Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Op Amp Differentiator
Enviado por
Muhammad HaroonDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Op Amp Differentiator
Enviado por
Muhammad HaroonDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
M-HAROON 4432 Bsc-ELE(4th semester)
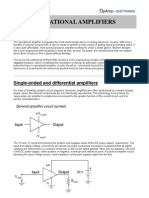
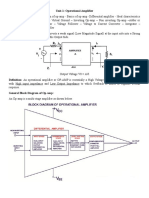
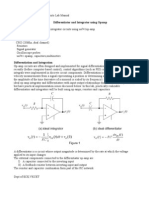
The basic Op-amp Differentiator circuit is the exact opposite to that of the integrator operational amplifier circuit. Here, the position of the capacitor and resistor have been reversed now the reactance, Xc is connected to the input terminal of the inverting amplifier The resistor, Rf forms the negative feedback element across the operational amplifier as normal This circuit performs the mathematical operation of Differentiation, that is it "produces a voltage output which is directly proportional to the input voltage's rate-of-change with respect to time".
The capacitor only allows AC type input voltage changes to pass through and whose frequency is dependant on the rate of change of the input signal At low frequencies the reactance of the capacitor is "High" resulting in a low gain (Rf/Xc) and low output voltage from the op-amp. At higher frequencies the reactance of the capacitor is much lower resulting in a higher gain and higher output voltage from the differentiator amplifier
At high frequencies an op-amp differentiator circuit becomes unstable and will start to oscillate. This is mainly due to the first-order effect, which determines the frequency response of the op-amp circuit causing a second-order response which, at high frequencies gives an output voltage far higher than what would be expected. To avoid this the high frequency gain of the circuit needs to be reduced by adding an additional small value capacitor across the feedback resistor Rf.
Relation for Vout
Therefore, the output voltage Vout is a constant-Rf.C times the derivative of the input voltage Vin with respect to time. The minus sign indicates a 180 degree phase shift because the input signal is connected to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier.
Disadvantages of differentiator circuit
The Op-amp Differentiator circuit in its basic form has two main disadvantages 1. One is that it suffers from instability at high frequencies 2. The capacitive input makes it very susceptible to random noise signals and any noise or harmonics present in the source circuit will be amplified more than the input signal itself This is because the output is proportional to the slope of the input voltage so some means of limiting the bandwidth in order to achieve closed-loop stability is required.
Op-amp Differentiator Waveforms
Improved Op-amp Differentiator Amplifier Circuit
Adding the input resistor Rin limits the differentiators increase in gain at a ratio of Rf/Rin. The circuit now acts like a differentiator amplifier at low frequencies and an amplifier with resistive feedback at high frequencies giving much better noise rejection. Additional attenuation of higher frequencies is accomplished by connecting a capacitor Cf in parallel with the differentiator feedback resistor, Rf. This then forms the basis of a Active high pass filter.
END
Thank You
Você também pode gostar
- Low Pass Filter 1st OrderDocumento7 páginasLow Pass Filter 1st OrdervlsijpAinda não há avaliações
- OpampDocumento12 páginasOpampSayyed SalmanAinda não há avaliações
- Operational AmplifiersDocumento49 páginasOperational AmplifiersKostas TressosAinda não há avaliações
- Analog Circuits: A. A. Lande, E & TC DeptDocumento96 páginasAnalog Circuits: A. A. Lande, E & TC DeptvmspraneethAinda não há avaliações
- EEE 245 - Op-Amp PDFDocumento53 páginasEEE 245 - Op-Amp PDFASD DSAAinda não há avaliações
- Opamp NotesDocumento5 páginasOpamp NotesVasim AkramAinda não há avaliações
- Linear and Digital Integrated Circuits: Uni T - 1 Operati Onal Ampli FierDocumento116 páginasLinear and Digital Integrated Circuits: Uni T - 1 Operati Onal Ampli FierBOGGULA SURENDAR REDDYAinda não há avaliações
- Summing Amplifier.Documento3 páginasSumming Amplifier.Majid AliAinda não há avaliações
- Differentiator ExperimentDocumento25 páginasDifferentiator ExperimentAlyaa Nadzirah Binti Shbini100% (1)
- What Is The Difference Between Active Filter and Passive Filter ApplicationsDocumento3 páginasWhat Is The Difference Between Active Filter and Passive Filter ApplicationsNaRi Plc100% (1)
- Intro Op AmpDocumento44 páginasIntro Op AmpNimish PrabhakarAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics II Refernce NotesDocumento129 páginasElectronics II Refernce NotesSri Harsha SappaAinda não há avaliações
- Why Co-simulation FrameworksDocumento5 páginasWhy Co-simulation FrameworksAbinaya UlagapaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 Transistors Opamp: December 17, 2021 1Documento73 páginasUnit 2 Transistors Opamp: December 17, 2021 1Abhishek SataleAinda não há avaliações
- Radio Engineering Design Exercise 2015Documento30 páginasRadio Engineering Design Exercise 2015Sadiqur Rahaman Sumon100% (2)
- Part IV OpampDocumento45 páginasPart IV OpampKunalAinda não há avaliações
- All About OpampDocumento46 páginasAll About OpampVamsi BobbaAinda não há avaliações
- Active High Pass and Low Pass FilterDocumento16 páginasActive High Pass and Low Pass FilterVINITA AGARWAL50% (2)
- Monostable MultivibratorDocumento15 páginasMonostable MultivibratorHema SundarAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On Analog ElectronicsDocumento334 páginasPresentation On Analog ElectronicssamuelAinda não há avaliações
- Analog Electronics Course OverviewDocumento36 páginasAnalog Electronics Course OverviewcooljseanAinda não há avaliações
- "Steady-State Modeling and Simulation of A Distribution Feeder With Distributed Energy Resources in A Real-Time Digital Simulation Environment PDFDocumento88 páginas"Steady-State Modeling and Simulation of A Distribution Feeder With Distributed Energy Resources in A Real-Time Digital Simulation Environment PDFEynher Abel RiascosAinda não há avaliações
- Dual Input Differential Amplifier GuideDocumento5 páginasDual Input Differential Amplifier GuidePrempal TomarAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Integrated Circuits Lab ManualDocumento104 páginasLinear Integrated Circuits Lab ManualNandha KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Ee101 Opamp 1Documento85 páginasEe101 Opamp 1Ankur SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Automatic Hand Sanitizer DispenserDocumento19 páginasAutomatic Hand Sanitizer Dispenserhamed razaAinda não há avaliações
- Simulation of Buck Converter with Synchronous RectifierDocumento7 páginasSimulation of Buck Converter with Synchronous RectifierThinh NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Op-Amp Circuits GuideDocumento21 páginasOp-Amp Circuits GuideVarun BishtAinda não há avaliações
- Seminar On: (Programmable Logic Controller)Documento21 páginasSeminar On: (Programmable Logic Controller)balajigururajAinda não há avaliações
- Operational Amplifier GuideDocumento56 páginasOperational Amplifier GuideVedang PavanjeAinda não há avaliações
- Deployment of Part-Time Academic Staff / Associate LecturersDocumento39 páginasDeployment of Part-Time Academic Staff / Associate LecturersKoh Kok Hui100% (1)
- LDICA Lecture Notes by A.Mounika PDFDocumento143 páginasLDICA Lecture Notes by A.Mounika PDFTwinkle Ratna100% (1)
- Feedback Amplifiers ExplainedDocumento21 páginasFeedback Amplifiers ExplainedKaviyaAinda não há avaliações
- OscillatorDocumento15 páginasOscillatorGerald Labios100% (2)
- Edc Lab ManualDocumento70 páginasEdc Lab ManualreneeshczAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Inverting Operational Amplifier ConfigurationDocumento10 páginasNon-Inverting Operational Amplifier ConfigurationMirHaiderAliShaurov100% (1)
- Electric Piano: Adam Estes and Yukimi MorimotoDocumento21 páginasElectric Piano: Adam Estes and Yukimi MorimotoBenjaminAinda não há avaliações
- Basic ElectronicsDocumento142 páginasBasic ElectronicsHarshitha CHALUMURI100% (1)
- Minor Project FileDocumento29 páginasMinor Project FilePoorva ShuklaAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualDocumento77 páginasElectronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualpdnkiranAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Phase Selector: A Mini-Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Requirements For The Award ofDocumento53 páginasDigital Phase Selector: A Mini-Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Requirements For The Award ofdondbAinda não há avaliações
- 2.0 Oscillators 2.0 Oscillators: Linear DC Power Supply and Various Types Linear DC Power Supply and Various TypesDocumento47 páginas2.0 Oscillators 2.0 Oscillators: Linear DC Power Supply and Various Types Linear DC Power Supply and Various TypesSadrina MahamudAinda não há avaliações
- Linear IC Guide for Op-Amps & ApplicationsDocumento146 páginasLinear IC Guide for Op-Amps & ApplicationsAnonymous n30qTRQPoIAinda não há avaliações
- Lectures On Operational AmplifiersDocumento22 páginasLectures On Operational AmplifiersRonald MulindeAinda não há avaliações
- Static Characeristic of A Measuring Instrument (Voltmeter)Documento4 páginasStatic Characeristic of A Measuring Instrument (Voltmeter)MRINMOY MANDALAinda não há avaliações
- OscillatorsDocumento90 páginasOscillatorsYesAinda não há avaliações
- 2.different Coupling Schemes Used in AmplifiersDocumento12 páginas2.different Coupling Schemes Used in AmplifiersMrs. P. Ganga BhavaniAinda não há avaliações
- LAB 1 Op AmpDocumento11 páginasLAB 1 Op AmpamirulAinda não há avaliações
- Flagbot Robotics Design ReportDocumento30 páginasFlagbot Robotics Design ReportPhuc HaAinda não há avaliações
- Op Amp As Adder and SubtractorDocumento2 páginasOp Amp As Adder and Subtractorchelam RAinda não há avaliações
- Aim: To Test Differentiator and Integrator Circuits Using Ua741op-AmpDocumento8 páginasAim: To Test Differentiator and Integrator Circuits Using Ua741op-AmpAvinash Nandakumar100% (1)
- Home Automation Using Arduino Wifi Module Esp8266Documento11 páginasHome Automation Using Arduino Wifi Module Esp8266Dr. M. Thillai Rani Asst Prof ECEAinda não há avaliações
- Difference Between Enhancement Type and Depletion Type MOSFETDocumento3 páginasDifference Between Enhancement Type and Depletion Type MOSFETAbhi KAinda não há avaliações
- CH 1 - Op-AmpDocumento65 páginasCH 1 - Op-AmpMohana VivanaAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics Analog OPAMPDocumento51 páginasElectronics Analog OPAMPPrashant SachdevAinda não há avaliações
- On IgbtDocumento19 páginasOn IgbtSayanta Saha100% (1)
- 2b RectifierDocumento21 páginas2b RectifierLove StrikeAinda não há avaliações
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsAinda não há avaliações
- Real-Time Simulation Technology for Modern Power ElectronicsNo EverandReal-Time Simulation Technology for Modern Power ElectronicsAinda não há avaliações
- Commissioning Advanced Lighting Systems: Trina Larsen, M.SC., P.Eng., LEED® APDocumento10 páginasCommissioning Advanced Lighting Systems: Trina Larsen, M.SC., P.Eng., LEED® APMuhammad HaroonAinda não há avaliações
- 16-Bit Viterbi Decoder ProcessorDocumento6 páginas16-Bit Viterbi Decoder ProcessorMuhammad HaroonAinda não há avaliações
- Data of IELTS For BeginersDocumento1 páginaData of IELTS For BeginersMuhammad HaroonAinda não há avaliações
- 202 Useful Exercises For IELTS PDFDocumento129 páginas202 Useful Exercises For IELTS PDFMian Rizwan100% (23)
- Swot Analysis of MobilinkDocumento19 páginasSwot Analysis of MobilinkMuhammad HaroonAinda não há avaliações
- OFDMDocumento14 páginasOFDMMuhammad HaroonAinda não há avaliações
- Interleaver Operation and DesignDocumento6 páginasInterleaver Operation and DesignMuhammad HaroonAinda não há avaliações
- Op Amp IntegratorDocumento14 páginasOp Amp IntegratorMuhammad Haroon50% (2)
- Organic Semiconductor and Its Applications: Sara SaediniaDocumento15 páginasOrganic Semiconductor and Its Applications: Sara SaediniaMuhammad HaroonAinda não há avaliações
- MOS Multiplier-Divider Cell For Analog VLSIDocumento3 páginasMOS Multiplier-Divider Cell For Analog VLSIShwetaGautamAinda não há avaliações
- Iot PPT 1Documento16 páginasIot PPT 1SajalAinda não há avaliações
- Lowara Grupuri de Pompare - Ghvseries-Td-En PDFDocumento120 páginasLowara Grupuri de Pompare - Ghvseries-Td-En PDFmariuspiAinda não há avaliações
- Mono 2.6W Class D Amplifier MAX98300: General Description FeaturesDocumento14 páginasMono 2.6W Class D Amplifier MAX98300: General Description FeaturesAndhi UznhAinda não há avaliações
- LM Ic 3205 PDFDocumento26 páginasLM Ic 3205 PDFAbu alwardAinda não há avaliações
- AS3930 Wakeup Reciever DatasheetDocumento43 páginasAS3930 Wakeup Reciever DatasheetVojtěch HauserAinda não há avaliações
- CMOS Circuit Design and Simulation FundamentalsDocumento12 páginasCMOS Circuit Design and Simulation FundamentalsPanku RangareeAinda não há avaliações
- Articulo - Coriolis Flowmeters Industrial Practice and Published Information - Baker1994Documento18 páginasArticulo - Coriolis Flowmeters Industrial Practice and Published Information - Baker1994Alex Willy Pilco NuñezAinda não há avaliações
- Biomedical Measurements and Transducers LectureDocumento10 páginasBiomedical Measurements and Transducers LectureMac Kelly JandocAinda não há avaliações
- DC Characteristics of Op-AmpDocumento7 páginasDC Characteristics of Op-AmpVENKATESWARLU MUVVA (PA2111004040011)Ainda não há avaliações
- 0-Web Catalouge 2016Documento132 páginas0-Web Catalouge 2016Sandeep KamatAinda não há avaliações
- Class C Amplifiers IntroDocumento8 páginasClass C Amplifiers IntroTebogo SekgwamaAinda não há avaliações
- Crysis Building DocsDocumento8 páginasCrysis Building DocsMat DowerAinda não há avaliações
- FM Superregenerative Receiver: Using Only Two TransistorsDocumento3 páginasFM Superregenerative Receiver: Using Only Two TransistorsJayceemikelAinda não há avaliações
- Facts About SWR and LossDocumento62 páginasFacts About SWR and Lossyo3fhmAinda não há avaliações
- Module 4 QuestionsDocumento7 páginasModule 4 QuestionsamaiscAinda não há avaliações
- RT 31026042019Documento1 páginaRT 31026042019Syed AshmadAinda não há avaliações
- Consumo Corriente HCU1500 PathtrakDocumento4 páginasConsumo Corriente HCU1500 PathtrakJuan Carlos MuñozAinda não há avaliações
- Grounding Transformer FAQs - Pacific Crest Transformers - Custom Liquid Filled Transformers & RepairDocumento8 páginasGrounding Transformer FAQs - Pacific Crest Transformers - Custom Liquid Filled Transformers & RepairVijai PrasathAinda não há avaliações
- Thomson Rca Scenium DLP Technikal Training ManualDocumento95 páginasThomson Rca Scenium DLP Technikal Training ManualRoberto De Leon Martinez100% (1)
- Principles of Communication Workbook p2Documento68 páginasPrinciples of Communication Workbook p2Shaina MabborangAinda não há avaliações
- Marantz 2270 Service ManualDocumento32 páginasMarantz 2270 Service ManualMrWasabiheadAinda não há avaliações
- LT 1246Documento12 páginasLT 1246aaronAinda não há avaliações
- How To Wire Up A Power Amplifier - UpdatedDocumento10 páginasHow To Wire Up A Power Amplifier - UpdatedAlessandro CardelliAinda não há avaliações
- R18 B.Tech 2-1 EEE SyllabusDocumento16 páginasR18 B.Tech 2-1 EEE SyllabusSravan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- EEG Brain-Computer Interface Project: Capstone Design Program: Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocumento33 páginasEEG Brain-Computer Interface Project: Capstone Design Program: Electrical and Computer EngineeringSwati SanghadiaAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Electronics 1968 04Documento84 páginasPractical Electronics 1968 04Carlos Soares100% (3)
- InfranorDocumento46 páginasInfranorKaryawan KoMang NyomanAinda não há avaliações
- Preliminary Technical DataDocumento4 páginasPreliminary Technical DataHeri AltisAinda não há avaliações
- BC3200 and BC3210 Blowdown ControllersDocumento32 páginasBC3200 and BC3210 Blowdown ControllersUriel VALANGEAinda não há avaliações