Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Experiment Number 5
Enviado por
Ali Hasan RazaDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Experiment Number 5
Enviado por
Ali Hasan RazaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
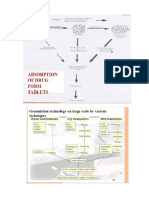
Experiment 5 Prepare Film Coated/Enteric Coated Tablets
Theory:
Film coating is discussion of thin film of polymer on the surface of the tablet core. Although the film coated tablets are possibly less elegant in appearance but they are considered more satisfactory than sugar coated tablets. Film coating process which places a skin tight coating of plastic like material over the compressed tablet was developed to produce coated tablets having essentially the same weight, size and shape as the originally compressed tablet.
Film Coating Formulation:
1. Film Former: A film former is capable of producing smooth thin film, reproducible under conventional coating conditions and applicable to variety of tablet shapes. There are two types of film formers: Enteric Film Formers: Cellulose acetate phthalate Acrylate polymer Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate Polyvinyl acetate phthalate Non-Enteric Film Formers: Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose USP Sodium carboxy methylcellulose USP Methyl hydroxyl ethylcellulose Ethylcellulose Hydroxypropyl cellulose Povidone USP
2. Solvent: It functions to dissolve or disperse the polymer and other additives and convey them to substrate surface. Examples: Water Chloroform Acetone Methanol Ethanol Methyl ethyl ketones Methylene chloride 3. Plasticizers: They produce flexibility and elasticity of the coating and thus provide durability. Examples: Castor oil Coconut oil Polyethylene glycol Glycerine Propylene glycol 4. Surfactants: They are used to enhance spreadability of the film during application. Examples: Sodium lauryl sulphate Hydrophilic polysorbates (tween) Hydrophobic sorbitan esters (span) 5. Colorants and Opaquants: They are used to make the appearance of the coated tablets handsome and distinctive. Examples: Iron oxide Titanium oxide Water soluble coating colors
6. Sweeteners and Flavourants: They are used to enhance the acceptability of tablet to the patient. Examples: Saccharine sodium 7. Glossants: They provide luster to the tablet without a separate polishing operation. Examples: Bees wax 8. Volatile Solvents: It is used to allow the spread of other components over the tablet while allowing rapid evaporation to permit an effective and speedy operation. Examples: Alcohol acetone mixture
Formulation:
Methocel (HPMC E-5) --------------------------28.3 g Polyethylene glycol (PEG400) ---------------- 2.8 g Specially denatured spirit --------------------- 230 ml Chloroform ----------------------------------------90 ml
Apparatus:
Beaker, Stirrer, Weighing balance, Hot air system, Coating pan, Hot air blower, Spraying gun.
Procedure:
Preparation of Coating Solution: 1. For the formulation of specially denatured spirit add 0.1% carbon tetrachloride. 2. First of all dissolve specially denatured spirit into chloroform. 3. Dissolve polyethylene glycol (PEG 400) into the solution. 4. At the end methocel (HPMC E-5) is dissolved by vigorous shaking in this solution.
Coating the Tablets: 1. First of all clean out the coating pan and switch on the exhaust system and hot air blower having temperature 70-80C. 2. Make the tablets dust free by blowing air. 3. Load the tablets in the coating pan. 4. Then apply the hot air on the tablets. 5. Rotate one-fourth of the pan for 2-3 minutes so that the temperature of the tablets reaches 40C. 6. This rotating procedure is continued until the cores become heated. 7. Then start continuous rotating of the pan and start the spraying of coating solution on the tablets at 40C by using spraying gun. 8. After the completion of spraying, dry the tablets for 5-10 minutes in rotating pan. The speed of rotating pan should be 2530 rpm. 9. After drying, pour out the tablets from the pan and spread them on tray and dry in an oven at about 50C.
Defects of Film Coating:
The defects of film coating include: 1. Picking and Sticking: This is when the coating removes a piece of tablet from the core. It is caused by over wetting the tablets, by under-drying or poor quality of the tablet. 2. Bridging: This occurs when the coating fills in the lettering or logo on the tablet and is typically caused by improper application of solution, poor design of the tablet embossing, high coating viscosity, and high percentage of solids in the solution or improper atomization pressure. 3. Erosion: This can be a result of soft tablets, an over wetted tablet surface, inadequate drying or lack of tablet surface strength.
4. Twinning: This is a term for two tablets that stick together during coating and it is a common problem with capsule shaped tablets. 5. Peeling and Frosting: This is a defect where a coating peels away from the tablet surface in a sheet. This could be due the defect in coating solution, over wetting, or high moisture content in the tablet core. 6. Chipping: This is a result of high pan speed, a friable tablet core or a coating solution that lacks a good plasticizer. 7. Molted Color: This refers to lack of color due to poor mixing of pigments. This occurs when coating solution is improperly prepared, the actual spray rate differs from the target rate or the tablet cores are cold. 8. Orange Peel: This refers to a coating texture that resembles the surface of an orange. It is usually the result of high atomization pressure in combination with spray rates that are too high. Removal of Defects of Film Coating: The defects of film coating can be removed by: 1. Proper wetting. 2. Proper drying. 3. Using proper coating solution. 4. Using appropriate spray rate. 5. Using appropriate atomization pressure.
Advantages of Film Coating:
1. Minimal weight increase. 2. Reduction in processing time. 3. Increase process efficiency and output. 4. Increased flexibility in formulation.
5. Enhance palatability by masking unpleasant taste or objectionable
odours. 6. Ease of ingestion. 7. Improve product appearance. 8. Protect tablets from light, oxidation and moisture.
Disadvantages of Film Coating:
1. 2. 3. 4. Increased drying time. Costly. Possible toxicity hazards especially if non polar solvents are used. Environmental pollution.
Role of Ingredients:
Methocel (HPMC E-5): Granulation binding agent, Water retaining agent. Polyethylene glycol (PEG400): Lubricating agent, Wetting agent Denatured spirit: Flavoring agent, Solvent Chloroform: Solvent
Você também pode gostar
- TabletsDocumento117 páginasTabletscontactamit_shah100% (1)
- T.Shivakumar: Kottam Institute of Pharmacy Jntu, A.PDocumento45 páginasT.Shivakumar: Kottam Institute of Pharmacy Jntu, A.PFree Escort ServiceAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet Coating PDFDocumento6 páginasTablet Coating PDFAsif Hasan Niloy100% (1)
- Tablet CoatingDocumento33 páginasTablet CoatingJames YenchoAinda não há avaliações
- Problems and Remedies For Tablet CoatingDocumento7 páginasProblems and Remedies For Tablet CoatingAnowar HossainAinda não há avaliações
- 3 PDF Original PDFDocumento30 páginas3 PDF Original PDFDevang GondaliyaAinda não há avaliações
- FRP Fish TanksDocumento33 páginasFRP Fish TanksA.Subin DasAinda não há avaliações
- Fiber Optic CablesDocumento24 páginasFiber Optic CablesARCC2030Ainda não há avaliações
- Aerodynamics of Paper AirplanesDocumento16 páginasAerodynamics of Paper AirplanesBrindleSmith111Ainda não há avaliações
- 2003-20 Communication Plan AttachmentDocumento6 páginas2003-20 Communication Plan Attachmentapi-3731879Ainda não há avaliações
- Coating ReviewDocumento20 páginasCoating ReviewsherepunjabAinda não há avaliações
- Defects in TabletsDocumento36 páginasDefects in TabletsSunil DarjiAinda não há avaliações
- Rainwater and Stormwater Harvesting Systems: Continuing Education From The American Society of Plumbing EngineersDocumento8 páginasRainwater and Stormwater Harvesting Systems: Continuing Education From The American Society of Plumbing Engineers185412Ainda não há avaliações
- Trouble Shooting Dewatering PumpDocumento136 páginasTrouble Shooting Dewatering PumpMuhammad NoorAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet Coating With Its DefectsDocumento56 páginasTablet Coating With Its Defectsjoshirohan100% (1)
- Tablet ManufactureDocumento10 páginasTablet ManufactureAdemola OgundiwinAinda não há avaliações
- 4350 9644 1 PBDocumento65 páginas4350 9644 1 PBWan MuhamammadAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet Coating Process: Made byDocumento25 páginasTablet Coating Process: Made byYuppie RajAinda não há avaliações
- CoatingDocumento50 páginasCoatingdwahyusafriAinda não há avaliações
- Gravure Trouble Shooting GuideDocumento28 páginasGravure Trouble Shooting Guidevahidpapar100% (2)
- Flexo Trouble Shooting Coloured PDFDocumento28 páginasFlexo Trouble Shooting Coloured PDFKay Thrygg83% (6)
- CapsulesDocumento60 páginasCapsulesprinceamitAinda não há avaliações
- Flexo Uv Ink TroubleshootingDocumento22 páginasFlexo Uv Ink TroubleshootingHiba Naser100% (1)
- Meat & Potatoes of Plastic Injection Moulding, Explanation & Guides TroubleshootingNo EverandMeat & Potatoes of Plastic Injection Moulding, Explanation & Guides TroubleshootingAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet CoatingDocumento45 páginasTablet CoatingIzamHamMandenoAinda não há avaliações
- Problems in Tablet ManufacturingDocumento8 páginasProblems in Tablet ManufacturingParag MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity9 PDFDocumento5 páginasActivity9 PDFSmitAinda não há avaliações
- 4 - MicroencapsulationDocumento39 páginas4 - MicroencapsulationindyAinda não há avaliações
- Processing Problems, Pharmaceutical Dosage FormsDocumento3 páginasProcessing Problems, Pharmaceutical Dosage FormsFleur Jeizl Perez100% (1)
- PelletsDocumento57 páginasPelletsHely PatelAinda não há avaliações
- 2017 Tel 1608Documento47 páginas2017 Tel 1608Alvaro Torres BozzoAinda não há avaliações
- Enteric Materials - Tablets Final Copy 2Documento10 páginasEnteric Materials - Tablets Final Copy 2Tulasee ReddiAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Dosage Form Part 3Documento24 páginasSolid Dosage Form Part 3Claire Marie AlvaranAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet CoatingDocumento51 páginasTablet CoatingsuminderAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet CoatingDocumento50 páginasTablet CoatingNaufal HanifAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture (5) Tablet Coating (Spring 2023)Documento35 páginasLecture (5) Tablet Coating (Spring 2023)ah1589681Ainda não há avaliações
- Tablet SalutDocumento9 páginasTablet SalutRiaaAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet DefectsDocumento2 páginasTablet Defectsophelion2112Ainda não há avaliações
- Tablet CoatingDocumento13 páginasTablet CoatingMaryam NoorAinda não há avaliações
- Processing ProblemDocumento3 páginasProcessing ProblemMeah PachecoAinda não há avaliações
- Name of DefectDocumento3 páginasName of DefectJana EncaboAinda não há avaliações
- CoatingDocumento19 páginasCoatingWond WossenAinda não há avaliações
- Minggu 10Documento56 páginasMinggu 10lailul apreliaAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmaceutical Tablet CoatingDocumento3 páginasPharmaceutical Tablet Coatingmkarim019Ainda não há avaliações
- Industrial Pharmacy - CoatingDocumento16 páginasIndustrial Pharmacy - CoatingSolomonAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet Coating - Final 2Documento20 páginasTablet Coating - Final 2kayes_abuAinda não há avaliações
- MQA204TDocumento30 páginasMQA204TAshimaAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet CoatingDocumento7 páginasTablet CoatingLakmi Nurul UciiAinda não há avaliações
- C-8 TabletDocumento129 páginasC-8 TabletLareina Uy Calubad67% (3)
- An Overview On Tablet CoatingDocumento4 páginasAn Overview On Tablet Coatingronahaniifah11Ainda não há avaliações
- Uc PDFDocumento15 páginasUc PDFPenAinda não há avaliações
- Tablets Aqeuos Film CoatingDocumento38 páginasTablets Aqeuos Film CoatingYuppie RajAinda não há avaliações
- Tablets-Part IIDocumento42 páginasTablets-Part IIali.menem15Ainda não há avaliações
- TabletDocumento14 páginasTabletIVLS AKCPAinda não há avaliações
- Methods of Micro EncapsulationDocumento54 páginasMethods of Micro Encapsulationanupnakat100% (7)
- 01.tablets (-I-)Documento25 páginas01.tablets (-I-)Subha ShankareeAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet CoatingDocumento15 páginasTablet CoatingKiaAinda não há avaliações
- PharmpediaDocumento56 páginasPharmpediaShyam Singh DasAinda não há avaliações
- RecubrimientoDocumento9 páginasRecubrimientoJavier CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Manufacture of Tablets (1 of 2)Documento120 páginas05 Manufacture of Tablets (1 of 2)Kyrie Gwynette OlarveAinda não há avaliações
- Film DefectDocumento3 páginasFilm Defectamitrameshwardayal100% (2)
- How To Make Arcylic Paint From Recycled PETDocumento4 páginasHow To Make Arcylic Paint From Recycled PETsimbanaitatendaAinda não há avaliações
- Common Tablet Problems and SolutionsDocumento2 páginasCommon Tablet Problems and SolutionsKumar GalipellyAinda não há avaliações
- TabletsDocumento78 páginasTabletsLoverboy ForuAinda não há avaliações
- 80415e015c47674- Microencapsulation الفرقه 5Documento52 páginas80415e015c47674- Microencapsulation الفرقه 5popmart21Ainda não há avaliações
- Flow charts of pharmaceutical quality control tests for different dosage formsNo EverandFlow charts of pharmaceutical quality control tests for different dosage formsAinda não há avaliações
- The Food Industry Innovation School: How to Drive Innovation through Complex OrganizationsNo EverandThe Food Industry Innovation School: How to Drive Innovation through Complex OrganizationsAinda não há avaliações
- Scania Jenerator DC1372A - 438-487kW PDFDocumento2 páginasScania Jenerator DC1372A - 438-487kW PDFMehmet ErenAinda não há avaliações
- Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm Based Design of StructuresDocumento1 páginaGrasshopper Optimization Algorithm Based Design of Structuresinvisible25Ainda não há avaliações
- Aluminium - Copper AlloysDocumento3 páginasAluminium - Copper AlloysRex RusselAinda não há avaliações
- Ricoh Shotmaster ZoomDocumento17 páginasRicoh Shotmaster Zoommanana mappleAinda não há avaliações
- Toyota Diesel Piston MedidasDocumento31 páginasToyota Diesel Piston MedidasCarlosArataAinda não há avaliações
- Typical Signage Drawings: Information Sign ManualDocumento49 páginasTypical Signage Drawings: Information Sign ManualMaynard BaricaAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis+of+Non Symmetrical+Flapping+AirfoilsDocumento18 páginasAnalysis+of+Non Symmetrical+Flapping+AirfoilsAsif HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Rental Power 70 KW: Specification SheetDocumento4 páginasRental Power 70 KW: Specification SheetDulguunkherlen BudkhandAinda não há avaliações
- Centrifugal PumpsDocumento6 páginasCentrifugal Pumpsjerome fajardoAinda não há avaliações
- MSDS - Molecular Sieve 4ADocumento4 páginasMSDS - Molecular Sieve 4AadeliaaaAinda não há avaliações
- E2186 Certif Conformidad - TomasDocumento6 páginasE2186 Certif Conformidad - TomasFRANCISCOAinda não há avaliações
- Netapp Cabling and Hardware BasicsDocumento14 páginasNetapp Cabling and Hardware BasicsAnup AbhishekAinda não há avaliações
- DC Rectifier - OrionDocumento12 páginasDC Rectifier - OrionLimbagaAinda não há avaliações
- Armare La Strapungere Pentru Palnsee Dale Jda B en D Teh 56465Documento24 páginasArmare La Strapungere Pentru Palnsee Dale Jda B en D Teh 56465mihaitimofteAinda não há avaliações
- TXL 025 12s Datasheet 1 en PDFDocumento11 páginasTXL 025 12s Datasheet 1 en PDFJulianCitoAinda não há avaliações
- What We Offer.: RemunerationDocumento8 páginasWhat We Offer.: Remunerationsurabhi mandalAinda não há avaliações
- Powershell Import Update Users Groups From CSV FileDocumento2 páginasPowershell Import Update Users Groups From CSV FilecrakchakibAinda não há avaliações
- A Primer On Spray Drying Chemical Engineering Nov09Documento7 páginasA Primer On Spray Drying Chemical Engineering Nov09Hikmah Triana HadiAinda não há avaliações
- Pre Accion PDFDocumento8 páginasPre Accion PDFjhoger2012Ainda não há avaliações
- Baseline Processing ReportDocumento17 páginasBaseline Processing ReportMAMAN MAMANAinda não há avaliações
- HPSIM Command Line InterfaceDocumento107 páginasHPSIM Command Line Interfacegverma80Ainda não há avaliações
- As BuiltDocumento12 páginasAs BuiltAnurag PandeyAinda não há avaliações