Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ob &gy
Enviado por
Thumz ThuminDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ob &gy
Enviado por
Thumz ThuminDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1. A. B. C. D. E. 2. A. B. C. D. E.
Which of the following is LEAST likely to be associated with preterm delivery? Incompetent cervix Polyhydramnios Uterine fibroids Abdominal pregnancy Previous preterm delivery Each of the following is a risk factor of puerperial infection EXCEPT: Caesarean section Premature rupture of membranes (PROM) Multiple vaginal examinations during labor Long labor multiparity
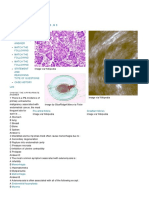
3. Regarding the features of the Proliferative Phase, which of the following is WRONG? A. At the beginning of the proliferative phase of uterine cycle, the endometrium is thin, about 12mm. B. During the proliferative phase of uterine cycle, the predominant change is evolution of the initially straight, narrow, and short endometrial glands into longer, tortuous structures. C. Throughout the proliferative phase of uterine cycle, the stroma is a dense compact layer, and vascular structures are infrequently. D. Histologically, during proliferative phase of uterine cycle, the glands have multiple mitotic cells and their organization changes from a low columnar pattern in the early period to a pseudostratified pattern before ovulation. E. The proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle is characterized by the cellular effects of progesterone. 4. A. B. C. D. E. Using the NST tracing in Figure 1, which of the following is TRUE? A fetus with this pattern is at risk for fetal death in utero within the next week The pattern demonstrates no fetal movement presented. The tracing meet the criteria for reactivity The pattern is common during the sleep cycle of the fetus The tracing shows the regular uterine contractions which demonstrates parturition initiated
Figure 1.
5. A 45-year-old patient with uterine leiomyomata found on pelvic examination complains of excessive uterine bleeding. Which of the following should be the next step in the management of this patient? A. myomectomy B. hysterectomy C. ultrasonography D. endometrial biopsy E. hysterosalpingography 6. The majority of deaths from cervical carcinoma are due to which of the following? A. local spread obstructing the ureters, causing renal failure B. brain metastasis with resultant cerebral hemorrhage C. hemorrhage into the pelvis from erosion of vessels by the tumor D. pulmonary failure secondary to metastatic disease filling the lungs E. bone metastasis causing crush injuries to the central nervous system. 7. A 26-year-old patient is found to have an 8-week size, irregular uterus. She does not complain of pain or excessive menstrual bleeding. Her Pap smear is normal and a pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is the best step in the management of this patient? A. continued observation B. endometrial biopsy C. cervical conization D. hysterectomy E. pelvic ultrasonography 8. Which of the following is the best therapy for secondary dysmenorrheal thought to be due to adenomyosis? A. cervical dilation B. cyclic OCs C. analgesics
D. hysterectomy E. testosterone injections 9. Which of the following is the most common pelvic mass associated with amenorrhea in a reproductive-age woman? A. follicular cyst B. corpus luteum cyst C. benign cystic teratoma D. leiomyoma E. pregnancy 10. A 21-year-old woman has amenorrhea, mild vaginal spotting, and pelvic pain. Her vital signs are blood pressure, 100/50mmHg; pulse, 110bpm; and temperature 98.60F. Abdominal examination shows left lower quadrant tenderness with rebound. Pelvic examination demonstrates a painful 4-cm left adnexal mass. A serum pregnancy test is positive. A hematocrit is 22%(normal, 35 to 45%). Which of the following is the best next step? A. observation B. estrogen therapy C. progesterone therapy D. methotrexate therapy E. surgery
11. The human pelvis is a complex structure. Which option includes all of the bones that make it up? A. Trochanter, hip socket, ischium, sacrum, and pubis B. Illium, ischium, pubis, sacrum, and coccyx. C. Illium, ischium, and pubis D. Sacrum, ischium, ilium, and pubis E. Trochanter, sacrum, coccyx, ilium, and pubis
12. Which of the following is the most important prognostic indicator of survival from advanced ovarian carcinoma? A. stage of disease B. grade of tumor differentiation C. nutritional status D. body mass index E. presence of sec steroid receptors 13. A 54-year-old healthy woman comes for an annual examination. Her last menstrual period(LMP) was 4 years ago. The physical examination is normal. Palvic examination shows vaginal atrophy and a small, mobile uterus. The right ovary is 2.5X4.5 cm in diameter. The left ovary is nonpalpable. Vaginal ultrasonography shows that the right ovary is similar in size to that of a premenopausal ovary. How do you advise this patient?
A. The ovaries of a postmenopausal woman are usually papable. B. The right ovary of a postmenopausal woman is usually palpable by right-handed examiners. C. A palpable ovary in a postmenopausal woman is suspicious for malignancy. D. The right ovary is still producing significant amounts of estrogen. E. The vaginal ultrasound is an unnecessary diagnositic test.
14. During normal delivery, an infant must pass through the maternal true pelvis. Which of the following most accurately describes the characteristics of the true pelvis? A. It has an oval outlet. B. It has three defining planes: an inlet, a midplane, and an outlet. C. It has an inlet made up of a double triangle. D. It is completely formed by two fused bones. E. It lies between the wings of the paired ileum.
15. During clinical pelvimetry, which of the following is routinely measured for evaluate the OUTLET? A. True conjugate B. Interspinal diameter C. Bispinous diameter D. Angle of pubic arch E. Intercristal diameter 16. Engagement is best defined as which of the following? A. when the greatest biparietal diameter of the head is level with the ischial spines B. when the greatest diameter of the fetal presenting part passes through the narrowest and lowest part of the maternal pelvis. C. when the presenting part goes through the pelvic inlet D. when the presenting part is below the ischial spines E. when the greatest biparietal diameter of the fetal head passes the pelvic inlet
17. A 32-year-old (G2P0) at term is admitted in labor with an initial cervical examination of 6cm dilatation, complete effacement, and the vertex at -1 station. Estimated fetal weight is 3.8kg, and her first pregnancy resulted in an uncomplicated vaginal delivery of a 3.0kg infant. After 2 hours, there is no cervical change. An intrauterine pressure catheter is placed. This shows two contractions in a 10-minute period, each with a strength of 30 mmHg. What is this abnormality of labor termed? A. prolonged latent phase B. active-phase arrest C. failure of decent D. protraction of descent E. arrest of latent phase
18. A patient calls your office complaining of continued heavy vaginal bleeding. She had an uncomplicated vaginal birth 2 weeks ago of her second child. The most likely diagnosis from the following differential is which of the following? A. uterine atony B. uterine rupture C. vaginal lacerations D. coagulopathies E. retained placental fragments 19. Fundal height, part of the obstetric examination, which of the information below is WRONG? A. Measurement should start at the variable point (the fundus) and continue to the fixed point (the clitoris) B. In centimeters, approximating the weeks of gestation beyond 18-20 weeks C. Is used to indirectly measure fetal growth in relation to gestational age D. A discrepancy between fundal height and gestation may indicate a fetus small or large for gestational age and should be investigated E. Fundal height is measured and recorded at each visit from second trimester, on an empty bladder, by using a non-elastic tape measure. 20. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following factors is NOT measured as part of a biophysical profile (BPP) amniotic fluid volume a contraction stress test (CST) a nonstress test (NST) fetal breathing motion fetal limb movements
21.Signs and symptoms that should alert you to the possibility of gestational trophoblastic disease include which of the following? A. persistent titer of hCG after pregnancy B. hematuria C. weight loss D. persistent postpartum anovulation E. nocturnal fever 22.Which of the following is the most common pelvic mass in postmenopausal woman? F. follicular cyst G. corpus luteum cyst H. germ cell tumor I. leiomyoma J. endometrioma 23.An 18-year-old woman presents for care because a condom broke during sexual
intercourse. Coitus occurred 1 day ago when she was at midcycle. She does not wish to be pregnant and will terminate the pregnancy if menses does not occur. Regarding her fear of pregnancy, which is the most appropriate next step in her management? K. advise her that unprotected midcycle coitus has a 5% risk of pregnancy L. prescribe intravaginal misoprostol M. advise immediate douching N. prescribe postcoital a brief course of oral contraception O. advise her to await her next menses before taking any action 24.The following methods are all hormonal contraception EXCEPT: P. condom Q. oral contracepative pill R. transdermal patch S. vaginal ring T. progesterone-only methods U. emergency contraception with RU486 25.Which of the following best describes a missed abortion? V. It is the death of the fetus that the patient does not realize has occurred. W. It is the death of the fetus in which the products of conception are retained after the embryo or fetus has died. X. It is the death of the fetus in which the products of conception are partially expelled. Y. It is the death of the fetus in which the products of conception cause bleeding and there is an open cervical os. Z. It is the death of the fetus in which the products of conception are no longer recognizable.
Você também pode gostar
- Medical Power of AttorneyDocumento4 páginasMedical Power of AttorneybrettAinda não há avaliações
- Decalcify Your Pineal Gland With These Herbs - Anima Mundi HerbalsDocumento16 páginasDecalcify Your Pineal Gland With These Herbs - Anima Mundi HerbalsSalomon Yves100% (4)
- Using Flowers For HealingDocumento28 páginasUsing Flowers For HealingKarina Castilhos100% (1)
- OB-GYN - MCQ - 2012 - 5th-Year - Mu - TahDocumento16 páginasOB-GYN - MCQ - 2012 - 5th-Year - Mu - TahHalah100% (1)
- Gyn 9 - All Gynecology 5 2021Documento22 páginasGyn 9 - All Gynecology 5 2021Menna Kamal100% (2)
- Types of EnemaDocumento6 páginasTypes of EnemaOmprakash Saini100% (2)
- Pain Is in The Brain HandoutDocumento39 páginasPain Is in The Brain Handoutgabitor100% (1)
- OBS and Gynaecology MCQ ReviewDocumento11 páginasOBS and Gynaecology MCQ ReviewnoblefxAinda não há avaliações
- Immediate Loading of Dental Implants PDFDocumento15 páginasImmediate Loading of Dental Implants PDFAmar Bimavarapu100% (2)
- Obstetrics & Gynecology MCQ's PDFDocumento46 páginasObstetrics & Gynecology MCQ's PDFFarooq KhanAinda não há avaliações
- 01.williams Obstetrics - Combined QuestionsDocumento23 páginas01.williams Obstetrics - Combined QuestionschristinejoanAinda não há avaliações
- ALL Ob-Gyn McqsDocumento297 páginasALL Ob-Gyn McqsPreeti ChouhanAinda não há avaliações
- Board Exams Ob Gyn 2009Documento12 páginasBoard Exams Ob Gyn 2009filchibuff50% (2)
- OngmcqsDocumento26 páginasOngmcqsMoody Summour67% (3)
- Multiple Choice Questions in Paediatric SurgeryNo EverandMultiple Choice Questions in Paediatric SurgeryNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- Obs 1 Bleeding in Early Pregnancy QuestionsDocumento9 páginasObs 1 Bleeding in Early Pregnancy QuestionsSalmonella TyphiAinda não há avaliações
- Obstetrics Test Blue PrintDocumento8 páginasObstetrics Test Blue Printjose carlo araojoAinda não há avaliações
- Mcqs - Obstetrics and Gynaecology (For Post Graduate Preparing For FNB and Professionals) Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocumento27 páginasMcqs - Obstetrics and Gynaecology (For Post Graduate Preparing For FNB and Professionals) Obstetrics and GynaecologyAnonymous kQCQ30Rq5OAinda não há avaliações
- Comprehensive Handbook Obstetrics & Gynecology 3rd EdNo EverandComprehensive Handbook Obstetrics & Gynecology 3rd EdNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Obs and Gyne Final All PDFDocumento268 páginasObs and Gyne Final All PDFملك عيسى100% (2)
- MCQ - On Obstetrics and Gynaecology PART 2Documento78 páginasMCQ - On Obstetrics and Gynaecology PART 2Kripa Susan100% (3)
- OB-GYNE 2 Batch 2017 Ratio PDFDocumento13 páginasOB-GYNE 2 Batch 2017 Ratio PDFAdrianAinda não há avaliações
- Behavioral Models of Binge-Type EatingDocumento8 páginasBehavioral Models of Binge-Type Eatingpechy83Ainda não há avaliações
- Jac Brown Specific Techniques vs. Common Factors 2015Documento17 páginasJac Brown Specific Techniques vs. Common Factors 2015Mayra HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Latest Gynecology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For PDFDocumento10 páginasLatest Gynecology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For PDFMohamed Al-zichrawy100% (1)
- FCE OB GYN 2007 Male 2nd RoatationDocumento8 páginasFCE OB GYN 2007 Male 2nd Roatationapi-3763146Ainda não há avaliações
- Delusional Disorder: by Dr. Min Min Phyo 27 May 2019Documento56 páginasDelusional Disorder: by Dr. Min Min Phyo 27 May 2019thu thuAinda não há avaliações
- 10-OBGYN-Glory GroupDocumento46 páginas10-OBGYN-Glory Groupanmar alkhudhriAinda não há avaliações
- EKG in IHDDocumento349 páginasEKG in IHDDinhLinh100% (1)
- MCQs Gynaec 2 - ObGynDocumento10 páginasMCQs Gynaec 2 - ObGynbmhsh100% (3)
- Blood TransfusionDocumento3 páginasBlood Transfusionjaja7lagunzadAinda não há avaliações
- Obstetrics and GynecologyDocumento4 páginasObstetrics and Gynecologychuppepay100% (3)
- Obs MCQs PRIMEsDocumento41 páginasObs MCQs PRIMEssk100% (3)
- Dorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryDocumento3 páginasDorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryE.R.OAinda não há avaliações
- 2022-23 OBG MMed 2 - 3btest 1 - KeyDocumento12 páginas2022-23 OBG MMed 2 - 3btest 1 - KeyKenneth ChandaAinda não há avaliações
- MRANZCOG Sample Multiple Choice Questions GOBDocumento4 páginasMRANZCOG Sample Multiple Choice Questions GOBdreamzbooksAinda não há avaliações
- Obst 5 - All Obstetrics 1 2021Documento22 páginasObst 5 - All Obstetrics 1 2021Menna KamalAinda não há avaliações
- مهم اسئلةDocumento19 páginasمهم اسئلةnada elfarraAinda não há avaliações
- Obg MCQSDocumento11 páginasObg MCQSShriyansh ChaharAinda não há avaliações
- Perks of Being A WallflowerDocumento11 páginasPerks of Being A Wallflowerapi-259692329100% (1)
- Gyna Full QDocumento43 páginasGyna Full QMohammed Isa HomidatAinda não há avaliações
- 1Documento10 páginas1drnsatyaprasadAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ Remake Group A 2022Documento16 páginasMCQ Remake Group A 2022V Sugrim100% (1)
- Obstetrics MCQsDocumento28 páginasObstetrics MCQsMenna KamalAinda não há avaliações
- Promotion OBGYNDocumento30 páginasPromotion OBGYNAloah122346Ainda não há avaliações
- Will Obstetri 2-8 Maret 2018Documento16 páginasWill Obstetri 2-8 Maret 2018Shandy Suwanto Putra100% (2)
- 11 16Documento27 páginas11 16Iful SaifullahAinda não há avaliações
- كامل نساءDocumento181 páginasكامل نساءYasser ArefAinda não há avaliações
- Obgy QN BNKDocumento21 páginasObgy QN BNKZemen addiss100% (1)
- Obgyn Questions 1-100Documento26 páginasObgyn Questions 1-100Fika AmaliaAinda não há avaliações
- DR Khaled Final Exam MCQ 2012 - 2013Documento89 páginasDR Khaled Final Exam MCQ 2012 - 2013ﻣﻠﻚ عيسى100% (2)
- Operative Gyn MCQ PDFDocumento10 páginasOperative Gyn MCQ PDFFentahun TadesseAinda não há avaliações
- Addis Ababa University Medical Entrance Exam ReviewDocumento21 páginasAddis Ababa University Medical Entrance Exam ReviewAbdi KebedeAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Women's Health Issues Through Case StudiesDocumento19 páginasUnderstanding Women's Health Issues Through Case Studiesstella pangestikaAinda não há avaliações
- DR Nadine Rev All (Samra's Edition)Documento313 páginasDR Nadine Rev All (Samra's Edition)Cyril I.Makar100% (1)
- OBGYN 1st Round 2021 AnsweredDocumento14 páginasOBGYN 1st Round 2021 AnsweredMuhammed Mostafa100% (4)
- 26-50 Maret 2019Documento8 páginas26-50 Maret 2019daniel_alexander_susenoAinda não há avaliações
- Obs and Gyn 6 Year Final Exam / 2012: A. PcosDocumento13 páginasObs and Gyn 6 Year Final Exam / 2012: A. PcosNashaat H. AlshawabkehAinda não há avaliações
- Question 3Documento19 páginasQuestion 3Anonymous LF9aizGhaAinda não há avaliações
- ObstetricsDocumento8 páginasObstetricsrevathidadam55555100% (1)
- Gyne 2018 5th year exam محلول PDFDocumento27 páginasGyne 2018 5th year exam محلول PDFMohammad HereshAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 2 (OBS) Jan 2018 RecallsDocumento19 páginasPaper 2 (OBS) Jan 2018 RecallshummaAinda não há avaliações
- OBG Question DiscussionDocumento19 páginasOBG Question DiscussionNesreden Jemal KedirAinda não há avaliações
- Soal MCQ UI 2009Documento14 páginasSoal MCQ UI 2009Suzette100% (1)
- Gynaemcq 120602094722 Phpapp02Documento7 páginasGynaemcq 120602094722 Phpapp02Melissa Aina Mohd Yusof100% (1)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology Practice QuestionsDocumento18 páginasObstetrics and Gynecology Practice QuestionsSuzetteAinda não há avaliações
- Rev 4 - General Gynecology 2022Documento28 páginasRev 4 - General Gynecology 2022Omar MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- Soal Usulan UnHas Juli 2019Documento25 páginasSoal Usulan UnHas Juli 2019Ibnu SinaAinda não há avaliações
- Obs Mcqs PaperDocumento11 páginasObs Mcqs PaperRuqaeya Saqib100% (1)
- 6th Year Obs&Gyne 2015Documento19 páginas6th Year Obs&Gyne 2015Rashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- 2003 2008 MCQDocumento81 páginas2003 2008 MCQIshola Segun SamuelAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ sample questions on mechanisms of labour and pregnancy complicationsDocumento11 páginasMCQ sample questions on mechanisms of labour and pregnancy complicationsMuhammad Bilal100% (2)
- Pregnancy quizDocumento8 páginasPregnancy quizpoker011007Ainda não há avaliações
- Rare autoimmune skin disease in pregnant 15-year-old: A case reportDocumento5 páginasRare autoimmune skin disease in pregnant 15-year-old: A case reportsri karuniaAinda não há avaliações
- Part A-7-Snake BiteDocumento7 páginasPart A-7-Snake Bitefernanda1rondelli0% (1)
- Case 7 - Newborn With Respiratory DistressDocumento10 páginasCase 7 - Newborn With Respiratory DistressSue HuangAinda não há avaliações
- Photodermatoses: An Approach to DiagnosisDocumento50 páginasPhotodermatoses: An Approach to DiagnosisShakilAinda não há avaliações
- EpsDocumento24 páginasEpsRosaldy MuhamadAinda não há avaliações
- Nine Steps To Occlusal Harmony FamdentDocumento5 páginasNine Steps To Occlusal Harmony FamdentGhenciu Violeta100% (1)
- Chloramphenicol: Ayen University - Al College of PharmacyDocumento7 páginasChloramphenicol: Ayen University - Al College of Pharmacyمحمد حميد عطيةAinda não há avaliações
- Anticoagulation in OrthopedicsDocumento32 páginasAnticoagulation in Orthopedicsehabede6445Ainda não há avaliações
- Arginine Metabolism and its Role in Growth, Health and DiseaseDocumento26 páginasArginine Metabolism and its Role in Growth, Health and Diseaseאנריקה שטרמר דיאטן קליניAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Antidiabetic Glicazide GuideDocumento3 páginasOral Antidiabetic Glicazide Guideshe'sgotyouhighAinda não há avaliações
- What Are The Causes of Albinism?Documento15 páginasWhat Are The Causes of Albinism?Viviana VarelaAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Pulp Capping in Primary Molars: Report of Two CasesDocumento3 páginasDirect Pulp Capping in Primary Molars: Report of Two Casesemie sitorusAinda não há avaliações
- Sodium Bicarbonate: PresentationDocumento3 páginasSodium Bicarbonate: Presentationmadimadi11Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsDocumento2 páginasDrug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsMae Ann Bueno CastillonAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes The Differences Between Types 1 and 2Documento13 páginasDiabetes The Differences Between Types 1 and 2leonard1971Ainda não há avaliações
- PATENT Annexure-A Domestic FilingDocumento24 páginasPATENT Annexure-A Domestic FilingMulayam Singh YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Anaesthesia and Myasthenia GravisDocumento12 páginasAnaesthesia and Myasthenia Gravis37435rlcAinda não há avaliações