Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
AP US History Pg. 33-40
Enviado por
xtransientTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
AP US History Pg. 33-40
Enviado por
xtransientDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
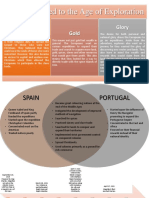
Homework #1 How did the voyages of Columbus change the world? page 33 (Portugal)-37; page 40 (Meanwhile)-45 I.
Portugal and the Atlantic, 1400-1500 A. Changes in maritime technology = European exploration 1. Triangular Arab sail 2. Caravel, more maneuverable vessel 3. Compass 4. Astrolabe B. Renaissance helps European's map sense. C. Portugal takes the first step 1. Led by Prince Henry "the navigator" (1394-1460) a. Takes control of African-European gold trade from Moroccans b. Encourages Portuguese sailors to explore i. Master Atlantic currents ii. Search for raid or trade opportunities. 2. First nation to capitalize a. Utilizing maritime technology b. Utilizing Renaissance findings. D. Following Henry's death 1. Portugal exports gold and slaves 2. Opens up trade prospective a. 1488 -Bartolomeu Dias reaches the Cape of Good Hope b. 1458 - Vasco de Gama goes around the Cape of Good Hope --> India II. The "New Slavery" and Racism A. Reasons for slavery 1. Indebtness 2. Captured in raids and wars B. Portuguese slave trade 1. 1482 - builds Elmina, on West Africa's Gold Coast 2. Primarily traded through African-controlled commercial networks 3. Slaves + local products --> trade to other Africans --> receive gold. 4. Effects a. African rulers not only received luxury products, but guns as well b. Conflicts among African communities rose c. South converts to Christianity, North converts to Islam C. Differences between slavery and "new slavery" 1. Caused conflict in West Africa 2. New extremes of dehumanization 3. Africans regarded as property rather than persons of low status D. Racial tension - Europeans justified enslaving blacks as their Christian duty III. To America and Beyond, 1492-1522 A. Christopher Columbus (1451-1506) 1. Son of a weaver from Italian port of Genoa 2. Learned geography by himself 3. Thought that Europeans could reach Asia by sailing westward across the Atlantic, rather than around Africa. 4. Religious fervor - wanted to spread Christianity 5. Ambition to win wealth and glory. B. Queen Isabella and King Ferdinand allow Columbus's journey, in fear of losing direct trade with Asia. 1. Sailed in search of gold 2. Additional contacts with Tainos in Cuba, Hispaniola, Haiti and Dominican Republic. C. Columbus a poor administrator, cheated of his rightful rewards. D. European interest surges 1. As a result, Isabella and Portgual's King John II sign the Treaty of Tordesillas 2. Treaty of Tordesillas a. Divides future discoveries between Spain and Portugal
b. England attempts to join the race despite the treaty. 3. John Cabot sent by Henry VII of England to explore E. Effect of European interest 1. Knowledge of a landmass that blocked the route to Asia 2. Voyages revealed a coastline from the Caribbean to Brazil 3. Landmass becomes known as America. F. Journey from America --> Asia 1. 1513 - Spaniard Vasco Nunez de Balboa finds Pacific Ocean 2. 1519 - Portuguese Ferdinand Magellan circumnavigates the world. IV. Spain's Conquistadors, 1492-1536 A. Christopher Columbus' achievements 1. America's first slave trader 2. First Spanish conqueror 3. Started the first American gold rush B. Crown takes direct control over Hispaniola 1. Extends search for gold 2. Results of Discovery a. Puerto Rico (1508) b. Jamaica (1510) c. Cuba (1511) C. Native Americans in Caribbean colonies 1. Great numbers died as a result of diseases 2. Colonists import Africans to replace Indians. D. 1519 - Hernan Cortes vs Aztecs 1. Quest to conquer Aztecs 2. Gained services of Malintzin (Malinche), aka Dona Marina. 3. Ignored Moctezuma II (1502-1520) offer, raiding palace and treasury. 4. Aztecs drive off Spanish, despite emperor's imprisonment. 5. Spanish reinforcements and smallpox epidemic defeat Aztecs 6. 1521 - Cortes overthrows Aztecs, building Mexico City. E. Incan Empire conquered by Francisco Pizarro between 1532-1536 V. The Columbian Exchange A. Introduction of diseases, domestic animals and agriculture. B. Mixing of peoples 1. Metis - both Indian and European descent 2. Mulatto - both European and African descent 3. African + Indian unions C. Sugar plantations and silver 1. Source of wealth for the Spanish. 2. Causes Spanish to want to dominate Europe VI. Spain's Northern Frontier A. Spanish's empire = Aztec + Inca + Indian States B. Spain's success draws conquistadors to Florida and New Mexico 1. Juan Ponce de Leon, founded Puerto Rico and "La Florida" (1513) 2. Alvar Nunez Cabeza de Vaca survives attacks by Apalachee Indians 3. De Soto searches for gold 4. Francisco Vasquez (1540-1542) leads expedition for conquering Southwest Mexico. C. Spain's interest turns to north of Mexico and Caribbean 1. 1565 - establishes a fortress at St. Augustine, Florida a. Served as a base for Catholic missions b. Guale, Powhatan and other Indians rebel, forcing missions to close. c. Franciscan missionaries successfully secure allegiance, but half of the converts killed due to illness. 2.. Juan de Onate founded New Mexico. a. Encomiendas - grants awarding Indian labor to wealthy colonists b. Spanish government replaces Onate in 1606 for mismanagement and excessive brutality. VII. France: Colonizing Canada A. France enters the race in 1524
1. King Francis I sends Giovanni de Verrazano to embark on the voyage 2. Jacques Cartier explores coasts of Newfoundland. B. France colonization attempts. 1. First colonizing attempt in 1541. a. Led by Cartier b. Fails due to unfriendly relations, including attacks. 2. France's next attempt of colonization 1562 a. Led by French Huguenots, Calvinists b. Seeking religious freedom c. Attempts to settle in Florida. d. Spanish executes Calvinists, believing them a threat to Protestantism. C. Fur trade 1. French dominates, due to demand by Europeans 2. Pelts --> axes, knives, copper kettles, cloth, and glass beads. ("Indian Trade") D. Samuel de Champlain establishes New France in 1608. 1. Allied with the Montagnais and Algonquians and the Hurons 2. Helps to defeat the Mohawks in exchange for access on the St. Lawrence. 3. Battle at Lake Champlain ended Indian-European relations. 4. French gained access to the Canadian interior a. Provide Indian allies with European goods b. Protected allies from Iroquois attacks.
Você também pode gostar
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Intolerable ActsDocumento16 páginasThe Intolerable ActstysonluneauAinda não há avaliações
- Phil Hist - MagellanDocumento15 páginasPhil Hist - MagellanViolet The ViolentAinda não há avaliações
- Plymouth and JamestownDocumento11 páginasPlymouth and Jamestownapi-263441388Ainda não há avaliações
- Colonial America TestDocumento5 páginasColonial America Test1012219Ainda não há avaliações
- The Fourth New World Voyage of Christopher ColumbusDocumento4 páginasThe Fourth New World Voyage of Christopher ColumbusJeremy JohnsonAinda não há avaliações
- Age of Exploration ProjectDocumento2 páginasAge of Exploration Projectapi-334282120Ainda não há avaliações
- All That Was Found of The Colonists at Roanoke Was The Word "Croatoan" Carved Into A TreeDocumento12 páginasAll That Was Found of The Colonists at Roanoke Was The Word "Croatoan" Carved Into A TreeAndi AndiAinda não há avaliações
- Give Me LibertyDocumento22 páginasGive Me Libertyapi-28584597475% (4)
- The Southern Colonies PowerpointDocumento18 páginasThe Southern Colonies PowerpointJessica100% (1)
- An English Settlement at JamestownDocumento7 páginasAn English Settlement at JamestownPatrick ThorntonAinda não há avaliações
- Encomienda Syst-WPS OfficeDocumento6 páginasEncomienda Syst-WPS OfficeNyx MagallanesAinda não há avaliações
- Timeline of CubaDocumento1 páginaTimeline of Cubaapi-453354340Ainda não há avaliações
- Expedition Report InfoDocumento5 páginasExpedition Report InfoPrincess AduanaAinda não há avaliações
- Study Guide AnswersDocumento2 páginasStudy Guide Answersapi-261097177Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit1 EarlyExplorersDocumento2 páginasUnit1 EarlyExplorersShower of Roses100% (2)
- Jamestown ColonyDocumento24 páginasJamestown ColonybobjoemanAinda não há avaliações
- Philippines and The Age of ExplorationDocumento5 páginasPhilippines and The Age of ExplorationalalaLarusshhAinda não há avaliações
- ElcanoDocumento2 páginasElcanoJester Olave AustriaAinda não há avaliações
- Aoe Rap Battle Lyrics and NotesDocumento8 páginasAoe Rap Battle Lyrics and Notesapi-315204685Ainda não há avaliações
- Colonial America Trivia QuestionsDocumento5 páginasColonial America Trivia Questionsgabriella56Ainda não há avaliações
- Explorers TestDocumento4 páginasExplorers Testapi-383863716Ainda não há avaliações
- Colonial AmericaDocumento16 páginasColonial Americaapi-367477549100% (1)
- Thanksgiving Vocabulary Matching WorksheetDocumento2 páginasThanksgiving Vocabulary Matching Worksheetapi-241263473Ainda não há avaliações
- 1st Lesson Plan - Christopher ColumbusDocumento4 páginas1st Lesson Plan - Christopher ColumbusAna SofiaAinda não há avaliações
- Christopher Columbus 1451 - 1506Documento9 páginasChristopher Columbus 1451 - 1506David Sam KendrickAinda não há avaliações
- World Exploration Study GuideDocumento4 páginasWorld Exploration Study GuideRachel FrankenfieldAinda não há avaliações
- Powerpoint Notes Unit 3 Lesson 1 Causes of The American RevolutionDocumento11 páginasPowerpoint Notes Unit 3 Lesson 1 Causes of The American Revolutionapi-261440325100% (1)
- 30 Questions About Pilgrims and PuritansDocumento31 páginas30 Questions About Pilgrims and Puritansapi-280780362Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Notes - American PageantDocumento3 páginasChapter 1 Notes - American PageantEmma Holcomb100% (2)
- Chapter 25 WorldDocumento12 páginasChapter 25 WorldJohn100% (1)