Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Text
Enviado por
Sabiha AfrozDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Text
Enviado por
Sabiha AfrozDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Characteristics Cloud computing exhibits the following key characteristics: Agility improves with users' ability to re-provision technological
infrastru cture resources. Application programming interface (API) accessibility to software that enabl es machines to interact with cloud software in the same way the user interface f acilitates interaction between humans and computers. Cloud computing systems typ ically use REST-based APIs. Cost is claimed to be reduced and in a public cloud delivery model capital e xpenditure is converted to operational expenditure.[10] This is purported to low er barriers to entry, as infrastructure is typically provided by a third-party a nd does not need to be purchased for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks. Pricing on a utility computing basis is fine-grained with usage-based opt ions and fewer IT skills are required for implementation (in-house).[11] The e-F ISCAL project's state of the art repository[12] contains several articles lookin g into cost aspects in more detail, most of them concluding that costs savings d epend on the type of activities supported and the type of infrastructure availab le in-house. Device and location independence[13] enable users to access systems using a web browser regardless of their location or what device they are using (e.g., PC , mobile phone). As infrastructure is off-site (typically provided by a third-pa rty) and accessed via the Internet, users can connect from anywhere.[11] Virtualization technology allows servers and storage devices to be shared an d utilization be increased. Applications can be easily migrated from one physica l server to another. Multi-tenancy enables sharing of resources and costs across a large pool of users thus allowing for: Centralization of infrastructure in locations with lower costs (such as real estate, electricity, etc.) Peak-load capacity increases (users need not engineer for highest possib le load-levels) Utilisation and efficiency improvements for systems that are often only 10 20% utilised.[14] Reliability is improved if multiple redundant sites are used, which makes we ll-designed cloud computing suitable for business continuity and disaster recove ry.[15] Scalability and Elasticity via dynamic ("on-demand") provisioning of resourc es on a fine-grained, self-service basis near real-time, without users having to engineer for peak loads.[16][17] Performance is monitored, and consistent and loosely coupled architectures a re constructed using web services as the system interface.[11] Security could improve due to centralization of data, increased security-foc used resources, etc., but concerns can persist about loss of control over certai n sensitive data, and the lack of security for stored kernels.[18] Security is o ften as good as or better than other traditional systems, in part because provid ers are able to devote resources to solving security issues that many customers cannot afford.[19] However, the complexity of security is greatly increased when data is distributed over a wider area or greater number of devices and in multi -tenant systems that are being shared by unrelated users. In addition, user acce ss to security audit logs may be difficult or impossible. Private cloud installa tions are in part motivated by users' desire to retain control over the infrastr ucture and avoid losing control of information security. we are true
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Descartes and The JesuitsDocumento5 páginasDescartes and The JesuitsJuan Pablo Roldán0% (3)
- Urban Transportation System Design and Feasibility Analysis A Case Study of Lagos Mega-CityDocumento8 páginasUrban Transportation System Design and Feasibility Analysis A Case Study of Lagos Mega-CityKaren EstradaAinda não há avaliações
- Ati - Atihan Term PlanDocumento9 páginasAti - Atihan Term PlanKay VirreyAinda não há avaliações
- Consti 2: Case Digests - Regado: Home Building & Loan Assn. V BlaisdellDocumento6 páginasConsti 2: Case Digests - Regado: Home Building & Loan Assn. V BlaisdellAleezah Gertrude RegadoAinda não há avaliações
- Roof Structure Collapse Report - HongkongDocumento11 páginasRoof Structure Collapse Report - HongkongEmdad YusufAinda não há avaliações
- Service Index PDF - PHP Content Id 2378053&content Tid 388906138&content Type TempDocumento2 páginasService Index PDF - PHP Content Id 2378053&content Tid 388906138&content Type Tempshiripalsingh0167Ainda não há avaliações
- PDF Issue 1 PDFDocumento128 páginasPDF Issue 1 PDFfabrignani@yahoo.comAinda não há avaliações
- Scott Kugle-Framed, BlamedDocumento58 páginasScott Kugle-Framed, BlamedSridutta dasAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Grammar, Vocabulary, and Pronunciation ADocumento7 páginas10 Grammar, Vocabulary, and Pronunciation ANico FalzoneAinda não há avaliações
- Flipkart Labels 23 Apr 2024 10 18Documento4 páginasFlipkart Labels 23 Apr 2024 10 18Giri KanyakumariAinda não há avaliações
- S0260210512000459a - CamilieriDocumento22 páginasS0260210512000459a - CamilieriDanielAinda não há avaliações
- Henry IV Part 1 Study GuideDocumento21 páginasHenry IV Part 1 Study GuideawtshfhdAinda não há avaliações
- PoetryDocumento5 páginasPoetryKhalika JaspiAinda não há avaliações
- La Bugal BLaan Tribal Association Inc. vs. RamosDocumento62 páginasLa Bugal BLaan Tribal Association Inc. vs. RamosAKnownKneeMouseeAinda não há avaliações
- Democratic EducationDocumento11 páginasDemocratic Educationpluto zalatimoAinda não há avaliações
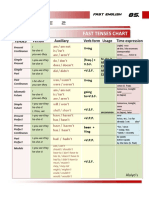
- Table 2: Fast Tenses ChartDocumento5 páginasTable 2: Fast Tenses ChartAngel Julian HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Pricing of Deposit ServicesDocumento37 páginasDesign and Pricing of Deposit ServicesThe Cultural CommitteeAinda não há avaliações
- Rong Sun ComplaintDocumento22 páginasRong Sun ComplaintErin LaviolaAinda não há avaliações
- Memorandum of Inderstanding Ups and GoldcoastDocumento3 páginasMemorandum of Inderstanding Ups and Goldcoastred_21Ainda não há avaliações
- Timeline of American OccupationDocumento3 páginasTimeline of American OccupationHannibal F. Carado100% (3)
- Principles of Natural JusticeDocumento20 páginasPrinciples of Natural JusticeHeracles PegasusAinda não há avaliações
- Adidas Case StudyDocumento5 páginasAdidas Case StudyToSeeTobeSeenAinda não há avaliações
- General Nursing Council of Zambia: Summary of Results For Each School December 2019 Qualifying Examinations SessionDocumento15 páginasGeneral Nursing Council of Zambia: Summary of Results For Each School December 2019 Qualifying Examinations SessionAndrew LukupwaAinda não há avaliações
- Options TraderDocumento2 páginasOptions TraderSoumava PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Sample of Notarial WillDocumento3 páginasSample of Notarial WillJF Dan100% (1)
- Muhammad Naseem KhanDocumento2 páginasMuhammad Naseem KhanNasim KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Action Plan Templete - Goal 6-2Documento2 páginasAction Plan Templete - Goal 6-2api-254968708Ainda não há avaliações
- Mulanay SummaryDocumento1 páginaMulanay SummaryJex Lexell BrionesAinda não há avaliações
- Running Wild Lyrics: Album: "Demo" (1981)Documento6 páginasRunning Wild Lyrics: Album: "Demo" (1981)Czink TiberiuAinda não há avaliações
- Firewall Training, Checkpoint FirewallDocumento7 páginasFirewall Training, Checkpoint Firewallgaurav775588Ainda não há avaliações