Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Notes Fore Fiction and Pressure For VIII Physics
Enviado por
Bhavesh DesaiDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Notes Fore Fiction and Pressure For VIII Physics
Enviado por
Bhavesh DesaiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Fore Fiction and Pressure for VIII Physics-Notes and Evaluation
FORCE AND PRESSURE
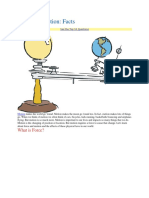
A force is a push or pulls acting on an object which changes or tends to change the state of the object. In the international system of units (SI System), the unit of force is Newton (N) that is named after Sir Isaac Newton. There are also other units like dyne, kilogram weight and pound. Action of force and its effects: A force Contact and non-contact forces Forces which act only when there is physical contact between two interacting objects are known as Contact forces. Forces which can act without physical contact between objects, i.e. those that can act from a distance, are called non-contact forces or field forces. Types of forces 1. Muscular force: This is the force we can exert with our bodies by using our muscles, e.g. pull, push, kick etc. These are contact forces 2. Magnetic force : Magnets exert forces of attraction or repulsion on other magnets. An important feature of magnetic force is that it can act from a distance, and is therefore of a non-contact force. 3. Electrostatic force: The force exerted by a charged body on another charged or uncharged body is known as electrostatic force. Electrostatic force is used to separate solid pollutant particles from smoke given out from factories. 4. Gravitational force : All objects in the universe exert a force on all other objects. This is called gravitational force. The gravitational force exerted by the Earth on all the bodies on its surface is called gravity. 5. Frictional force : The fact that the rolling ball comes to rest after some time shows that there must be a force acting on it which tends to slow it down. This force seems to be more on rough surfaces than on smooth surfaces. The force acting against the relative motion of surfaces in contact is called frictional force or friction. 6. Tension Force:Strings, ropes and chains can only pull on things! The force of pull supplied by strings, ropes or chains is called the tension force. The tension force is always directed along the length of the thing doing the pulling (string, rope, chain). i g ce: is the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it.
8. Applied Force: An applied force is a force that is applied to an object by a person or another object. If a person is pushing a desk across the room, then there is an applied force acting upon the object. The applied force is the force exerted on the desk by the person. Mass and Weight : The mass of an object is the amount of matter that is contained by the object; the weight of an object is the force of gravity acting upon that object. The mass of an object (measured in kg) by Pan Balance and will be the same no matter where in the universe that object is located. On the other hand, the weight of an object (measured in Newton) by Spring balance and will vary according to where in the universe the object is. Type of friction: Static friction:
The block remains at rest because a force of friction, equal but opposite to the applied pull, comes into action between the surfaces. Increase the force a little. The block des not move. This means that the force of friction has increased to balance the pulling force on the block. If the pulling force P is increased further, at a certain stage the block begins the move on the table. At this point the friction developed has reached the maximum value F for the two surfaces. This is called static friction. Kinetic or sliding friction Continue pulling the block with the spring balance, so that it slides at a steady speed. The reading on the spring balance is also steady and is slightly less than the static friction. This is a measure of the kinetic or sliding friction between the two surfaces. Kinetic or sliding friction is less than static friction. Rolling friction Repeat the above procedure using an identical wooden block provided with wheels on either side. The reading on the spring balance when the block moves with a steady speed is much less than the sliding friction measured above. Rolling friction is less than sliding friction. Advantages of friction Friction plays an important role in our daily life. 1) Without friction we would slip and fall every time we attempt to walk or run. There is very little friction on a wet polished floor. That is why it is easy to slip on such a floor. 2) Friction causes nails and screws to hold on to walls. 3) It would not be possible to light a matchstick without friction between its head and the side of the matchbox. 4) Cars and buses are able to run on roads because of friction between the tyres and the road. 5) Without friction writing on paper would be impossible as the tip of the pen will slip on paper. 6) It is because f f icti when brakes are applied. Disadvantages of friction Friction is a nuisance in some circumstances. 1) The heat produced in the moving parts of machinery due to friction results in wear and tear of the parts. 2) Forest fires are caused due to friction between branches of threes rubbing against each other. 3) Tyres of vehicles and soles of footwear wear out because of friction. 4) Energy is wasted in overcoming the force of friction. Minimizing friction 1) By using a suitable lubricant, like oil (for light machinery) or grease (for heavy machinery). This betwee the b ake sh es a d wheels that bicycles andautomobiles stop
helps because fluid friction is less than solid friction 2) By using wheels and ball bearings. Use of wheels between surface moving over each other reduces friction. Ball bearingshave small balls of steel between steel surfaces. Because of the balls the steel surfaces can easily moves over each other. 3) By making the rubbing surfaces smooth by polishing them. 4) Friction due to air (air resistance) or water is reduced by using streamlined shapes inaeroplanes or ships. A streamlined shape is narrow in front and broader at the back. Birds and aquatic animals have streamlined shapes which held them in flying or swimming.
Você também pode gostar
- P WEEK IV Force and Pressure VIIIDocumento22 páginasP WEEK IV Force and Pressure VIIISesha Sai KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Forces: 4 July 2015Documento32 páginasForces: 4 July 2015SoniaAlexAinda não há avaliações
- Report On FrictionDocumento6 páginasReport On FrictionYogesh RanjanAinda não há avaliações
- Force and Pressure Handout Std8 PDFDocumento8 páginasForce and Pressure Handout Std8 PDFSaghana SaravanakarthikAinda não há avaliações
- Forces and MotionDocumento29 páginasForces and MotionMoeez Ahmad100% (1)
- Topic 3 Force and EnergyDocumento45 páginasTopic 3 Force and EnergyAnthonyDomAinda não há avaliações
- Friction and the Laws of Motion - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo EverandFriction and the Laws of Motion - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksAinda não há avaliações
- Synchronous ManufacturingDocumento18 páginasSynchronous ManufacturingPatricia Romero100% (1)
- FrictionDocumento29 páginasFrictionYu ErinAinda não há avaliações
- Fisher™ FIELDVUE™ DVC6200 SIS Digital Valve ControllerDocumento116 páginasFisher™ FIELDVUE™ DVC6200 SIS Digital Valve ControllerMohsen HeidariAinda não há avaliações
- Force Work EnergyDocumento28 páginasForce Work EnergyRitam DasAinda não há avaliações
- Types of ForcesDocumento7 páginasTypes of ForcesimanuelsukarnoAinda não há avaliações
- Energy, Force, & Motion: Sixth Grade Science ExperimentsNo EverandEnergy, Force, & Motion: Sixth Grade Science ExperimentsNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- Chapter - 11: Force and PressureDocumento15 páginasChapter - 11: Force and PressurePraveen MaramAinda não há avaliações
- XI Maths WorksheetDocumento23 páginasXI Maths WorksheetBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- SRI FireFighting Equipments 2012 PDFDocumento46 páginasSRI FireFighting Equipments 2012 PDFsullamsAinda não há avaliações
- Python Programming TutorialDocumento195 páginasPython Programming TutorialilyesingenieurAinda não há avaliações
- Radio Link Analysis and Data Collection-20120110-ADocumento23 páginasRadio Link Analysis and Data Collection-20120110-AHICHAMAinda não há avaliações
- Frictional Forces: Friction ForceDocumento6 páginasFrictional Forces: Friction ForceAnoop Mohan ChemnikarAinda não há avaliações
- FRICTIONAL FORCESzDocumento9 páginasFRICTIONAL FORCESzjohn onesmoAinda não há avaliações
- Force, Pressure & FrictionDocumento3 páginasForce, Pressure & FrictionvuppalasampathAinda não há avaliações
- Force and FrictionDocumento11 páginasForce and FrictionFred H HalderAinda não há avaliações
- FORCESDocumento4 páginasFORCESNirvana SuggieAinda não há avaliações
- ForcesDocumento6 páginasForcesshinde.sampada1923Ainda não há avaliações
- Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Revision NotesDocumento4 páginasClass 8 Science Chapter 11 Revision NotesneilAinda não há avaliações
- Physics DefinitionDocumento6 páginasPhysics DefinitionMin Aung KyawAinda não há avaliações
- Force and MotionDocumento14 páginasForce and MotionNoel AvilaAinda não há avaliações
- Notes Physics Viii CH12 Friction by Ankur SharmaDocumento4 páginasNotes Physics Viii CH12 Friction by Ankur SharmaDRISHTI SINGHAinda não há avaliações
- ThihaDocumento36 páginasThihaMax LorentzAinda não há avaliações
- E102 - AgustinDocumento20 páginasE102 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinAinda não há avaliações
- Forces: Newtons (N)Documento4 páginasForces: Newtons (N)rajsacksAinda não há avaliações
- Reading PagesDocumento32 páginasReading Pagesapi-249475958Ainda não há avaliações
- Laws of Motion: ExamplesDocumento6 páginasLaws of Motion: ExamplesYohan PonchaAinda não há avaliações
- Module - 5: Force & Friction: I. Newton's First Law of MotionDocumento14 páginasModule - 5: Force & Friction: I. Newton's First Law of Motionapi-3766872Ainda não há avaliações
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocumento54 páginasNewton's Laws of Motionjhegster saclutiAinda não há avaliações
- Force - Summary Notes: Noncontact Forces, E.g., Gravitational Force, Electrical Force, and Magnetic ForceDocumento3 páginasForce - Summary Notes: Noncontact Forces, E.g., Gravitational Force, Electrical Force, and Magnetic ForceVenu GopalAinda não há avaliações
- Module 5 - Newton's Laws of MotionDocumento5 páginasModule 5 - Newton's Laws of MotionAllen Simon BaulaAinda não há avaliações
- FrictionDocumento12 páginasFrictionJyoti ShresthaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics ProjectDocumento23 páginasPhysics Projectkaushik17yadavAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Force?: DefinitionDocumento5 páginasWhat Is Force?: Definitionمحمد ایمانAinda não há avaliações
- FORCE & PRESSURE NotesDocumento1 páginaFORCE & PRESSURE NotesPraveen KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Report No. 2Documento13 páginasReport No. 2Alex QuirimitAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To A New Topic : Bushara Abdulkareem NO:37 1 Semester B.Ed PhysicalscienceDocumento22 páginasAn Introduction To A New Topic : Bushara Abdulkareem NO:37 1 Semester B.Ed PhysicalsciencebushAinda não há avaliações
- EfdsDocumento2 páginasEfdsClint SusarnoAinda não há avaliações
- ST00602 Lec2 Forces and MotionDocumento115 páginasST00602 Lec2 Forces and MotionImran AminAinda não há avaliações
- Biomechanics in Physical Education Sports and ResearchDocumento26 páginasBiomechanics in Physical Education Sports and ResearchEinn D. FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Forceandmotion 181112055529Documento36 páginasForceandmotion 181112055529FernandoAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 and 5Documento11 páginasUnit 3 and 5RayyanAinda não há avaliações
- FORCESDocumento11 páginasFORCESJennieAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 8 Science Ch-11 Force and Pressure (Notes)Documento9 páginasGrade 8 Science Ch-11 Force and Pressure (Notes)SoniaAinda não há avaliações
- Module 5 - Newton - S Laws of MotionDocumento6 páginasModule 5 - Newton - S Laws of MotionAllen Simon BaulaAinda não há avaliações
- Friction: Reference: Theory of Machines by R.S. Khurmi & J.K.GuptaDocumento17 páginasFriction: Reference: Theory of Machines by R.S. Khurmi & J.K.GuptaSaad AliKhan100% (2)
- Forces: Miss Ramdehal Integrated Science Form 1.4 &1.6Documento18 páginasForces: Miss Ramdehal Integrated Science Form 1.4 &1.6Naseeb AliAinda não há avaliações
- Practical 2: Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocumento18 páginasPractical 2: Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcespersonwithheartAinda não há avaliações
- 8th Force and Pressure Living Science AnswerDocumento3 páginas8th Force and Pressure Living Science AnswerAshu100% (1)
- Applied Mechanics Chapter 3 FrictionDocumento25 páginasApplied Mechanics Chapter 3 FrictionHari PyakurelAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Force? 2. How Is The Car Able To Move and Stop? 3. What Is Keeping It On The Ground?Documento11 páginasWhat Is A Force? 2. How Is The Car Able To Move and Stop? 3. What Is Keeping It On The Ground?Cinara RahimovaAinda não há avaliações
- Science Force, Energy, Simple MachineDocumento5 páginasScience Force, Energy, Simple MachineJOSE RENE CASILIAinda não há avaliações
- 8th CLASS PS Handbook2023 2024Documento76 páginas8th CLASS PS Handbook2023 2024YachiAinda não há avaliações
- Tribology 17me742: What Is Friction?Documento31 páginasTribology 17me742: What Is Friction?Vyshu Sonu100% (1)
- Class VIII I.I.T.foundation, N.T.S.E.& Science Olympiad Curriculum & Chapter NotesDocumento83 páginasClass VIII I.I.T.foundation, N.T.S.E.& Science Olympiad Curriculum & Chapter NotesYo83% (6)
- Q3 WK1 Day 1 ScienceDocumento31 páginasQ3 WK1 Day 1 SciencevinnAinda não há avaliações
- 021 G12 STEM Newton's Law of Motion CDocumento7 páginas021 G12 STEM Newton's Law of Motion CMariaAinda não há avaliações
- Handout Force and Motion S2Documento13 páginasHandout Force and Motion S2rozy kjsAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Project WorkDocumento12 páginasPhysics Project WorkNatasha ChandraAinda não há avaliações
- P2-Motion & Force PDFDocumento5 páginasP2-Motion & Force PDFHarshaWakodkarAinda não há avaliações
- SM 12 Math Eng 201617Documento192 páginasSM 12 Math Eng 201617Bhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Viva Voce QuestionsDocumento2 páginasViva Voce QuestionsBhavesh Desai100% (1)
- CBSE Class 12 English - Flamingo PoemsDocumento56 páginasCBSE Class 12 English - Flamingo PoemsBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Comacta CBSE 12 EnglishDocumento49 páginasComacta CBSE 12 EnglishBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Cbse Xi Physics Test PapersDocumento14 páginasCbse Xi Physics Test PapersBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- EnglishDocumento193 páginasEnglishBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Science Question Bank STD XI Session 2014-15Documento39 páginasComputer Science Question Bank STD XI Session 2014-15Bhavesh Desai0% (1)
- 11 Chemistry Impq Ch01 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry KvsDocumento8 páginas11 Chemistry Impq Ch01 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry KvsBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Class 10 Ncert Solution Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and CoordinationDocumento7 páginasClass 10 Ncert Solution Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and CoordinationBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Me N Mine English Solutions X Second Term For Website 8 Aug 2011Documento83 páginasMe N Mine English Solutions X Second Term For Website 8 Aug 2011Ankish Gupta70% (20)
- MK JH DK, D Iuuk: New Wave in Hindi Class - X (Term - I) Course B Section: C (Ikb Iqlrd, Oa Iwjd Iqlrd)Documento8 páginasMK JH DK, D Iuuk: New Wave in Hindi Class - X (Term - I) Course B Section: C (Ikb Iqlrd, Oa Iwjd Iqlrd)Bhavesh Desai50% (2)
- CBSE Class X Hindi Study Material Part B PDFDocumento61 páginasCBSE Class X Hindi Study Material Part B PDFBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class X Biology - Life Processs Key NotesDocumento18 páginasCBSE Class X Biology - Life Processs Key NotesBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Eco-Sectors of The Indian Economy - Term1 - Class10Documento4 páginasEco-Sectors of The Indian Economy - Term1 - Class10Bhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Class X EconomicsDocumento3 páginasClass X EconomicsBhavesh Desai0% (1)
- 10th Civics Power SharingDocumento2 páginas10th Civics Power SharingBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Klauke - Bi-Metal Lugs & ConnectorsDocumento6 páginasKlauke - Bi-Metal Lugs & ConnectorsBiplab PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture (SM Construction, Types and Operation)Documento32 páginasLecture (SM Construction, Types and Operation)kyaw winAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Lab Experiment 6Documento6 páginasPhysics Lab Experiment 6Peter Sam CoAinda não há avaliações
- Plan Holders ReportDocumento8 páginasPlan Holders ReportSusan KunkleAinda não há avaliações
- Taglio Sez Circ 2Documento3 páginasTaglio Sez Circ 2mariorossi_4Ainda não há avaliações
- TR 541 2Documento78 páginasTR 541 2Omar Marghani SalmaAinda não há avaliações
- Plsed309005en (Web)Documento174 páginasPlsed309005en (Web)Arifin SaniAinda não há avaliações
- ABB Contactor Wear GuidelinesDocumento12 páginasABB Contactor Wear GuidelinesPhuc PhamAinda não há avaliações
- CFRD 05 - BayardoDocumento23 páginasCFRD 05 - BayardodiegofernandodiazsepAinda não há avaliações
- Business Plan: Syeda Zurriat & Aimen RabbaniDocumento11 páginasBusiness Plan: Syeda Zurriat & Aimen RabbanizaraaAinda não há avaliações
- Table (.) Wastewater Storage Tank (STO1)Documento4 páginasTable (.) Wastewater Storage Tank (STO1)Chelsea MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Grain Diameter (MM) Strength (Mpa) : 0.015 170 Mpa 0.025 158 Mpa 0.035 151 Mpa 0.050 145 MpaDocumento1 páginaGrain Diameter (MM) Strength (Mpa) : 0.015 170 Mpa 0.025 158 Mpa 0.035 151 Mpa 0.050 145 MpaTEBATSOAinda não há avaliações
- Astm D 3241 - 02 - RdmyndetmdjbDocumento13 páginasAstm D 3241 - 02 - RdmyndetmdjbSamuel EduardoAinda não há avaliações
- MAWS301 Datasheet B210396EN-C LowResDocumento2 páginasMAWS301 Datasheet B210396EN-C LowResmumapaduriiiAinda não há avaliações
- MetamterialsDocumento3 páginasMetamterialsdhruba88Ainda não há avaliações
- Is 13935 2009 PDFDocumento33 páginasIs 13935 2009 PDFManojKumawatRjAinda não há avaliações
- KX Tde600 FeatureDocumento460 páginasKX Tde600 Featureabg121Ainda não há avaliações
- Building Applied Natural Language GenerationDocumento32 páginasBuilding Applied Natural Language Generationrat86Ainda não há avaliações
- VP422 HDTV10A Service Manual PDFDocumento25 páginasVP422 HDTV10A Service Manual PDFDan Prewitt0% (1)
- Farheen Begum Mobile: +91 9849952279 E-Mail: Career ObjectiveDocumento2 páginasFarheen Begum Mobile: +91 9849952279 E-Mail: Career ObjectiveMohammed AsifAinda não há avaliações
- SmartBright LED Downlight G3Documento11 páginasSmartBright LED Downlight G3Puji SnAinda não há avaliações
- Numerical Modeling of MHD Convective Heat and Mass Transfer in Presence of First-Order Chemical Reaction and Thermal RadiationDocumento20 páginasNumerical Modeling of MHD Convective Heat and Mass Transfer in Presence of First-Order Chemical Reaction and Thermal Radiationmanasdutta3495Ainda não há avaliações
- Gujarat Technological University: A Project Report On:-Automatic Water Purification SystemDocumento11 páginasGujarat Technological University: A Project Report On:-Automatic Water Purification SystemJay KakadiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Modeling Complex Zo For Op AmpsDocumento28 páginasModeling Complex Zo For Op Ampswalid OUNISAinda não há avaliações
- Pipe and Tube Operations - DaytonaDocumento123 páginasPipe and Tube Operations - Daytonaramon nava0% (1)
- En Webclima ManualDocumento44 páginasEn Webclima ManualGajendra RathoreAinda não há avaliações