Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Nursing Care Plans
Enviado por
fanvicfayDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Nursing Care Plans
Enviado por
fanvicfayDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
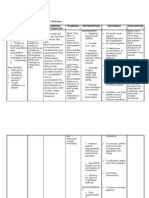
Nursing Care Plans Pulmonary Tuberculosis TB Nursing diagnosis ineffective Airway Clearance related to Thick, viscous, or bloody secretions
Fatigue, poor cough effort Tracheal or pharyngeal edema Nursing goal: Respiratory Status: Airway Patency Nursing Intervention Nursing Care Plans Pulmonary Tuberculosis TB
Airway Management: Assess respiratory function, such as breath sounds, rate, rhythm, and depth, and use of accessory muscles. Rationale Diminished breath sounds may reflect Atelectasis. Rhonchi and wheezes indicate accumulation of secretions and inability to clear airways, which may lead to use of accessory muscles and increased work of breathing. Note ability to expectorate mucus and cough effectively; document character and amount of sputum and presence of Hemoptysis Rationale Expectoration may be difficult when secretions are very thick as a result of infection or inadequate hydration. Blood tinged or frankly bloody sputum results from tissue breakdown in the lungs and may require further evaluation and intervention Place client in semi- or high Fowlers position. Assist client with coughing and deep-breathing exercises Rationale Positioning helps maximize lung expansion and decreases respiratory effort. Maximal ventilation may open Atelectasis areas and promote movement of secretions into larger airways for expectoration. Clear secretions from mouth and trachea, suction as necessary. Rationale Prevents obstruction and aspiration. Suctioning may be necessary if client is unable to expectorate secretions. Maintain fluid intake of at least 2,500 ML/day unless contraindicated Rationale High fluid intake helps thin secretions, making them easier to expectorate Humidify inspired oxygen Rationale Prevents drying of mucous membranes and helps thin secretions Administer medications, as indicated, for example: Mucolytic agents, such as acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) Rationale Reduces the thickness and stickiness of pulmonary secretions to facilitate clearance Bronchodilators, such as oxtriphylline (Choledyl) and theophylline (TheoDur) Rationale Increases lumen size of the tracheobronchial tree, thus decreasing resistance to airflow and improving oxygen delivery Corticosteroids (prednisone) Rationale May be useful in the presence of extensive involvement with profound hypoxemia and when inflammatory response is life-threatening Be prepared for and assist with emergency intubation Rationale Intubation may be necessary in rare cases of bronchogenic TB accompanied by laryngeal edema or acute pulmonary bleeding. Evaluation (Expected Out Come) Nursing Care Plans Pulmonary Tuberculosis TB Nursing diagnosis ineffective Airway Clearance: Maintain patent airway. Expectorate secretions without assistance. Demonstrate behaviors to improve or maintain airway clearance. Participate in treatment regimen, within the level of ability and situation. Identify potential complications and initiate appropriate actions.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Gas Exchange, risk for impaired Risk factors may include Decrease in effective lung surface, atelectasis Destruction of alveolar-capillary membrane Thick, viscous secretions Bronchial edema Possibly evidenced by [Not applicable; presence of signs and symptoms establishes anactual diagnosis.] DESIRED OUTCOMES/EVALUATION CRITERIAPATIENT WILL: Respiratory Status: Gas Exchange (NOC) Report absence of/decreased dyspnea. Demonstrate improved ventilation and adequate oxygenation of tissues by ABGs within acceptable ranges
NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Knowledge, deficient [Learning Need] regarding condition, treatment, prevention, self-care, and discharge needs May be related to Lack of exposure to/misinterpretation of information Cognitive limitations Inaccurate/incomplete information presented Possibly evidenced by Request for information Expressed misconceptions about health status Lack of or inaccurate follow-through of instructions/behaviors Expressing or exhibiting feelings of being overwhelmed DESIRED OUTCOMES/EVALUATION CRITERIAPATIENT WILL: Knowledge: Illness Care (NOC) Verbalize understanding of disease process/prognosis and prevention. Initiate behaviors/lifestyle changes to improve general well-being and reduce risk of reactivation of TB. Identify symptoms requiring evaluation/intervention. Describe a plan for receiving adequate follow-up care. Verbalize understanding of therapeutic regimen and rationale for actions
Nursing care plans 1. Objectives Verbalization of inaccurate information Asking of questions Diagnosis: Deficient knowledge related to misinterpretation on information Rationale: knowledge deficit is a lack of cognitive information or psychomotor skills required for health recovery, maintenance, or health promotion. (NCP Book by Gulanick & Myers 6th Edition pp 116) Short Term Goal After 2 days of NI Patient will demonstrate motivation to learn, and identify perceived learning needs. And verbalize understanding of desired content Long Term Goal After 4 days of NI patient will be able follow the given/taught instructions Interventions 1. Determine who will be the learner. Patient, mother, sister. Insufficient knowledge
Many patients may view themselves as dependent on the watchers and may not be willing to learn
Você também pode gostar
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 páginasAsthma Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceCyrus De Asis92% (24)
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento7 páginas1 Ineffective Breathing PatternKrisJane Ratilla Abiva100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plans of PneumoniaDocumento16 páginasNursing Care Plans of Pneumoniaha,hr12480% (5)
- Nursing Process of PneumoniaDocumento5 páginasNursing Process of Pneumoniatin2x061275% (8)
- 1Documento50 páginas1Sujit BhushanAinda não há avaliações
- Verbal De-Escalation Agitated PatientDocumento9 páginasVerbal De-Escalation Agitated PatientArhip CojocAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 páginaIneffective Airway ClearanceVittena Eloisa VibarAinda não há avaliações
- Below Are 8 Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans (NCP)Documento16 páginasBelow Are 8 Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans (NCP)Diana CarinoAinda não há avaliações
- PneumoniaDocumento17 páginasPneumoniajustin_saneAinda não há avaliações
- PNEUMONIADocumento2 páginasPNEUMONIAcastanedamarrianeveniceAinda não há avaliações
- Bronchitis Nursing Care PlanDocumento8 páginasBronchitis Nursing Care PlanBryan NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- PTB NCPDocumento12 páginasPTB NCPNiel LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Ncp's FOR PLEURAL EFFUSIONDocumento4 páginasNcp's FOR PLEURAL EFFUSIONHania Polangi100% (1)
- Nursing ManagementDocumento4 páginasNursing ManagementjeponieAinda não há avaliações
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocumento7 páginasPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 páginasNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP IsoDocumento4 páginasNCP IsoBriccio Calingin IIIAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing DiagnosisDocumento7 páginasNursing DiagnosisMariya Mikaela Garcia SoledadAinda não há avaliações
- BronchiectasisDocumento40 páginasBronchiectasisyana jaeAinda não há avaliações
- NCP SDocumento8 páginasNCP SMarvie CadenaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing InterventionsDocumento18 páginasNursing InterventionsMark BellAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Pleural EffusionDocumento9 páginasNursing Care Plan For Pleural EffusionJoseph Angelo Fortuna Carmona100% (1)
- NCP For COPD and Acute PainDocumento7 páginasNCP For COPD and Acute PainLenny SucalditoAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento9 páginasNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis For AsthmaDocumento6 páginasNursing Diagnosis For AsthmaTINAIDA33% (3)
- Appendectomy Possible NCPDocumento6 páginasAppendectomy Possible NCPIrish Nicole DC100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaDocumento8 páginasNursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaKannanAinda não há avaliações
- 312 Respi Scenario ReviewerDocumento13 páginas312 Respi Scenario Reviewer11 - JEMELYN LOTERTEAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento7 páginasNursing Diagnosis Impaired Gas ExchangeZycon Rodney Ae'zecquel Gachallan50% (2)
- Guillain - Barre Syndrome (Polyradiculoneuritis)Documento7 páginasGuillain - Barre Syndrome (Polyradiculoneuritis)Nadjmiah N. GuilingAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumonia AlgorithmDocumento3 páginasPneumonia AlgorithmBien ChuAinda não há avaliações
- ThyroidectomyDocumento11 páginasThyroidectomySherina W. EddingAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocumento4 páginasChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseSeraphina SolanAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Proper 1Documento6 páginasNCP Proper 1Noreen PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Iniego Carlo Jay)Documento9 páginasRespiratory Distress Syndrome (Iniego Carlo Jay)Carlojay IniegoAinda não há avaliações
- AssesmentDocumento9 páginasAssesmentmizrypAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Interventions For CAPDocumento5 páginasNursing Interventions For CAPthomasfinley44Ainda não há avaliações
- Tugas Pola Nafas Tidak AktifDocumento19 páginasTugas Pola Nafas Tidak Aktiffemy lia utamiAinda não há avaliações
- Inp Cu 7 CopdDocumento26 páginasInp Cu 7 CopdMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareAinda não há avaliações
- Inp Midterms MergedDocumento67 páginasInp Midterms MergedMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareAinda não há avaliações
- PNEUMONIADocumento24 páginasPNEUMONIAwheeyycoldandhot55Ainda não há avaliações
- CHOLECYSTECTOMYDocumento3 páginasCHOLECYSTECTOMYlovelysummerAinda não há avaliações
- NCP TBDocumento6 páginasNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsJazzmin Angel ComalingAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento6 páginasIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaAinda não há avaliações
- Status AsthmaticusDocumento15 páginasStatus AsthmaticusDaianne Joy DonatoAinda não há avaliações
- Comprehensive ExaminationDocumento8 páginasComprehensive ExaminationAnonymous dquW2YmO7Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Management Nursing Interventions RationaleDocumento6 páginasNursing Management Nursing Interventions RationaleKim RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Tolleno (Pneumonia ER)Documento4 páginasTolleno (Pneumonia ER)Hannah TollenoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP PTBDocumento9 páginasNCP PTBecbarticanAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Cardio PrintDocumento7 páginasNCP Cardio PrintNicole MapiliAinda não há avaliações
- BRONCHIECTASISDocumento36 páginasBRONCHIECTASISVince Peliño De MesaAinda não há avaliações
- NSG MGT Asthma (Autosaved)Documento14 páginasNSG MGT Asthma (Autosaved)sarikaAinda não há avaliações
- Chest Physiotherapy or Techniques in Cardio Pulmonary Physiotherapy A Running CommentaryDocumento5 páginasChest Physiotherapy or Techniques in Cardio Pulmonary Physiotherapy A Running CommentaryGopi KrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- What Is COPD? Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Signs and SymptomsDocumento11 páginasWhat Is COPD? Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Signs and SymptomsCecil Bhang-i Cacay - PabloAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento9 páginasIneffective Airway ClearanceFatiha Sri Utami TamadAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Studies: The Forced Expiratory Volume Over 1 Second (FEVDocumento7 páginasDiagnostic Studies: The Forced Expiratory Volume Over 1 Second (FEVKushan SenanayakaAinda não há avaliações
- Bronchiectasis: A Beginner's 3-Step Guide on Managing Bronchiectasis Through Natural Methods and Diet, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanNo EverandBronchiectasis: A Beginner's 3-Step Guide on Managing Bronchiectasis Through Natural Methods and Diet, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanAinda não há avaliações
- Bronchiectasis Demystified: Doctor’s Secret GuideNo EverandBronchiectasis Demystified: Doctor’s Secret GuideAinda não há avaliações
- COPD Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing COPD Symptoms, With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanNo EverandCOPD Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing COPD Symptoms, With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanAinda não há avaliações
- A Practical Guide to Common Presenting Complaints in Primary CareNo EverandA Practical Guide to Common Presenting Complaints in Primary CareAinda não há avaliações
- Case Based Discussion 2-Adjustment Disorder Year 5 Rotation 5Documento26 páginasCase Based Discussion 2-Adjustment Disorder Year 5 Rotation 5Priya GKAinda não há avaliações
- Nama Kelompok: 1. Ahmad Kasyaf 2. Tio Rizki Kurniawan Kelas: Ix 1Documento9 páginasNama Kelompok: 1. Ahmad Kasyaf 2. Tio Rizki Kurniawan Kelas: Ix 1didy rachmanAinda não há avaliações
- Growth of World PopulationDocumento6 páginasGrowth of World Populationsally hakutangwiAinda não há avaliações
- ScabiesDocumento6 páginasScabiesJayson ShieldsAinda não há avaliações
- AnemiaDocumento10 páginasAnemiaRamesh VaradharajanAinda não há avaliações
- Day 1 General Objective:: CognitiveDocumento2 páginasDay 1 General Objective:: CognitiveReihann N. EdresAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacological Review of AnticoagulantsDocumento16 páginasPharmacological Review of AnticoagulantsDiplomski Seminarski RadoviAinda não há avaliações
- Plica PDFDocumento7 páginasPlica PDFIVAN VERGARAAinda não há avaliações
- تشخيص صعوبات تعلم الرياضيات عند تلاميذ السنة الرابعة متوسط (دراسة ميدانية بولاية سيدي بلعباس) .Documento26 páginasتشخيص صعوبات تعلم الرياضيات عند تلاميذ السنة الرابعة متوسط (دراسة ميدانية بولاية سيدي بلعباس) .mohamed abdelhafidh slimAinda não há avaliações
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDocumento3 páginasPre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasAinda não há avaliações
- Goal Attainment Scaling: Its Use in Evaluating Pediatric Therapy ProgramsDocumento22 páginasGoal Attainment Scaling: Its Use in Evaluating Pediatric Therapy ProgramsAna Corina LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Improving Breast Health Care For N.S. Women: M Y Min DSDocumento4 páginasImproving Breast Health Care For N.S. Women: M Y Min DSRyan DugganAinda não há avaliações
- Pe12 l03 180801065451Documento31 páginasPe12 l03 180801065451Joy TanaleonAinda não há avaliações
- Sigma-Alrich SDS (Year 2020)Documento9 páginasSigma-Alrich SDS (Year 2020)BigbearBigbearAinda não há avaliações
- Apollo Case AnalysisDocumento8 páginasApollo Case AnalysismuddanapAinda não há avaliações
- Health (Las) - Consumer HealthDocumento3 páginasHealth (Las) - Consumer HealthRainier DoctoleroAinda não há avaliações
- Super Top Up Health Plan IIMKAADocumento3 páginasSuper Top Up Health Plan IIMKAAcharankviAinda não há avaliações
- PKDocumento155 páginasPKonline TheldaAinda não há avaliações
- Women's Empowerment and Agenda For EmpowermentDocumento14 páginasWomen's Empowerment and Agenda For EmpowermentAnil Dhungana100% (1)
- Hepatic Hemangioma: CausesDocumento2 páginasHepatic Hemangioma: CausesEliza StanescuAinda não há avaliações
- Notes:: Sons Lives AwayDocumento4 páginasNotes:: Sons Lives Awaykuriakose mathewAinda não há avaliações
- DR Reddys Sustainability Summary Report 13 15Documento24 páginasDR Reddys Sustainability Summary Report 13 15Mridul SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Health Safety Report 2015 PDFDocumento51 páginasHealth Safety Report 2015 PDFPedro HenriquesAinda não há avaliações
- Anthroposophy Autoimmune - Diseases PDFDocumento30 páginasAnthroposophy Autoimmune - Diseases PDFpenfo100% (1)
- Kecelaruan 7 - Tidur 2019Documento27 páginasKecelaruan 7 - Tidur 2019YasHie PwincsZaAinda não há avaliações
- University of Waterloo - 2016 CIW National Report - How Are Canadians Really Doing?Documento96 páginasUniversity of Waterloo - 2016 CIW National Report - How Are Canadians Really Doing?RBeaudryCCLEAinda não há avaliações
- PTSD Research Paper-1Documento5 páginasPTSD Research Paper-1Foram PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition: Pregnancy AND Lactation: Enriquez R. Cayaban, RN, LPT, MANDocumento44 páginasNutrition: Pregnancy AND Lactation: Enriquez R. Cayaban, RN, LPT, MANCarl Josef C. GarciaAinda não há avaliações