Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Science Circulatory and Respiratory System
Enviado por
Prithvi NarasimhanDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Science Circulatory and Respiratory System
Enviado por
Prithvi NarasimhanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Science Respiratory and Circulatory System Quiz Respiratory System Breath To remove CO2, waste and bring O2 Respiratory
y System Regulates pH of blood, contains receptors for sense of smell, filters inhaled air, produces sound, rids body of water and heat via exhalation Nose - Receptors for smell stimuli -Warms, moistens, filters air -Modifies speech sounds Pharynx -Common passageway for air and food -Epiglottis covers trachea when swallowing to prevent chocking Larynx -Above trachea -Contains vocal cords, elastic folds of tissue that vibrate when air passes, produces sound Trachea -Supported by cartilage, lined by mucus to trap particles -Cilla moves mucus and trapped particles up to pharynx Bronchi -Two large tubes that lead to lungs -From bronchus to bronchioles to alveoli Lungs and Alveoli -Lung has 350 mill alveoli, 750 sp ft of surface area for gas exchange -O2 diffuses in, CO2 diffuses out -Red blood cells single file through alveoli capillaries, maximize blood cells diffusion of 02, diffusion of CO2 to alveoli -Hemoglobin in red blood cells increase carrying capacity Diaphram -Tightly seals chest cavity -Inhalation, diaphragm contracts, flattens, expands volume of chest cavity -Lower pressure per volume created, air comes in to stabilize -Exhalation when diaphragm relaxes, pulls up, decrease volume of chest cavity -Higher pressure per volume, air goes out to stabilize -Controlled by medulla oblongata (brain stem) monitor ONLY Co2 levels via pH of blood -CO2 reacts with water to form carbonic acid, lowers pH -More acidity of blood, higher breathing rate -Decrease of O2 levels make no difference Diseases -Laryngitis - inflammation of larynx -Blocked trachea treated by abdominal thrusts, a tracheotomy, or intubation -Bronchitis inhaled irritants cause excess mucus, coughing, inflammation, frequent infections -Asthma smooth muscles surrounding bronchioles spasm and constrict passageway of air -Pneumonia infection or inflammation of alveoli, cant transfer gases Problems -Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
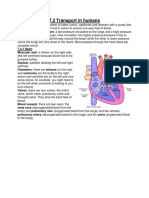
-Found in exhaust fumes, furnaces, heaters, smoke -Binds to hemoglobin 200 times more strongly than 02, interferes with ETC in mitochondria -Oderless, colorless, need CO detectors -Cigarette smoking -Contains: Carbon Monoxide, Nicotine(addictive), Tar(contains carcinogens) -Cardiovascular disease: raises blood pressure, damages blood vessels, causes buildup of plaque -Cancer: increases risk of cancer in respiratory areas -Emphysema: damages alveoli, lungs expand less, slow suffocation, long, progressive death -Chronic bronchitis paralyzes cilia in respiratory tract, bronchi become swollen, clogged with mucus Circulatory System -Deoxygenated blood enters heart from Superior, Inferior Vena Cava -Goes into right atrium, right atrium pumps blood to right ventricle -Blood enters right ventricle via Tricuspid Valve -Ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to pulmonary valve -Goes through pulmonary artery to lung and gets oxygenated -Oxygenated blood goes to left atrium via pulmonary vein -Gets pumped to mitral valve into left ventricle -Then gets pumped to aortic valve and goes to aorta -Aorta takes blood everywhere in body Vein Artery -Towards heart -Away from heart -Thinner, lower pressure -Thicker walls, more pressure from -Usually deoxygenated blood heart pumping -Exception, pulmonary vein -Smooth muscles for making veins -Smooth muscles, valves keep wider direction -Pushed by heart pumping pressure -No pressure from heart to -Usually oxygenated push blood -Deoxygenated if not part of aorta -Skeletal muscles push blood cycle, like pulmonary artery -Coronary artery, branch of aorta, gives oxygenated blood to heart cells
Capillaries Cell thin walls, small vessels, blood single file for nutrient, O2 diffusion to tissues
Blood Circulation -Heart located near center of chest -Hollow muscle, enclosed in pericardium -Two thin layers of epithelial and connective tissue -Heartbeat 2 networks of muscle fibers in heart, atrium and ventricle -When one fiber stimulated, all fibers stimulated -Network contracts at same time -Contraction begins in small group of cardiac muscle cells in right atrium, called senatorial node -Pace for heartbeat kept -Impulse picked u by atrioventrical node of fibers, taken to fibers in ventricles -Once contracts, blood flows out of heart -Neurotransmitters release signals based on blood needs Blood Pressure Heart contracts, makes wave of pressure, keeps blood flowing -Sphygmomanometer is blood pressure meter, cuff in upper arm, pumps air to stop blood flow, measures pressure at release -Sensory neurons detect blood pressure, send impulse to medulla oblongata -Releases neurotransmitters, if low blood pressure, smooth muscles contract -Kidneys remove water from blood, less pressure, (happens when heart hormones detect high blood pressure) Diseases Atherosclerosis: fatty deposits, plaque build, blocks blood flow, increases blood pressure, if too much build up, obstructs tissues beyond point
High Blood Pressure heart works harder, damages heart muscles, blood vessels Heart Attack If corornary artery blocked, O2 blocked, part of heart dies, Stroke blood clots to brain, brain cells die due to no o2 Blood Cells Kidney Regulates blood volume, blood pressure via releasing plasma to raise blood pressure pH maintained by bicarbonate buffering system, removes CO2, regulates ph to keep O2 Anemia Decrease in oxygen carrying capacity: low red blood cells, low hemoglobin, deformed red blood cells Plasma 70% of blood, 90% water, 10% dissolved salts, nutrients, enzymes, hormones, waste, plasma proteins -Plasma Proteins 3 Groups -Albumins regulate osmotic pressure, blood volume, helps transfer substances -Globulins are antibodies -Fibrinogens allow blood to clot Red Blood Cell Most numerous cells, millions in 1ml of blood, transports o2, color from hemoglobin (protein that binds to O2 in lung, transports) -thin center, produced in red bone marrow, hemoglobin fills cells, pushes out nucleus, organelles, live only 120 days White Blood Cells 1:700 red blood cells, produced n red bone marrow, have nucleus but no hemoglobin -Mature in thymus and bone marrow, exposed to foreign substances -Engulf any foreign substances -Some slip across capillary walls, attack invading organisms in body tissue -Amount increased when body fighting Blood Clots -Pieces of cytoplasm enclosed in cell membrane from large cells in bone marrow -Become sticky when encounter broken blood vessel, release clotting factors -Converts fibrinogen into sticky fibrin, prevents bleeding Lymphatic System -Blood leaks into surround tissue, lymphatic tissue keeps blood -Leakage vital for nutrient movement into tissue -Mainly plasma leaks, called lymph, returned to circulatory system via superior vena cava -Many nodes around lymph areas act as filters, with white blood cells to filter out foreign particles -Pushed by skeletal muscles -White blood cells in lymph kill pathogens -Lymph vessels in villi absorb fats and fat soluble vitamins, carry them to blood -Edema is swelling of tissues with fluid, occurs when lymph doesnt take blood leak Placenta -Temporary organ, creatied during pregnancy -Nourishes fetus selectively, selectively diffuses some nutrients from mom -No pathogens, acts as buffer -Secretes proteins to hide it from moms immune system from being attacked -Secretes hormones so fetus gets what it wants -Umbilical vein drains fetal blood from placenta to fetal heart, brings nutrients, O2 -Artery carries fetal blood away from fetal heart to placenta, removes CO2, waste -Fetal heart has connection between atria, foramen ovale, allows blood shortcut, goes to left ventricle automatically -Blood bypasses going to lung for no reason, already oxygenated, goes through ductus arteriosus, shortcut from pulmonary artery to aorta -Everything covered after birth -Umbilical cord cut, placenta comes out
Você também pode gostar
- Transport in Human: Composition of BloodDocumento5 páginasTransport in Human: Composition of Bloodelise limAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory Systemand Respiratory SystemDocumento39 páginasCirculatory Systemand Respiratory SystemEbb Edel QuibodAinda não há avaliações
- Science 9 Q1Documento7 páginasScience 9 Q1MADELYN QUIMBOAinda não há avaliações
- Human TransportDocumento6 páginasHuman Transportkavya.gulatiAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory Systemand Respiratory SystemDocumento35 páginasCirculatory Systemand Respiratory SystemLV BENDANAAinda não há avaliações
- Prepared By: Maria Lourdes P. SagunDocumento50 páginasPrepared By: Maria Lourdes P. SagunAGLDAinda não há avaliações
- Cardio and Respi ReviewerDocumento14 páginasCardio and Respi ReviewerJustine GacayanAinda não há avaliações
- Blood and Circulation, iGCSE BiologyDocumento4 páginasBlood and Circulation, iGCSE BiologyMisterBlueSky89% (9)
- Circulatory System NotesDocumento31 páginasCirculatory System NotesJMHenry0% (1)
- Transport in Mammal: and The Circulatory SystemDocumento54 páginasTransport in Mammal: and The Circulatory SystemNadeem IqbalAinda não há avaliações
- (Human) Transport Systems pt2Documento7 páginas(Human) Transport Systems pt2QI EN, NATALIE CHUAAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in HumansDocumento8 páginasTransport in HumansRaima QaiserAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento6 páginasCardiovascular SystemKerwin LimAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in Animals BIOLOGY bySATRIADocumento7 páginasTransport in Animals BIOLOGY bySATRIASatria HalimAinda não há avaliações
- Science ReviewerDocumento19 páginasScience ReviewerfluyuuyyyAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in AnimalsDocumento4 páginasTransport in AnimalsToto BrownAinda não há avaliações
- Body Systems AnatomyDocumento9 páginasBody Systems AnatomyDeepikaAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 1-Lifestyle, Health & Risk: WaterDocumento11 páginasTopic 1-Lifestyle, Health & Risk: Waternimz1992Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 - Blood and CirculationDocumento10 páginasChapter 5 - Blood and Circulationonlooker.eternityAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento2 páginasChapter 6api-304486052Ainda não há avaliações
- The Circulatory SystemDocumento4 páginasThe Circulatory SystemJoiSatannAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory SystemDocumento5 páginasCirculatory SystemDiane YapAinda não há avaliações
- The Circulatory StstemDocumento6 páginasThe Circulatory StstemCherisse MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular System PPT FeDocumento26 páginasCardiovascular System PPT FeAngel Grace GaliasAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 1 Revision NotesDocumento6 páginasTopic 1 Revision NotesAldrin Tom100% (1)
- science review material包括了LymphaticDocumento7 páginasscience review material包括了Lymphaticjamieli234Ainda não há avaliações
- Respiratory System: A System That Help You BreatheDocumento5 páginasRespiratory System: A System That Help You BreatheFynn NiallAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory SystemDocumento19 páginasCirculatory SystemСоня КропельницкаяAinda não há avaliações
- Bio NotesDocumento6 páginasBio NotesJessica KunderAinda não há avaliações
- 2 CardioDocumento26 páginas2 Cardiorashmi_harryAinda não há avaliações
- ANAPHY FinalDocumento2 páginasANAPHY Finalreized02Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento6 páginasCardiovascular SystemNatalie Odette Zárate BeristainAinda não há avaliações
- Bio ReviewDocumento7 páginasBio ReviewLim MonyratanakAinda não há avaliações
- Biology 5Documento10 páginasBiology 5iolie demetriouAinda não há avaliações
- Animal Test ReviewDocumento14 páginasAnimal Test Reviewtinaroseg6Ainda não há avaliações
- Heart Physiology and DisordersDocumento9 páginasHeart Physiology and DisordersLottie EvansAinda não há avaliações
- POINTERS-SCIENCE Grade 9 Quarter 1Documento7 páginasPOINTERS-SCIENCE Grade 9 Quarter 1Lunyl DelloAinda não há avaliações
- Science Notes - Body SystemsDocumento6 páginasScience Notes - Body SystemsSarvika DusheAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Tipos de Válvulas en El CorazónDocumento8 páginas4 Tipos de Válvulas en El CorazóngenesisAinda não há avaliações
- Biology RevisionDocumento11 páginasBiology RevisionifratsubhaAinda não há avaliações
- Science 9 Q1Documento7 páginasScience 9 Q1MADELYN QUIMBOAinda não há avaliações
- GIDB4288666-Circulatory System NotesDocumento6 páginasGIDB4288666-Circulatory System Notessky moonAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer ScienceDocumento12 páginasReviewer Scienceethansuico13Ainda não há avaliações
- C10Documento318 páginasC10azfdin50% (2)
- Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With Other Organ SystemsDocumento16 páginasRespiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With Other Organ SystemsAlelli Bianca Daniel AlipioAinda não há avaliações
- 3.1 CirculatorySystemDocumento29 páginas3.1 CirculatorySystemMuhammad AsfarAinda não há avaliações
- Best Basic Circulatory SystemDocumento44 páginasBest Basic Circulatory SystemJerilee SoCute WattsAinda não há avaliações
- Evolution of The Circulatory SystemDocumento47 páginasEvolution of The Circulatory SystemWwwanand111Ainda não há avaliações
- Transport in AnimalsDocumento7 páginasTransport in Animalstmoatshe96Ainda não há avaliações
- Circulatory, Excretory and Lymphatic Syst.Documento8 páginasCirculatory, Excretory and Lymphatic Syst.Angela Gutierrez GomezAinda não há avaliações
- The Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemDocumento28 páginasThe Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemShamaeNogaAinda não há avaliações
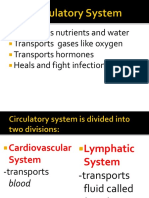
- Transports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsDocumento46 páginasTransports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsElla LlamasAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory SystemDocumento14 páginasCirculatory SystemTracey MusclowAinda não há avaliações
- Pe Exam PrepDocumento5 páginasPe Exam PrepMaria IezhitsaAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in AnimalsDocumento12 páginasTransport in AnimalsJedidiah DickAinda não há avaliações
- 07 - Cardiovascular System DeclutteredDocumento47 páginas07 - Cardiovascular System DeclutteredCatherine SyAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory - Circulatory SystemDocumento3 páginasRespiratory - Circulatory SystemClaude PeñaAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory and Respiratory SystemDocumento49 páginasCirculatory and Respiratory SystemAmy SaraAinda não há avaliações
- 5.2 Transport in HumansDocumento11 páginas5.2 Transport in Humans박찬우Ainda não há avaliações
- PintoOCPDtreatmentchapter PDFDocumento16 páginasPintoOCPDtreatmentchapter PDFSabrina HortopanAinda não há avaliações
- Coronary Artery Bypass SurgeryDocumento3 páginasCoronary Artery Bypass Surgeryapi-355048975Ainda não há avaliações
- Guidelines Develeopment Skills Labs MedicalCollegesDocumento2 páginasGuidelines Develeopment Skills Labs MedicalCollegesChandan MishraAinda não há avaliações
- EHOPE GuidelinesDocumento5 páginasEHOPE GuidelinesranAinda não há avaliações
- Theorist Task Stage Patient Description 1. Erik Erikson Generativity vs. StagnationDocumento8 páginasTheorist Task Stage Patient Description 1. Erik Erikson Generativity vs. StagnationRina CebreroAinda não há avaliações
- Application Form For Financial Assistance For Cme ProgrammesDocumento14 páginasApplication Form For Financial Assistance For Cme ProgrammesAnsar AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Neo Launch .Rand 6ifp79iaori5qDocumento2 páginasNeo Launch .Rand 6ifp79iaori5qAnonymous sfkedkymAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Clinical Pharmacology 9th Edition Visovsky Test BankDocumento7 páginasIntroduction To Clinical Pharmacology 9th Edition Visovsky Test BankJeremyBellotdfx100% (18)
- Paracetamol PODocumento3 páginasParacetamol POSheena GallardoAinda não há avaliações
- Case StudyDocumento27 páginasCase Studyapi-313356122Ainda não há avaliações
- UW Qbank Step-3 MWDocumento513 páginasUW Qbank Step-3 MWSukhdeep Singh86% (7)
- Gynec and Obs. Topic Fetal DistressDocumento45 páginasGynec and Obs. Topic Fetal DistressRajdeep ParmarAinda não há avaliações
- RMPDocumento55 páginasRMPKaty Sanchez100% (1)
- CMS 1450 (UB 04) InstructionsDocumento12 páginasCMS 1450 (UB 04) InstructionsKarna Palanivelu67% (3)
- Pregnant Trying To Conceive: Zika Virus: Everything Pregnant Women Should KnowDocumento7 páginasPregnant Trying To Conceive: Zika Virus: Everything Pregnant Women Should KnowClaireAinda não há avaliações
- Comparison - VA Gulf War Research Strategic Plan As Revised by VA Staff - 05-31-2012Documento69 páginasComparison - VA Gulf War Research Strategic Plan As Revised by VA Staff - 05-31-2012Anthony HardieAinda não há avaliações
- Iptec Teaching LogDocumento2 páginasIptec Teaching Logapi-508924243Ainda não há avaliações
- Haloperidol: Brand Name: HaldolDocumento15 páginasHaloperidol: Brand Name: Haldolteguh aminAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Sem Sport Science Assignment ContentDocumento9 páginas1st Sem Sport Science Assignment ContentKobasen LimAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Accountability - An Important Aspect of Clinical ResearchDocumento15 páginasDrug Accountability - An Important Aspect of Clinical ResearchTrialJoinAinda não há avaliações
- Yanoff DukerDocumento8 páginasYanoff DukerFerdinando BaehaAinda não há avaliações
- Management For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocumento3 páginasManagement For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiamarivohAinda não há avaliações
- 82medical NegligenceDocumento35 páginas82medical Negligencepcarsten-1Ainda não há avaliações
- 5 Processes of LaborDocumento2 páginas5 Processes of LaborElla Rene MartinAinda não há avaliações
- Ophthalmology Clinical Vignettes Oral Exam Study GuideDocumento12 páginasOphthalmology Clinical Vignettes Oral Exam Study Guideonur temizsoyluAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan ON AppendicitisDocumento14 páginasLesson Plan ON AppendicitisrevathyAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study On Normal Vaginal DeliveryDocumento24 páginasCase Study On Normal Vaginal DeliveryPabhat Kumar80% (30)
- Laughter Yoga Leader Manual PDFDocumento61 páginasLaughter Yoga Leader Manual PDFlighteagles131100% (4)
- Lesson Plan On Procedure of Bed BathDocumento9 páginasLesson Plan On Procedure of Bed Bathchinchu64% (14)
- Morphine (Astramorph)Documento1 páginaMorphine (Astramorph)Adrianne BazoAinda não há avaliações