Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CGIntroAndHardware 0c
Enviado por
sidra_yousuf_1Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CGIntroAndHardware 0c
Enviado por
sidra_yousuf_1Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Computer Graphics
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
Hardware
(Display Technologies and Devices) III
August 1, 2012
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
Display Devices and Technologies
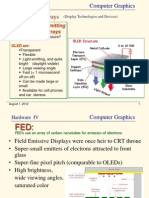
1. CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) 2. LCD , TFT LCD (Liquid Crystal Display, Thin Film Transistor LCD) 3. PLASMA 4. OLED (Organic Light-emitting Diode) 5. FED (Field Emissive Display) 6. SED (Surface-conduction Electron-emitter Display) 7. IMOD (Interferometric Modulator) 8. EL (Electroluminescent display) 9. Electronic Paper 10.Surface Technology 11.Wall Displays 12.Holographic Displays 13.3D Displays With and Without Glasses 14.No-Touch Displays (hand movements)
August 1, 2012
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
Basics of LCD Display
August 1, 2012
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
LCD Display
August 1, 2012
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
LCD Display & TFT Technology
A TFT monitor uses thin-film transistor technology for the ultimate LCD display. The benefit of a TFT monitor is a separate, tiny transistor for each pixel on the display. Because each transistor is so small, the amount of charge needed to control it is also small. This allows for very fast re-drawing of the display, as the image is re-painted or refreshed several times per second.
August 1, 2012
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
Pros & Cons
Drawbacks of LCD Display
Narrow viewing angle Fragile Fixed resolution and aspect ratio. Longer response time Lower contrast Cost is high Less power consumption Small weight Less glare no flicker and bright Images not distorted
Advantages of LCD:
August 1, 2012
Hardware III Plasma Display
Computer Graphics
Gas Plasma Discharge Principle
August 1, 2012
Hardware III Plasma Display
Inside the Display: Gas and Electrodes The xenon and neon gas in a plasma display is contained in hundreds of thousands of tiny cells positioned between two plates of glass. Long electrodes are also sandwiched between the glass plates, on both sides of the cells. The address electrodes sit behind the cells, along the rear glass plate.
Computer Graphics
August 1, 2012
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
The transparent display electrodes, which are surrounded by an insulating dielectric material and covered by a magnesium oxide protective layer, are mounted above the cell, along the front glass plate. Both sets of electrodes extend across the entire screen. The display electrodes are arranged in horizontal rows along the screen and the address electrodes are arranged in vertical columns. As you can see in the diagram below, the vertical and horizontal electrodes form a basic grid. To ionize the gas in a particular cell, the plasma display's computer charges the electrodes that intersect at that cell. It does this thousands of times in a small fraction of a second, charging each cell in turn. When the intersecting electrodes are charged (with a voltage difference between them), an electric current flows through the gas in the cell. As we saw in the last section, the current creates a rapid flow of charged particles, which stimulates the gas atoms to release ultraviolet photons.
August 1, 2012
10
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
Plasma Display
August 1, 2012
11
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
Phosphors: ZnS:Ag, Y3Al5O12:Ce, and Y2SiO5:Ce. ZnO, Cd:ZnS, Y2O2S:Eu The released ultraviolet photons interact with phosphor material coated on the inside wall of the cell. Phosphors are substances that give off light when they are exposed to other light. When an ultraviolet photon hits a phosphor atom in the cell, one of the phosphor's electrons jumps to a higher energy level and the atom heats up. When the electron falls back to its normal level, it releases energy in the form of a visible light photon. The phosphors in a plasma display give off colored light when they are excited. Every pixel is made up of three separate subpixel cells, each with different colored phosphors. One subpixel has a red light phosphor, one subpixel has a green light phosphor and one subpixel has a blue light phosphor. These colors blend together to create the overall color of the pixel. By varying the pulses of current flowing through the different cells, the control system can increase or decrease the intensity of each subpixel color to create hundreds of different combinations of red, green and blue. In this way, the control system can produce colors across the entire spectrum.
August 1, 2012 12
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
Pros & Cons
Drawbacks of Plasma:
Phosphor burn-in (overdrive) Power consumption and heat dissipation Pixel pitch is coarse (.8mm - 1 mm)
Advantages of Plasma:
Wider viewing angles (160 degrees H&V) Saturated colors, lower gray levels Faster video switch times (full motion 60 Hz)
August 1, 2012
13
Hardware III
Computer Graphics
End
Hardware III
August 1, 2012
14
Você também pode gostar
- Computer Graphics: Prof. Muhammad SaeedDocumento16 páginasComputer Graphics: Prof. Muhammad Saeedsidra_yousuf_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- Curves EquationsDocumento6 páginasCurves Equationssidra_yousuf_1Ainda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- CGIntroAndHardware 0dDocumento16 páginasCGIntroAndHardware 0dsidra_yousuf_1Ainda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- ERD ExamplesDocumento8 páginasERD Examplesdesairakesh100% (2)
- An SEO-Optimized Title for a Document on Database ConceptsDocumento37 páginasAn SEO-Optimized Title for a Document on Database Conceptssidra_yousuf_1Ainda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Computer Graphics: Prof. Muhammad SaeedDocumento12 páginasComputer Graphics: Prof. Muhammad Saeedsidra_yousuf_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Solution stoichiometry calculations tutorialDocumento6 páginasSolution stoichiometry calculations tutorialJayakumar SankaranAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Water Permeability of Concrete and Its Relationship With StrengthDocumento9 páginasThe Water Permeability of Concrete and Its Relationship With StrengthReny AkmaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Moldex3D R14 FEA Interface IntroductionDocumento46 páginasMoldex3D R14 FEA Interface IntroductionmadhukeshwartAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- EfkaPB2720 TDSDocumento2 páginasEfkaPB2720 TDSSebastian GonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Non Linear PharmacokineticsDocumento64 páginasNon Linear PharmacokineticsMoganaa LakshmiAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Practical List BOP 353PDocumento2 páginasPractical List BOP 353Pved.g007Ainda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Test Bank For Anatomy and Physiology 1st Edition Michael MckinleyDocumento37 páginasTest Bank For Anatomy and Physiology 1st Edition Michael Mckinleyreidelsebirew100% (12)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- T1 1 E Automotive 072Documento15 páginasT1 1 E Automotive 072Marian OstrowskiAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Absorption of Carbon Dioxide Into Aqueous Blends of Diethanolamine and MethyldiethanolamineDocumento11 páginasAbsorption of Carbon Dioxide Into Aqueous Blends of Diethanolamine and MethyldiethanolamineAnkit KumarAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Waterproofing 2022Documento8 páginasWaterproofing 2022VR RajAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- Estimating Crystallite Size Using XRDDocumento105 páginasEstimating Crystallite Size Using XRDKrizelle Ann HugoAinda não há avaliações
- EMW Filtertechnik - GT (GB)Documento9 páginasEMW Filtertechnik - GT (GB)Nguyễn Kim HùngAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 BSC Intermediate (Yr9-Yr10) Paper With AnswersDocumento18 páginas2016 BSC Intermediate (Yr9-Yr10) Paper With AnswerskirtiAinda não há avaliações
- 2020-Microbial Nanotechnology For Bioremediation of Industrial WastewaterDocumento8 páginas2020-Microbial Nanotechnology For Bioremediation of Industrial WastewaterAmin ZamaniAinda não há avaliações
- Elastomer PropertiesDocumento72 páginasElastomer PropertiesBashu PoudelAinda não há avaliações
- Initial Results On Electron Beam Generation Using Pyroelectric CrystalsDocumento3 páginasInitial Results On Electron Beam Generation Using Pyroelectric CrystalsParticle Beam Physics LabAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- DPP 25C Goc Mesomeric 1686185793412Documento3 páginasDPP 25C Goc Mesomeric 1686185793412Aditya KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Org. Chem. (Chapter 8)Documento25 páginasOrg. Chem. (Chapter 8)Jia LinAinda não há avaliações
- Adsorption, Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism, and Computational Studies of Aza Indica For Mild SteelDocumento16 páginasAdsorption, Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism, and Computational Studies of Aza Indica For Mild Steeldanish.hakeem251Ainda não há avaliações
- Handbook of DetergentsDocumento13 páginasHandbook of DetergentsEmilyAinda não há avaliações
- Rankine & Carnot Cycle - Power Plant Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocumento4 páginasRankine & Carnot Cycle - Power Plant Questions and Answers - SanfoundryShubhendra YadavAinda não há avaliações
- B. Tech. - I (All Branches) ASP102ABC (T) : Engineering Physics (Theory) L T P C 3 0 2 4Documento2 páginasB. Tech. - I (All Branches) ASP102ABC (T) : Engineering Physics (Theory) L T P C 3 0 2 4Harikrishna ShenoyAinda não há avaliações
- Ellamera Formulation Guide - Dec 2022 UpdatedDocumento31 páginasEllamera Formulation Guide - Dec 2022 UpdatedMarvin Dias Santos100% (1)
- Thermodynamic Fundamentals of Refrigeration, Cryogenics and Low Temperature Physics Problems For ColloquiumDocumento27 páginasThermodynamic Fundamentals of Refrigeration, Cryogenics and Low Temperature Physics Problems For ColloquiumPawel WAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Chromatography and Its Applications PDFDocumento234 páginasChromatography and Its Applications PDFmeriemAinda não há avaliações
- Nigsch 2006 Melting Point Prediction EmployingDocumento11 páginasNigsch 2006 Melting Point Prediction EmployingEthan MananiAinda não há avaliações
- PV ParaffinDocumento40 páginasPV ParaffinAbi DesonAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento3 páginasAssignment 1Yeleti FamilyAinda não há avaliações
- Structure Determination:: Proton 1.00728 U Neutron 1.00866 U Electron 0.00055 UDocumento12 páginasStructure Determination:: Proton 1.00728 U Neutron 1.00866 U Electron 0.00055 Ufouad elferdiAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical Method Development and Validation For The Test Related Substances of Pomalidomide in Pomalidomide CapsulesDocumento8 páginasAnalytical Method Development and Validation For The Test Related Substances of Pomalidomide in Pomalidomide CapsulesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações