Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Invertebrates H
Enviado por
f1940003Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Invertebrates H
Enviado por
f1940003Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
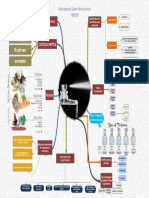
Invertebrates
Diversity of Animals Porifera Cnidaria
Platyhelminthes
Nematoda Mollusca Annelida Arthropoda Echinodermata
A. Origin of Animals 1. Animals are believed to have evolved from colonial protozoans called choanoflagellates
B. Characteristics 1. Eukaryotic 2. Multicellular 3. Heterotrophic
4. Lack Cell Walls
5. Diploid
C. Classification 1. Sponges (Porifera) 2. Stinging Celled (Cnidaria)
3. Flatworms (Platyhelminthes)
4. Roundworms (Nematoda) 5. Soft Bodied (Mollusca) 6. Segmented Worms (Annelida) 7. Jointed Leg (Arthropoda) 8. Spiny Skin (Echinodermata) 9. Vertebrates (Chordata)
A. Porifera Diversity 1. There are 9,000 known species of sponges B. Characteristics 1. Resemble a porous tube with many incurrent opennings (ostia) one excurrent opening (osculum) 2. Lack true tissue 3. Body consists of two layers of cells a. outer: protection b. inner: collar cells c. between: amoebocytes in jelly-like material
C. Classification 1. There are 3 classes of porifera
D. Habitat 1. Adults are sessile- anchored to the ocean floor 2. Feed on filtered particles (bacteria) 3. Larvae swim with flagella
a. outer: protection b. inner: collar cells c. between: amoebocytes in jelly-like material
B. Characteristics 1. Resemble a tube with one opening 2. Lack true tissue 3. Body consists of two layers of cells
a. calcarea- calcium carbonate spicules b. demospongia- spongin fibers c. hexactinellida- calcium carbonate & silica spicules
C. Classification 1. There are 3 classes of porifera
Cnidaria A. Diversity B. Characteristics C. Classification
D. Habitat
A. Diversity 1. There are 9,000 known species of stinging celled animals (formerly coelenterata)
B. Characteristics 1. True tissues 2. Radial symmetry
3. Use tentacles with stinging cells to capture prey
4. Food is digested in a gastrovascular cavity 5. Nerve net allows for sensing 6. Polyp anchored* 7. Medusa free-swimming**
C. Classification 1. There are 3 classes of cnidarians a. hydrozoa- hydra b. scyphozoans- jellyfish c. anthozoans- sea anemones 2. Phylum Ctenophora
a. comb jellies (colloblasts)
D. Habitat 1. Most are slow moving or sessile 2. Found in tropical and temperate waters a. shallow ocean floors b. bottoms of ponds c. drifting in water currents 3. Feed on small fish/plankton.
B. Characteristics 1. True tissues 2. Radial symmetry
3. Use tentacles with stinging cells to capture prey
Platyhelminthes A. Diversity B. Characteristics C. Classification
D. Habitat
A. Diversity 1. There are 20,000 known species of flatworms
B. Characteristics 1. Three tissue layers 2. Bilateral symmetry
3. Food is digested in a gastrovascular cavity
4. Moves using cilia on ventral side a. muscles allow twisting and turning 5. Centralized nervous system a. eye spots detect light
b. side flaps used for smell
B. Characteristics 1. Three tissue layers
a. endoderm (digestive) b. mesoderm (muscle) c. ectoderm (skin)
B. Characteristics 1. Three tissue layers
B. Characteristics 1. Three tissue layers
a. anterior (head) b. posterior (tail) c. dorsal (back)
B. Characteristics 1. Three tissue layers
d. ventral (belly)
C. Classification 1. There are 3 classes of platyhelminthes a. turbellaria- planarians b. trematoda- flukes c. cestoidea- tapeworms
D. Habitat 1. 2. Freshwater and Marine Some are parasitic
Nematoda A. Diversity B. Characteristics C. Classification
D. Habitat
A. Diversity 1. There are 15,000 known species of roundworms
B. Characteristics 1. 2. Pseudocoelom false body cavity Complete digestive system
C. Classification 1. There are 2 classes of nematoda a. Secernentea- ascaris, Guinea worm, heartworm, hookworm, lungworm, pinworm b. Adenophorea- trichinella, whipworm
D. Habitat 1. 2. 3. Aquatic Freshwater and marine Terrestrial soil and around plant roots Internal Parasites
Mollusca A. Diversity B. Characteristics C. Classification
D. Habitat
A. Diversity 1. There are 150,000 known species of soft bodied animals
B. Characteristics 1. 2. Open circulatory system Muscular Foot - locomotion
3.
4.
Radula scrapes food
Mantle secretes shell
C. Classification 1. 2. 3. Gastropod snails and slugs Bivalve clams, oysters, mussels, scallops Cephalopods squid, octopus, cuttlefish, nautilus
D. Habitat 1. 2. Aquatic freshwater and marine Few are terrestrial
Annelida A. Diversity B. Characteristics C. Classification
D. Habitat
A. Diversity 1. There are 15,000 known species of segmented worms
B. Characteristics 1. True Coelom a. Pharynx, Esophagus, Crop, Gizzard, Intestines 2. Closed circulatory system a. 5 aortic arches b. ventral artery
c. dorsal vein
3. Bristle-like setae (8 per segment) 4. Ventral nerve cord 5. Nephridia excrete waste (2 per segment)
C. Classification 1. 2. Polychaeta Bristleworms Oligochaeta - Earthworm
3.
Hirudinea - Leeches
D. Habitat 1. 2. Aquatic mostly marine Terrestrial
3.
External parasites
Arthropoda A. Diversity B. Characteristics C. Classification
D. Habitat
A. Diversity 1. There are 1,000,000 known species of jointed leg animals
B. Characteristics 1. 2. Jointed Legs Exoskeleton made of chitin
3.
4.
Segmented body
Open circulatory system_
C. Classification 1. Arthropods are classified into 4 classes a. crustaceans b. arachnids c. insects d. myriapods
2. Crustaceans include decapods (lobsters, crayfish, crabs, & shrimp), Isopods, Copepods and Barnacles
3. Arachnids include spiders, ticks, mites, and scorpions
Echinodermata A. Diversity B. Characteristics C. Classification
D. Habitat
A. Diversity 1. There are 7,000 known species of spiny skinned animals
B. Characteristics 1. 2. 3. 4. Water vascular system Tube feet used for feeding and locomotion Appear to have radial symmetry as adults Deuterostome
C. Classification 1. 2. Sea Stars Brittle Stars
3.
4. 5.
Sea Cucumbers
Sand Dollars Sea Urchin
D. Habitat 1. Marine
Brittle Star
Sea Star
Sea Cucumber
Sea Cucumber
Sea Cucumber
Sand Dollar
Sea Urchin
Sea Urchin
Sea Basket
Chordata A. Diversity B. Characteristics C. Classification
D. Habitat
A. Diversity 1.
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (120)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Chapin Columbus DayDocumento15 páginasChapin Columbus Dayaspj13Ainda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Dummies Guide To Writing A SonnetDocumento1 páginaDummies Guide To Writing A Sonnetritafstone2387100% (2)
- Sample Behavioral Interview QuestionsDocumento3 páginasSample Behavioral Interview QuestionssanthoshvAinda não há avaliações
- Spanish ProjectDocumento32 páginasSpanish Projectf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- KYC - AML - Oct, 13Documento7 páginasKYC - AML - Oct, 13f1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- RealOptionValuations FMUSSDocumento8 páginasRealOptionValuations FMUSSf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Deposit Accounts - Sep, 13Documento5 páginasTypes of Deposit Accounts - Sep, 13f1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Double Entry Journal 2Documento2 páginasDouble Entry Journal 2f1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Deposit Accounts - Sep, 13Documento5 páginasTypes of Deposit Accounts - Sep, 13f1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Entropy: Information Theory and Dynamical System PredictabilityDocumento38 páginasEntropy: Information Theory and Dynamical System Predictabilityf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- FDR's New DealDocumento43 páginasFDR's New Dealf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Summer Reading AssignmentDocumento3 páginasSummer Reading Assignmentf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Vegetron Case - 7th Ed. - Template - 1Documento26 páginasVegetron Case - 7th Ed. - Template - 1f1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Portfolio Optimization - Boddie - Previous EdDocumento2 páginasPortfolio Optimization - Boddie - Previous Edf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- History Freshman Project EssayDocumento5 páginasHistory Freshman Project Essayf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Cultural Political AlignmentsDocumento1 páginaCultural Political Alignmentsf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Black-Scholes Abandon ProjectDocumento4 páginasBlack-Scholes Abandon Projectf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Invertebrates HDocumento262 páginasInvertebrates Hf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Management of Severe or Dangerous HeadachesDocumento10 páginasManagement of Severe or Dangerous Headachesf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Entropy: Information Theory and Dynamical System PredictabilityDocumento38 páginasEntropy: Information Theory and Dynamical System Predictabilityf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Vertebrates - HDocumento188 páginasVertebrates - HehshonorsbioAinda não há avaliações
- Summer Acceleration Application 2013Documento1 páginaSummer Acceleration Application 2013f1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- GATEway Flyer Reg - 2013Documento7 páginasGATEway Flyer Reg - 2013f1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- MemoirDocumento4 páginasMemoirf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Traybon Martin CaseDocumento1 páginaTraybon Martin Casef1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Vertebrates: Fishes Amphibians Reptiles Birds MammalsDocumento8 páginasVertebrates: Fishes Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammalsf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- AVC RadiologiaDocumento19 páginasAVC Radiologiaf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Sources of Long Term Finance 1194352169348636 3Documento21 páginasSources of Long Term Finance 1194352169348636 3glyssaenAinda não há avaliações
- Hello WorldDocumento1 páginaHello Worldf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Writing Research Reports: Written Analysis and CommunicationDocumento39 páginasWriting Research Reports: Written Analysis and Communicationf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Writing Research Reports: Written Analysis and CommunicationDocumento39 páginasWriting Research Reports: Written Analysis and Communicationf1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- 1524298Documento54 páginas1524298f1940003Ainda não há avaliações
- Thomas Noochan Pokemon Review Final DraftDocumento6 páginasThomas Noochan Pokemon Review Final Draftapi-608717016Ainda não há avaliações
- Test 1Documento9 páginasTest 1thu trầnAinda não há avaliações
- StatisticsAllTopicsDocumento315 páginasStatisticsAllTopicsHoda HosnyAinda não há avaliações
- DHBVNDocumento13 páginasDHBVNnitishAinda não há avaliações
- 15.597 B CAT en AccessoriesDocumento60 páginas15.597 B CAT en AccessoriesMohamed Choukri Azzoula100% (1)
- Conceptual Diagram of Ways To Increase SalesDocumento1 páginaConceptual Diagram of Ways To Increase SalesO6U Pharmacy RecordingsAinda não há avaliações
- Grossman 1972 Health CapitalDocumento33 páginasGrossman 1972 Health CapitalLeonardo SimonciniAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To EthicsDocumento4 páginasIntro To EthicsChris Jay RamosAinda não há avaliações
- KBC Autumn Regatta 2023 Saturday Race ScheduleDocumento2 páginasKBC Autumn Regatta 2023 Saturday Race SchedulezainAinda não há avaliações
- Morocco Top ScientistsDocumento358 páginasMorocco Top Scientistsa.drioicheAinda não há avaliações
- Different Types of Classrooms in An Architecture FacultyDocumento21 páginasDifferent Types of Classrooms in An Architecture FacultyLisseth GrandaAinda não há avaliações
- Order of Magnitude-2017Documento6 páginasOrder of Magnitude-2017anon_865386332Ainda não há avaliações
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV) : Presented By: Laith AbbasDocumento30 páginasNetwork Function Virtualization (NFV) : Presented By: Laith AbbasBaraa EsamAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Kartikeya Thadani Reg No.: 19bma0029Documento4 páginasName: Kartikeya Thadani Reg No.: 19bma0029Kartikeya ThadaniAinda não há avaliações
- PT - Science 5 - Q1Documento4 páginasPT - Science 5 - Q1Jomelyn MaderaAinda não há avaliações
- Alcatraz Analysis (With Explanations)Documento16 páginasAlcatraz Analysis (With Explanations)Raul Dolo Quinones100% (1)
- SEW Products OverviewDocumento24 páginasSEW Products OverviewSerdar Aksoy100% (1)
- Electronic ClockDocumento50 páginasElectronic Clockwill100% (1)
- Understanding SIP RE-INVITEDocumento6 páginasUnderstanding SIP RE-INVITESK_shivamAinda não há avaliações
- Sayyid DynastyDocumento19 páginasSayyid DynastyAdnanAinda não há avaliações
- LM213 First Exam Notes PDFDocumento7 páginasLM213 First Exam Notes PDFNikki KatesAinda não há avaliações
- CAP214 Web Devlopment PDFDocumento9 páginasCAP214 Web Devlopment PDFAlisha AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- SQ1 Mogas95Documento1 páginaSQ1 Mogas95Basant Kumar SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- Togaf Open Group Business ScenarioDocumento40 páginasTogaf Open Group Business Scenariohmh97Ainda não há avaliações
- Nandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Documento336 páginasNandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Digitaladda IndiaAinda não há avaliações
- Contoh RPH Ts 25 Engish (Ppki)Documento1 páginaContoh RPH Ts 25 Engish (Ppki)muhariz78Ainda não há avaliações
- Weill Cornell Medicine International Tax QuestionaireDocumento2 páginasWeill Cornell Medicine International Tax QuestionaireboxeritoAinda não há avaliações