Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
The Ideal Gas Law and Gas Stoichiometry Hon)
Enviado por
Camilo RosasDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
The Ideal Gas Law and Gas Stoichiometry Hon)
Enviado por
Camilo RosasDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
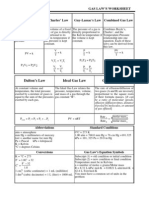
The Ideal Gas Law and Gas Stoichiometry: *Ideal Gas Law Remember molar volume?
? 1 mole of a gas occupies ________ at STP. o STP is: 1 atm, 273 K; 760 mm Hg, 273 K; 101.3 kPa, 273 K We can combine molar volume with Boyles, Charles, and Gay-Lussacs laws to create something called the ideal gas law. A gas is IDEAL when its particles take up no space and have no intermolecular forces between them. The ideal gas law does not deal with changing conditions, but allows us to calculate moles, pressure, volume, or temperature of a gas at specific conditions: these #s: o
PV = nRT
n represents number of moles R is a CONSTANT, called the ideal gas constant. You need to know
R = 0.0821
L atm mol K
R = 8.314
L kPa mol K
Example: Calculate the number of moles of gas contained in a 3.0-L vessel at 3.00 x 102 K with a pressure of 1.50 atm:
Practice problems: 1. Determine the temperature, in celcius, of 2.49 moles of gas contained in a 1.00-L vessel at a pressure of 143 kPa.
2. Calculate the volume that a 0.323-mol sample of gas will occupy at 265 K and a pressure of 0.900 atm.
3. How many grams of oxygen gas are present in a sample that occupies a 2.00-L container at 117 kPa and 35.1oC?
*Gas Stoichiometry: We know from Avagadro that 1 mole of any gas occupies the same volume at STP. We can relate moles of gas to volume of a gas in a chemical reaction: o CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) What volume of oxygen is needed to produce 6.0 L of carbon dioxide?
Volume-Volume problems are the same as Mole-Mole problems that we learned earlier. Volume-Mass problems: Use volume relationships to perform volume-volume calculations, and use the ideal gas law to calculate the moles for the temperature and pressure conditions given. Ex: Ammonia is synthesized from hydrogen and nitrogen gases: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) If 5.00 L of nitrogen gas react completely at a constant pressure and temperature of 3.00 atm and 298 K, how many grams of ammonia are produced?
1.
2KClO3 2 KCl + 3O2
If 5.00 g of KClO3 is decomposed at a pressure of 123 kPa and a temperature of 35.0 0C, what volume of oxygen gas will be produced? (HINT: use the ideal gas law to convert moles of O2 to L of O2)
2.
Propane (C3H8) decomposes to form carbon and hydrogen gas. Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
If 15.3 g of propane react at a temperature of 1150C and a pressure of 1.06 atm, what volume of hydrogen gas will be produced?
3.
Write a balanced equation for the combustion of methane (CH4).
If the reaction is carried out in a vessel with a temperature of 200 0C and a pressure of 0.95 atm, how many grams of water vapor will be produced from 10.5 L of methane?
4.
2H2O2(aq) 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
Calculate the mass of hydrogen peroxide needed to obtain 0.460 L of oxygen gas at 107 kPa and 5.0 0 C.
5.
Ammonia gas reacts with oxygen gas to produce nitrogen monoxide gas and water. Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
If 35.0 L of ammonia reacts with excess oxygen at 298oC and 0.85 atm, what mass of water vapor will be produced?
Você também pode gostar
- Worksheet GasesDocumento6 páginasWorksheet GasesakladffjaAinda não há avaliações
- GLWS9Documento6 páginasGLWS9Vince HernándezAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Law Lecture NotesDocumento4 páginasGas Law Lecture NotesHazel Jane JaponAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 29 - Other Gas Laws 2Documento16 páginasLesson 29 - Other Gas Laws 2Jenny YoonAinda não há avaliações
- 1.3 Reacting Mass and VolumeDocumento29 páginas1.3 Reacting Mass and VolumeCrystalAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 6Documento2 páginasTutorial 6Anis AzwaAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Laws LecDocumento43 páginasGas Laws LecJune Francis AngAinda não há avaliações
- Ideal Gas LawDocumento46 páginasIdeal Gas LawlnaveenkAinda não há avaliações
- 01 The Gas Laws-Complete STDocumento55 páginas01 The Gas Laws-Complete STRyan RamlawiAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Laws Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRT: R 0.0821 (L Atm) / (K Mol) or R 8.31 L Kpa / (K Mole)Documento5 páginasGas Laws Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRT: R 0.0821 (L Atm) / (K Mol) or R 8.31 L Kpa / (K Mole)Alyssa ColeAinda não há avaliações
- Ideal Gas LawDocumento1 páginaIdeal Gas LawIsko XDAinda não há avaliações
- Chem 1A Chapter 5 Exercises: Boyle's LawDocumento5 páginasChem 1A Chapter 5 Exercises: Boyle's LawSheryll de GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamic 1Documento312 páginasThermodynamic 1Daniel Wang100% (5)
- Gas Laws: Physics IiDocumento33 páginasGas Laws: Physics IiEsmeralda Tapiz100% (1)
- Gas Law WorksheetDocumento3 páginasGas Law WorksheetRonaldo Manaoat50% (2)
- Gay-Lussac-6 7 VN Avogadros Law-CombinedDocumento48 páginasGay-Lussac-6 7 VN Avogadros Law-Combinednathanielstanaj.mAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Chapter 6Documento2 páginasTutorial Chapter 6ayuni nadhirahAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 2Documento15 páginasTopic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 2burcak gecAinda não há avaliações
- HW 2 - ChemDocumento14 páginasHW 2 - ChemStephanieAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 - Gases Gas LawsDocumento22 páginasLecture 2 - Gases Gas LawsWillie MojataleAinda não há avaliações
- Physical, Inorganic & Organic Chem QnsDocumento45 páginasPhysical, Inorganic & Organic Chem QnsMarvin NdashimyeAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry20 UnitBReviewDocumento5 páginasChemistry20 UnitBReviewgeorgia robinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 2 - Gas LawsDocumento27 páginasLesson 2 - Gas LawsJoanna Ruth SeproAinda não há avaliações
- Module 5.2b: Gas Laws Part 2Documento26 páginasModule 5.2b: Gas Laws Part 2Ryan PazonAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Laws Worksheet IIDocumento4 páginasGas Laws Worksheet IIJensen Ryan LimAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 9 - CHM420 - Sept 2020Documento2 páginasTutorial 9 - CHM420 - Sept 2020Hai AwakAinda não há avaliações
- Screenshot 2023-02-23 at 8.35.47 AMDocumento36 páginasScreenshot 2023-02-23 at 8.35.47 AMWaluse MwaleAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Laws 201314 Review Sheet W Answers 2Documento4 páginasGas Laws 201314 Review Sheet W Answers 2Leighton RowlandAinda não há avaliações
- PHYCHEMDocumento12 páginasPHYCHEM22-00248Ainda não há avaliações
- Gas LawDocumento16 páginasGas LawmillergraAinda não há avaliações
- Anchor Guide GasesDocumento6 páginasAnchor Guide GasesDaniel ZhangAinda não há avaliações
- Gaseous State Iit NumericalsDocumento5 páginasGaseous State Iit NumericalssamareshcmondalAinda não há avaliações
- IAS Calcuating Molar Volumes and Ideal Gas BehaviourDocumento18 páginasIAS Calcuating Molar Volumes and Ideal Gas BehaviourNico Van De CasteeleAinda não há avaliações
- Gen Chem Revision 2013 PDFDocumento2 páginasGen Chem Revision 2013 PDFPSCAinda não há avaliações
- SCES1094 Tutorial 2Documento21 páginasSCES1094 Tutorial 2SN2-0622 NURUL ADLYNA BINTI LOKMANAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Gaseous State CHM131Documento2 páginasTutorial Gaseous State CHM131asyhqnaAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Laws Packet Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRTDocumento5 páginasGas Laws Packet Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRTJose Barrera GaleraAinda não há avaliações
- Science Quest Reviewer Gas LawsDocumento5 páginasScience Quest Reviewer Gas LawsEva esperaAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Laws Problem Set (Edited)Documento2 páginasGas Laws Problem Set (Edited)Kurt Bidua0% (1)
- Cpp-Gaseous State - RGVDocumento2 páginasCpp-Gaseous State - RGVGauri KabraAinda não há avaliações
- Gases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryDocumento20 páginasGases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryAshley Marie ChildersAinda não há avaliações
- Effusion Diff and Gas Stoich Notes Outline AnswersDocumento4 páginasEffusion Diff and Gas Stoich Notes Outline Answersissa sherryAinda não há avaliações
- GASES2Documento53 páginasGASES2Beri NaysAinda não há avaliações
- Combined Avogadros and Ideal Gas LawsDocumento25 páginasCombined Avogadros and Ideal Gas Lawslevi0417Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemistry SheetsDocumento10 páginasChemistry Sheetshebaneyar74Ainda não há avaliações
- PHY210 Tutorial Chapter 6 Part 2Documento1 páginaPHY210 Tutorial Chapter 6 Part 2Littlekittens CatsAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 - Gas LawsDocumento55 páginasChapter 11 - Gas Lawsjim tannerAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Laws Worksheet With Keys Grade 10Documento2 páginasGas Laws Worksheet With Keys Grade 10Mark Lloyd ColomaAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Chemistry 1Documento49 páginasEngineering Chemistry 1Rasha HajaratAinda não há avaliações
- GASESSDocumento10 páginasGASESSAndrea Martinez ZepedaAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Gases PDFDocumento70 páginas6 Gases PDFRogerine RoyAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture II Part 1Documento19 páginasLecture II Part 1badeth.pagcaliwagan23Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4+5 - Thermodynamics (With Answers)Documento49 páginasChapter 4+5 - Thermodynamics (With Answers)ngu lonAinda não há avaliações
- Gay Lussac Combined Avogadro Ideal Gas Law ApplicationDocumento28 páginasGay Lussac Combined Avogadro Ideal Gas Law ApplicationAlexandra Venice Ann M. PerezAinda não há avaliações
- GasesDocumento84 páginasGasesmdnishathasan141Ainda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics TutorialDocumento43 páginasThermodynamics TutorialDineo Pampier50% (2)
- Gas Laws WorksheetDocumento3 páginasGas Laws WorksheetJEROME CALUMBAAinda não há avaliações
- AIR QUALITY AND POLLUTION (TKA 3301) LECTURE NOTES 4-Chemistry of Air Pollution N Ideal Gas LawDocumento66 páginasAIR QUALITY AND POLLUTION (TKA 3301) LECTURE NOTES 4-Chemistry of Air Pollution N Ideal Gas Lawmamat88Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - Gas LawDocumento52 páginasChapter 1 - Gas LawLolindah ChinAinda não há avaliações
- Dokumen - Tips - Ideal Gas Law 5584a8a9dcd51Documento24 páginasDokumen - Tips - Ideal Gas Law 5584a8a9dcd51Earl CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Applications of First Law of Thermodynamics CbuDocumento15 páginasApplications of First Law of Thermodynamics CbuChimwemwe KaongaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemsheets As 1027 (Amount of Substance)Documento38 páginasChemsheets As 1027 (Amount of Substance)Steve XieAinda não há avaliações
- Dot Point CoreDocumento70 páginasDot Point CoreShagun Varma100% (2)
- Ae6050 HW1Documento3 páginasAe6050 HW1dsblendoAinda não há avaliações
- How To Measure Carbon Dioxide: Operation Principle of Infrared SensorsDocumento4 páginasHow To Measure Carbon Dioxide: Operation Principle of Infrared SensorsDejan BošnjakAinda não há avaliações
- 6.23 Equation of State Prediction of Carbon Dioxide PropertiesDocumento70 páginas6.23 Equation of State Prediction of Carbon Dioxide Propertiessaulatlone100% (1)
- Pages From Leak Test Level 2Documento63 páginasPages From Leak Test Level 2ManivannanMudhaliarAinda não há avaliações
- DLP Grade 7-10 Matter With LinkDocumento105 páginasDLP Grade 7-10 Matter With Linknita floresAinda não há avaliações
- Physical ChemistryDocumento141 páginasPhysical ChemistryUsman Samuel BabalolaAinda não há avaliações
- Buku Kimia Fisika PDFDocumento405 páginasBuku Kimia Fisika PDFHasrilia Beskara0% (1)
- Chap 18Documento94 páginasChap 18noscribdyoucantAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge ChemistryDocumento100 páginasCambridge ChemistryBraweet SapkotaAinda não há avaliações
- Magnesium and Hydrochloric Acid Lab ReportDocumento12 páginasMagnesium and Hydrochloric Acid Lab ReportJack Murphy69% (13)
- Silo - Tips - Macroscopic Balances For Nonisothermal SystemsDocumento18 páginasSilo - Tips - Macroscopic Balances For Nonisothermal Systemsmarlenys cuevasAinda não há avaliações
- Nongui, Gelina Anne A. Che 508 - Prelim ExamDocumento12 páginasNongui, Gelina Anne A. Che 508 - Prelim ExamDezzerie SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Thermodynamics and MolDocumento151 páginasPhysics Thermodynamics and MolSuzaki KurushiAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics 2018 (Repaired)Documento15 páginasThermodynamics 2018 (Repaired)carolAinda não há avaliações
- GASESDocumento101 páginasGASESdwyquishAinda não há avaliações
- FSCT2204 ThermoD Unit 1Documento24 páginasFSCT2204 ThermoD Unit 1Emperor'l BillAinda não há avaliações
- Property Data: 4.1 Unit SystemDocumento60 páginasProperty Data: 4.1 Unit SystemAnonymous N3LpAXAinda não há avaliações
- States of Matter: Lakshya Daily Assignment (LDA-1) Theory QuestionDocumento18 páginasStates of Matter: Lakshya Daily Assignment (LDA-1) Theory QuestionArnav AmbreAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDocumento68 páginasEnergy Analysis of Closed Systems Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyChuck NorrisAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Pure Substances: Noor Hafizah UyupDocumento109 páginasProperties of Pure Substances: Noor Hafizah UyupDIey ChokiEyAinda não há avaliações
- Vacuum PhysicsDocumento24 páginasVacuum PhysicsThomas BranleyAinda não há avaliações
- Jntuk 2 1 Thermodynamics Nov 2017 Q.PDocumento8 páginasJntuk 2 1 Thermodynamics Nov 2017 Q.PsaiAinda não há avaliações
- Thermo 5th Chap14 P115Documento27 páginasThermo 5th Chap14 P115Pablo Isuart HdzAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics Lecture 1Documento30 páginasThermodynamics Lecture 1Ssegirinya WilberforceAinda não há avaliações
- Labintas, MarilouDocumento3 páginasLabintas, Marilouyeng botzAinda não há avaliações
- Behaviour of Real GasesDocumento7 páginasBehaviour of Real GasesAltaf Rather100% (1)