Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Wattmeter
Enviado por
Govindaraju RajuDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Wattmeter
Enviado por
Govindaraju RajuDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
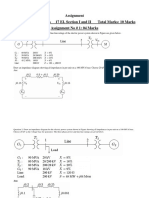
PERTEMUAN 13
PENGUKURAN DAYA
Introduction
Power may be defined as the rate at which energy is transformed oe
made available
In almost all cases the power in a d.c. circuit is best measured by
separately measuring quantities, V and I and by computing P=VI
In case of a.c. circuits the instantaneous power varies continuously
as the current and voltage go through a cycle of values
The fact that the power factor is involved in the expression for the
power means that a wattmeter must be used instead of merely an
ammeter and voltmeter.
Wattmeter
A wattmeter is essentially an inherent combination of an ammeter
and a voltmeter and, therefore , consists of two coils known as
current coil and pressure coil.
Wattmeter connection:
Wattmeter Errors
Error due to inductance of pressure coil
Error due to pressure coil capacitance
Error due to Eddy currents : soild metal parts are removed as far away from
the current coil as possible
( )
wattmeter of ading power True Re
cos cos
cos
=
u u
u
u
cot sin
sin
Error due to power loss in pressure coil or current coil
There are two method of connecting wattmeters in the circuit for
measurement of power, as shown in figure below (a) and (b).
Fig (a) :
Fig (b) :
c
r I W reading Wattmeter
2
+ =
p
r R
V
W reading Wattmeter
+
+ =
2
Measurement of Power in Single Phase A.C. Circuit
3-voltmeter method
Disadvantages : (i) Even small errors in measurement of voltages may
cause serious errors in the value of power, (ii) Supply voltage higher than
normal voltage is required
R
V V V
P
2
2
2
2
1
2
3
=
2 1
2
2
2
1
2
3
2
cos
V V
V V V
=
3-Ammeter method
The disadvantages of measurement of power by 3 voltmeters are overcome
in this method
( )
2
2
2
1
2
3
2
I I I
R
P =
2 1
2
2
2
1
2
3
2
cos
I I
I I I
=
Measurement of power in conjuction with instrument
transformers
This method is used when the currents and voltages of the circuits
to be measured are high
Figure below shows a measurement of power with wattmeter in
conjunction with instrument transformers in single phase A.C.
circuits
Vector diagram for inductive load
Vector diagram for capasitive load
o | u =
( ) o | u u
=
cos cos
cos
K
o | u + + =
( ) o | u u
+ +
=
cos cos
cos
K
Measurement of Power in 3-Phase Circuit
Measurement of power in 3-
phase, 4-wire circuits-----------
P=W
1
+W
2
+W
3
Measurement of power in 3-
phase, 3-wire circuits-------------
P=W
1
+W
2
+W
3
3-wattmeter method of measuring
3-phase power of delta connected
P=W
1
+W
2
+W
3
1-wattmeter method of measuring
balanced 3-phase power (a) star
connected, (b) delta connected
P=3W
2-wattmeter method of measuring
3-phase 3-wire power :
(a) star connected,
P=W
1
+W
2
(b) delta connected
P=W
1
+W
2
Determination of P.F. from Wattmeter Reading
If load is balanced, then p.f. of the
load can be determined from the
wattmeter readings
Vector diagram for balanced star
connected inductive load -----
The watt-ratio Curve ----------
p.f. can be determined from
reading of two wattmeters
( )
2 1
2 1 1
3
tan cos cos
W W
W W
+
Você também pode gostar
- Automatic Braking System in E-BikesDocumento14 páginasAutomatic Braking System in E-BikesPranesh.MAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas Transmisi Daya ListrikDocumento4 páginasTugas Transmisi Daya ListrikYordan RakaAinda não há avaliações
- Common Emitter Un Bypassed Emitter - Fixed Bias ConfigurationDocumento14 páginasCommon Emitter Un Bypassed Emitter - Fixed Bias ConfigurationForge lastAinda não há avaliações
- Undip Analisa Ganguan Hubung Singkat Transmisi 150 KVDocumento19 páginasUndip Analisa Ganguan Hubung Singkat Transmisi 150 KVTatang FestiyawanAinda não há avaliações
- Load Characteristics: M. Afnan HabibiDocumento32 páginasLoad Characteristics: M. Afnan HabibiAnesia AlferdoAinda não há avaliações
- Electromechanical InstrumentsDocumento17 páginasElectromechanical Instrumentsอภิฌาน กาญจนวาปสถิตย์Ainda não há avaliações
- GP1A30R: OPIC Photointerrupter With Encoder FunctionDocumento4 páginasGP1A30R: OPIC Photointerrupter With Encoder FunctionnospherathusAinda não há avaliações
- Deteksi Kerusakan Motor InduksiDocumento7 páginasDeteksi Kerusakan Motor InduksifaturAinda não há avaliações
- PID Control Buck Converter by Using Arduino UNODocumento52 páginasPID Control Buck Converter by Using Arduino UNOveerakumar BITAinda não há avaliações
- Power System Stability - Computaton of Critical Clearing Time and PDFDocumento67 páginasPower System Stability - Computaton of Critical Clearing Time and PDFBelayneh TadesseAinda não há avaliações
- EE Homework - Partially CompletedDocumento8 páginasEE Homework - Partially CompletedRickAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Sequence and Logic Control?Documento6 páginasWhat Is Sequence and Logic Control?Marwan ShamsAinda não há avaliações
- Jawaban Soal Opdal 3.1 PDFDocumento4 páginasJawaban Soal Opdal 3.1 PDFYudi SaputraAinda não há avaliações
- Kecerdasan Buatan: Artificial IntelligenceDocumento30 páginasKecerdasan Buatan: Artificial IntelligenceWahyu HPAinda não há avaliações
- Eee5451 Lab1Documento30 páginasEee5451 Lab1sekelanilunguAinda não há avaliações
- ATV12 Communication Parameters BBV51917 1.4IE05bDocumento12 páginasATV12 Communication Parameters BBV51917 1.4IE05bRicardo Rodriguez ParedesAinda não há avaliações
- Sistem Pengendali LiftDocumento20 páginasSistem Pengendali LiftSyam Aji100% (1)
- T3 TugasDocumento15 páginasT3 TugasSri rahayuAinda não há avaliações
- ASGN Ethernet Loopback DesignDocumento4 páginasASGN Ethernet Loopback DesignsenthilAinda não há avaliações
- BJT PDFDocumento14 páginasBJT PDFRaka Satria PradanaAinda não há avaliações
- Torque-Speed Characteristic Induction Motor Plot: M-File MatlabDocumento2 páginasTorque-Speed Characteristic Induction Motor Plot: M-File MatlabGiorgio Rendra VilariZ'tAinda não há avaliações
- Handout LISTRIK DINAMIS Bahasa InggrisDocumento10 páginasHandout LISTRIK DINAMIS Bahasa Inggriscicha 25Ainda não há avaliações
- Potential Transformer Catalog ABBDocumento4 páginasPotential Transformer Catalog ABBstudent_ujjwol3163Ainda não há avaliações
- Straight Twist Joint1Documento22 páginasStraight Twist Joint1al_198967% (3)
- Measurement of ResistanceDocumento20 páginasMeasurement of ResistanceWanjala WilliamAinda não há avaliações
- H-Bridge DC Motor Direction ControllerDocumento7 páginasH-Bridge DC Motor Direction ControllerKhan ElmeAinda não há avaliações
- Integrated Gate Commutated ThyristorDocumento3 páginasIntegrated Gate Commutated ThyristorKishore CkAinda não há avaliações
- Model Rangkaian Model Matematik STLDocumento21 páginasModel Rangkaian Model Matematik STLRidho Dwi LaksonoAinda não há avaliações
- Data Sheet Pompa SentrifugalDocumento2 páginasData Sheet Pompa Sentrifugalsiaga 1Ainda não há avaliações
- Preface: Licensing AgreementDocumento58 páginasPreface: Licensing AgreementNarcis Patrascu100% (1)
- Unit4 PDFDocumento36 páginasUnit4 PDFAayush SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- SKMM1113 Week 6 - Torsion (Inderterminate)Documento3 páginasSKMM1113 Week 6 - Torsion (Inderterminate)kamalnathAinda não há avaliações
- PSA Assignment For 17 ELDocumento6 páginasPSA Assignment For 17 ELIzhar Ahmed NoohpotoAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Vibrations MEC4110 Unit IDocumento10 páginasMechanical Vibrations MEC4110 Unit Iniaz kilam100% (1)
- Metoda Pengujian GeneratorDocumento52 páginasMetoda Pengujian Generatorsarwant_wantAinda não há avaliações
- Sdof DynDocumento29 páginasSdof DynAnkur KurmiAinda não há avaliações
- Rancangan Anggaran Biaya Pembuatan Trainer PLC: NO Nama Jumlah Harga Satuan Harga Total Nama Toko Metode PembelianDocumento1 páginaRancangan Anggaran Biaya Pembuatan Trainer PLC: NO Nama Jumlah Harga Satuan Harga Total Nama Toko Metode PembelianXI TME 1Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 4 Diode Circuits NewDocumento76 páginasLecture 4 Diode Circuits Newصدام حسینAinda não há avaliações
- Lorentz PS1200 BrochureDocumento4 páginasLorentz PS1200 BrochureJavier ZanettiAinda não há avaliações
- Artikel PLTSDocumento8 páginasArtikel PLTSKojiro HadateAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Analysis of Buck ConverterDocumento18 páginasDesign and Analysis of Buck Converterk rajendraAinda não há avaliações
- TC-1 User ManuelDocumento13 páginasTC-1 User ManuelBruno Šer100% (1)
- 1a-Sensor Resistif-1 PDFDocumento45 páginas1a-Sensor Resistif-1 PDFSat SatrioAinda não há avaliações
- Toshiba 2SK4107 DatasheetDocumento6 páginasToshiba 2SK4107 DatasheetPedro PerezAinda não há avaliações
- MK204A IDT Overcurrent Relay User's GuideDocumento4 páginasMK204A IDT Overcurrent Relay User's GuideArie DinataAinda não há avaliações
- (ACTA Universitatis Cibiniensis) Testing The Performance of A Single-Phase Autotransformer On MATLABSimulinkDocumento6 páginas(ACTA Universitatis Cibiniensis) Testing The Performance of A Single-Phase Autotransformer On MATLABSimulinkbeimanalfredoAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On Power and Torque of Induction MotorDocumento30 páginasPresentation On Power and Torque of Induction MotorNewCandle100% (1)
- Presentation 1Documento15 páginasPresentation 1Ajay Talajiya0% (1)
- ExCap5 PDFDocumento9 páginasExCap5 PDFChorrinha ChorraAinda não há avaliações
- ETO EXAM Notescover 1Documento2 páginasETO EXAM Notescover 1Tun Lin NaingAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 2Documento2 páginasAssignment 2Borhan ShaikatAinda não há avaliações
- Transmisi - VOLTAGE DROPDocumento9 páginasTransmisi - VOLTAGE DROPOkIlhamMuhammadAinda não há avaliações
- Elemen MesinDocumento23 páginasElemen MesinMonika NikaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - III Measuring InstrumentsDocumento62 páginasUnit - III Measuring InstrumentsjyothirAinda não há avaliações
- E1 - Controlled Rectifiers PDFDocumento92 páginasE1 - Controlled Rectifiers PDFmitulAinda não há avaliações
- Power MeasurementDocumento13 páginasPower MeasurementagsparxAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Wattmeter MethodsDocumento13 páginas2 Wattmeter MethodsPrashant ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Power MeasurementDocumento30 páginasPower Measurementphani5016Ainda não há avaliações
- Power, Testing, and Grounding of Electronic SystemsNo EverandPower, Testing, and Grounding of Electronic SystemsAinda não há avaliações
- Ready For Telecom Installation (Rfti) Inspection Checklist: Participants Name Position Contact No. CompanyDocumento15 páginasReady For Telecom Installation (Rfti) Inspection Checklist: Participants Name Position Contact No. Companyjohn helyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 DDDDocumento13 páginasChapter 4 DDDRishavAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 - Three-Phase Induction MotorsDocumento93 páginasUnit 4 - Three-Phase Induction MotorsMaribe TshegoAinda não há avaliações
- Otm250E4Cm230C Motorized C/O SwitchDocumento3 páginasOtm250E4Cm230C Motorized C/O SwitchbilalAinda não há avaliações
- Operator Manual: Hybrid Quiet Diesel Power System HQDSADocumento122 páginasOperator Manual: Hybrid Quiet Diesel Power System HQDSATrung LêAinda não há avaliações
- Atmel 46104 SE M90E36A ApplicationNoteDocumento43 páginasAtmel 46104 SE M90E36A ApplicationNoteKaik Wulck BassanelliAinda não há avaliações
- Eee4227: Power System Protection Term: Mid-TermDocumento23 páginasEee4227: Power System Protection Term: Mid-TermKazi ShahadatAinda não há avaliações
- Calculation of TmsDocumento6 páginasCalculation of TmsMihir PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Avc63-7, Avc63-7D, Avc63-7F Voltage Regulators: Eatures EnefitsDocumento2 páginasAvc63-7, Avc63-7D, Avc63-7F Voltage Regulators: Eatures Enefitsraju bonthaAinda não há avaliações
- Ac, DC, or Ac/Dc Hipot/Megohmmeters: PhenixDocumento4 páginasAc, DC, or Ac/Dc Hipot/Megohmmeters: PhenixUlyyszesz AalvaaraadooAinda não há avaliações
- Floating Neutral Impacts in Power Distribution - EEPDocumento9 páginasFloating Neutral Impacts in Power Distribution - EEPAbhishek DasAinda não há avaliações
- 03 X-Ray Imaging System 3Documento34 páginas03 X-Ray Imaging System 3Qubi SolutAinda não há avaliações
- Circuit Details and Test ResultsDocumento2 páginasCircuit Details and Test ResultsVitaliy TymoshenkoAinda não há avaliações
- SMC7000HVDocumento4 páginasSMC7000HVKirsten HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Psas Ut1-QbDocumento7 páginasPsas Ut1-QbNaveen RajAinda não há avaliações
- The Sakaka Solar Power PlantDocumento4 páginasThe Sakaka Solar Power Plantعبدالعزيز الفيفيAinda não há avaliações
- ANSI / IEEE Standards CollectionDocumento5 páginasANSI / IEEE Standards CollectionhkundakAinda não há avaliações
- The Top 10 Biggest Geothermal Power Plants in The WorldDocumento7 páginasThe Top 10 Biggest Geothermal Power Plants in The WorldSteven Ulysses KagayutanAinda não há avaliações
- Data Base Points DNP3 Rev00Documento72 páginasData Base Points DNP3 Rev00LparejaMorenoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 16Documento2 páginasChapter 16velisbarAinda não há avaliações
- User Manual Ups Manual (Ydc3300-0.9) 30k - 40kDocumento42 páginasUser Manual Ups Manual (Ydc3300-0.9) 30k - 40kCesar CesarAinda não há avaliações
- 04.pil - Pnoz 1 EnglishDocumento3 páginas04.pil - Pnoz 1 Englishsaat plcAinda não há avaliações
- 1150 PDFDocumento80 páginas1150 PDFPeraAinda não há avaliações
- 351A PS IM SettingsSheets 20211203Documento52 páginas351A PS IM SettingsSheets 20211203Adilson Leite ProençaAinda não há avaliações
- CCVT-VT Test ProtocolDocumento6 páginasCCVT-VT Test Protocolemad mallickAinda não há avaliações
- Protection and Switchgear Assignment PDFDocumento21 páginasProtection and Switchgear Assignment PDFRishali ChandraseakaranAinda não há avaliações
- NHPC Limited - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento4 páginasNHPC Limited - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDinesh MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- Module 6 - TorsionDocumento23 páginasModule 6 - TorsionNadine KyrahAinda não há avaliações
- PEE, IIEE Fellow, APEC Engr., ACPE: Power System Analysis I (Electrical Transmission Lines)Documento27 páginasPEE, IIEE Fellow, APEC Engr., ACPE: Power System Analysis I (Electrical Transmission Lines)Hendrick Brian QuezaAinda não há avaliações