Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
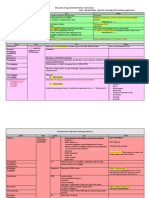
Sympathetic Ns (Adrenergic) Parasympa NS (Cholinergic)
Enviado por
Jov May DimcoTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sympathetic Ns (Adrenergic) Parasympa NS (Cholinergic)
Enviado por
Jov May DimcoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
DRUGS AFFECTING AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM by: Ms. Jovelyn May C.
Dimco Nervous System: CNS & PNS PNS: Somatic (SNS) & Autonomic (ANS) ANS: Sympathetic, Parasympathetic, Enteric Enteric Nervous System- controls GIT -maintains secretion and motility of intestines -independent from SNS, ANS -Auerbach plexus & Meissner plexus -Neurotransmitters: Noncholinergic Nonadrenergic Ex: Neoropeptide Y, substance P, adenosine triphosphate SOMATIC Voluntary/under volitional control 1-neuron system No ganglia vs AUTONOMIC Involuntary/autonomic 2-neuron system Presence of ganglia PARASYMPA (CHOLINERGIC) NS
**How is message transmitted? SYMPATHETIC NS(ADRENERGIC) I.Anatomical Difference roots/origin Thoracolumbar roots (T1-T12; L1-L5) location of ganglia Length of fiber: Preganglionic fiber Postganglionic II. Neurotransmitters Preganglionic Postganglionic III.Receptors Ganglionic End organ IV. Organ Responses General Heart Eyes Blood vessels Bronchi GIT: sphincters GIT: intestinal walls GUT: bladder walls GUT: sphincters Near spinal cord Short Long
Craniosacral (cranial nerves 3,7,9,10; S2-S4) Near the organs innervated Long Short
Acetylcholine NE, Epi, Dopamine Nicotinic , , dopamine receptors Fright, flight, fight Chronotropic, inotropic, dromotropic Pupillodilation = mydriasis *radial muscles Vasoconstriction Bronchodilation Closure/contraction Dilation/relaxation(constipation) Relaxation (urinary retention) Closure
Acetylcholine Acetylcholine Nicotinic Nicotinic & muscarinic Rest & digest bradycardia Pupilloconstriction = miosis *ciliary muscles Vasodilation Bronchoconstriction Opening/relaxation Contraction (bowel movement) Contraction Opening
Sweat glands Reproductive system
Apocrine=increase sweating Ejaculation
Eccrine= sweating Erection
increase
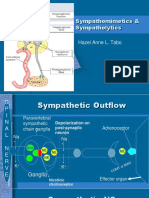
Sympathetic Nervous System: Steps in the biosynthesis of NT: NE Site: presynaptic postganglionic sympathetic fiber 1.Active uptake of TYROSINE into presynaptic fiber 2.Tyr DOPA enzyme:tyrosine hydroxylase *rate-limiting step DOPA- dihydroxyphenylalanine 3.DOPA dopamine enzyme: dopa decarboxylase (-) Reserpine (-) Metyrosine Drugs
4.storage/ uptake of dopamine to presynaptic vesicle Site: presynaptic vesicle 5.Dopamine NE (stored/protected from degradation) enzyme: dopamine hydroxylase
6.action potential; influx of Ca ++; fusion of vesicle to cell membrane 7. exocytosis/release of NE (-) Bretyllium, Guanethidine (+) Ephedrine, Amphetamine, Shabu, Angiotensin II, Tyramine 8. Fate of NE a)diffuse into the synapse; destroyed by COMT *COMT- catechol-o-methyltransferase b)bind to postsynaptic , , dopamine receptors; intracellular response; destruction by COMT c) bind to presynaptic 2 receptor; Negative feedback effect d) Re-uptake into presynaptic nerve fiber; 70% of NE lost; conservation *most important mechanism of loss (-) Cocaine, TCAs (-) Pyrogallol (-) Pyrogallol
***MAO = monoamine oxidase enzyme found inside the presynaptic fiber = destroys NE, DOPA, dopamine ** Tyramine-rich foods: cheese, red wine, beer, fermented products, yeast products, chicken liver
Effects of Sympathetic Stimulation: Receptors 1 Location Blood vessels Radial muscles of the iris Sphincter muscles of GIT & urinary bladder Pilomotor smooth muscle Presynaptic nerve terminal Postsynaptic nerve fiber: BV, muscles Heart JG apparatus Bronchial smooth muscles Intestinal smooth muscles Uterine smooth muscles Vascular smooth muscles Skeletal muscles Heart Adipose tissues Renal and sphlanchnic circulation CNS Response Vasoconstriction Mydriasis Constriction/closure GIT: constipation Bladder: urinary retention Contraction/erection of hair Vasodilation ciliary Vasoconstriction Chronotropic, Dromotropic, Inotropic RAAS, secretion and synthesis of rennin Bronchodilation Relaxation Uterine relaxation (tocolytic effect) Vasodilation Fasciculations, tremors, palpitation Tachycardia Lipolysis Vasodilation Stimulation of CNS
2 1 2
3 D1 D2,D3,D4
Sympathetic agonists/ Sympathomimetic drugs/ Adrenergic Agonists: I.Direct-acting II.Mixed acting III. Indirect-acting A. Non-selective -Metaraminol A. Releasers -Epi -Ephedrine -Amphetamine -NE - shabu -Dopamine - Tyramine - AII B. Selective B. Re-uptake Inhibitors -1 -cocaine -2 - TCA -1 -2 - nonselective MOA: Direct-acting Drugs drugs directly activates alpha, beta or dopamine receptors Indirect-acting Drugs drugs increase/enhance the release of NE Epinephrine Uses: 1) primary cardiac stimulant (for cardiac rescucitation) -ACLS (Advanced Cardiac Life Support) -max. dose: none until heart starts pumping again -(dose: 1-3 mg every 3-5 mins)
2) DOC: mx of anaphylactic shock AS: most severe form of allergic reaction due to excessive release of histamine from mast cells. s/sx: generalized rash, flushing, hypotension, bronchospasm MOA of EPI: 1 = vasoconstriction 2 = bronchodilation, inhibition of histamine release 3)Anesthetic adjunct for local vasoconstriction 4)as Dipinefrin (pivalic ester of EPI)- for glaucoma Toxicity: darkening of fingertips Synthesis: adrenal medulla Norepinephrine (no 2 effect) Uses: 1) cardiac stimulant 2) mx of septic shock Dopamine Dose-dependent effect: D1 induce dieresis (for urinary retention ex. BPH) -improve renal perfusion 1- inotropic for septic shock- DOC 1-vasoconstricting dose- raise BP in hypotensive states 1-selective Effect: vasoconstriction Uses: -Decongestants: nasal & ophthalmic -Raise BP in hypotensive states SE: 1) may worsen HPN 2)urinary retention in males with BPH 3) rhinitis medica mentosa- nasal sprays: < 3 days 4) tolerance PO > 5days CI: HPN, BPH Ex: 1) Phenylephrine 2) Propylhexedrine 3) Oxymetazoline 4) Tetrahydrozoline 5) Xylometazoline 6) Methoxamine 2-selective Effect: vasodilation Uses: anti-HPN presynaptic: vasodilation Decongestant postsynaptic: vasoconstriction Drugs: 1) **Methyldopa (Aldomet ) 2) **Clonidine (Catapress) 3) Guanfacine 4) Guanabenz 1-selective Drug: Dobutamine- use DOC for mx of cardiogenic shock 2-selective Effect: bronchodilation, uterine relaxation (tocolytic effect) Uses: 1) Bronchial asthma 2)Tocolytic effect: Terbutaline, Ritodrine, Isoxuphrine, Salbutamol
3)for bradycardia 4)for hyperkalemia SE: 1) tolerance- adm on PRN basis only 4)palpitations 2) Muscle tremors 5) hypercalcemia 3)hypokalemia 6)hyperglycemia Drugs: SA Terbutaline, Salbutamol, Fenoterol, Ritodrin, Isoxuphrine LA Formoterol (OXIS), Salmeterol (SEREVENT), Bambuterol (BAMBEC) -nonselective Drug: Isoproterenol- 1st drug available as MDI Toxicity: cardiotoxic Tolerance: to 2 effects Use: cardiac stimulant Releasers = calcium-acting drugs promote NE release D1-selective agonist Drug: Fenoldopam- vasodilator -use: for BPH and urinary retention Cocaine -powerful vasoconstrictor -stimulant TCAs increase NE Centrally-acting Sympathomimetics Effects: 1) CNS stimulation- wakefulness, increased alertness, seizure 2) loss of appetite- anorexiant effect Drugs: 1) Amphetamine- ADHD in children 2) Methamphetamine- shabu 3) Phenmetrazine 4)Methylphenidate 5)Phentermine 6)Fenfluramine 7) PPA Ephedrine stimulates the receptors and the release of NE Uses: 1) nasal decongestant 2) vasoconstrictor to raise BP in surgery which is lowered by anesth 3) used to treat asthma 4) present in fat burners Sympatholytics/ Sympathetic Antagonists/ Adrenergic Antagonists I.-blockers A.Nonselective C.Selective 2 -Phenoxybenzamine -Yohimbine -Phentolamine -Tolazoline B.Selective 1 -Prazosin -Doxazosin -Terazosin
II.-blockers A.Nonselective -Propanolol B.Selective 1 -M- Metoprolol -A Acebutolol -B Betaxalol, Bisoprolol -A- Atenolol -E- Esmolol C. ISA Effect -P- Pindolol -A- Acebutolol -L- Labetalol
D.MSA -P-A-
E. with -blocking effect -Labetalol -Carvedilol
- L-P- Propanolol - M- Metoprolol
Phenoxybenzamine- irreversible/ noncompetitive Uses: 1) preoperative control of HPN in patients with pheochromocytoma 2) control symptoms of Raynauds phenomenon (intermittent claudication) 3) used to control symptoms in carcinoid syndrome **Pheochromocytoma- hypersecretory tumor of the adrenal medulla leading to excessive release of NE &Epi -s/sx: flushing, severe headache, HPN, severe tachycardia, sympathetic sweating **Carcinoid syndrome- cancer of the enterochromaffin cells (storage sites of 5HT) leading to oversecretion of serotonin -s/sx: flushing, severe headache, palpitation Phentolamine- reversible/competitive Uses: 1) pre-op mx of pheochromocytoma; dx of pheochromocytoma 2) for Raynauds phenomenon 3) Intracavenous injection- for penile erection due to erectile dysfunction zosins Uses: 1) 1st line of drugs for essential HPN 2) relief of urinary retention for BPH SE: First-dose Phenomenon- syncope and orthostatic hypotension Yohimbine (experimental drug for impotence) Locally post synaptic 2 = vasodilation Systemically presynaptic 2 = vasoconstriction -blockers Uses: 1) HPN 2) anti-angina 3) anti-arrhythmia 4) migraine 5) Glaucoma- Timolol 6) control sx of hyperthyroidism 7) familial tremors INDERAL SE: 1. Rebound tachycardia and HPN 2. exacerbate bronchospasm in bronchospastic disorders 3. heart block 4. can mask symptoms of hypoglycemia **Diabetic shock
Você também pode gostar
- Biochemistry Review Question: Protein MetabolismDocumento13 páginasBiochemistry Review Question: Protein MetabolismrashitaAinda não há avaliações
- Autacoids: H1 Receptor Allergic and Anaphylactic Responses H2 Receptor Secretion of Acid and PepsinDocumento3 páginasAutacoids: H1 Receptor Allergic and Anaphylactic Responses H2 Receptor Secretion of Acid and PepsinMarkyAinda não há avaliações
- Drug AllergyDocumento61 páginasDrug Allergyadysti100% (1)
- Module 4 - Basic Pharmacology UpdateDocumento42 páginasModule 4 - Basic Pharmacology UpdateWin Htet0% (1)
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersDocumento5 páginasCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- Chapter 43 - Beta-LactamDocumento7 páginasChapter 43 - Beta-LactamErika De JesusAinda não há avaliações
- This Study Resource Was: Hesi Pharmacology Test Bank 2018 RN V2 14 Total QuestionsDocumento3 páginasThis Study Resource Was: Hesi Pharmacology Test Bank 2018 RN V2 14 Total QuestionsCrystal B Costa78Ainda não há avaliações
- Pharma CollectionDocumento40 páginasPharma CollectionMuhd Nico DariyantoAinda não há avaliações
- Cancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationDocumento5 páginasCancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationOndari gisemba OSINDEAinda não há avaliações
- CNS DrugsDocumento8 páginasCNS DrugsSheral Aida100% (2)
- Pharmacology Reviewer 001Documento7 páginasPharmacology Reviewer 001Kath MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Firecracker Pathoma Companion 2017Documento9 páginasFirecracker Pathoma Companion 2017Zia HaywoodAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology - Section 23 - Antibiotics 2Documento5 páginasPharmacology - Section 23 - Antibiotics 2Pathalee ThalpavilaAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicDocumento13 páginasPharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicSherlock HolmesAinda não há avaliações
- Adrenergic Receptors ChartDocumento1 páginaAdrenergic Receptors ChartLeon ChenAinda não há avaliações
- Metabolic Disorders 01Documento41 páginasMetabolic Disorders 01Brent LagartoAinda não há avaliações
- Cholinergic DrugsDocumento44 páginasCholinergic Drugskhuzaima9100% (1)
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocumento37 páginasPharmacology FirecrackerRehan Usman100% (1)
- DR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry-Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources For Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively Short TimeDocumento1 páginaDR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry-Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources For Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively Short TimeDr Kumar Ponnusamy100% (1)
- Pharma CNS DRUGS Part 1Documento13 páginasPharma CNS DRUGS Part 1reference booksAinda não há avaliações
- Krok - Base PharmacologyDocumento149 páginasKrok - Base PharmacologyHemant GargAinda não há avaliações
- Antibiotic GuideDocumento6 páginasAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- Pharmacology II OutlineDocumento52 páginasPharmacology II Outlinerjones53Ainda não há avaliações
- MDS-6-Mock-exam-QAE - Unlocked FINALDocumento70 páginasMDS-6-Mock-exam-QAE - Unlocked FINALSubhashAinda não há avaliações
- BIO-GEN INNO-VISION 2012 - DR Kumar Ponnusamy 1 Min Papers On Inborn Errors of AA Metab & DNA RNADocumento12 páginasBIO-GEN INNO-VISION 2012 - DR Kumar Ponnusamy 1 Min Papers On Inborn Errors of AA Metab & DNA RNADr Kumar PonnusamyAinda não há avaliações
- PharmacologyDocumento35 páginasPharmacologyJan Michael ArtiagaAinda não há avaliações
- Anticholinergic MnemonicDocumento1 páginaAnticholinergic Mnemonictainah07Ainda não há avaliações
- QuizletDocumento104 páginasQuizletS.Ainda não há avaliações
- VERSION 2 of ICM ShelfDocumento5 páginasVERSION 2 of ICM ShelfheylllAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Documento2 páginasPharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology 1Documento53 páginasPharmacology 1Dawn WRein LegaspiAinda não há avaliações
- Case Studies PharmacologyDocumento6 páginasCase Studies PharmacologyZaigham HammadAinda não há avaliações
- Impactednurse Nurses Reference PackDocumento2 páginasImpactednurse Nurses Reference PackRaenell CurryAinda não há avaliações
- Metabolism of XenobioticsDocumento5 páginasMetabolism of XenobioticsJanelle Bondad100% (2)
- Pharmacology Dr. Scott PDFDocumento90 páginasPharmacology Dr. Scott PDFSingey LhendupAinda não há avaliações
- First Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsDocumento23 páginasFirst Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsLaura Lopez RocaAinda não há avaliações
- Autacoids For Med.Documento140 páginasAutacoids For Med.Feysal AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Argus 5 1 Test CasesDocumento11 páginasArgus 5 1 Test CasespponnapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Muscarinic and Anti-MuscarinicsDocumento3 páginasMuscarinic and Anti-MuscarinicsElleJBAinda não há avaliações
- Drug of ChoiceDocumento2 páginasDrug of ChoiceRia Tiglao Fortugaliza100% (1)
- AutacoidsDocumento103 páginasAutacoidsKamran Ali100% (2)
- Approach To Comatose Child: DR G.VenkateshDocumento83 páginasApproach To Comatose Child: DR G.VenkateshG VenkateshAinda não há avaliações
- Pall CareDocumento81 páginasPall Careडा. सत्यदेव त्यागी आर्यAinda não há avaliações
- Table: Selected Antibacterial Antibiotics Antibiotics THAT . Mechanism of Action Names of Drugs Notes and ProblemsDocumento4 páginasTable: Selected Antibacterial Antibiotics Antibiotics THAT . Mechanism of Action Names of Drugs Notes and ProblemsTJAinda não há avaliações
- Block 13 Patho SlidesDocumento62 páginasBlock 13 Patho SlidesLennon Ponta-oyAinda não há avaliações
- Usmle World Step 1 Pharmacology: Question ListDocumento73 páginasUsmle World Step 1 Pharmacology: Question ListAnonymous 4txA8N8etAinda não há avaliações
- Cheat Sheet For CancerDocumento4 páginasCheat Sheet For CancerEffie Cloe Marie BitengAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Documento4 páginasDrug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Leyla MajundaAinda não há avaliações
- Hematologic DisordersDocumento32 páginasHematologic DisordersQuolette ConstanteAinda não há avaliações
- Lippincott Questions CH 2Documento15 páginasLippincott Questions CH 2rajuAinda não há avaliações
- A New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMDocumento26 páginasA New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMKartik Mendiratta100% (1)
- DRUG SUMMARY TABLE - Anticoagulantes y AntiagregantesDocumento3 páginasDRUG SUMMARY TABLE - Anticoagulantes y AntiagregantesManuel BetancurAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology A ReviewDocumento15 páginasPharmacology A ReviewKathrynne MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- PharmacologyDocumento120 páginasPharmacologyFluffy_iceAinda não há avaliações
- Path NotesDocumento111 páginasPath NotesNirav Patel100% (1)
- PG Notes 3Documento29 páginasPG Notes 3Eliza SparkAinda não há avaliações
- Pharma NewestDocumento131 páginasPharma NewestPaolo Montańa EzparasAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsDocumento35 páginasLecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsakramuddaulaAinda não há avaliações
- L9 Sympathomimetics Lytics REVISED 2017 PDFDocumento49 páginasL9 Sympathomimetics Lytics REVISED 2017 PDFVea AngelesAinda não há avaliações
- Appellee Vs VS: en BancDocumento34 páginasAppellee Vs VS: en Bancdenbar15Ainda não há avaliações
- Ocampo v. EnriquezDocumento128 páginasOcampo v. EnriquezNicole AAinda não há avaliações
- South China Sea RulingDocumento501 páginasSouth China Sea RulingAnonymous zBCMh8j100% (1)
- Enrile - v. - People PDFDocumento72 páginasEnrile - v. - People PDFJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 Macapagal Arroyo - v. - People PDFDocumento111 páginas2016 Macapagal Arroyo - v. - People PDFDarla GreyAinda não há avaliações
- 213485-2018-Republic v. SerenoDocumento261 páginas213485-2018-Republic v. SerenoKristina B DiamanteAinda não há avaliações
- 211511-2018-People v. AmarelaDocumento16 páginas211511-2018-People v. AmarelaButch Maat100% (2)
- People Vs TanDocumento5 páginasPeople Vs TanJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Enrile - v. - People PDFDocumento72 páginasEnrile - v. - People PDFJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Annex A-RR22-2020NOD V03Documento2 páginasAnnex A-RR22-2020NOD V03Fo LetAinda não há avaliações
- 02-8-13-SC 2004 Rules On Notarial PracticeDocumento20 páginas02-8-13-SC 2004 Rules On Notarial PracticeRudmar Angelo EcaldreAinda não há avaliações
- Enrile - v. - People PDFDocumento72 páginasEnrile - v. - People PDFJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 Macapagal Arroyo - v. - People PDFDocumento111 páginas2016 Macapagal Arroyo - v. - People PDFDarla GreyAinda não há avaliações
- Consultation InformationDocumento2 páginasConsultation InformationJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Defenses CounterclaimDocumento2 páginasAnswer Defenses CounterclaimJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Termination LetterDocumento2 páginasTermination LetterJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Consultation InformationDocumento2 páginasConsultation InformationJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Comelec Resolution No. 10211Documento33 páginasComelec Resolution No. 10211Jov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- With Specific Denial Only - Negative DefenseDocumento1 páginaWith Specific Denial Only - Negative DefenseMon Cristhoper B. PasiaAinda não há avaliações
- Grace Poe, League of CitiesDocumento6 páginasGrace Poe, League of CitiesJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- 2019 Legal FeesDocumento2 páginas2019 Legal FeesJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Answers by Persons Sued Under Common NameDocumento1 páginaAnswers by Persons Sued Under Common NameMark Vincent Salvador CuchapinAinda não há avaliações
- Answer With Cross-ClaimDocumento1 páginaAnswer With Cross-ClaimJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Specific Denial Under Oath of Document Attached To PleadingDocumento1 páginaSpecific Denial Under Oath of Document Attached To PleadingJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Affirmative Defense Based On The Forced and IntimidationDocumento1 páginaAffirmative Defense Based On The Forced and IntimidationJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Affirmative Defense Based On IllegalityDocumento1 páginaAffirmative Defense Based On IllegalityJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Affirmative Defense Based On The Statute of LimitationsDocumento1 páginaAffirmative Defense Based On The Statute of LimitationsJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Affirmative Defense On FraudDocumento1 páginaAffirmative Defense On FraudBembol MirasolAinda não há avaliações
- Affirmative Defense Based On ReleaseDocumento1 páginaAffirmative Defense Based On ReleaseJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- Affirmative Defense Based On Former RecoveryDocumento1 páginaAffirmative Defense Based On Former RecoveryJov May DimcoAinda não há avaliações
- E351 Full PDFDocumento13 páginasE351 Full PDFajes coolAinda não há avaliações
- Bonica's Management of PainDocumento31 páginasBonica's Management of PainChaitanya LankaAinda não há avaliações
- San Pedro Cactus of MysteryDocumento16 páginasSan Pedro Cactus of MysteryZeus MoureAinda não há avaliações
- Neurohumoral Transmission - Meaning and Steps - AnimalsDocumento9 páginasNeurohumoral Transmission - Meaning and Steps - AnimalsPragnesh ParmarAinda não há avaliações
- Current Use and Advances in Vasopressors and Inotropes Support in ShockDocumento13 páginasCurrent Use and Advances in Vasopressors and Inotropes Support in ShockJose Luis Espino MacielAinda não há avaliações
- Adrenaline PDFDocumento8 páginasAdrenaline PDFkarpanaiAinda não há avaliações
- Ch21 Conversion of Amino Acids To Specialized ProductsDocumento62 páginasCh21 Conversion of Amino Acids To Specialized Productsendale gebregzabherAinda não há avaliações
- Stress Management in Young Adults: Implications of Mandala Coloring On Self-Reported Negative Affect and Psychophysiological ResponseDocumento13 páginasStress Management in Young Adults: Implications of Mandala Coloring On Self-Reported Negative Affect and Psychophysiological ResponseMira PriscillaAinda não há avaliações
- Furman 2014 MARDDocumento10 páginasFurman 2014 MARDJuan Hernández GarcíaAinda não há avaliações
- ART Adrenaline and NoradrenalineDocumento9 páginasART Adrenaline and NoradrenalineHECTORIBZAN ACERO SANDOVALAinda não há avaliações
- Golongan Obat Prekursor Dan OotDocumento2 páginasGolongan Obat Prekursor Dan Ootherfandi ahmadAinda não há avaliações
- KEY ANSWERS.109 Questions and Rationale On Psychotic DisordersDocumento21 páginasKEY ANSWERS.109 Questions and Rationale On Psychotic DisordersBecca Jhoy Emong100% (2)
- UD RPP 6 TrigonometriDocumento12 páginasUD RPP 6 TrigonometriJalia FardilaAinda não há avaliações
- Emotion Focused CopingDocumento8 páginasEmotion Focused CopingMahrukh KhalidAinda não há avaliações
- Neurotransmitters and Scoliosis EbookDocumento14 páginasNeurotransmitters and Scoliosis EbookyounessiusAinda não há avaliações
- AntidepressantsDocumento17 páginasAntidepressantsVimal BhagatAinda não há avaliações
- Autonomic Nervous System YASER BIDAHDocumento19 páginasAutonomic Nervous System YASER BIDAHGhalia Tarek Al Hassan100% (2)
- Melanin Physics by NEB HERUDocumento241 páginasMelanin Physics by NEB HERUNeb Heru91% (81)
- Daftar ZAT AKTIF OOT PREKURSORDocumento3 páginasDaftar ZAT AKTIF OOT PREKURSORida nurmaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Adrenergic SystemDocumento6 páginasAdrenergic SystemdocsAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry of NeurotransmissionDocumento47 páginasBiochemistry of NeurotransmissionTariq MahmoodAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology A - Sympathetic Drugs Reviewer Ver 2.0 PDFDocumento2 páginasPharmacology A - Sympathetic Drugs Reviewer Ver 2.0 PDFJohn Benedict BondocAinda não há avaliações
- Melphalan (Mefulta®) Melphalan 50 MG Powder and Solvent For Solution For Injection Per InfusionDocumento1 páginaMelphalan (Mefulta®) Melphalan 50 MG Powder and Solvent For Solution For Injection Per InfusionTAJ PHARMA — A Health Care ProviderAinda não há avaliações
- Autonomic Nervous System DrugsDocumento128 páginasAutonomic Nervous System DrugsMubashra Habib100% (1)
- (Neurology-Laboratory and Clinical Research Developments) Calabro Rocco Salvatore-Male Sexual Dysfunctions in Neurological Diseases From Pathophysiology To Rehabilitation (Neurology-Laboratory and CLDocumento196 páginas(Neurology-Laboratory and Clinical Research Developments) Calabro Rocco Salvatore-Male Sexual Dysfunctions in Neurological Diseases From Pathophysiology To Rehabilitation (Neurology-Laboratory and CLcriki_blonduAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology IDocumento82 páginasPharmacology IMelanieAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology TestDocumento88 páginasPharmacology TestIrinotecanAinda não há avaliações
- Neurobiological Theories of Mental DisordersDocumento12 páginasNeurobiological Theories of Mental DisordersNovelyn Kaye Ramos CalanogaAinda não há avaliações
- Oxford Textbook of Sleep Disorders.2017Documento554 páginasOxford Textbook of Sleep Disorders.2017Mykhailo Lysianskyi100% (1)
- Principles of Emergency NursingDocumento4 páginasPrinciples of Emergency NursingShamera MahabassalAinda não há avaliações
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (81)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNo EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNo EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNo EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (26)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNo EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNo EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsAinda não há avaliações
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryNo EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.No EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (110)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNo EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNo EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlNo EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (58)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingNo EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1138)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningNo EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNo EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (170)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNo EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (328)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNo EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)