Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
No 7 (SCCP&TCAP&INAP)
Enviado por
Javeria AjazTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
No 7 (SCCP&TCAP&INAP)
Enviado por
Javeria AjazDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
HUAWEI
CCS7 Signaling System
HUAWEI
Chapter 1
Chapter 2 Chapter 3
SCCP
TCAP INAP
HUAWEI
Chapter 1
SCCP
SCCP: Signaling Connection Control Part
HUAWEI
Where is SCCP?
INAP
TUP ISUP
CAP
TCAP SCCP
MAP
MTP
INAP: IN Application Protocol CAP: CAMEL Application Part TUP: Telephone User Part MTP: Message Transfer Part
MAP: Mobile Application Part TCAP: Transaction Capability Application Part ISUP: ISDN User Part SCCP: Signaling Connection Control Part
4
HUAWEI
What is SCCP?
In No.7 signaling systemSCCP and MTP layer three together are responsible for signaling network layer function. SCCP expends the MPT functions in the following points:
Enable to convey various non-circuit-related signaling message.
Provide enhanced addressing and routing function, and enable to achieve the direct global transmission between different CCS7 networks by using GT addressing.
Expend the user part of MTP. SCCP supports up to 256 kinds of sub systems in stead of 16 in MTP. Enable to provide connectionless service and connectionoriented service.
5
HUAWEI
Service Functions of SCCP Network
According to the various service requirement needed by user, the SCCP provides four classes of service: two for connectionless services and two for connection-oriented services. The four classes are: Class 0: Basic connectionless class. Class 1: In-sequence delivery connectionless class. Class 2: Basic connection-oriented class.
Class 3: Flow control connection-oriented class.
HUAWEI
Addressing and Routing Functions of SCCP
The SCCP routing provides a powerful address translation function, which requires for connectionless and connectionoriented service. The SCCP routing provides a powerful addressing information translation function on behalf of its users. The routing function also responds to the MTP and SCCP congestion reports. Addressing within the SCCP of CCS7 makes use of three separate elements: DPC; Global Title (GT); Sub-System Number (SSN);
7
HUAWEI
Primitive
In CCS7 system, the information exchange between two adjacent layers is called primitive which includes primitive name, primitive type and primitive parameters. There are four types of primitives: Request Indication Response
Confirmation
HUAWEI
Primitives between SCCP and SCCP-User
Primitives between SCCP and SCCP-User (TCAP) are N_Primitives. The connectionless services use the following N_Primitives: N_UNITDATA_REQis used when SCCP-User requires SCCP to send data. N_UNITDATA_INDis used when SCCP reports the received data to SCCP-User. N_NOTICE_INDis used when SCCP reports the reason why the SCCP-User data cannot be sent to peer point. N-Primitives can be traced on SSP maintenance terminal.
9
HUAWEI
N_UNITDATA Parameters
N-UNITDATA_IND and N-UNITDATA_REQ have the same parameters. SCCP-USER Octet (83H) Routing Label (DPCOPCSLS) Sequence Control (SLS) Protocol Class (81H) Parameter Location Pointer (Called Address, Caller Address, User Data Pointer)
Called Address (Destination Address)
Caller Address (Source Address) User Data (SCCP-User Data to be sent by SCCP transparently, SCCP makes no change to them)
10
HUAWEI
N_NOTICE Parameters
N_NOTICE has the same parameter structure with N_UNITDATA, but the Protocol Class is changed to return reason.
11
HUAWEI
SCCP Message Types
Message is the information exchanged by the same layers in two signaling points. There are 17 kinds of SCCP messages. Among them UDT (Unit Data) and UDTS (Unit Data Service) are used for connectionless services. The codes for UDT and UDTS are 09H and 0AH. INAP only uses UDT messages
12
HUAWEI
Chapter 2
TCAP
TCAP: Transaction Capability Application Part
13
HUAWEI
Applications of TCAP
Applications of TCAP:
Data Exchange between switching systems Switching systems access network database center Network databases establish remote operation dialogue
Examples of TCAP applications: Mobile service applications Free phone service (800-service) Credit Card calling Operation & Maintenance applications
14
HUAWEI
Dialogue
Dialogue is the association established between two TC users exchanging data. Whenever two signaling points are going to exchange data, they will setup a dialogue via TCAP. It is TCAP that initiates, maintains and releases of a dialogue. But TCAP does not care the functions of the dialogue. The procedure of message exchange between two signaling points is similar to man-machine dialogue mode, which involves all necessary messages such as BEGIN and END.
15
HUAWEI
Component
Component is the protocol data unit exchanged between TC users. i.e. the information exchanged in a dialogue is just a set components. Components are defined by TC-Users. Components include the invoke operation by initiator and the returned result of the operation. The operation is decided by applications, e.g. number translation.
16
HUAWEI
The Relationship Between Dialogue and Component
A dialogue has one or more components. A service procedure is just one dialogue. i.e. all the operations of a service procedure buildup a dialogue, the dialogue is the carrier of the operations.
17
HUAWEI
Categories of TCAP Components
InvokeINVis used to send an operation request to remote TC-User. Return Result-LastRR-Lis used to return the components of final result of last INV operation. Return Result-not LastRR-NLis used to return the components of non-final result of last INV operation. Return ErrorREis used to return the components of error information, in which an error code is embedded RejectRJis used to reject last INV operation, in which a problem code is embedded.
18
HUAWEI
Classes of TCAP Operations
According to different requirements of operation results, TCAP are classified into 4 classes: Class 1: Result will be returned no matter the operation is successful or not. i.e. a RR-L, RR-NL or RE must be returned. Class 2: Only when the operation fails, a RE will be returned. Class 3: Only when the operation succeeds, a RR-L or RR-NL will be returned. Class 4: No result returned no matter the operation is successful or not.
19
HUAWEI
TC Primitives
TCAP and TC-User exchange data via TC_Primitives. There are 16 kinds of TC_Primitives, among them there 9 Component TC-Primitives which are related to components and 7 Dialogue TC-Primitives which are related to dialogues. The TC_Primitives from TCAP to TC-User are Indication primitives, from TC-User to TCAP are Request primitives.
20
HUAWEI
Component TC_Primitives (1)
TCINVOKE is used to invoke an operation. TCRESULTL is used to return the result of an operation. TCRESULTNL is similar to TCRESULTL, but only returns the middle result. Note: all above primitives have both Indication and Request types.
21
HUAWEI
Component TC_Primitives (2)
TCUERROR is a Request Primitive which is used to return the error code when the operation fails although TC-User has received the correct operation request.
TCUREJECTis a Request Primitive which is used to return reject code when TC-User has received an incorrect operation request.
TCUCANCEL is a Request Primitive which is used for TCUser to request TCAP to cancel an operation.
22
HUAWEI
Component TC_Primitives (3)
TCLCANEL is an Indication Primitive which is used to notify TC-User an operation is overtime. TCLREJECT is an Indication Primitive which is used to reject an operation by local TCAP. TCRREJECTis an Indication Primitive which is used to reject an operation when remote TCAP rejects the operation.
23
HUAWEI
Types of TCAP Dialogues
There are two types of TCAP dialogues. Unstructured Dialogue in which only unidirectional (UNI) messages are included. No response to be returned from opposite point in unstructured dialogue (e.g. a dialogue for sending an alarm message). Intelligent Network seldom uses this kind of dialogues. Structured Dialogue has initiating, maintaining and ending processes. It has BEGIN, CONTINUE and END or ABORT messages. Intelligent Network just uses this kind of dialogues.
24
HUAWEI
Dialogue TC_Primitives (1)
TC-UNI TC-User or TCAP request to begin a UNI dialogue. TCBEGIN Request or indicate to begin a dialogue. Request or indicate to maintain a
TCCONTINUE dialogue. TCEND
Request or indicate to end a dialogue.
25
HUAWEI
Dialogue TC_Primitives (2)
TCUABORTRequest to abort a dialogue. TCPABORTIndicate TC-User to abort a dialogue because of the error in transaction layer. TCNOTICEIndicate TC-User that the network service provider cannot provide the required service (e.g. STP does not support INAP).
26
HUAWEI
An Example of TCAP Process
Node2 (SCP) SSP begins a dialogue to query the balance of a calling card subscriber. SCP asks SSP to return the password.
Node1 (SSP) TC-Begin
TC-Invoke (Invoke) TC-Continue TC-Invoke (Invoke) TC-Continue
TC-Result-L (RR-L)
TC-End TC-Result-L (RR-L)
SSP returns the password.
SCP returns balance of the subscriber.
27
HUAWEI
Chapter 3
INAP
INAP: Intelligent Network Application Part
28
HUAWEI
The Functions of INAP
INAP defines operation criterion among the IN functional entities SSF, SCF, SRF and SDF. INAP is transmitted by SCCP UDT data, using connectionless services.
29
HUAWEI
The Relationship Between INAP and SCCP
INAP usually uses DPC+SSN routing mode of SCCP. INAP can also use GT routing mode of SCCP.
INAP uses class 0 and class 1 connectionless services of SCCP.
30
HUAWEI
INAP Operation Categories
Class 1: Result will be returned no matter the operation is successful or not. i.e. a RR-L, RR-NL or RE must be returned. Class 2: Only when the operation fails, a RE will be returned. Class 3: Only when the operation succeeds, a RR-L or RR-NL will be returned. Class 4: No result returned no matter the operation is successful or not.
31
HUAWEI
INAP Operations
INAP is a kind of TC-User. In INAP protocol, all INAP operations are also classified into 4 classes. Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Activate Service Filtering, P&C Initial DP, RRBE AT
Class 4
RC, BER
32
HUAWEI
IDP: Initial DP
IDP is the first INAP message sent from SSP to SCP, requesting SCP to establish the control relationship for an IN call. The parameters included in IDP are: access code, service key (the unique identifier of an IN service), caller number, called number, number attributes, etc.
33
HUAWEI
RRBE: Request Report BCSM Event
RRBE is sent from SCP to SSP, requesting SSP to configure DP dynamically. When SSP meets these DPs in later call process, SSP will report call information to SCP. RRBE provides SCP the condition of controlling calls. The parameters of RRBE include DP type, DP condition, etc. One RRBE can configure several DPs.
34
HUAWEI
CTR: Connect To Resource
CTR is sent from SCP to SSP, requesting SSP to connect the user to IP. CTR provides the users the condition of using IP. If IP is integrated with SSP, SSP makes only the internal connection with IP. If IP is independent from SSP, SSP communicates IP via TUP messages, connecting the users to IP through PSTN voice channels.
35
HUAWEI
P&C: Prompt & Collect User Informati
P&C is sent from SCP to SSP, requesting IP to play voice prompts the users and collect the users input. P&C needs IP to return operation results.
36
HUAWEI
DFC: Disconnect Forward Connect
DFC is sent from SCP to SSP, requesting SSP to disconnect the connection between the users and IP.
37
HUAWEI
AC: Apply Charging
AC is sent from SCP to SSP, requesting SSP to charge the call. The parameters of AC include: charge class, the balance of the subscriber, charging party, etc.
38
HUAWEI
Connect
Connect is sent from SCP to SSP, requesting SSP to connect the users to the designated number.
39
HUAWEI
ACR: Apply Charging Report
ACR is sent from SSP to SCP, reporting the charge result. The parameters in ACR include: the call start time, call end time, call length, caller number, called number, charging number, fee, etc.
40
HUAWEI
ERB: Event Report BCSM
ERB is sent from SSP to SCP when SSP detects the DPs configured by SCP in last RRBE message, reporting the call information to SCP.
41
HUAWEI
RC: Release Call
RC is sent from SCP to SSP, requesting SSP to release the occupied IN call resources.
42
HUAWEI
PA: Play announcement
PA is sent from SCP to SSP, requesting IP to play voice prompts to the users. PA does not need result return from IP.
43
HUAWEI
SRR: Specialized Resource Report
SRR is sent from SSP to SCP, notifying SCP the end of playing announcement.
44
HUAWEI
AT: Activity Test
SCP sends AT to SSP every 6 minutes when the call is established to check the communication between SSP and SCP. If SSP can return AT_ack, the communication is good. If no AT_ack returns to SCP, the communication is broken, and SCP will release the resources occupied this IN call.
45
HUAWEI
An Example of INAP (FPH Service)
SSP Initial DP
SCP
Request Report BCSM Event
Apply Charging
Connect
Apply Charging Report BCSM Event Report Release Call
46
HUAWEI
An Example of INAP (Continue)
47
HUAWEI
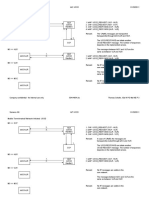
SCCPTCAP and INAP (FPH Service)
INAP
TC-BEGIN-REQ TC-INVOKE-REQ N_UNITDATA-IND TC-CONTINUE-IND Request Report Bcsm Event TC-INVOKE-IND TC-CONTINUE-IND Apply Charging TC-INVOKE-IND TC-CONTINUE-IND Connect TC-INVOKE-IND TC-CONTINUE-REQ TC-INVOKE-REQ TC-CONTINUE-REQ Event Report BCSM TC-INVOKE-REQ TC-END-IND Release Call TC-INVOKE-IND N_UNITDATA-IND UDT MSU N_UNITDATA-REQ UDT MSU N_UNITDATA-REQ UDT MSU N_UNITDATA-IND N_UNITDATA-IND UDT UDT MSU UDT MSU
AP
InitialDP
TCAP
N_UNITDATA-REQ
SCCP
UDT
MTP
MSU
SCP
MSU
Apply Charging Report
AP: Application Process, which processes IN calls in SSP.
48
Você também pode gostar
- LTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencyNo EverandLTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencySeppo HämäläinenAinda não há avaliações
- 0aa000008 Ss7 Protocol Issue2.0Documento49 páginas0aa000008 Ss7 Protocol Issue2.0Cristhian OñaAinda não há avaliações
- 01-Chapter 1 H.248Documento22 páginas01-Chapter 1 H.248aranibarm67% (3)
- TCAPDocumento70 páginasTCAPSanghamitra Roy ChoudhuryAinda não há avaliações
- UMTS Call FlowDocumento124 páginasUMTS Call Flowakifiqbal11Ainda não há avaliações
- SMS Over LTE - HALDocumento63 páginasSMS Over LTE - HALAsit SwainAinda não há avaliações
- IP-SM-GW Transport - How SMS is Sent over IP in VoLTE NetworksDocumento12 páginasIP-SM-GW Transport - How SMS is Sent over IP in VoLTE Networksabhijit010379Ainda não há avaliações
- Handover Interfaces For Lawful InterceptionDocumento271 páginasHandover Interfaces For Lawful InterceptionMarco LushangaAinda não há avaliações
- Acs For Tcap Users 20110324Documento23 páginasAcs For Tcap Users 20110324as.singh89Ainda não há avaliações
- Document With FeaturesDocumento256 páginasDocument With FeaturesNitinAinda não há avaliações
- 3GPP TS 33.107 - Lawful Interception Architecture and FunctionsDocumento404 páginas3GPP TS 33.107 - Lawful Interception Architecture and FunctionsJohn WiratamaAinda não há avaliações
- Configuring SIP-I InterfaceDocumento5 páginasConfiguring SIP-I InterfaceTatiana Marz AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Cs1 Core Inap NewDocumento81 páginasCs1 Core Inap NewNitin SinglaAinda não há avaliações
- Camel PPSDocumento82 páginasCamel PPSmugeshpv90Ainda não há avaliações
- 05-Chapter 5 SIGTRAN PDFDocumento112 páginas05-Chapter 5 SIGTRAN PDFMarouane Elmoatadid BillahAinda não há avaliações
- CCS7 (Isup)Documento120 páginasCCS7 (Isup)dayoladejo777Ainda não há avaliações
- CDG 117 Inter Standard Roaming White Paper Ver2.0Documento49 páginasCDG 117 Inter Standard Roaming White Paper Ver2.0Clarence W HayesAinda não há avaliações
- Ss7 Dsi ConfigDocumento191 páginasSs7 Dsi ConfigChaitanya Javvaji's100% (1)
- Evolved EPC For LTE by Cisco 1Documento70 páginasEvolved EPC For LTE by Cisco 1Virender SinghAinda não há avaliações
- One Picture To Understand RBTDocumento1 páginaOne Picture To Understand RBTAhmedAinda não há avaliações
- T1 and E1 PCM systems explainedDocumento10 páginasT1 and E1 PCM systems explainedPrafull BAinda não há avaliações
- Analyzing SS7/Sigtran Attacks Using Wireshark, Tshark & SnortDocumento68 páginasAnalyzing SS7/Sigtran Attacks Using Wireshark, Tshark & SnortLuca GarufiAinda não há avaliações
- LZT1235374 03 BDocumento16 páginasLZT1235374 03 BMohamed shabanaAinda não há avaliações
- Sigtran Connectuon by CiscoDocumento75 páginasSigtran Connectuon by CiscoKomunitasGerakanCintaJagapuraAinda não há avaliações
- PDN 078927Documento164 páginasPDN 078927Cesarsanfelice100% (1)
- PGW Troubleshooting 01Documento530 páginasPGW Troubleshooting 01sl4dyAinda não há avaliações
- DNS Procedures Ts - 129303v100500pDocumento59 páginasDNS Procedures Ts - 129303v100500pJesner LugoAinda não há avaliações
- TK150 Rel 45 - SG - v1.0.Documento136 páginasTK150 Rel 45 - SG - v1.0.Fred_SPbAinda não há avaliações
- Ericsson UCIP Library for XML-RPC CallsDocumento3 páginasEricsson UCIP Library for XML-RPC Callsyannis_benAinda não há avaliações
- GSM Number Portability TrainingDocumento261 páginasGSM Number Portability TrainingFred_SPbAinda não há avaliações
- 5282.SMS Over M2PA Lab Instructions PDFDocumento4 páginas5282.SMS Over M2PA Lab Instructions PDFAhmed SharifAinda não há avaliações
- CDR Format Epg Rel 8Documento13 páginasCDR Format Epg Rel 8Assem Abdelraheem Asaad100% (1)
- GSM Introductory OverviewDocumento49 páginasGSM Introductory Overviewtimilehin100% (1)
- GSM Call Path CourseDocumento75 páginasGSM Call Path CourseHeraa FarooqAinda não há avaliações
- UA 011101 SG7000 System Overview ISSUE1.1 20050103Documento33 páginasUA 011101 SG7000 System Overview ISSUE1.1 20050103Cristhian OñaAinda não há avaliações
- 02 - MGW For MSSDocumento41 páginas02 - MGW For MSSNadjib KaAinda não há avaliações
- Services and Charging: ObjectivesDocumento16 páginasServices and Charging: ObjectivesBSSAinda não há avaliações
- Sample DiameterDocumento42 páginasSample DiameterAnonymous gJHAwzEAinda não há avaliações
- SMS DocumentDocumento80 páginasSMS Documentvetonim47Ainda não há avaliações
- OWG000204 Interworking With HLR Data Configuration (IP) - Issue1.1Documento32 páginasOWG000204 Interworking With HLR Data Configuration (IP) - Issue1.1Kumaraguru Sathiyaseelan100% (1)
- Fe MGWDocumento34 páginasFe MGWAmin100Ainda não há avaliações
- Livre AoIP PDFDocumento135 páginasLivre AoIP PDFfdbttTKLCAinda não há avaliações
- Technical White Paper For Huawei SPS Signaling AccountingDocumento31 páginasTechnical White Paper For Huawei SPS Signaling AccountingaranibarmAinda não há avaliações
- LTE RoamingDocumento4 páginasLTE RoamingSumber RejekiAinda não há avaliações
- Real Time Developer Studio TutorialDocumento126 páginasReal Time Developer Studio Tutorialza_wizardAinda não há avaliações
- USSD Call Flows PDFDocumento2 páginasUSSD Call Flows PDFAntariksha SinghAinda não há avaliações
- SMSC 1Documento52 páginasSMSC 1Manivannan LoganathanAinda não há avaliações
- MSOFTX3000 BSC ConfigurationDocumento29 páginasMSOFTX3000 BSC Configurationkguru2807100% (1)
- GSM Voice Mail Service TDM Call ControlDocumento68 páginasGSM Voice Mail Service TDM Call ControlAmi DollmakerAinda não há avaliações
- IR.34-V9.1 - Guidelines For IPX Provider Networks (Previously Inter-Service Provider IP Backbone Guidelines)Documento50 páginasIR.34-V9.1 - Guidelines For IPX Provider Networks (Previously Inter-Service Provider IP Backbone Guidelines)a_big_friendAinda não há avaliações
- BICC ProtocolDocumento8 páginasBICC ProtocolsinansafaaAinda não há avaliações
- 23.4 SCTP: Message Boundaries Each Message Is Independent of Any Other Message. This Is ADocumento1 página23.4 SCTP: Message Boundaries Each Message Is Independent of Any Other Message. This Is ATushar SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- S6a Diameter InterfaceDocumento139 páginasS6a Diameter Interfacetemporal11Ainda não há avaliações
- International Roaming GuideDocumento76 páginasInternational Roaming Guidevijrag_bit100% (1)
- Diameter Protocol Explained - Capability NegotiationDocumento10 páginasDiameter Protocol Explained - Capability NegotiationGGSNAinda não há avaliações
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkNo EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkAinda não há avaliações
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkNo EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- Making Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessNo EverandMaking Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessAinda não há avaliações
- 2Fw@Iktvo9Ua Xy1I94B: Ruang Final: Tukul3276 Ruang LN: Destroyer174Documento1 página2Fw@Iktvo9Ua Xy1I94B: Ruang Final: Tukul3276 Ruang LN: Destroyer174Mackmoer M ZakariaAinda não há avaliações
- OSI reference model layers explainedDocumento27 páginasOSI reference model layers explainedwesen destaAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Uart Eth Wifi ModuleDocumento37 páginasEmbedded Uart Eth Wifi ModulebuildmetAinda não há avaliações
- Troubleshooting Status Code 25 Errors in NetBackupDocumento6 páginasTroubleshooting Status Code 25 Errors in NetBackupHooman MohagheghAinda não há avaliações
- Sip Isdn Call FlowDocumento6 páginasSip Isdn Call FlowphuongldAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Networks: BITS PilaniDocumento104 páginasComputer Networks: BITS Pilanishiva subramaniyanAinda não há avaliações
- Proteus Sensor Quick Start GuideDocumento1 páginaProteus Sensor Quick Start GuideThe FannyAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction, Networks Types, TopologyDocumento50 páginasIntroduction, Networks Types, TopologyShahriar Haque50% (2)
- ACOS 5.1.0 Configuring VRRP-A High Availability: For A10 Thunder Series 7 December 2019Documento108 páginasACOS 5.1.0 Configuring VRRP-A High Availability: For A10 Thunder Series 7 December 2019李潇100% (1)
- Complete Guide To NMAPDocumento7 páginasComplete Guide To NMAPPulkit R AggarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Troubleshooting Switch Issues: Ethernet LansDocumento13 páginasTroubleshooting Switch Issues: Ethernet Lansamapreet.scorpioAinda não há avaliações
- Huawei - Ont Hg8546mDocumento9 páginasHuawei - Ont Hg8546mWalterFilhoAinda não há avaliações
- 4 ASBSC Configuring IP InterfacesDocumento80 páginas4 ASBSC Configuring IP InterfacesasifhaidertgAinda não há avaliações
- LTE Radio Protocol StackDocumento1 páginaLTE Radio Protocol StackzakiAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To WPA SupplicantDocumento7 páginasIntroduction To WPA SupplicantSailajaUngatiAinda não há avaliações
- Huawei Enterprise Product Portfolio 2012Documento84 páginasHuawei Enterprise Product Portfolio 2012NVAinda não há avaliações
- DGS-1510 Series Firmware Release Notes v1.70.012 (For WW)Documento22 páginasDGS-1510 Series Firmware Release Notes v1.70.012 (For WW)anthonyAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA Dis4 - Chapter 1 - Introducing Network Design Concepts - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Documento94 páginasCCNA Dis4 - Chapter 1 - Introducing Network Design Concepts - PPT (Compatibility Mode)http://heiserz.com/100% (1)
- Step-By-Step Guide To Deploying Windows Firewall and IPsec PoliciesDocumento114 páginasStep-By-Step Guide To Deploying Windows Firewall and IPsec PoliciessthefanefefaAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 0320-NET Slide-DeckDocumento42 páginas2018 0320-NET Slide-Deckmasterlinh2008Ainda não há avaliações
- INTERNET, INTRANET & EXTRANET COMPAREDDocumento66 páginasINTERNET, INTRANET & EXTRANET COMPAREDCharish CabeltesAinda não há avaliações
- Architecture Issues in 4g NetworkDocumento12 páginasArchitecture Issues in 4g Networkvinay kumar yadavAinda não há avaliações
- Nguyen-Doan-Nhat-Minh 2b 3b 4a 4b 4cDocumento32 páginasNguyen-Doan-Nhat-Minh 2b 3b 4a 4b 4cNhat MinhAinda não há avaliações
- 3.4.4 Lab Research Networking StandardsDocumento4 páginas3.4.4 Lab Research Networking StandardsTran Nguyen Phuoc An (K18 HCM)Ainda não há avaliações
- Bootp and DHCPDocumento3 páginasBootp and DHCPankitAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco 5500 Series Wireless Controllers: Maximum Performance and ScalabilityDocumento8 páginasCisco 5500 Series Wireless Controllers: Maximum Performance and ScalabilityarryfakhAinda não há avaliações
- Routing and Routing Protocols - IntroductionDocumento20 páginasRouting and Routing Protocols - IntroductionwaseemshaikAinda não há avaliações
- 231622161730AFEFDocumento5 páginas231622161730AFEFTito JohnsonAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna 4Documento10 páginasCcna 4Chozha RajanAinda não há avaliações
- Call flow network frameworkDocumento22 páginasCall flow network frameworkTajinder SummanAinda não há avaliações