Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
SCCP
Enviado por
rajrockzrajDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SCCP
Enviado por
rajrockzrajDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
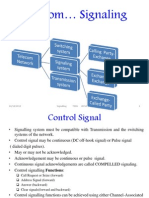
Functions of the SCCP
establishment and control of signalling connections (i.e. logical ,end-to-end' connections between signalling points via the common channel signalling links). possibility of world-wide addressing for signalling points. SCCP possesses its own routing label. connection-oriented or connectionless message transfer additional functions for the transfer of messages between exchanges and other signalling points (e.g. databases). combined with the MTP as the Network Service Part (NSP).
Connectionless services provide the SCCP userwith the ability to transfer signalling messages without the establishment of a signalling connection Connection-oriented services signalling connections are established and controlled by the SCCP user these kinds of connections are comparable with dialled telephone connections
Signalling Information Field (SIF) of SCCP MSUs
Order of octet transmission
Routing label Message type code Mandatory fixed part
Mandatory variable part
Pointers to parameters Pointer to start of optional part Parameters Parameters End of optional parameters
Optional part
SCCP
Slide 3
Tektronix
SCCP Message types
This table contains an indication of the applicability of the various message types to the relevant classes of protocol.
SCCP message types
1/2
Classes Message type CR Connection Request CC Connection Confirm CREF Connection Refused RLSD Released RLC Release Complete DT1 Data Form 1 DT2 Data Form 2 AK Data Acknowledgement X Type of message in this protocol class. 0 1 2 X X X X X X X X 3 X X X X X Code 0000 0001 0000 0010 0000 0011 0000 0100 0000 0101 0000 0110 0000 0111 0000 1000
SCCP
Slide 7
Tektronix
SCCP message types
2/2
Classes Message type UDT Unidata UDTS Unidata Service ED Expedited Data EA Expedited Data Acknowledgement RSR Reset Request RSC Reset Confirm ERR Protocol Data Unit Error IT Inactivity Test X Type of message in this protocol class. X X 0 X X 1 X X X X X X X X 2 3 Code 0000 1001 0000 1010 0000 1011 0000 1100 0000 1101 0000 1110 0000 1111 0001 0000
SCCP
Slide 8
Tektronix
Two basic categories of addresses are distinguished:
SCCP addressing
Global Title (GT)
Global Title (GT) is an address which cannot directly be used for routing in the
signalling network.
The GT translation function of the SCCP is required which transfers the GT to a
point code and a SSN.
The determined DPC can either be the destination point or a transfer Point in the
signalling network.
The address translation is continoued until the destination point is reached.
Destination Point Code (DPC) and Subsystem Number (SSN)
DPC ans SSN allow direct routing by the SCCP and MTP. The translation
function of the SCCP is not required.
SCCP
Slide 11
Tektronix
4.1
Structure of the BSSAP
The BSSAP consists of three parts: Base Station System Management Application Part (BSSMAP) Direct Transfer Application Part (DTAP) A distribution function
Format of BSSAP Distribution Data Unit
The distribution of messages between the DTAP and BSSMAP functions is performed by the distribution sublayer. The protocol for this sublayer consists of the management of a Distribution Data Unit. Each SCCP User Data Field necessarily contains such a Distribution Data Unit as a header followed by the actual DTAP layer 3- or BSSMAP message.
Structure of a BSSAP message
DTAP 1 2 3 4 L+3 Discrimination DLCI Distribution Data Unit Length Indicator L Length Indicator Layer 3 Message Layer 3 message
BSSAP Slide 4
BSSMAP 1 Discrimination
2 3 L+2
Length Indicator L Layer 3 Message
Tektronix
Functions of the ISDN-user part
the signalling functions for the control of calls, for the processing of services and facilities and for the administration of circuits in ISDN (voice and non-voice applications). interfaces to MTP and SCCP for the transport of message signal units. ISDN-UP can use SCCP functions for end-to-end signalling offers Bearer and Supplementary services
Functions provided by ISUP
BASIC SERVICES
establishment supervision release of circuit switched network connections between subscribers NUMBER IDENTIFICATION SUPPLEMENTARY SERVICES Direct-Dialling-In (DDI) Multiple Subscriber-Number (MSN) Calling Line Identification Presentation (CLIP) Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR) Connected Line Identification Presentation (COLP) Connected Line Identification Restriction (COLR) Malicious Call Identification (MCID) Sub-addressing (SUB) CALL OFFERING SUPPLEMENTARY SERVICES Call Transfer (CT) Call Forwarding Busy (CFB) Call Forwarding No Reply (CFNR) Call Forwarding Unconditional (CFU) Call Deflection (CD) Line Hunting (LH) Explicit Call Transfer (ECT) Single Step Call Transfer (SCT) CALL COMPLETION SUPPLEMENTARY SERVICES Call Waiting (CW) Call Hold (HOLD) Completion of Calls to Busy Subscribers (CCBS) Terminal Portability (TP)
General ISUP messages format
Signalling Information Field (SIF) of ISUP MSUs
Order of octet transmission
Routing label Circuit identification code Message type code Mandatory fixed part
Mandatory variable part
Pointers to parameters Pointer to start of optional part Parameters Parameters End of optional parameters
Optional part
ISUP
Slide 2
Tektronix
MULTIPARTY SUPPLEMENTARY SERVICES Conference Calling (CONF) Three-Party Service (3PTY) COMMUNITY OF INTEREST SUPPLEMENTARY SERVICES Closed User Group (CUG) Private Numbering Plan (PNP) Multi-Level Precedence and Preemption (MLPP) CHARGING SUPPLEMENTARY SERVICES International Telecommunication Charge Card Advice of Charge (AOC) Reverse Charge (REV) ADDITIONAL INFORMATION TRANSFER SUPPLEMENTARY SERVICE User-to-User Signalling (UUS)
Você também pode gostar
- A Hand-Made Wi-Fi Gun! A Powerful Antenna For A Wi-Fi DIY !Documento27 páginasA Hand-Made Wi-Fi Gun! A Powerful Antenna For A Wi-Fi DIY !Radomir Nesic100% (1)
- NSN Core Complete IntegrationDocumento207 páginasNSN Core Complete IntegrationAjay Kumar100% (3)
- HCIE-Datacom V1.0 Lab GuideDocumento426 páginasHCIE-Datacom V1.0 Lab GuidedelplayAinda não há avaliações
- Telecom Basics: E1 Voice Theorm ErlangDocumento23 páginasTelecom Basics: E1 Voice Theorm ErlangCheikh Ahmet Tidiane DiengAinda não há avaliações
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandAinda não há avaliações
- Analyzing CCM TracesDocumento54 páginasAnalyzing CCM TracesSunjay BhallaAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Signalling - CCS7 SignallingDocumento49 páginasDigital Signalling - CCS7 Signallingsuryakumar_r13113041Ainda não há avaliações
- Signalling Connection Control PartDocumento5 páginasSignalling Connection Control ParttanchoAinda não há avaliações
- 4' Day SS7Documento60 páginas4' Day SS7nemazzeoAinda não há avaliações
- MSC SCCP 1Documento24 páginasMSC SCCP 1kingkhankAinda não há avaliações
- SS7 Signaling BasicDocumento23 páginasSS7 Signaling BasicrainieroAinda não há avaliações
- Ss 7Documento49 páginasSs 7Tri NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Signaling ProtocolsDocumento41 páginasSignaling ProtocolsSalim Khan100% (2)
- 07 SCCPDocumento39 páginas07 SCCPHarish SAinda não há avaliações
- Gestion de Redes de Telecomunicaciones-3Documento51 páginasGestion de Redes de Telecomunicaciones-3Adolfo MedmorAinda não há avaliações
- SCCPDocumento39 páginasSCCPHarish SAinda não há avaliações
- IP SignallingDocumento27 páginasIP SignallingvashishthanuragAinda não há avaliações
- GSM Signalling ProcedureDocumento60 páginasGSM Signalling ProcedureSudheera IndrajithAinda não há avaliações
- CIC in A SS7 Message ?: Identifies A Transaction 2M Arks Identifies The Signaling ConnectionDocumento14 páginasCIC in A SS7 Message ?: Identifies A Transaction 2M Arks Identifies The Signaling ConnectionmichaelgodfatherAinda não há avaliações
- GSM SignallingDocumento25 páginasGSM SignallingSoniya PanwarAinda não há avaliações
- Pubate Satienpoch: SCCP: Signaling Connection Control PartDocumento23 páginasPubate Satienpoch: SCCP: Signaling Connection Control PartAnuj NayakAinda não há avaliações
- UMTS FamilyDocumento92 páginasUMTS FamilyAshish GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- SE2900 Product Introduction ISSUE 1.10Documento4 páginasSE2900 Product Introduction ISSUE 1.10Oluwole OlamideAinda não há avaliações
- SS7 Signaling SystemDocumento24 páginasSS7 Signaling SystemAmro GoneimAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd Generation Systems: - Review of Cellular Wireless Networks - UmtsDocumento39 páginas3rd Generation Systems: - Review of Cellular Wireless Networks - Umtsselvadpm5Ainda não há avaliações
- 06 NO7 TheoryDocumento96 páginas06 NO7 TheoryAdekunle OlopadeAinda não há avaliações
- Layered Architectures TutorialDocumento20 páginasLayered Architectures TutorialMalathi ArunAinda não há avaliações
- CdmaDocumento1 páginaCdmaflatelecom938Ainda não há avaliações
- Signalling in TelecommunicationDocumento45 páginasSignalling in TelecommunicationShishir NaikAinda não há avaliações
- T Rec Q.712 198811 S!!PDF eDocumento12 páginasT Rec Q.712 198811 S!!PDF eDonald TaseAinda não há avaliações
- GSM Signalling ConceptsDocumento25 páginasGSM Signalling ConceptsThirupathi SubbaiahAinda não há avaliações
- AN1630 - High Performance Communication NetworksDocumento17 páginasAN1630 - High Performance Communication NetworksPavithra SunAinda não há avaliações
- SIGTRANDocumento57 páginasSIGTRANRaghav ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Interfaces For All Functios-29 March.2016Documento6 páginasInterfaces For All Functios-29 March.2016erbiliAinda não há avaliações
- 3G Sesion 2Documento70 páginas3G Sesion 2Chaucer LópezAinda não há avaliações
- GSM Call Flow ProceduresDocumento54 páginasGSM Call Flow ProceduresKafayat Aheer100% (5)
- 09-Overview of Telecommunication NetworkDocumento39 páginas09-Overview of Telecommunication NetworkMohamed TatouAinda não há avaliações
- MTP 3 MTP 3: Isup IsupDocumento14 páginasMTP 3 MTP 3: Isup IsupkmehdiAinda não há avaliações
- Telecommunication Switching System Signalling PDFDocumento34 páginasTelecommunication Switching System Signalling PDFUdhay Prakash60% (5)
- Ccs7over IpDocumento35 páginasCcs7over IpshridonAinda não há avaliações
- GBO - 013 - E1 - 1 GSM Signaling System-48Documento48 páginasGBO - 013 - E1 - 1 GSM Signaling System-48Clive MangwiroAinda não há avaliações
- RTTC Pune Presents..: An-RaxDocumento31 páginasRTTC Pune Presents..: An-RaxShishir NaikAinda não há avaliações
- GB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-01Documento40 páginasGB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-01JaneYinAinda não há avaliações
- ITU-T Common Channel Signalling System No. 7 (CCSS7, CCS7Documento35 páginasITU-T Common Channel Signalling System No. 7 (CCSS7, CCS7dhanasekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Recommendation Q.712: Definition and Function of SCCP MessagesDocumento8 páginasRecommendation Q.712: Definition and Function of SCCP Messagesman1982roAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Acronyms: Join Youtube Channel Link HereDocumento41 páginasComputer Acronyms: Join Youtube Channel Link HereietruchikaAinda não há avaliações
- Ewsd Overview One DayDocumento58 páginasEwsd Overview One DayWaqar AsmatAinda não há avaliações
- 04 SS7Documento54 páginas04 SS7Kulbhushan Singh BishtAinda não há avaliações
- Gbo 001 E1 1 GSM Basic-40Documento40 páginasGbo 001 E1 1 GSM Basic-40Clive MangwiroAinda não há avaliações
- Ss7 Protocol Suite - Bicc - Bisup - Dup - Isup - Map - Mtp-2 - Mtp-3 - q2140 - SCCP - Tcap - TupDocumento18 páginasSs7 Protocol Suite - Bicc - Bisup - Dup - Isup - Map - Mtp-2 - Mtp-3 - q2140 - SCCP - Tcap - TupAman Deep SinghAinda não há avaliações
- GSM Signaling System-48Documento48 páginasGSM Signaling System-48sburki89Ainda não há avaliações
- GSMDocumento130 páginasGSMhelpbgpAinda não há avaliações
- GB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-40Documento40 páginasGB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-40Didier TangaAinda não há avaliações
- Sigtran PPT FinalDocumento108 páginasSigtran PPT Finalbabulgsm0% (2)
- GSM ProtocolsDocumento11 páginasGSM ProtocolsMohammed RiyazAinda não há avaliações
- 6v102 PDFDocumento16 páginas6v102 PDFtetrapoltestAinda não há avaliações
- Sigtran Protocols-M3ua M2paDocumento9 páginasSigtran Protocols-M3ua M2paJawahar SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Ewsd System Architecture: Modular in All RespectsDocumento17 páginasEwsd System Architecture: Modular in All RespectsOluwaseun EmmaAinda não há avaliações
- LTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and Performance MeasurementNo EverandLTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and Performance MeasurementAinda não há avaliações
- IP Telephony: Deploying VoIP Protocols and IMS InfrastructureNo EverandIP Telephony: Deploying VoIP Protocols and IMS InfrastructureAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile Terminal Receiver Design: LTE and LTE-AdvancedNo EverandMobile Terminal Receiver Design: LTE and LTE-AdvancedAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Computer Networks - CS716 Power Point Slides Lecture 42Documento48 páginasAdvanced Computer Networks - CS716 Power Point Slides Lecture 42Taran AulakhAinda não há avaliações
- VPN1 5Documento2 páginasVPN1 5arun0076@gmail.comAinda não há avaliações
- Archer AX55 Pro (EU&US) 1.0 - DatasheetDocumento8 páginasArcher AX55 Pro (EU&US) 1.0 - DatasheetAhmet AteşAinda não há avaliações
- Configuring A LAN With DHCP and VLANs (Support) - Cisco SystemsDocumento8 páginasConfiguring A LAN With DHCP and VLANs (Support) - Cisco SystemsyihoAinda não há avaliações
- Anna Univ May - June Model Questions High Performance Computer Networks Question Paper June 2011-2013 - Anna University Results 2013 - Anna Univ Updates PDFDocumento2 páginasAnna Univ May - June Model Questions High Performance Computer Networks Question Paper June 2011-2013 - Anna University Results 2013 - Anna Univ Updates PDFMurali DharanAinda não há avaliações
- Huawei HoloSens SDC C6620-Z23 DatasheetDocumento5 páginasHuawei HoloSens SDC C6620-Z23 DatasheetDavincho SarangoAinda não há avaliações
- HMI Cable Selection Guide 20100820Documento9 páginasHMI Cable Selection Guide 20100820Aldo PeñaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report - Cisco Router ConfigurationDocumento20 páginasLab Report - Cisco Router ConfigurationfelipebrazilAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco Router MBSSDocumento36 páginasCisco Router MBSSSuresh Rao J100% (1)
- 9tut TutorialsDocumento119 páginas9tut TutorialsLa Yohda Stasella100% (1)
- Lab Assignment 8 Object: Data Communication & Computer Networks (EE 300) 2016-EE-139Documento4 páginasLab Assignment 8 Object: Data Communication & Computer Networks (EE 300) 2016-EE-139SaRosh RaeesAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 5: Cisco Device Access Control: 1.1 DetailsDocumento20 páginasLab 5: Cisco Device Access Control: 1.1 Detailscharles81Ainda não há avaliações
- Error CompletoDocumento864 páginasError CompletojoseingaperezAinda não há avaliações
- PNMSJ: Pasolink Network Management System JavaDocumento33 páginasPNMSJ: Pasolink Network Management System JavaAndre SorovskyAinda não há avaliações
- Data and Computer Communications: Tenth Edition by William StallingsDocumento31 páginasData and Computer Communications: Tenth Edition by William StallingsHasanAinda não há avaliações
- nG1 EE LabGuide v634Documento101 páginasnG1 EE LabGuide v634Mukund KumarAinda não há avaliações
- EE-357: Computer and Communication Networks Spring Semester 2020Documento3 páginasEE-357: Computer and Communication Networks Spring Semester 2020Nayab TajvedAinda não há avaliações
- Virtualize and Install Kali Linux On VMWare Player (Includes Tor Browser Bundle) - YouTubeDocumento4 páginasVirtualize and Install Kali Linux On VMWare Player (Includes Tor Browser Bundle) - YouTubeorangota100% (1)
- Cifrado y Autenticación CUCM v1.0Documento22 páginasCifrado y Autenticación CUCM v1.0SergioAinda não há avaliações
- CP 443-1 Advanced Manual Part BDocumento85 páginasCP 443-1 Advanced Manual Part BAutomation WorksAinda não há avaliações
- Email Systems: Vinay KesarDocumento18 páginasEmail Systems: Vinay KesarAnonymous RrGVQjAinda não há avaliações
- Linux Commands Exercise IIT-BDocumento2 páginasLinux Commands Exercise IIT-BsiddheyAinda não há avaliações
- Duration in Duration Format Title Course Type Knowledge Transfer OEMDocumento12 páginasDuration in Duration Format Title Course Type Knowledge Transfer OEMDinesh vpAinda não há avaliações
- Common TCP/IP Protocols and Ports: Protocol Tcp/Udp Port Number DescriptionDocumento3 páginasCommon TCP/IP Protocols and Ports: Protocol Tcp/Udp Port Number DescriptionsreedharkundirAinda não há avaliações
- Connect Two Routers On A Home NetworkDocumento2 páginasConnect Two Routers On A Home NetworkPappu KhanAinda não há avaliações
- DAG1000-8S VoIP Gateway User ManualDocumento82 páginasDAG1000-8S VoIP Gateway User ManualJoaquin Soler DuránAinda não há avaliações
- PDF ALCATEL LUCENT IP Networking OmniSwitch 6600 FamilyDocumento12 páginasPDF ALCATEL LUCENT IP Networking OmniSwitch 6600 Familycuong955Ainda não há avaliações