CBCMangesh kevadkarAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment-I - LSM - Steel IntroDocumento1 páginaAssignment-I - LSM - Steel IntroMangesh kevadkarAinda não há avaliações
- Some of Website On Energy ConservationDocumento1 páginaSome of Website On Energy ConservationMangesh kevadkarAinda não há avaliações
- SimuPlot5 ManualDocumento25 páginasSimuPlot5 Manualikorishor ambaAinda não há avaliações
- 6.6 Notes - Trapezoids and KitesDocumento12 páginas6.6 Notes - Trapezoids and KitesAbrar DirdasawiAinda não há avaliações
- Anova 1Documento11 páginasAnova 1vijay2101Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 (Laplace Transform)Documento14 páginasChapter 3 (Laplace Transform)EmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- Flint Water Crisis Hypothesis Test: Dan LulsegedDocumento12 páginasFlint Water Crisis Hypothesis Test: Dan LulsegedDtwaAinda não há avaliações
- Calculate The Gradients of The Following Linear Graphs. Remember, GradientDocumento10 páginasCalculate The Gradients of The Following Linear Graphs. Remember, GradientSuman JoyAinda não há avaliações
- Jaime Sandoval Real EstateDocumento3 páginasJaime Sandoval Real EstateJaime R. SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- How To Calculate P90 (Or Other PXX) PV Energy Yield Estimates - SolargisDocumento8 páginasHow To Calculate P90 (Or Other PXX) PV Energy Yield Estimates - SolargisgoyalmanojAinda não há avaliações
- A K 2 0 0 e R R o R M e S S A G e e X P L A N A T I o N SDocumento142 páginasA K 2 0 0 e R R o R M e S S A G e e X P L A N A T I o N SYatno GomiAinda não há avaliações
- Newsletter April 3-7Documento1 páginaNewsletter April 3-7api-245696657Ainda não há avaliações
- Amsler WearDocumento223 páginasAmsler WearmarictomAinda não há avaliações
- Math 6 DLP 1 - Giving Meaning of Exponent and Base Giving The Value of Numbers Involving Exponent PDFDocumento9 páginasMath 6 DLP 1 - Giving Meaning of Exponent and Base Giving The Value of Numbers Involving Exponent PDFZyreen Joy ServanesAinda não há avaliações
- Stat Module 5Documento10 páginasStat Module 5Remar Jhon PaineAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Activity 8 and 9 Class IxDocumento4 páginasLab Activity 8 and 9 Class IxSiddhant NarayanAinda não há avaliações
- Solved Multiple Choice Questions of DataDocumento40 páginasSolved Multiple Choice Questions of Datamini projectAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Letter 001/3/2021: Complex AnalysisDocumento19 páginasTutorial Letter 001/3/2021: Complex AnalysisKyle MaharajAinda não há avaliações
- Handover Parameter 2GDocumento17 páginasHandover Parameter 2GSon EricAinda não há avaliações
- RM 4Documento37 páginasRM 4RHEALYN GEMOTOAinda não há avaliações
- Resolução Do Capítulo 4 - Equilíbrio de Corpos Rígidos PDFDocumento231 páginasResolução Do Capítulo 4 - Equilíbrio de Corpos Rígidos PDFMalik PassosAinda não há avaliações
- Tax Evasion PDFDocumento34 páginasTax Evasion PDFCristinaZLAinda não há avaliações
- Aristo Zenon Ve Stadyum ParadoksuDocumento21 páginasAristo Zenon Ve Stadyum Paradoksuaysel alagozAinda não há avaliações
- GATE ECE Solved Paper - 2005Documento24 páginasGATE ECE Solved Paper - 2005Shashi KanthAinda não há avaliações
- 0607 QS026 - 2 PDFDocumento7 páginas0607 QS026 - 2 PDFjokydin92Ainda não há avaliações
- How To Draw Block DiagramDocumento6 páginasHow To Draw Block DiagramAbdulrahmanAinda não há avaliações
- CS 132 Discrete Structures in Computer Science Syllabus Spring 2017Documento3 páginasCS 132 Discrete Structures in Computer Science Syllabus Spring 2017Jimmy DoreAinda não há avaliações