Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Environmental Impact Assessment Rev4
Enviado por
Rucha KagneDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Environmental Impact Assessment Rev4
Enviado por
Rucha KagneDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
EIA
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is used to identify the environmental and social impacts of a project prior to decision-making. It aims to predict environmental impacts at an early stage in project planning and design, find ways and means to reduce adverse impacts, shape projects to suit the local environment and present the predictions and options to decision-makers. By using EIA both environmental and economic benefits can be achieved, such as reduced cost and time of project implementation and design, avoided treatment/clean-up costs and impacts of laws and regulations.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Activities involved
Baseline data collection primary and secondary Understanding Project characteristics Superimposing project characteristics on the baseline Prediction of impacts Environmental Management Plans Presenting the report to decision makers
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental components
Land Air Noise Water Ecology Socioeconomic
Environmental Impact Assessment
Land Environment
Location setting (Regional) Location setting (Local) Land Use Pattern Soil characteristics
Environmental Impact Assessment
THE MALANJKHAND MINE in Balaghat district of Madhya Pradesh, in an area that was once forested land on which Adivasis depended.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Air Environment
Reconnaissance Survey Air Quality Topography and meteorology
Wind Temperature and Humidity Rainfall
Environmental Impact Assessment
Air Environment Windrose at site: Max/Min/Mean annual temperature: Frequency of inversion: Frequency of cyclones/tornadoes/cloud burst: Ambient air quality data:
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental Impact Assessment
Noise Sources of Noise and Vibrations Ambient noise level Traffic
Environmental Impact Assessment
Water Environment
Surface water Ground water Surface drainage Sewerage and waste water disposal Water quality
Surface water Ground water
Environmental Impact Assessment
Ecology
Environmental Impact Assessment
Socio economic environment Demographic structure Infrastructure resource base Health status Economy Endemic health problems in the area due to waste water/air/soil borne diseases Health care system existing
Environmental Impact Assessment
Identification and assessment of impacts
Air Environment
Construction phase Operation phase Air quality modelling Modelling results Modelling Assessment of impact
Noise Environment
Environmental Impact Assessment
Identification and assessment of impacts
Water Environment Land Environment Biological Environment Socio-economic Environment Infrastructure
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental impact statement
Air Environment Noise Environment Water Environment Land and Biological Environment Socio-economic Environment Impact Matrix
Environmental Parameters
Development Projects Ports and Harbours Airports
Rapid Transit
Highways Oil/Gas pipelines Significant Impact
Moderate to Significant Impact
Insignificant Impact
Surface Water Quality Air Quality Seismology Erosion Land Quality Fisheries Forests Terrestrial Wildlife Noise Land Use Aesthetics Industries Resettlement Archeological Historical significance Public Health Socio-economic
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental management plan
Formulation of EMP is an important outcome of EIA process Has cost implications, monitoring and audit requirements during project life cycle Typically consists of specific measures (WWTP, APC, Noise barriers, green belt) with details sufficient to enable realistic cost and time estimates EMPs need not mean management of issues alone and could include opportunities for enhancement
Environmental Impact Assessment
Asking pertinent questions to issues
Can the activity related to an issue be eliminated? Or modified? Can be relocated w.r.t. sensitive environmental receptor? Can protection or buffers be provided around sensitive receptors? Combinations of the above effective? Residual issues? Who will remain affected?
Environmental Impact Assessment
Negative impacts may also be linked to mitigation measures, eg. Hazardous waste disposal Systemic view needed. Mitigation measures also need to be screened for impacts
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental management plan
Construction phase Operation phase
Air Environment Noise Environment Water Environment Land Environment Solid Waste Socio-Economic Environment
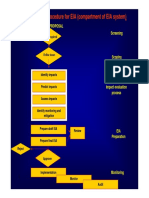
EIA Process in India
Issues with quality of EIA reports
Improper / Inadequate scoping of EIA Consultants not having adequate understanding for developing EIA Cut and paste jobs No checks on competence of EIA consultants No liability for EIA consultants
NABET (National Accreditation Board for Education and Training) Criteria for Registration of EIA Consultant Organizations
Você também pode gostar
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocumento37 páginasEnvironmental Impact AssessmentAbdul KarimAinda não há avaliações
- L 2: Environmental Impact AssessmentDocumento34 páginasL 2: Environmental Impact AssessmentVaidh Prakash ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Eia UnitoDocumento12 páginasEia UnitoFede BrunoAinda não há avaliações
- Element 3 Environmental Impact AssessmentsDocumento6 páginasElement 3 Environmental Impact Assessmentszaigham naqviAinda não há avaliações
- 273 Environmental Impact IevaluacionDocumento95 páginas273 Environmental Impact IevaluacionDiego SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- EIA's role in constructionDocumento29 páginasEIA's role in constructionRachit AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- EIA Environmental SettingDocumento50 páginasEIA Environmental Settingmanjani938Ainda não há avaliações
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) : Project Management CourseDocumento33 páginasEnvironmental Impact Assessment (EIA) : Project Management Courseg.suvoAinda não há avaliações
- InroductionDocumento66 páginasInroductionpraveen.civilAinda não há avaliações
- EIA Case Study of Highway Project WideningDocumento10 páginasEIA Case Study of Highway Project WideningSRUTHI FRANCIS M.Tech Environmental Engineering 2020-2022Ainda não há avaliações
- Training Programme: Environmental Management SystemDocumento23 páginasTraining Programme: Environmental Management SystemChandrakant HalliAinda não há avaliações
- Components of Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) - Environment NotesDocumento8 páginasComponents of Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) - Environment NotesAminullah HamidiAinda não há avaliações
- EIA Scheme-Version 3 - Jun. 2015 - HRDocumento20 páginasEIA Scheme-Version 3 - Jun. 2015 - HRRutuja GameyAinda não há avaliações
- Waste Land ReclamationDocumento23 páginasWaste Land ReclamationTanisha VyasAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Aspects and ObjectivesDocumento4 páginasEnvironmental Aspects and Objectivesum erAinda não há avaliações
- ReportDocumento66 páginasReportMailene UmadhayAinda não há avaliações
- EIA Process GuideDocumento19 páginasEIA Process GuidebbnAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)Documento15 páginasEnvironmental Impact Assessment (EIA)Babu VeeraraghavanAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocumento17 páginasEnvironmental Impact AssessmentRonn ArtajoAinda não há avaliações
- CH 14 Integration Methods MetricsDocumento42 páginasCH 14 Integration Methods MetricsEnviroLandUsePlanAinda não há avaliações
- Rapid Environmental Impact Assessment ToolkitDocumento15 páginasRapid Environmental Impact Assessment ToolkitJakir Hossain TonyAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocumento20 páginasEnvironmental Impact AssessmentDanish RaisAinda não há avaliações
- EIA Lecture for Project Management CourseDocumento33 páginasEIA Lecture for Project Management Courseg4goharAinda não há avaliações
- Concepts of Environmental Impact Assessment (Eia) : Scoping Techniques Baseline Data GenerationDocumento12 páginasConcepts of Environmental Impact Assessment (Eia) : Scoping Techniques Baseline Data GenerationUnigwe Chinanu OdinakaAinda não há avaliações
- EIA Process, IEE, TOR Dr. Wesam Al MadhounDocumento65 páginasEIA Process, IEE, TOR Dr. Wesam Al MadhounTigst Tigst YzachewAinda não há avaliações
- Environment Life Cycle AssessmentDocumento4 páginasEnvironment Life Cycle Assessmentshreya royAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocumento7 páginasEnvironmental Impact AssessmentLyra Mae PeruchoAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Impact Identification MethodologiesDocumento17 páginasEnvironmental Impact Identification MethodologiesRavi Shankar0% (1)
- L1 - Basic ConceptsDocumento67 páginasL1 - Basic Conceptsshivani100% (1)
- Environmental Management Practice in RMG SectorDocumento8 páginasEnvironmental Management Practice in RMG SectorSharif Mrh100% (1)
- Initial Environmental Review (Iee) : DR Zahiruddin Khan Iese-NustDocumento12 páginasInitial Environmental Review (Iee) : DR Zahiruddin Khan Iese-NustMustafa AliAinda não há avaliações
- An Analysis of Environmental Impacts of Various Environmental Aspects For Indian Manufacturing IndustriesDocumento9 páginasAn Analysis of Environmental Impacts of Various Environmental Aspects For Indian Manufacturing IndustriesInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- KYAMBOGO UNIVERSITY BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING PROGRAMME TACKLES ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTIONDocumento14 páginasKYAMBOGO UNIVERSITY BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING PROGRAMME TACKLES ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTIONTrarubo ArimaAinda não há avaliações
- VDB 4333 Chap-3Documento85 páginasVDB 4333 Chap-3Kasturi BSCEAinda não há avaliações
- Environment Quality Management Dbit Kbam PDFDocumento7 páginasEnvironment Quality Management Dbit Kbam PDFSnehal KoliAinda não há avaliações
- EIA - 4 Prediction & MitigationDocumento36 páginasEIA - 4 Prediction & MitigationAsala CosmeticsAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - Environmental Impact AssessmentDocumento8 páginas2 - Environmental Impact Assessmentevrian peruchoAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Impact Assesment and Its AdvantagesDocumento4 páginasEnvironmental Impact Assesment and Its AdvantagesmariyaAinda não há avaliações
- EIA Guide Module 5 Renewable EnergyDocumento190 páginasEIA Guide Module 5 Renewable EnergyAdithya HariprakashAinda não há avaliações
- Little Money Spent On Education, Health Care EtcDocumento5 páginasLittle Money Spent On Education, Health Care Etcsumaiya miliAinda não há avaliações
- Monde JarDocumento19 páginasMonde JarMyra M. DivinagraciaAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental PlanningDocumento11 páginasEnvironmental PlanningZuhair A. RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Economic Evaluation of Environmental ImpactDocumento11 páginasEconomic Evaluation of Environmental ImpactRaquel RossAinda não há avaliações
- EIADocumento43 páginasEIAnp27031990100% (3)
- Environmental Planning & ManagementDocumento17 páginasEnvironmental Planning & ManagementShiva Ramavath100% (1)
- Environmental Impact of Infrastructure: Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaDocumento20 páginasEnvironmental Impact of Infrastructure: Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaAngelli Juelar NaiganAinda não há avaliações
- Sibaram Behera 109BT0020 Department of Biotechnology and Medical EngineeringDocumento20 páginasSibaram Behera 109BT0020 Department of Biotechnology and Medical Engineeringsibaram24Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit3.SEA EIA AQiDocumento56 páginasUnit3.SEA EIA AQiGbenga AdewumiAinda não há avaliações
- Week 10 - Envrionmental AssessmentDocumento50 páginasWeek 10 - Envrionmental Assessmentannapoorna c kAinda não há avaliações
- L.I 1652 0il and Gas GhanaDocumento30 páginasL.I 1652 0il and Gas GhanaSamuel Maclean ArthurAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - I - Basic Concepts of EIADocumento151 páginasUnit - I - Basic Concepts of EIAvadyala kavyaAinda não há avaliações
- Philippine EIA System - Final Na Gyud2Documento9 páginasPhilippine EIA System - Final Na Gyud2James Torres Gonida100% (1)
- RAPID EIA TOOL FOR ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTSDocumento13 páginasRAPID EIA TOOL FOR ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTSnp27031990Ainda não há avaliações
- Environmental Impacts and Aspects Register EngDocumento9 páginasEnvironmental Impacts and Aspects Register EngsjmpakAinda não há avaliações
- ENVE 314 EIADocumento21 páginasENVE 314 EIAAkbey Apaydın100% (1)
- CET415 - M3 - Ktunotes - inDocumento63 páginasCET415 - M3 - Ktunotes - inTheerthaAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Waste Management Solutions Reduce PollutionDocumento4 páginasIndustrial Waste Management Solutions Reduce Pollutionmaryam gullAinda não há avaliações
- Sustainability Studies: Environmental and Energy ManagementNo EverandSustainability Studies: Environmental and Energy ManagementAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Waste Treatment HandbookNo EverandIndustrial Waste Treatment HandbookNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Hazardous Substances and Human Health: Exposure, Impact and External Cost Assessment at the European ScaleNo EverandHazardous Substances and Human Health: Exposure, Impact and External Cost Assessment at the European ScaleAinda não há avaliações
- Pe7 q1 Mod2 Basic-Exercise-ProgramDocumento22 páginasPe7 q1 Mod2 Basic-Exercise-ProgramMark Christian PatricioAinda não há avaliações
- NEWCROSS Site Survey - Rev1Documento37 páginasNEWCROSS Site Survey - Rev1eke23Ainda não há avaliações
- Symposium BullyingDocumento28 páginasSymposium BullyingJackielyn CatallaAinda não há avaliações
- Ward D - Freida McFaddenDocumento239 páginasWard D - Freida McFaddenHassan ZayanAinda não há avaliações
- History + Mission +SWOTDocumento2 páginasHistory + Mission +SWOThangchan_superchibiAinda não há avaliações
- OCI Inventario Obsesivo Compulsivo (Foa, 2002)Documento11 páginasOCI Inventario Obsesivo Compulsivo (Foa, 2002)Margarita100% (1)
- Comm 602 Assignment 1Documento4 páginasComm 602 Assignment 1hamiltjw2Ainda não há avaliações
- Stretching - Anderson, Bob PDFDocumento194 páginasStretching - Anderson, Bob PDFxehupatl100% (6)
- Lesson Plan (Contagion) Vers. 1Documento2 páginasLesson Plan (Contagion) Vers. 1Jabez CabahugAinda não há avaliações
- Table of Contents:: Mariam Tariq L1F07BBAM0060 Nabeela Sattar L1F07BBAM2159 Sana Akbar L1F07BBAM2085Documento9 páginasTable of Contents:: Mariam Tariq L1F07BBAM0060 Nabeela Sattar L1F07BBAM2159 Sana Akbar L1F07BBAM2085Raheem AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- DSMDocumento2 páginasDSMOtilia EmaAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Logbook: Medical Parasitology Department GIT Module 104Documento16 páginasPractical Logbook: Medical Parasitology Department GIT Module 104Kareem DawoodAinda não há avaliações
- Safety Officer Interview NotesDocumento3 páginasSafety Officer Interview Notesaulianur564830100% (3)
- Krav Maga To Empower KidsDocumento7 páginasKrav Maga To Empower KidshectorhugoarAinda não há avaliações
- Cholesteatoma and Congenital Cholesteatoma Important PointsDocumento6 páginasCholesteatoma and Congenital Cholesteatoma Important PointsSuprit Sn100% (1)
- AVJ Ablation Vs CardioversionDocumento6 páginasAVJ Ablation Vs CardioversionAndy CordekAinda não há avaliações
- BoltonDocumento26 páginasBoltonDryashpal SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Guiasgold2023 16235v2.1 Es-Pocket WMVDocumento55 páginasGuiasgold2023 16235v2.1 Es-Pocket WMVFABIO JAVIER BRAVO SALDARRIAGAAinda não há avaliações
- 3 MAIN B February 23Documento13 páginas3 MAIN B February 23Student Access SLMC-IMAinda não há avaliações
- Ohsas 18001Documento36 páginasOhsas 18001santhurkc67% (3)
- 2011 Fyi Report DocumentDocumento110 páginas2011 Fyi Report DocumentSmart Horizons Lifetime Training SolutionsAinda não há avaliações
- Effective Communication for InterpretersDocumento5 páginasEffective Communication for InterpretersRaimundo SousaAinda não há avaliações
- The Use of Glucommanan Flour From Gembili Tuber (Dioscorea Esculenta L.) As Gelling Agent in Chicken SausagesDocumento11 páginasThe Use of Glucommanan Flour From Gembili Tuber (Dioscorea Esculenta L.) As Gelling Agent in Chicken SausagesFadhil IkramAinda não há avaliações
- Bangladesh Labor Code 2006Documento20 páginasBangladesh Labor Code 2006taleb_ctgAinda não há avaliações
- Board 4-CHNDocumento30 páginasBoard 4-CHNKira100% (22)
- Physical Fitness TestDocumento8 páginasPhysical Fitness Testalaskador03Ainda não há avaliações
- Peace Corps Violation of Office of Victim Advocate Clearances by OVA Employee DI-16-0254 WB CommentsDocumento26 páginasPeace Corps Violation of Office of Victim Advocate Clearances by OVA Employee DI-16-0254 WB CommentsAccessible Journal Media: Peace Corps DocumentsAinda não há avaliações
- SelectionList R1 WebDocumento586 páginasSelectionList R1 WebVishakha SutarAinda não há avaliações
- The Dark Triada Personality A Review PDFDocumento18 páginasThe Dark Triada Personality A Review PDFAvengingBrainAinda não há avaliações
- SOP Health Services Management MSCDocumento2 páginasSOP Health Services Management MSCHafiz Mohammad Shuputra50% (2)