Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Abbreviation
Enviado por
santhyakunjumonDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Abbreviation
Enviado por
santhyakunjumonDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Abbreviation 1. Ac 2. pc 3. po or PO 4. cap 5. dil 6. H 7. hs 8. kg or Kg 9. l or L 10. OD 11. OS 12. OU 13. Prn 14. Q 15. Qam 16. q2h 17.
Qod 18. Stat 19. Tab 20. Susp 21. Sup 22. CBR 23. BRP 24. ad lib 25. Od 26. bid 27. tid 28. qid 29. gr 30. gtt 31. mcg or ug 32. cc 33. A 34. Am 35. Bid 36. C 37. cc (ml) 38. c/o 39. d/c 40. Dx 41. Hs 42. MOR 43. Mg 44. ml (cc) 45. Npo 46. OTC 47. p 48. Pm 49. Po 50. Rx 51. S 52. Tbsp. 53. Tsp 54. XR, XL, CR, LA,SR
Explanation before meals after meals by mouth Capsule dissolve, dilute Hour at bedtime/hours of sleep Kilogram Liter right eye left eye both eyes when needed Every every morning every two hours every other day Immediately Tablet suspension suppository complete bed rest bathroom privileges freely, as desired once a day twice a day three times a day four times a day grain drop Microgram `ml Before Morning twice daily With cubic centimeter complains of Discontinue Diagnosis Bedtime medication observation Record Milligram Milliliter nothing by mouth over-the-counter After Afternoon by mouth (oral) Prescription Without Tablespoon Teaspoon extended release
Major Classifications of Medications 1. Analgesic 2. Antacid 3. Antianxiety 4. Antiasthmatic 5. Antibacterial/Antibiotic 6. Anticoagulant 7. Anticonvulsant 8. Antidepressant 9. Antidiarrheal 10.Antidote 11.Antiemetic 12.Antifungal 13.Antihistamine 14.Antihypertensive 15.Antipsychotic 16.Antipyretic 17.Antitussive 18.Antiulcer 19.Antiviral 20.Bronchodilator 21.Cardiovascular Agent 22.Diuretic 23.Expectorant 24.Gastrointestinal Stimulant 25.Glucocorticoids 26.Hormones 27.Hypoglycemic Medication 28.Laxative 29.Non steroidal Anti Inflammatory Agents 30.Over the Counter(OTC) 31.Psychotropic 32.Skeletal Muscle Relaxants 33.Sedative/Hypnotic 34.Stimulant 35.Topical Steroid relieves pain reduces or eliminates acids in the stomach decreases anxiety treats asthma kills or slows the growth of bacteria slows blood clotting prevents or stops seizures relieves depression stops or decreases diarrhea counteracts overdoses of medication or toxic substances controls nausea and vomiting treats fungal infections reduces symptoms of allergies decreases high blood pressure treats psychosis and controls behavior reduces fever relieves cough treats heartburn and decreases secretion of stomach acid manages or prevents viral infections treats bronchospasm in asthma treats heart and circulatory disorders increases urine output induces cough and movement of fluid from respiratory tract stimulates motility of the upper GI tract and accelerates stomach emptying reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system treats hormone deficiency including diabetes, hypothyroidism and menopause treats and controls diabetes stimulates and loosens the bowels control pain, fever and inflammatory conditions such as muscle or joint pain medications that do not require a prescription treats behavior/mental health issues stops muscle spasms and relieves painful musculoskeletal conditions induces sleep schedule II controlled substance which produces central nervous system stimulation reduces inflammation of various skin conditions due to dermatitis, insect bites, poison ivy, and the like
Formula for computation of dosage: Oral medications: solids Desired dose= quantity of drug Stock Dose (D/S=Q) ex: An antihypertensive agent, minoxidil(Loniten)5mg p.o is ordered. Stock is 2.5mg/tab. How many tablets should be administered? Answer: D= 5mg =2tablets S = 2.5mg/tablet Formula for computation of dosage: Oral medications: Liquid preparations Desired dose X Dilution = Quantity of drug Stock Dose ex: Paracetamol 250mg / 5 ml , give 500 mg P.O every 4 hours RTC. Answer: D= 500mg X 5ml =10ml S = 250 mg
Você também pode gostar
- Icu IntroDocumento120 páginasIcu IntrosanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study CholecystitisDocumento13 páginasCase Study Cholecystitissanthyakunjumon100% (1)
- VavaDocumento56 páginasVavasanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- RINJUDocumento67 páginasRINJUsanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroenterology MCQDocumento2 páginasGastroenterology MCQsanthyakunjumon100% (7)
- Cardiac QuizDocumento2 páginasCardiac QuizsanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- Perioperative Nursing CareDocumento30 páginasPerioperative Nursing CaresanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus SleDocumento18 páginasSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Slesanthyakunjumon100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Nursing ResearchDocumento5 páginasChapter 1 - Introduction To Nursing ResearchKathrina Ioannou100% (3)
- Quiz On Normal Lab ValuesDocumento3 páginasQuiz On Normal Lab ValuessanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- UGI DisordersDocumento108 páginasUGI DisorderssafeheavenAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Endocrine SystemDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Endocrine SystemsanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction - To Medical Surgical NursingDocumento24 páginasIntroduction - To Medical Surgical Nursingsanthyakunjumon0% (1)
- NLN Pharmacology Study Guide Final 6-3-2013Documento65 páginasNLN Pharmacology Study Guide Final 6-3-2013الأغا محمد زكارنة100% (2)
- Essential Facts For Med-Surg Nurses: Emergency Cardiac DrugsDocumento7 páginasEssential Facts For Med-Surg Nurses: Emergency Cardiac DrugssanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- AntibioticsDocumento6 páginasAntibioticssanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- DB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaDocumento5 páginasDB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaNeil Alcazaren かわいいAinda não há avaliações
- QuizDocumento12 páginasQuizsanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary Assessment: Why This Is ImportantDocumento1 páginaIntegumentary Assessment: Why This Is ImportantsanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- Historyandevolutioofnursing Final 130325045149 Phpapp02Documento45 páginasHistoryandevolutioofnursing Final 130325045149 Phpapp02santhyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- 634460688028561250Documento56 páginas634460688028561250santhyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- B.SC - Nursing SyllabusDocumento145 páginasB.SC - Nursing Syllabussanthyakunjumon0% (1)
- Diabetes PathophysiologyDocumento2 páginasDiabetes PathophysiologyRyan MulanoAinda não há avaliações
- AV Aids IntroductionDocumento29 páginasAV Aids Introductionsanthyakunjumon100% (1)
- Case Study HypertensionDocumento7 páginasCase Study Hypertensionsanthyakunjumon67% (3)
- Angiogram HindiDocumento8 páginasAngiogram HindisanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Surgical InstrumentsDocumento37 páginasBasic Surgical Instrumentsapi-2658787991% (33)
- AV Aids IntroductionDocumento29 páginasAV Aids Introductionsanthyakunjumon100% (1)
- Medical/Surgical Asepsis: Presented By: Cynthia Bartlau, RN, PHN, MSNDocumento23 páginasMedical/Surgical Asepsis: Presented By: Cynthia Bartlau, RN, PHN, MSNsanthyakunjumonAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Surgical InstrumentsDocumento37 páginasBasic Surgical Instrumentsapi-2658787991% (33)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Electrical Safety Program Sample PDFDocumento14 páginasElectrical Safety Program Sample PDFPeter GeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- Sickle-Cell AnemiaDocumento11 páginasSickle-Cell Anemiahalzen_joyAinda não há avaliações
- Production of Blue Ternate (Clitoria Ternatea) Flower Extracts in Hand SanitizerDocumento37 páginasProduction of Blue Ternate (Clitoria Ternatea) Flower Extracts in Hand SanitizerDiane Vill100% (1)
- Corn SpecDocumento4 páginasCorn SpecJohanna MullerAinda não há avaliações
- Certification of Psychology Specialists Application Form: Cover PageDocumento3 páginasCertification of Psychology Specialists Application Form: Cover PageJona Mae MetroAinda não há avaliações
- Building An ArgumentDocumento9 páginasBuilding An ArgumentunutulmazAinda não há avaliações
- Appointments Boards and Commissions 09-01-15Documento23 páginasAppointments Boards and Commissions 09-01-15L. A. PatersonAinda não há avaliações
- Acute k9 Pain ScaleDocumento1 páginaAcute k9 Pain Scaleapi-367949035Ainda não há avaliações
- 2) Water Quality and Health in Egypt - Dr. AmalDocumento50 páginas2) Water Quality and Health in Egypt - Dr. AmalAlirio Alonso CAinda não há avaliações
- Staples Worklife Magazine - Winter 2019Documento68 páginasStaples Worklife Magazine - Winter 2019Anonymous fq268KsS100% (1)
- From Solidarity To Subsidiarity: The Nonprofit Sector in PolandDocumento43 páginasFrom Solidarity To Subsidiarity: The Nonprofit Sector in PolandKarimMonoAinda não há avaliações
- Moosa Amandio PDFDocumento12 páginasMoosa Amandio PDFMussa AmândioAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Master FileDocumento62 páginasDrug Master FileAjay GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Theoretical Models of Nursing Practice AssignmentDocumento6 páginasTheoretical Models of Nursing Practice Assignmentmunabibenard2Ainda não há avaliações
- Galvanised Wrought Iron Pipes and Water QualityDocumento1 páginaGalvanised Wrought Iron Pipes and Water QualityKingsleyOwunariDokuboAinda não há avaliações
- Ontario Works Service Delivery Model CritiqueDocumento14 páginasOntario Works Service Delivery Model CritiquewcfieldsAinda não há avaliações
- Normal FloraDocumento28 páginasNormal FloraMuhammad KashifAinda não há avaliações
- My Good Habits - Welcome Booklet 2 - 1Documento17 páginasMy Good Habits - Welcome Booklet 2 - 1lisa_ernsbergerAinda não há avaliações
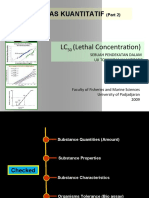
- LC (Lethal Concentration) : Uji Toksisitas KuantitatifDocumento31 páginasLC (Lethal Concentration) : Uji Toksisitas Kuantitatifbagi_fileAinda não há avaliações
- Marriage and Later PartDocumento25 páginasMarriage and Later PartDeepak PoudelAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Acn-IiDocumento80 páginasNursing Acn-IiMunawar100% (6)
- Supersize Me: An Exploratory Analysis of The Nutritional Content in Mcdonald's Menu ItemsDocumento7 páginasSupersize Me: An Exploratory Analysis of The Nutritional Content in Mcdonald's Menu ItemsIjahss JournalAinda não há avaliações
- Substance Abuse Counseling Complete 5th EditionDocumento379 páginasSubstance Abuse Counseling Complete 5th Editionnintendoagekid86% (59)
- Debona 2016Documento23 páginasDebona 2016Biomontec Biomontec BiomontecAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Audit ScheduleDocumento2 páginasNursing Audit ScheduleArvinjohn Gacutan0% (1)
- Tridosha Made Easy The Basic Ayurvedic Principle (Janardhana V Hebbar, Raghuram Ys, Manasa S)Documento621 páginasTridosha Made Easy The Basic Ayurvedic Principle (Janardhana V Hebbar, Raghuram Ys, Manasa S)Sumit SardarAinda não há avaliações
- Asset Integrity Know HowDocumento6 páginasAsset Integrity Know HowFatemeh MehrbakhshAinda não há avaliações
- Innovation - Edipeel Prolongs Fruit Shelf Life, Reduces SpoilageDocumento5 páginasInnovation - Edipeel Prolongs Fruit Shelf Life, Reduces SpoilageahosfhaofahfouaAinda não há avaliações
- Beddtiot ORTHO / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocumento60 páginasBeddtiot ORTHO / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyAinda não há avaliações
- Safe Haven Thesis StatementDocumento5 páginasSafe Haven Thesis Statementangelabaxtermanchester100% (2)