Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Frame Relay Switch
Enviado por
Subhrendu Guha NeogiDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Frame Relay Switch
Enviado por
Subhrendu Guha NeogiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
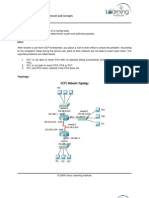
CONFIGURING THE FRAME RELAY SWITCH STEP 1.
Change the router's name to frame-switch Enter configuration mode by using the following command: Router# configure terminal Change the host name of the router to frame-switch by using the following command: Router(config)# hostname frame-switch STEP 2. Enable the router to become a frame-relay switch Configure the router to act as a frame relay switch by using the following command: frame-switch(config)# frame-relay switching STEP 3. Configure the frame relay switch's interfaces Enter interface configuration mode for the first connected serial interface, e.g. serial 0: frame-switch(config)# interface serial 0 Remove the IP address: frame-switch(config-if)# no ip address Set the clock rate to 64000: frame-switch(config-if)# clock rate 64000 Set the encapsulation type to Frame Relay: frame-switch(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relay Set the LMI type to ANSI: frame-switch(config-if)# frame-relay lmi-type ansi Set the Frame Relay interface type to dce: frame-switch(config-if)# frame-relay intf-type dce Enable the interface: frame-switch(config-if)# no shutdown Repeat the commands above for the other connected interfaces on the frame relay switch.
STEP 4. Configuring the end-point routers and their interfaces Change the host name of the router to 2501-A, 2501-B, or 2501-C, as shown in the network diagram by using the following command: Router(config)# hostname 2501-A Enter interface configuration mode for the connected serial interface: 2501-A(config)# interface serial 0 Assign the IP address as shown in the diagram (ie. for router 2501-A, use 10.10.12.2 with subnet 255.255.255.240): 2501-A(config-if)# ip address 10.10.12.2 255.255.255.240 Set the encapsulation type to Frame Relay: 2501-A(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relay Set the LMI type to ANSI: 2501-A(config-if)# frame-relay lmi-type ansi Enable the interface: 2501-A(config-if)# no shutdown Repeat the steps above for the other end-point routers. STEP 5. Verify your progress On the frame-switch, use the show interface command to verify the operation for all connected interfaces. The output should be as following: frame-switch# show interface serial 1 STEP 6. Configure DLCI mappings Now we need to configure the DLCI mappings for each interface by using the frame-relay route command. The format for this command is: frame-switch(config-if)# frame-relay route <input dlci> interface <output interface> <output dlci> You need to configure the appropriate mappings on all the connected interface on the frame relay switch. Following are the commands that need to be configured for our example network. frame-switch#configure terminal frame-switch(config)# interface serial 1 frame-switch(config-if)# frame-relay route 100 interface s3 101 frame-switch(config-if)# frame-relay route 300 interface s2 301 frame-switch(config-if)# interface serial 2 frame-switch(config-if)# frame-relay route 201 interface s3 200 frame-switch(config-if)# frame-relay route 301 interface s1 300 frame-switch(config-if)# interface serial 3 frame-switch(config-if)# frame-relay route 200 interface s2 201 frame-switch(config-if)# frame-relay route 101 interface s1 100 STEP 7. Verify configuration and connection Go to one of the endpoints and look at the output of some of the "show frame-relay" commands. You can see the DLCI mappings have propagated to the endpoints. You don't need to set them up on the endpoints, only on the switch. Display the frame relay DLCI mappings by using the following command: 2501-A# show frame-relay map Display the frame relay pvc statistics by using the following command: 2501-A# show frame-relay pvc 2501-A# ping 10.10.12.3
2501-A# ping 10.10.12.4 frame-switch# show frame route This first CCNA TechLab covers a couple of basic configuration tasks, such as setting passwords and enabling IP routing using RIP. You will need a lab setup similar to the network diagram below:
Before you start, make sure you clear both routers' configuration using the Router#erase startup-config command. First we will configure RouterA, after the router reboots, the following message will be displayed: Type no and press ENTER. Press ENTER again when the message Press RETURN to get started appears. Type enable at the Router> command prompt to enter Privileged Exec mode, notice the prompt chances to Router#.
CONFIGURING THE FIRST ROUTER STEP 1. Change the router's host name to RouterA Enter configuration mode using the following command: Router#configure terminal Change the host name of the router to RouterA using the following command : Router(config)#hostname RouterA RouterA(config)# Notice how changing the hostname immediately affects the prompt. Remember that you are configuring the running configuration.
STEP 2. Disable domain lookups To prevent the router from interpreting every incorrectly typed command as a host name and trying to resolve it to an IP address to setup a telnet connection with it, use the following command: RouterA(config)#no ip domain-lookup STEP 3. Configure passwords First set the enable password to cisco123 using the following command: RouterA(config)#enable secret cisco123
Next, set the password for telnet connections to cisco456 using the following commands: RouterA(config)#line vty 0 4 RouterA(config-line)#password cisco456 RouterA(config-line)#login Although the enable secret command is used to encrypt the enable password, other passwords stored in the router's configuration should be encrypted as well. To do this, use the following command: RouterA(config)#service password-encryption STEP 4. Configuring the Ethernet interface Enter Interface configuration mode for the Ethernet interface, using the following command: RouterA(config)#interface Ethernet 0 Give it the description "Connected to LAN" using the following command: RouterA(config-if)#description Connected to LAN1 Configure the IP address (see diagram for correct address) for the interface using the following command: RouterA(config-if)#ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0 Enable the interface using the following command: RouterA(config-if)#no shutdown STEP 5. Configure the serial WAN interface Switch to Interface configuration mode for the first Serial interface, using the following command: RouterA(config)#interface Serial 0 Give it the description "Direct connection to RouterB" using the following command: RouterA(config-if)#description connected to RouterB Configure the IP address (see diagram for correct address) for the interface using the following command: RouterA(config-if)#ip address 192.168.22.5 255.255.255.0 Configure the interface to use PPP encapsulation using the following command: RouterA(config-if)#encapsulation ppp Enable the interface using the following command: RouterA(config-if)#no shutdown STEP 6. Configure RIP Use the following command to enable RIP on RouterA: RouterA(config)#router rip Configure the router to receive and send only RIP Version 2 packets using the following command: RouterA(config-router)#version 2 Use the following commands to specify the networks directly connected to the router:
RouterA(config-router)#network 192.168.11.0 RouterA(config-router)#network 192.168.22.0 STEP 7. Save configuration To copy the currently running active configuration to NVRAM, so it will be used the next time you reload the router, use the following command: RouterA#copy running-config startup-config STEP 8. Configuration second router To configure the other router, RouterB, repeat the steps above. Use the network diagram to determine the correct addressing and names. To enable the back-to-back serial connection between te routers, you need to configure one router as DCE using the following command in Interface configuration mode for the serial connection on RouterB: RouterB(config-if)#clock rate 64000 STEP 9. Verify and test the configuration Verify using the ping command Host A to Host B, make sure you configured both hosts to use the nearest router's interface as the default gateway in the TCP/IP settings. On both routers, run the following command in Privileged Exec mode to determine which device is the DCE: Router#show controllers s0 On one of the routers, run the following command in Privileged Exec mode to display the parameters and current state of the active routing protocol process, and examine the output: Router#show ip protocols Use the following command to verify routing table entries on both routers: Router#show ip route Use the following command to list a summary of the interface's IP information and status on both routers, and examine the output: Router#show ip interface Use the same command with the brief option, and the notice output: Router#show ip interface brief
R1 int s0/0 no ip address encapsulation frame-relay int s0/0.23 multipoint description PARTIAL-MESH CONNECTION TO R2-R3 ip add 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.248 encapsulation frame-relay frame-relay map ip 192.168.23.2 102 broadcast
frame-relay map ip 192.168.23.3 103 broadcast int s0/0.4 point-to-point description P2P CONNECTION TO R4 ip add 192.168.14.1 255.255.255.252 encapsulation frame-relay frame-relay interface-dlci 104 R2 int s0/0 no ip address encapsulation frame-relay int s0/0.23 multipoint description PARTIAL-MESH CONNECTION TO R1-R3 ip add 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.248 encapsulation frame-relay frame-relay map ip 192.168.23.1 201 broadcast frame-relay map ip 192.168.23.3 203 broadcast R3 int s0/0 no ip address encapsulation frame-relay int s0/0.23 multipoint description PARTIAL-MESH CONNECTION TO R1-R2 ip add 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.248 encapsulation frame-relay frame-relay map ip 192.168.23.1 301 broadcast frame-relay map ip 192.168.23.2 302 broadcast R4 int s0/0 no ip address encapsulation frame-relay int s0/0.1 point-to-point description P2P CONNECTION TO R1 ip add 192.168.14.2 255.255.255.252 encapsulation frame-relay frame-relay interface-dlci 401
Você também pode gostar
- Routing in General Distance Vector RoutingDocumento75 páginasRouting in General Distance Vector RoutingSubhrendu Guha NeogiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Case StudyDocumento6 páginasChapter 1 Case StudySubhrendu Guha Neogi100% (1)
- Ip Address ClassDocumento6 páginasIp Address ClassSubhrendu Guha NeogiAinda não há avaliações
- C++ Lab Manual - 2011Documento19 páginasC++ Lab Manual - 2011Subhrendu Guha Neogi50% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- 3 3 1 Material Sorter Design ChallengeDocumento3 páginas3 3 1 Material Sorter Design Challengeapi-343534512Ainda não há avaliações
- Economics BasisDocumento14 páginasEconomics BasiskumarAinda não há avaliações
- Rubber FaberDocumento10 páginasRubber FabersoldatechAinda não há avaliações
- 1SDA066479R1 Rhe xt1 xt3 F P Stand ReturnedDocumento3 páginas1SDA066479R1 Rhe xt1 xt3 F P Stand ReturnedAndrés Muñoz PeraltaAinda não há avaliações
- APP157 CoP For Site Supervision 2009 202109Documento92 páginasAPP157 CoP For Site Supervision 2009 202109Alex LeungAinda não há avaliações
- PT 0817 Cebu Room Assignment PDFDocumento16 páginasPT 0817 Cebu Room Assignment PDFPhilBoardResultsAinda não há avaliações
- Sd-1-Parts-Book Manual Propietario SpreaderDocumento30 páginasSd-1-Parts-Book Manual Propietario Spreadergabriel sanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Libeskind Daniel - Felix Nussbaum MuseumDocumento6 páginasLibeskind Daniel - Felix Nussbaum MuseumMiroslav MalinovicAinda não há avaliações
- Fasteners Lecture 11-20-03Documento67 páginasFasteners Lecture 11-20-03laponggaAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Panel Data MSC PG: NO Panel Desc Panel CodeDocumento6 páginasElectrical Panel Data MSC PG: NO Panel Desc Panel CodeAjeng AyuAinda não há avaliações
- Draft ITP Pipeline Recertification Pearl OILDocumento3 páginasDraft ITP Pipeline Recertification Pearl OILIrsyad RosyidiAinda não há avaliações
- Ilovepdf Merged MergedDocumento209 páginasIlovepdf Merged MergedDeepak AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- CT2000 Manual EN 20151202 PDFDocumento634 páginasCT2000 Manual EN 20151202 PDFKhang NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- YcivDocumento68 páginasYcivBelhassen Saddadi100% (2)
- EMI RFI Generation From LRT SystemsDocumento27 páginasEMI RFI Generation From LRT SystemsShahidan StellarAinda não há avaliações
- R123 UpdateDocumento2 páginasR123 Updateasayed_1@hotmail.comAinda não há avaliações
- Cloud Computing - Feb-Mar 2017Documento40 páginasCloud Computing - Feb-Mar 2017Abhishek SinghAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Term Physics ReviewerDocumento5 páginas2nd Term Physics ReviewerAlfredo L. CariasoAinda não há avaliações
- Battery Power Management For Portable Devices PDFDocumento259 páginasBattery Power Management For Portable Devices PDFsarikaAinda não há avaliações
- CTLG MINI08engDocumento48 páginasCTLG MINI08enggadacz111Ainda não há avaliações
- Standard Costing ExercisesDocumento3 páginasStandard Costing ExercisesNikki Garcia0% (2)
- MOTOR Brushless ss2814 Xiii 1000kvDocumento1 páginaMOTOR Brushless ss2814 Xiii 1000kvsalah eddineAinda não há avaliações
- RE 2017 EOT Brochure 4ADocumento20 páginasRE 2017 EOT Brochure 4AOrangutan SolutionsAinda não há avaliações
- Phys114 Ps 1Documento11 páginasPhys114 Ps 1Reine Amabel JarudaAinda não há avaliações
- Brochure sp761lfDocumento10 páginasBrochure sp761lfkathy fernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Unistream-Installation Operation & MaintenanceDocumento24 páginasUnistream-Installation Operation & MaintenanceJoanna Lauer-TrąbczyńskaAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics (5th Edition) - Munson, OkiishiDocumento818 páginasFundamentals of Fluid Mechanics (5th Edition) - Munson, OkiishiMohit Verma85% (20)
- Dec 2022Documento8 páginasDec 2022John CAinda não há avaliações
- Porting Relations 2 StrokesDocumento10 páginasPorting Relations 2 Strokespistonbreaker100% (8)
- Design of Bolted Beam Splice Connections According To EC3Documento11 páginasDesign of Bolted Beam Splice Connections According To EC3Franklyn Genove100% (2)