Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Physics Chapter 14 and 15
Enviado por
lollypop1288Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Physics Chapter 14 and 15
Enviado por
lollypop1288Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
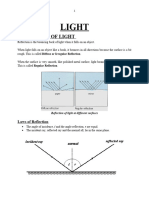
REFRACTION Light rays reflect and refract.
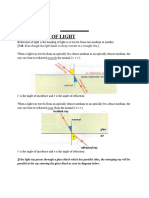
If the light slows down, it bends toward the normal line (glass < air). Angles are measured with the normal line. Light rays are reversible. LAW OF REFRAC
c = 3 108 m/s v is always less than c, so n >1 for all media. nair = 1.000293 n is dimensionless. n is a measure of the optical density of a material.
Angles
must be measured with the normal.
LENSES-REFRACTION A lens is a transparent object that converges or diverges light by refraction. A converging lens is thicker at the middle. A diverging lens is thinner at the middle. Light actually bends at each surface. However, for thin lenses, we can show light bending only once at the center of the lens. Focal length (f) is the distance from the focal point (F) to the center of the lens.
Refraction-Sign Conventions p is positive if the object is in front of the lens.
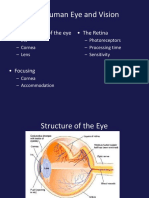
q is positive if the image is behind the lens (real and inverted). q is negative if the image is in front of the lens (virtual and upright). f is positive for converging lenses and negative for diverging lenses. h and h are positive if upright and negative if inverted. The Eye and Corrective Lenses-REfractiom Light is refracted at both the cornea (outer surface) and the lens. When functioning properly, the converging lens can adjust so that the image is focused on the retina. Muscles adjust the thickness of the lens. Many people are nearsighted (myopia) and cant see distant objects clearly. Older people are often farsighted (hyperopia) and cant see nearby objects. The lens becomes inflexible with age and cant be made thicker to focus on nearby objects. Nearsightedness The image forms in front of the retina, possibly because the retina is too long. What type of lens is needed in front of the eye to correct the problem, converging or diverging? Explain your reasoning. Answer: a diverging lens Farsighted The image forms behind the retina, possibly because the lens is inflexible. What type of lens is needed in front of the eye to correct the problem, converging or diverging? Explain your reasoning. Answer: a converging lens Combining Lenses Microscopes and refracting telescopes use two lenses. The objective lens forms a real image that is located inside the focal point of the eyepiece. The eyepiece magnifies the first image, creating a large virtual image.
Total internal reflection occurs if the angle in the denser medium is too great. Light cant emerge so it is reflected back internally. Occurs if the angle is greater than the critical angle (c). Used in fiber optics, right angle prisms, and diamond cutting.
c occurs when the angle in the less dense medium is 90. At the critical angle, the emerging ray travels along the surface. At greater angles, the rays are totally internally reflected.
hot air near the earths surface.
Mirages are caused by the refraction of light as it strikes the
This phenomena can be observed when driving on blacktop roads on hot summer days. Inverted cars can be seen approaching, with the actual cars up above them.
Dispersion Refraction or n depends on the wavelength. Longer wavelengths refract less. Prisms disperse the light into a spectrum. Chromatic aberration is a lens problem where different colors focus at different points. Can lead to imperfect images for cameras with less expensive lenses.
Refraction: Why does the lawnmower turn when it strikes the grass? The right wheel slows down before the left one. Light waves behave in the same way. Refraction is the bending (change in direction) of light when it travels from one medium into another. Caused by a change in speed
Você também pode gostar
- Facts of Light: The Qualities of Light Every Photographer Needs to KnowNo EverandFacts of Light: The Qualities of Light Every Photographer Needs to KnowAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 7 5Documento29 páginasLecture 7 5mysaustine1Ainda não há avaliações
- Decoding Light: Siva PrasadDocumento30 páginasDecoding Light: Siva PrasadAWS DEVELOPERAinda não há avaliações
- CH 4 Human Eye Notes NewDocumento10 páginasCH 4 Human Eye Notes Newsatwik ChakrabortyAinda não há avaliações
- Delhi Public School: Structure of EyeDocumento10 páginasDelhi Public School: Structure of Eyekakashi sAinda não há avaliações
- Optical InstrumentsDocumento30 páginasOptical InstrumentsSAWATI KUMARI100% (1)
- Optical InstrumentsDocumento30 páginasOptical InstrumentsSAWATI KUMARIAinda não há avaliações
- Add Slide AbberationDocumento119 páginasAdd Slide AbberationRaissaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Optics For Photogrammetry: Janak Raj JoshiDocumento32 páginasBasic Optics For Photogrammetry: Janak Raj JoshiAshish ChaliseAinda não há avaliações
- Orca Share Media1581407485099Documento15 páginasOrca Share Media1581407485099EmmanAinda não há avaliações
- Hecht - Chapter 5Documento48 páginasHecht - Chapter 5JunHyoung KimAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 EyeDocumento28 páginasChapter 5 EyeKoushik Roy SwtHrtAinda não há avaliações
- LIGHT PART II: Reflection, Refraction, Mirrors and Lenses The Big IdeaDocumento24 páginasLIGHT PART II: Reflection, Refraction, Mirrors and Lenses The Big IdeanidharshanAinda não há avaliações
- LightDocumento6 páginasLightNishi ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Refraction: DR Intan Dwi Rahayu SPMDocumento52 páginasRefraction: DR Intan Dwi Rahayu SPMlaksonoAinda não há avaliações
- L 31 Light and Optics-3: - Images Formed by MirrorsDocumento20 páginasL 31 Light and Optics-3: - Images Formed by MirrorsZainuddin Surkan HAinda não há avaliações
- Ray OpyicsDocumento56 páginasRay OpyicsDhruv JainAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedDocumento40 páginasCHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedPriyaa JayasankarAinda não há avaliações
- WP4 Light WavesDocumento16 páginasWP4 Light Waveswarona letangAinda não há avaliações
- Refraksi YennyDocumento72 páginasRefraksi Yenny1910096Ainda não há avaliações
- A Concave Spherical Mirror: F R/2 1/s+1/s 1/f M - S /sDocumento19 páginasA Concave Spherical Mirror: F R/2 1/s+1/s 1/f M - S /sNathan KingAinda não há avaliações
- Mirrors and Lenses: and How Brain Adapts To The Image Reflected or AbsorbedDocumento20 páginasMirrors and Lenses: and How Brain Adapts To The Image Reflected or AbsorbedJoy Perez100% (1)
- 2 Chapter5eyeDocumento34 páginas2 Chapter5eyeSanjeev KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Light - 3 G8 23-24Documento57 páginasLight - 3 G8 23-24hassanaayan03Ainda não há avaliações
- The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocumento4 páginasThe Human Eye and The Colourful WorldArun Arul David100% (1)
- Refraction: Dr. Boyke Sisprihattono, SPMDocumento53 páginasRefraction: Dr. Boyke Sisprihattono, SPMPurnomo Ponco NugrohoAinda não há avaliações
- GNR649 Lecture33 Optics TelescopesDocumento36 páginasGNR649 Lecture33 Optics TelescopesR KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Optical TelescopeDocumento30 páginasOptical TelescopeAbdul Rasyid ZakariaAinda não há avaliações
- Retinos PDFDocumento83 páginasRetinos PDFPaulo Gan100% (2)
- Lens & MirrorDocumento8 páginasLens & Mirrordivya singh100% (1)
- Refraction Error: Alvina Elsa BidariDocumento25 páginasRefraction Error: Alvina Elsa BidariBayu AdityaAinda não há avaliações
- Updaed Clinical Optics and Refraction - SG (1851)Documento55 páginasUpdaed Clinical Optics and Refraction - SG (1851)TalalAinda não há avaliações
- Human Eye NotesDocumento10 páginasHuman Eye NotesBhavesh KalkhandaAinda não há avaliações
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 11 2017Documento13 páginasStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 11 2017satishAinda não há avaliações
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocumento6 páginasRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsJasdeep SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Total Internal ReflectionDocumento24 páginasTotal Internal ReflectionasyiqqinAinda não há avaliações
- A Sound Person's Guide To LightingDocumento4 páginasA Sound Person's Guide To LightingnidharshanAinda não há avaliações
- 7.1 Answers: RememberingDocumento21 páginas7.1 Answers: RememberingDanny TAinda não há avaliações
- Thin Lenses: Prepared By: Jenno S. Lantaya, OdDocumento31 páginasThin Lenses: Prepared By: Jenno S. Lantaya, OdKwenzie FortalezaAinda não há avaliações
- Tom Optics 2012Documento60 páginasTom Optics 2012Jasper Catabay UganizaAinda não há avaliações
- Telescope 140915062428 Phpapp01Documento28 páginasTelescope 140915062428 Phpapp01Gregorius Agung Aryasatya WardhanaAinda não há avaliações
- 5793565-Class 10 - Science - Phy - Human Eye and The Colourful World - Handouts - Shyni & VipinaDocumento9 páginas5793565-Class 10 - Science - Phy - Human Eye and The Colourful World - Handouts - Shyni & VipinaUrmila GAinda não há avaliações
- LightDocumento48 páginasLightDhruv TalwareAinda não há avaliações
- Pengenalan Teleskop Kursus Ilmu Falak OIFDocumento42 páginasPengenalan Teleskop Kursus Ilmu Falak OIFHariyadi D. PutragaAinda não há avaliações
- Sight 3 Eye-1Documento38 páginasSight 3 Eye-1yankhochataika04Ainda não há avaliações
- Reflection & RefractionDocumento50 páginasReflection & Refractionannette.geesiawan1Ainda não há avaliações
- HPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 10-1Documento45 páginasHPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 10-1Praise NehumambiAinda não há avaliações
- RefraksiDocumento42 páginasRefraksiGalihAinda não há avaliações
- Chapt07 LectureDocumento39 páginasChapt07 LectureHardev SinghAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Science 2Q Quiz ReviewerDocumento10 páginas10 Science 2Q Quiz ReviewersJIqsAinda não há avaliações
- Optical SystemDocumento23 páginasOptical SystemluckyAinda não há avaliações
- OpticsDocumento56 páginasOpticsahsan shahAinda não há avaliações
- Defects in Vision: Observed Effect Underlying Cause DescriptionDocumento2 páginasDefects in Vision: Observed Effect Underlying Cause DescriptionNirmalrahul_1990Ainda não há avaliações
- Refraction 2Documento47 páginasRefraction 2RuDy RaviAinda não há avaliações
- Light-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocumento10 páginasLight-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldsidztoucheAinda não há avaliações
- Uee - 51Documento13 páginasUee - 51Nandini PerlaAinda não há avaliações
- PhysicsDocumento14 páginasPhysicsManish PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Coursebook: Track Your ProgressDocumento5 páginasCoursebook: Track Your ProgressKrishaAinda não há avaliações
- WP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2Documento11 páginasWP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2matsweamogelang89Ainda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetism and Optics - Historical ChronologyDocumento12 páginasElectromagnetism and Optics - Historical ChronologyFrederick David TombeAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No. 6 SpectrosDocumento6 páginasExperiment No. 6 SpectrosArianne Balaoing80% (5)
- Presented For CMA Analytical Workshop 2012 Neal LeddyDocumento55 páginasPresented For CMA Analytical Workshop 2012 Neal LeddygprjesAinda não há avaliações
- Grids and Scatter ReductionDocumento79 páginasGrids and Scatter ReductionMondiaal Financial ServicesAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Nasim Zafar: COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus IslamabadDocumento43 páginasDr. Nasim Zafar: COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus IslamabadAhmerz Chillz WinterzAinda não há avaliações
- Sylvania BKD Dual BeamKat HID Floodlight Spec Sheet 1-87Documento4 páginasSylvania BKD Dual BeamKat HID Floodlight Spec Sheet 1-87Alan MastersAinda não há avaliações
- XRD BasicsDocumento5 páginasXRD Basics777894292Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 4Documento20 páginasUnit 4Parth PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Current Applied Physics: Shalom Ann Mathews, D. Rajan BabuDocumento15 páginasCurrent Applied Physics: Shalom Ann Mathews, D. Rajan BabuSoham MukherjeeAinda não há avaliações
- M. Kramer - Propagation and Damping of M +1 and M - 1 Helicon Modes in An Inhomogeneous Plasma ColumnDocumento4 páginasM. Kramer - Propagation and Damping of M +1 and M - 1 Helicon Modes in An Inhomogeneous Plasma ColumnHimaszAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 3 Thermal RadiationDocumento7 páginasExperiment 3 Thermal RadiationSheila Roselley100% (2)
- Electro Optic EffectDocumento8 páginasElectro Optic EffectAlfonso MeerAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank For First Year First Sem Question Bank For Physics-I Regulation 20913Documento21 páginasQuestion Bank For First Year First Sem Question Bank For Physics-I Regulation 20913PRIYA RAJIAinda não há avaliações
- Part 2 Questions OnlyDocumento42 páginasPart 2 Questions Onlyarmando licanda BSE Math 2AAinda não há avaliações
- Waveguides S NotesDocumento84 páginasWaveguides S NotesjuniAinda não há avaliações
- 4f SystemDocumento4 páginas4f SystemĐặng Thái NhậtAinda não há avaliações
- Flir p65 Thermal Imaging CameraDocumento2 páginasFlir p65 Thermal Imaging CameraMiguel NavaAinda não há avaliações
- BJ - Cable Type - EN - TCD210042AA - CATALOG - WDocumento2 páginasBJ - Cable Type - EN - TCD210042AA - CATALOG - WJORGE RODAinda não há avaliações
- (Miller05) JPhysChemB - Sensitivity of Metal Nanoparticle Surface Plasmon Resonance To The Dielectric EnvironmentDocumento10 páginas(Miller05) JPhysChemB - Sensitivity of Metal Nanoparticle Surface Plasmon Resonance To The Dielectric EnvironmentspinbrionesAinda não há avaliações
- J Phys Condens Matter 18 (2006) 165Documento16 páginasJ Phys Condens Matter 18 (2006) 165Balakrishnaiah RAinda não há avaliações
- GE Fluorescent Trimline T8 Lamps Brochure 4-88Documento4 páginasGE Fluorescent Trimline T8 Lamps Brochure 4-88Alan MastersAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Pinhole CameraDocumento5 páginasWhat Is A Pinhole CameraSuniil PachisiaAinda não há avaliações
- FTIR and Raman Spectroscopy ReaderDocumento22 páginasFTIR and Raman Spectroscopy Readerchemist25Ainda não há avaliações
- Laser and Its ApplicationsDocumento147 páginasLaser and Its Applicationsviji nanduAinda não há avaliações
- Pentacon Six-02Documento28 páginasPentacon Six-02Melissa Moreira TYAinda não há avaliações
- Lighting DesignDocumento34 páginasLighting DesignMitiMehta2290% (29)
- OPTICS For Optometry StudentsDocumento336 páginasOPTICS For Optometry StudentsSmaraAinda não há avaliações
- Modul-5 Panduan Design FTTH 2014 VER 1.1Documento75 páginasModul-5 Panduan Design FTTH 2014 VER 1.1Ivan FernaldyAinda não há avaliações
- A Technical Seminar Report: "Optical Computing"Documento6 páginasA Technical Seminar Report: "Optical Computing"ABHII REDDY GAinda não há avaliações
- PM15 U25A Specialty FibersDocumento4 páginasPM15 U25A Specialty FiberscolinyAinda não há avaliações