Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Econ Chapter 35
Enviado por
Matt David TelkerDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Econ Chapter 35
Enviado por
Matt David TelkerDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Matt Telker Mr. Beler AP Macroeconomics 04.23.
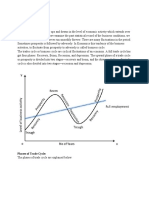
12 Chapter 35: The Short-Run Trade-Off between Inflation and Unemployment I. The Phillips Curve A. a curve that shows the short-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment B. Aggregate Demand, Aggregate Supply, and the Phillips Curve 1. The Phillips curve simply shows the combination of inflation and unemployment that arise in the short run as shifts in the aggregate-demand curve move the economy along the short-run aggregate-supply curve 2. An increase in aggregate demand for goods and services leads to a larger output of goods and services and a higher price level. Larger output means greater employment and, thus, a lower rate of employment 3. The higher the price level in the current year, the higher the rate of inflation 4. Monetary and fiscal policy can move an economy along the Phillips curve Shifts in the Phillips Curve: The Role of Expectations A. The Long-Run Phillips Curve 1. Classical theory points to growth in the money supply as the primary determinant of inflation, but classical theory also states that monetary growth does not affect real variables such as output and employment. a. Long run curve is vertical, unemployment will always gravitate back to its normal rate 2. The vertical curve is an expression of the classical idea of monetary neutrality B. The Meaning of Natural 1. Natural rate of unemployment is not necessarily the socially desirable rate of unemployment, nor is it constant over time 2. New union uses market power to raise real wages. This results in excess worker supply, higher natural rate of unemployment 3. To reduce natural rate of unemployment, policymakers should look to policies that improve the functioning of the labor market C. The Short-Run Phillips Curve 1. Unemployment Rate = Natural rate of unemployment a(actual inflation expected inflation) Shifts in the Phillips Curve: The Role of Supply Shocks A. Supply shock an event that directly alters firms costs and prices, shifting the economys aggregate-supply curve and thus the Phillips curve 1. Oil price increase B. Combination of rising prices and falling output is called stagflation
II.
III.
IV.
The Cost of Reducing Inflation A. The Sacrifice Ratio 1. the number of percentage points of annual output lost in the process of reducing inflation by one percentage point 2. A typical estimate is 5 a. For each percentage point that inflation is reduced, 5 percent of annual output must be sacrificed B. Rational Expectations and the Possibility of Costless Disinflation 1. Rational expectations the theory according to which people optimally use all the information they have, including information about government policies, when forecasting the future 2. according to those rational-expectation theorists, sacrifice ration estimates were unreliable guides since people take their expectations of inflation into account when policies change
Você também pode gostar
- 28 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocumento10 páginas28 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supplyjaden.toh.2023Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson 26 ActivityDocumento5 páginasLesson 26 ActivityRandy WangAinda não há avaliações
- Macroeconomics: GDP, Business Cycles, Keynesian ModelDocumento24 páginasMacroeconomics: GDP, Business Cycles, Keynesian Modelmonica rajuAinda não há avaliações
- The Short-Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and UnemploymentDocumento27 páginasThe Short-Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and UnemploymentNedaabdiAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 030Documento18 páginasChap 030George WagihAinda não há avaliações
- A. Monetary and Fiscal Policy: Unit FiveDocumento10 páginasA. Monetary and Fiscal Policy: Unit FiveShoniqua JohnsonAinda não há avaliações
- Case StudyDocumento8 páginasCase Studya_mohapatra55552752Ainda não há avaliações
- InflationDocumento10 páginasInflationRavi PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 35: The Short-Run Trade-Off Between Inflation and UnemploymenDocumento5 páginasChap 35: The Short-Run Trade-Off Between Inflation and UnemploymenTrần Ngọc Châu GiangAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 4: The Full Macroeconomic Model ObjectivesDocumento26 páginasLesson 4: The Full Macroeconomic Model ObjectivesAChristensen1299Ainda não há avaliações
- Economie en AnglaisDocumento11 páginasEconomie en AnglaisKévin PereiraAinda não há avaliações
- The GDP Deflactor - IsDocumento3 páginasThe GDP Deflactor - IsNetha CjAinda não há avaliações
- ECN 111 Chapter 17 Lecture Notes: Short-Run Phillips CurveDocumento2 páginasECN 111 Chapter 17 Lecture Notes: Short-Run Phillips CurveAleihsmeiAinda não há avaliações
- Economics BoardsDocumento26 páginasEconomics BoardsmegaAinda não há avaliações
- Inflarion-Types-Determinants-And-EffectsDocumento15 páginasInflarion-Types-Determinants-And-EffectssourojeetsenAinda não há avaliações
- Business Cycle Unemployment and Inflation 2Documento22 páginasBusiness Cycle Unemployment and Inflation 2GeloAinda não há avaliações
- Term ReportDocumento5 páginasTerm ReportHaider AbbasAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation Unemployment Relationship Phillips CurveDocumento21 páginasInflation Unemployment Relationship Phillips CurveYatin GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of Inflation On PovertyDocumento5 páginasImpact of Inflation On PovertyVincent QuitorianoAinda não há avaliações
- Eco Group AssignmentDocumento10 páginasEco Group AssignmentMr ArmadilloAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Macro NotesDocumento112 páginasAdvanced Macro NotesAlexander MunaAinda não há avaliações
- Economics InflationDocumento14 páginasEconomics InflationTanmay SinghalAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation:: Types, Causes, Measurement & Philips CurveDocumento22 páginasInflation:: Types, Causes, Measurement & Philips CurveNabin SijaliAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation: Q - 1 Give The Definition of Inflation and Explain Its NatureDocumento11 páginasInflation: Q - 1 Give The Definition of Inflation and Explain Its NatureShilpan ShahAinda não há avaliações
- MacroeconomicsDocumento4 páginasMacroeconomicsPrerna MakhijaniAinda não há avaliações
- Nicholson SnyderDocumento16 páginasNicholson SnyderHenry DunaAinda não há avaliações
- AD-AS Model Explains Economic FluctuationsDocumento8 páginasAD-AS Model Explains Economic Fluctuations- OriAinda não há avaliações
- CHAP 33 - Group3Documento15 páginasCHAP 33 - Group3thaothuvg2004Ainda não há avaliações
- Meaning and Types of InflationDocumento7 páginasMeaning and Types of Inflationaparajita promaAinda não há avaliações
- EDEV 311 Inflation UnemploymentDocumento29 páginasEDEV 311 Inflation UnemploymentViviene Seth Alvarez LigonAinda não há avaliações
- Microeconomics AssignmentDocumento6 páginasMicroeconomics AssignmentHiya ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- GDP Equals The Value of The Final Goods and GDP Is The Sum of Value Added in The GDP Is The Sum of Incomes in The Economy During ADocumento15 páginasGDP Equals The Value of The Final Goods and GDP Is The Sum of Value Added in The GDP Is The Sum of Incomes in The Economy During AAkashAinda não há avaliações
- Aggregate Supply DemandDocumento9 páginasAggregate Supply DemandDom PaciaAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation and Unemployment: What Is The Connection?Documento24 páginasInflation and Unemployment: What Is The Connection?sajid93Ainda não há avaliações
- MBA Sem-1 Unit 4 Part II EfmDocumento35 páginasMBA Sem-1 Unit 4 Part II EfmasifbhaiyatAinda não há avaliações
- 14economic DevelopmentDocumento7 páginas14economic DevelopmentChristine Joy TabangayAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation & UnemploymentDocumento21 páginasInflation & UnemploymentGaurav AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Number: 14 Topic: The Short Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and UnemploymentDocumento7 páginasLesson Number: 14 Topic: The Short Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and Unemploymentletlet liitAinda não há avaliações
- Keynesian Vs Classical Models and PoliciesDocumento8 páginasKeynesian Vs Classical Models and PoliciesSibhat TilahunAinda não há avaliações
- UnemploymentDocumento10 páginasUnemploymentGoonshikha RamguttyAinda não há avaliações
- Causes of InflationDocumento4 páginasCauses of InflationAlina SlavuAinda não há avaliações
- MacroeconomicsDocumento6 páginasMacroeconomicsAbdur Rafay Mohyuddin100% (2)
- AD AS QuestionsDocumento15 páginasAD AS QuestionsRizka SyarifAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Money and BankingDocumento11 páginasIntroduction To Money and BankingAyomikunAinda não há avaliações
- (123doc) - Chapter-35Documento5 páginas(123doc) - Chapter-35Pháp NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocumento26 páginasAggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyYashik SahniAinda não há avaliações
- The Phillips Curve: Inflation and Unemployment RelationshipDocumento18 páginasThe Phillips Curve: Inflation and Unemployment RelationshipParimita Sarma100% (1)
- Executive Summary: Economic Environment Business InflationDocumento52 páginasExecutive Summary: Economic Environment Business Inflationsj_mukherjee5506Ainda não há avaliações
- The Phillips Curve in Macau and Its Implications For Macroeconomic PolicyDocumento15 páginasThe Phillips Curve in Macau and Its Implications For Macroeconomic PolicysaidAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment of InflationDocumento13 páginasAssignment of InflationSaira KousarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10: Output, Inflation, and Unemployment: Alternative ViewsDocumento11 páginasChapter 10: Output, Inflation, and Unemployment: Alternative Viewsstanely ndlovuAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3: Business Cycle, Inflation and UnemploymentDocumento28 páginasChapter 3: Business Cycle, Inflation and UnemploymentChristian Jumao-as MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- ECO401 Short NotesDocumento9 páginasECO401 Short NotesMuhammad FarooqAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation in India.... FinalDocumento14 páginasInflation in India.... Finalappu_gudapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation-Conscious Investments: Avoid the most common investment pitfallsNo EverandInflation-Conscious Investments: Avoid the most common investment pitfallsAinda não há avaliações
- SR Trade-Off- Phillips CurveDocumento13 páginasSR Trade-Off- Phillips CurveraviAinda não há avaliações
- Aggregate Demand & Aggregate SupplyDocumento41 páginasAggregate Demand & Aggregate SupplyAlison FernandesAinda não há avaliações
- The Phillips curve relationship between inflation and unemploymentDocumento28 páginasThe Phillips curve relationship between inflation and unemploymentDinda syafiraAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation: Types, Causes and Effects (With Diagram)Documento13 páginasInflation: Types, Causes and Effects (With Diagram)Muhammad NaveedAinda não há avaliações
- Prayoga Dwi N - Summary CH 27Documento4 páginasPrayoga Dwi N - Summary CH 27Prayoga Dwi NugrahaAinda não há avaliações
- Pda Report MalasiquiDocumento9 páginasPda Report MalasiquimikerossieAinda não há avaliações
- Fixed Assets Interview Questions in R12Documento21 páginasFixed Assets Interview Questions in R12devender143Ainda não há avaliações
- Nature and Scope 1Documento1 páginaNature and Scope 1chIAinda não há avaliações
- Short-Run Technology ConstraintDocumento4 páginasShort-Run Technology ConstraintTasnim SghairAinda não há avaliações
- Variance Analysis 5.11Documento2 páginasVariance Analysis 5.11George Buliki100% (2)
- Econ 200 Problem SetsDocumento9 páginasEcon 200 Problem SetsSylvester BotelhoAinda não há avaliações
- Setup TaxbraDocumento18 páginasSetup Taxbradri0510Ainda não há avaliações
- Kaushik Basu - Understanding and Controlling InflationDocumento56 páginasKaushik Basu - Understanding and Controlling Inflationlniyer55Ainda não há avaliações
- Potain MD 265 B1 J12Documento4 páginasPotain MD 265 B1 J12viksofAinda não há avaliações
- Recueil D'exercices Corrigés de MicroéconomieDocumento73 páginasRecueil D'exercices Corrigés de MicroéconomieHa YouAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1 - FinalDocumento10 páginasAssignment 1 - FinalarafatAinda não há avaliações
- SDF Budget Q&A: ReportingDocumento3 páginasSDF Budget Q&A: ReportingKembol KepAinda não há avaliações
- Managerial Economics Syllabus and Question BankDocumento7 páginasManagerial Economics Syllabus and Question BankPraveen BadliAinda não há avaliações
- MM 1 010 Lot Size CalculationDocumento4 páginasMM 1 010 Lot Size Calculationaudi404Ainda não há avaliações
- Question 1: Answer The Following QuestionsDocumento4 páginasQuestion 1: Answer The Following QuestionsAkramElKomeyAinda não há avaliações
- CH 13 Hull OFOD8 TH EditionDocumento31 páginasCH 13 Hull OFOD8 TH EditionAlex WanowskiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5 - Market Equlibrium and Concept of Elasticity of Demand and Its ApplicationDocumento80 páginasLecture 5 - Market Equlibrium and Concept of Elasticity of Demand and Its ApplicationnivecAinda não há avaliações
- Macroeconomics and Housing A Review of The LiteratureDocumento40 páginasMacroeconomics and Housing A Review of The LiteraturemurtajihAinda não há avaliações
- Management Accounting G3 - : Graduation LevelDocumento4 páginasManagement Accounting G3 - : Graduation LevelQadirAinda não há avaliações
- Absolute AdvantageDocumento4 páginasAbsolute AdvantageKrishna Das Kota0% (1)
- Course Outline: Financial Markets and The EconomyDocumento3 páginasCourse Outline: Financial Markets and The EconomyHanan ILyasAinda não há avaliações
- Textbook Statistics TalebDocumento17 páginasTextbook Statistics TalebDom DeSiciliaAinda não há avaliações
- Deco401 Microeconomic Theory English PDFDocumento428 páginasDeco401 Microeconomic Theory English PDFkanishkAinda não há avaliações
- Analyze Equity Risk vs Market with Historical BETADocumento6 páginasAnalyze Equity Risk vs Market with Historical BETALuisMendiolaAinda não há avaliações
- Pain Handout PDFDocumento7 páginasPain Handout PDFPatrick Snell100% (2)
- This Spreadsheet Supports Analysis of The Case, "The Investment Detective" (Case 18)Documento5 páginasThis Spreadsheet Supports Analysis of The Case, "The Investment Detective" (Case 18)Chittisa Charoenpanich100% (1)
- D4 Winkler Rule of The Half 2015Documento7 páginasD4 Winkler Rule of The Half 2015VIVIANAAinda não há avaliações
- ECO 301 Homework I: Positive vs Normative AnalysisDocumento4 páginasECO 301 Homework I: Positive vs Normative AnalysisVarunJainAinda não há avaliações
- Solution.: ST ND RD THDocumento4 páginasSolution.: ST ND RD THhaggaiAinda não há avaliações