Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Drug Study
Enviado por
Felecidario TaerDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Drug Study
Enviado por
Felecidario TaerDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
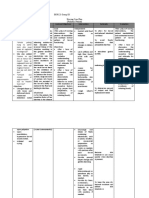
DRUG STUDY
DRUGS NAME: Bisacodyl (Bisacodyl)
Dose / Frequency : I tab po @hs x 2 doses
Classification Mechanism of Action
Stimulant laxative that increases peristalsis, probably by direct effect on smooth muscle of the intestine, by irritating the muscle or stimulating the colonic intramural plexus. Drug also promotes fluid accumulation in colon and small intestine.
Indication
ContraIndications
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug or its components and in those with rectal bleeding, gastroenteritis, intestinal obstruction, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, orother symptoms of appendicitis or acute surgical abdomen.
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
Dizziness, abdominal cramps, vomiting, diarrhea, alkalosis,tetany
Laxatives
preparation for surgery
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. Give drug at times that dont interfere with scheduled activities or sleep. Soft, formed stools are usually produced 15 to 60 minutes after rectal use. 2. Before giving for constipation, determine whether patient has adequate fluid intake, exercise and diet. 3. Advise patient to swallow enteric-coated tablet whole to avoid GI irritation. Instruct him not to take within1 hour of milk or antacid. 4. Advise patient to report adverse effects to prescriber. 5. Tables and suppositories are used together to clean the colon before and after surgery and before barium enema.
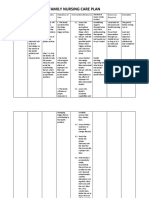
DRUGS NAME:Metronidazole (Metronidazole)
Dose / Frequency : 1 cap 500mg BID
Classification Mechanism of Action
Undergoes intracellular chemical reduction during anaerobic metabolism. After metronidazole is reduced, it damages DNAs helical structure and breaks its strands, which inhibits bacterial nucleic acid synthesis and causes cell death
Indication
Trichomoniasis, Refractory trichomoniasis, Pelvic inflammatory disease, Bacterial Vaginosis
ContraIndications
Breast-feeding, hypersensitivity to metronidazole or its components
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
CNS: headache, seizures, fever, vertigo, dizziness, confusion, irritability, depression, weakness, insomnia CV: edema, flushing EENT: rhinitis, sinusitis GI: nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping or pain, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth GU: darkened urine, vaginitis, polyuria, dysuria, cystitis, dryness of vagina and vulva, genital puritus Musculoskeletal: transient joint pain Respiratory: upper respiratory tract infection Skin: rash
Antibiotic, Amebicide, Antiprotozoal
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. If pt has adverse CNS reactions, such as seizures or peripheral neuropathy, tell prescriber and stop drug immediately. 2. Monitor pt with severe liver disease because slowed metronidazole metabolism may cause drug to accumulate in the body and increase the risk of adverse effects. 3. If skin irritation occurs, apply topical gel less frequently or discontinue it, as ordered. 4. Monitor CBC and culture and sensitivity test if therapy lasts longer than10 days or if second course of treatment is needed. 5. Caution patient to avoid alcohol while being treated with vaginal preparation.
DRUGS NAME: Conjugated estrogen (Premarin)
Dose / Frequency : 0.625 mg 4 tabs TID
Classification Mechanism of Action
Increases synthesis of DNA, RNA, and protein in responsive tissues, also reduces release of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones from the pituitary gland
Indication
Vulvar or vaginal atrophy, Abnormal uterine bleeding (hormonal imbalance).
ContraIndications
Contraindicated in pregnant patients and in patients with thrombophlebitis, thromboembolic disorders, estrogendependent neoplasia, breast or reproductive cancer (except for palliative treatment), or undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding.
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
CNS: dizziness, headache, stroke and seizure CV: edema, pulmonary embolism, MI GI: dyspepsia, GI pain, nausea, constipation or diarrhea, flatulence, peptic ulceration and vomiting GU: renal failure Hematologic: decreased platelet adhesion, prolonged bleeding time Skin: diaphoresis, prurotus, rash GI: nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, bloating, increased appetite EENT: worsening myopia or astigmatism GU: breakthrough bleeding, amenorrhea, altered cervical secretion Hepatic: cholestatis jaundice Skin: melasma, chloasma, hairloss, dermatitis Metabolic: weight changes, hypercalcemia Other: breast tenderness changes in libido
Estrogen
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. Periodically monitor lipid levels, blood pressure, body weight, and hepatic function. 2. Glucose tolerance may be impaired. Monitor glucose level closely in patients with diabetes. 3. If pt has adverse CNS reactions tell prescriber and stop drug immediately. 4. Tell diabetic patient to report elevated glucose level so that antidiabetic dosage can be adjusted. 5. Encourage patient to stop smoking because of the risk of CV complications
DRUGS NAME: Zinnat (Cefuroxime Sodium)
Dose / Frequency : 500 mg I tab BID (D4)
Classificatio n Mechanism of Action
Secondgeneration cephalosporins that inhibitscellwall synthesis, promoting osmotic instability; usually bactericidal.
Indication
Treatment of infections caused by sensitive bacteria
ContraIndications
Sensitivity to cephalosporins and related antibiotics; pregnancy (category B), lactation.
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
CV: phlebitis, thrombophlebitis GI: diarrhea, nausea, anorexia, vomiting Hematologic: hemolytic anemia Skin: maculopapular and erythematous rashes, urticaria, pain, induration, sterile abscesses, temperature elevation Other: hypersensitivity reaction, serum reaction
Cephalos porins
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. Monitor patient for signs symptoms of superinfection. 2. Determine history of hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins, and history of allergies, particularly to drugs, before therapy is initiated. 3. Report onset of loose stools or diarrhea. Although pseudomembranous colitis. 4. Monitor I&O rates and pattern: Especially important in severely ill patients receiving high doses. Report any significant changes. 5. Tell patient to take drug as prescribed, even after he or she feels better.
DRUGS NAME: Adalat GITS (Nifedipine)
Dose / Frequency : 30 mg 1 tab OD
Classification
Calcium channel blocker
Mechanism of Action
Thought to inhibit calcium ion influx across cardiac and smooth-muscle cells, decreasing contractility and oxygen demand. Also may dilate coronary arteries and arteriole.
Indication
Hypertension
ContraIndications
Contraindicated in patients with bronchial asthma, sinus bradycardia and greater than first-degree heart block, cardiogenic shock, and overt heart failure.
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
CNS: dizziness, light headedness, headache, weakness, syncope, nervousness CV: flushing peripheral, edema, heart failure, MI, hypotension, palpitations EENT: nasal congestion GI: nausea, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal discomfort Musculoskeletal: muscle cramps Respiratory: dyspnea, pulmonary edema, cough Skin: rash, pruritus
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. Monitor Blood pressure and heart rate regularly, especially in patients who take beta-blockers or antihypertensives. 2. Watch for symptoms of heart failure. 3. Monitor blood sugar in diabetic patients. Nifedipine has diabetogenic properties. 4. Encourage patient to stop smoking while taking the nifedipine. 5. Observe 10 rights in giving the drugs.
DRUGS NAME: BP norm (Fosinopril Sodium)
Dose / Frequency : 10 mg tab OD
Classificatio n
ACE inhibitor, Antihperten sives
Mechanism of Action
May inhibit ACE, preventing conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. Less angiotensin II decreases peripheral arterial resistance, thus decreasing aldosterone secretion, which reduces sodium and water retention and lowers blood pressure.
Indication
Hypertensio n and Heart failure
ContraIndications
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug or other ACE inhibors and in breastfeeding women.
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
CNS: dizziness, stroke, headache fatigue, paresthesia, sleep disturbance CV: MI, chest pain, angina pectoris, rhythm disturbance, palpitations, hypotension, orthostatic hypotension EENT: tinnitus, sinusitis GI: pancreatitis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dry mouth, abdominal distention and pain, constipation GU: sexual dysfunction, renal insufficiency, hepatitis Metabolic: Hypercalemia Musculoskeletal: musculoskeletal pain Respiratory: dry, persistent, tickling, non-productive cough, bronchospasm Skin: Urticaria, rash, photosensitivity reactions, pruritus Other: angioedema, decrease libido, gout
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. Monitor Blood Pressure for drug effects. 2. Monitor Potassium intake and potassium level. Diabetic patients, those with impaired renal function, and those receiving drugs that can increase potassium level may develop hyperkalemia. 3. Assess renal and hepatic function before and periodically throughout therapy. 4. Tell patient to avoid salt substitutes; these products may contain potation, which can cause high potassium level in patients taking drug. 5. Instruct patient to call prescriber if he develops easy bruising or bleeding; swelling of tongue, lips, face, eyes, mucous membranes, arms, or legs; difficulty swallowing or breathing; and hoarseness.
DRUGS NAME: Lipitor (Atorvastatin calcium)
Dose / Frequency : 80 mg tab OD pc dinner
Classification
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, Antilipemics
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits HMGCoA reductase, and early(ratelimiting) step in cholesterol biosynthesis.
Indication
In patients with clinically evident coronary heart disease, to reduce the risk of nonfatal MI, fatal and nonfatal strokes, angina, heart failure, and revascularization procedures. To reduce the risk of MI, stroke, angina, or revascularization procedures in patient with multiple risk factors for CAD but who dont yet have the disease.
ContraIndications
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and in those with active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations of transaminase levels. Contraindicated in pregnant and breastfeeding women and in women of childbearing age.
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
CNS: headache, asthenia, insomnia CV: peripheral edema EENT: Pharyngitis, Rhinitis, Sinusitis GI: Abdominal Pain, Constipation, Diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, nausea GU: UTI
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. Patient should follow a standard cholesterol-lowering diet before and during therapy. 2. Before treatment, assess patient for underlying causes for hypercholesterolemia and obtain a baseline lipid profile. Obtain periodic liver function test result and lipid levels before starting treatment and at 6 and 12 weeks after initiation, of after an increase in dosage and periodically thereafter. 3. Drug may be given as a single dose at any time of day, with or without food. 4. Advise patient to inform prescriber of adverse reactions, such as muscle pain, malaise, and fever. 5. Warn patient to avoid alcohol.
DRUGS NAME: Iterax (Hydroxyzine diHCL)
Dose / Frequency : 25 mg I tab P.O
Classification
Piperazine derivative
Mechanism of Action
A piperazine antihistamine whose action may result from suppression of activity in certain essential regions of the subcortical area of the CNS.
Indication
Anxiety, Preoperative and Postoperative adjunctive therapy for sedation, pruritus, Psychiatric and emotional emergencies, including acute alcoholism, nausea and vomiting (excluding nausea and vomiting of pregnancy), Antepartum and post partum adjunctive therapy.
ContraIndications
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug, Early pregnancy; hypersensitivity to hydroxyzine or cetirizine and breast feeding women.
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
CNS: drowsiness, involuntary motor activity GI: dry mouth, constipation SKIN: Pain at I.M. injection site OTHER: Hypersensitivity reactions
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. If patient takes other CNS drugs, watch for oversedation. 2. Elderly patient maybe more sensitive to adverse anticholinergic effects; monitor these patients for dizziness, excessive sedation, confusion, hypotension, and syncope. 3. Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require alertness and good coordination until effects of drug are known. 4. Tell patient to avoid alcohol while taking drug. 5. Warn woman of childbearing age to avoid use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
DRUGS NAME: Dormicum (midazolam hydrochloride)
Classification
Mechanism of Action
May potentiate the effects of GABA, depress the CNS, and suppress the spread of seizure activity.
Indication
Sedation in Premed before surgical or diagnostic procedures, induction and maintenance of anesthesia.
ContraIndications
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and in those with acute angle-closure glaucoma, shock, coma, or acute alcohol intoxication.
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
Nausea, vomiting,headache, hiccoughs, laryngospasm, dyspnea hallucination, drowsiness, amnesic episode.
Benzodiaze pine
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. Have oxygen and resuscitation equipment available in case of severe respiratory depression. 2. Monitor blood pressure, heart rate and rhythm, respirations, airway integrity, and arterial oxygen saturation during procedure. 3. Use cautiously in patients with uncompensated acute illness and in elderly or debilitated patients. 4. Because drug diminishes patients recall of events around the time of surgery, provide written information, family member instructions, and follow-up contact. 5. Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require alertness of good coordination until effects of drug are known.
DRUGS NAME: Ketamine (Ketamine HCl) Dose / Frequency : 1 ml
Classification
Dissociative anesthetic, hallucinogen, psychotomim etic
Mechanism of Action
Ketamine has been shown to block afferent impulses associated with the affectiveemotional component of pain perception within the medical medullary reticular formation, to suppress spinal cord activity, and to interact with several central nervous system (CNS) transmitter systems. Ketamine blocks the NMDA glutamate receptor by a dual mechanism, blocking both the closed channel from the aqueous phase and the closed channel from the membrane phase.
Indication
Anesthetic agent for diagnostic and surgical procedures that do not require skeletal muscle relaxation.
ContraIndications
Patients in whom significant BP elevation would be a serious hazard; hypersensitivity to the drug.
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
Blurred vision, confusion, drowsiness, increased or decreased blood pressure or heart rate Mental status changes, nausea, vomiting
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. Monitor circulatory and respiratory status 2. Assess the blood pressure of the patient before the administration. 3. Theophylline should not be coadministered with ketamine, it may interact and can cause unpredictable seizure. 4. Because of rapid induction following the initial IV injection, the patient should be in a supported position during administration. 5. Rapid administration may result in respiratory depression and enhanced pressor response.
DRUGS NAME: Cefuroxime Sodium (Zegen) Dose / Frequency : 1 ml
Classification
Secondgeneration cephalosporin
Mechanism of Action
Ketamine has been shown to block afferent impulses associated with the affectiveemotional component of pain perception within the medical medullary reticular formation, to suppress spinal cord activity, and to interact with several central nervous system (CNS) transmitter systems. Ketamine blocks the NMDA glutamate receptor by a dual mechanism, blocking both the closed channel from the aqueous phase and the closed channel from the membrane phase.
Indication
Anesthetic agent for diagnostic and surgical procedures that do not require skeletal muscle relaxation.
ContraIndications
Patients in whom significant BP elevation would be a serious hazard; hypersensitivity to the drug.
Side Effects/ Toxic Effect
Blurred vision, confusion, drowsiness, increased or decreased blood pressure or heart rate Mental status changes, nausea, vomiting
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: 1. Monitor circulatory and respiratory status 2. Assess the blood pressure of the patient before the administration. 3. Theophylline should not be coadministered with ketamine, it may interact and can cause unpredictable seizure. 4. Because of rapid induction following the initial IV injection, the patient should be in a supported position during administration. 5. Rapid administration may result in respiratory depression and enhanced pressor response.
Você também pode gostar
- Consenso Brasileiro Sculptra CorporalDocumento7 páginasConsenso Brasileiro Sculptra CorporalAndré Mauricio Freire Pires100% (1)
- Daily Management Plan - 1Documento2 páginasDaily Management Plan - 1Felecidario Taer0% (1)
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocumento3 páginasCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementNathanielle Keith PENASOAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Catapres. Losartan, Nootropil Cefuroxime, ArcoxiaDocumento2 páginasDrug Study Catapres. Losartan, Nootropil Cefuroxime, Arcoxiajoy_monterubioAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento15 páginasDrug StudyMarc AnchetaAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs and NCPDocumento4 páginasDrugs and NCPApril Anne CostalesAinda não há avaliações
- Tetanus Toxoid Vaccine Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 páginasTetanus Toxoid Vaccine Nursing Care PlanDwight DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Demographic Profile, Bubbleshe, Discharge Planning Methods Edited... Wala Pa Yung NCP KODocumento6 páginasDemographic Profile, Bubbleshe, Discharge Planning Methods Edited... Wala Pa Yung NCP KONicoh AvilaAinda não há avaliações
- Post-Partum CareDocumento4 páginasPost-Partum CarejoethemangoAinda não há avaliações
- of ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALISDocumento12 páginasof ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALISMaricel Agcaoili GallatoAinda não há avaliações
- Kawasaki DiseaseDocumento7 páginasKawasaki DiseaseRitamariaAinda não há avaliações
- College of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinDocumento4 páginasCollege of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinAnika PleñosAinda não há avaliações
- Cho Chon FatsDocumento26 páginasCho Chon FatsKit LaraAinda não há avaliações
- Family Coping Index..Documento3 páginasFamily Coping Index..Lharra Cagulada-PostranoAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cue: Sto: StoDocumento8 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cue: Sto: Stoluisa bautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessing The IntegumentaryDocumento73 páginasAssessing The IntegumentaryHelena Meurial HilkiahAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study On DigoxinDocumento8 páginasDrug Study On DigoxinDonald BidenAinda não há avaliações
- Involving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialDocumento10 páginasInvolving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialAngel MayAinda não há avaliações
- CC Chua, Prince Robert C. Reflection Paper 4ADocumento1 páginaCC Chua, Prince Robert C. Reflection Paper 4APrince Robert ChuaAinda não há avaliações
- Physical exam and review of systemsDocumento3 páginasPhysical exam and review of systemsBianx Flores DosdosAinda não há avaliações
- Self-Care Deficit Related To Inability To Perceive Body Part (Bathing)Documento2 páginasSelf-Care Deficit Related To Inability To Perceive Body Part (Bathing)lilpeabea100% (1)
- Case Presentation Hypokalemic ManDocumento61 páginasCase Presentation Hypokalemic ManHussain AzharAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Acute PainDocumento3 páginasNCP Acute PainSian Grace AsadaAinda não há avaliações
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationDocumento2 páginasBrand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationChristine Pialan SalimbagatAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento14 páginasDrug StudyRaff GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- 11 NCP Pressure UlcerDocumento6 páginas11 NCP Pressure UlcerICa MarlinaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 32: Nursing Care of A Family With A School-Aged ChildDocumento10 páginasChapter 32: Nursing Care of A Family With A School-Aged ChildJordan GougerAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Domperidone CompressDocumento1 páginaDrug Study Domperidone CompressAngelica TolledoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study MetoprololDocumento2 páginasDrug Study MetoprololHannah Angelu CabadingAinda não há avaliações
- Javier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Documento7 páginasJavier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Julie AnnAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento11 páginasDrug StudyNedemar OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Zoloft (Sertraline)Documento1 páginaZoloft (Sertraline)Adrianne BazoAinda não há avaliações
- Prio, FNCP, HTPDocumento11 páginasPrio, FNCP, HTPEmerick DomingoAinda não há avaliações
- FNCP Form Health Deficit AsthmaDocumento3 páginasFNCP Form Health Deficit Asthmakappa100% (1)
- Diabetes Insipidus HandoutDocumento4 páginasDiabetes Insipidus HandoutllianAinda não há avaliações
- Guide in Making The FCA 1Documento18 páginasGuide in Making The FCA 1Zedrake CaraanAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plans for Fever, Rashes & Knowledge DeficitDocumento10 páginasNursing Care Plans for Fever, Rashes & Knowledge DeficitRobin HaliliAinda não há avaliações
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Documento3 páginasZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- Intake & Output Monitoring Sheet: 11 PM 11-7 1000 ML 0 550 ML 0 0Documento2 páginasIntake & Output Monitoring Sheet: 11 PM 11-7 1000 ML 0 550 ML 0 0Renea Joy ArruejoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento9 páginasDrug StudyCris SolisAinda não há avaliações
- CroupDocumento10 páginasCroupEl Justinson Puspos100% (1)
- Handout # 10Documento22 páginasHandout # 10Ram August100% (1)
- Duphaston PDFDocumento4 páginasDuphaston PDFmarcusjanaAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento4 páginasNCPShella CondezAinda não há avaliações
- NCP1 - EpisiotomyDocumento2 páginasNCP1 - EpisiotomyCarmel Joy DifuntorumAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDrug StudyCharlyn Mae BirondoAinda não há avaliações
- Filipino Culture, Values, and Practices in Relation To Difficult Childbearing and ChildrearingDocumento8 páginasFilipino Culture, Values, and Practices in Relation To Difficult Childbearing and ChildrearingRheeanne AmilasanAinda não há avaliações
- OMEPRAZOLEDocumento2 páginasOMEPRAZOLEJenny Pearl PasalAinda não há avaliações
- Mfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasMfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Myasthenia Gravis Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Myasthenia Gravis Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle AcenaAinda não há avaliações
- DrugDocumento3 páginasDrugPeace Andong PerochoAinda não há avaliações
- Celecoxib CelebrexDocumento1 páginaCelecoxib CelebrexBeverly Ann de LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Rectal and Vaginal Suppository Insertion GuideDocumento2 páginasRectal and Vaginal Suppository Insertion GuideMariah Jane TaladuaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasDrug StudyMiru มิริวAinda não há avaliações
- Amoxicillin Drug Study: Mechanism, Uses, Side Effects, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento10 páginasAmoxicillin Drug Study: Mechanism, Uses, Side Effects, and Nursing Responsibilitieskierjohn237343Ainda não há avaliações
- Folic Acid Benefits, Uses, Side EffectsDocumento3 páginasFolic Acid Benefits, Uses, Side EffectsDadybooboo2013Ainda não há avaliações
- EvistaDocumento18 páginasEvistaBrankoPopovićAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Interventions CHFDocumento3 páginasNursing Interventions CHFbanyenye25100% (1)
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocumento11 páginasName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz On Pediatric NursingDocumento3 páginasQuiz On Pediatric NursingFelecidario TaerAinda não há avaliações
- Daily Recording of Activities - 1Documento2 páginasDaily Recording of Activities - 1Felecidario TaerAinda não há avaliações
- SyllabusDocumento3 páginasSyllabusFelecidario Taer0% (1)
- Gram Book Guidance For The Rational Use of AntimicrobialsDocumento281 páginasGram Book Guidance For The Rational Use of AntimicrobialsPetrisor GheorghiuAinda não há avaliações
- Pokok 10.1Documento96 páginasPokok 10.1Apotek PinkAinda não há avaliações
- Dental Disease in Pet Rabbits 3 Jaw AbscessesDocumento11 páginasDental Disease in Pet Rabbits 3 Jaw AbscessesBrvo CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Pregnancy With EpilepsyDocumento40 páginasPregnancy With EpilepsyNaman MishraAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0735109710023739 MainDocumento36 páginas1 s2.0 S0735109710023739 MainsinamirjaniAinda não há avaliações
- Assessing Vital Signs and Poisoning SymptomsDocumento76 páginasAssessing Vital Signs and Poisoning SymptomsmasorAinda não há avaliações
- No. Kode Barang Nama Barang Exp. Date StockDocumento12 páginasNo. Kode Barang Nama Barang Exp. Date StocknafilaAinda não há avaliações
- Operan Rawat InapDocumento2 páginasOperan Rawat InapFarmasi Primaya HospitalAinda não há avaliações
- Approved Egyptian Drug IndexDocumento1.702 páginasApproved Egyptian Drug IndexMahmoud SamiAinda não há avaliações
- Targeted Temperature Management in Brain Injured  Patients PDFDocumento23 páginasTargeted Temperature Management in Brain Injured  Patients PDFCamilo Benavides BurbanoAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture-9 CLNP 221 Pharmacy OrganisationDocumento28 páginasLecture-9 CLNP 221 Pharmacy OrganisationalshmryalmwydAinda não há avaliações
- Acitretin Use in DermatologyDocumento11 páginasAcitretin Use in DermatologyBryan NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study PharmacologyDocumento3 páginasDrug Study PharmacologyZyrene RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- Treatment Approach To Patients With Severe Insulin ResistanceDocumento8 páginasTreatment Approach To Patients With Severe Insulin ResistanceAlan Jacobo MorenoAinda não há avaliações
- Manage hypertension with LisinoprilDocumento2 páginasManage hypertension with LisinoprilKristinelou Marie Reyna100% (1)
- (25599283 - Journal of Psychedelic Studies) Long-Lasting Analgesic Effect of The Psychedelic Drug Changa - A Case ReportDocumento7 páginas(25599283 - Journal of Psychedelic Studies) Long-Lasting Analgesic Effect of The Psychedelic Drug Changa - A Case ReportMariaAinda não há avaliações
- Propylthiouracil Drug StudyDocumento7 páginasPropylthiouracil Drug StudyAlexandrea MayAinda não há avaliações
- 415 1689 1 PB PDFDocumento2 páginas415 1689 1 PB PDFChandula SuriyapperumaAinda não há avaliações
- DR Rajesh MujariyaDocumento22 páginasDR Rajesh MujariyaRajesh MujariyaAinda não há avaliações
- Suppositories: An Underutilized Dosage Form: Is There A Difference Between Oral and Rectal Absorption?Documento5 páginasSuppositories: An Underutilized Dosage Form: Is There A Difference Between Oral and Rectal Absorption?HellcroZAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Pain Readings and Learning AimsDocumento2 páginasChronic Pain Readings and Learning AimskadyAinda não há avaliações
- Fucoxanthin From Phaeodactylum Tricornutum NanoencapsulationDocumento22 páginasFucoxanthin From Phaeodactylum Tricornutum NanoencapsulationalmaliagustiningrumAinda não há avaliações
- Formularium Obat RSDocumento2 páginasFormularium Obat RSMyzard AriefAinda não há avaliações
- Letters To The Editor: Mania Induced by High Content Caffeinated Energy DrinksDocumento8 páginasLetters To The Editor: Mania Induced by High Content Caffeinated Energy DrinksDan PutraAinda não há avaliações
- Development of Baccharis Dracunculifolia (Asteraceae) Essential Oil Nanoemulsion and Its Biological Activity On Pre-Pupae of Cochliomyia Hominivorax (Diptera: Calliphoridae)Documento16 páginasDevelopment of Baccharis Dracunculifolia (Asteraceae) Essential Oil Nanoemulsion and Its Biological Activity On Pre-Pupae of Cochliomyia Hominivorax (Diptera: Calliphoridae)Sabrina JonesAinda não há avaliações
- Asthma MBBS Jackson 2022Documento80 páginasAsthma MBBS Jackson 2022Morgan BaileyAinda não há avaliações
- 1 - Introduction To Drug Development For 2022 Lecture1Documento14 páginas1 - Introduction To Drug Development For 2022 Lecture1addisu afrassaAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple SclerosisDocumento45 páginasMultiple Sclerosispriyanka bhowmikAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs For Anxiety P Colg RP 3Documento48 páginasDrugs For Anxiety P Colg RP 3Theola FrancescaAinda não há avaliações