Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
IHRM PPT - 2
Enviado por
dharm287Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
IHRM PPT - 2
Enviado por
dharm287Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
IHRM is the interplay among three dimensions HR activities,types of employees,and countries of operation. 1.
. The three broad activities of IHRM,namely procurement,allocation and utilising cover all the six activities of domestic HRM.The six functions of domestic HRM are HR planning,employee hiring,training and development,remuneration,performance management, and industrial relations. 2. The three national or country categories involved in IHRM activities are the host country ,the home country and other countries.
3. The three types of employees of an international business are host country nationals, parent country nationals, and third country nationals. For ex IBM which employs Australian citizen in its Australian operations, often sends US citizen to Asia- Pacific countries on assignment, and may send some of its Singaporean employees to its Japanese operations. Host country where a subsidiary is located Home country where the company has its headquarters. And Other countries that may be the source of labour and finance.
Domestic HRM and IHRM compared The main characterstics of IHRM are 1. More HR activities 2. Need for a broader perspective 3. More involvement in employee personal lives. 4. Changes in emphasis as the workforce mix of expatriates and locals vary. 5. Risk exposure, and 6. More external influences
International businesses adopt three approaches to staffing Ethnocentric Approach all key management positions are held by parent country nationals, more appropriate during the early phases of international business. Polycentric Approach the polycentric staffing requires host country nationals to be hired to manage subsidiaries, while parent country nationals occupy key positions at corporate headquarters. Geocentric Approach this staffing criteria seeks the best people for key jobs throughout the organization, regardless of nationality.
The Expatriate Problem
Life cycle of an expatriate assignment - Determining the need for an expatriate assignment - Identifying and then selecting likely candidates. - Pre assignment training - Departure - Post arrival orientation and training - Crisis and adjustment of crisis and failure - Assignment aboard or repatriation and adjustment.
Reasons for Expatriot failure
.
US Firms Inability of spouse to adjust Managers inability to adjust Other family reasons Personal or emotional maturity Inability to cope with larger international responsibilites.
Japanese Firms Inability to cope with larger international responsibilities Difficulties with the environment Personal or emotional problems Lack of technical competence Inability of spouse to adjust
Factors in Expatriate Selection Individual Technical Ability Cross Cultural Suitability Family Requirements Situation Country cultural requirements Language MNC requirements
Factors influencing international compensation
MNC internal environment
Goal orientation Capacity to pay Competetive strategy Organisational culture Internal workforce composition - Labour relations - Subsidiary role
MNC external environment
Parent nationality Labour market Local culture Competitors strategy
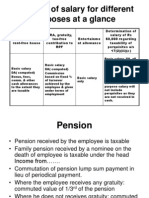
Components of Expat Compensation 1.Base salary 2.Benefits 3.Allowances 4.Incentives 5.Taxes
Base salary - is the primary component of a packages of allowances many of which are directly related to the base salary (e.g. foreign service premium,cost of living index,housing allowance ) as well as the basis for in service benefits and pension contributions. Benefits major element of remuneration. Issues Include 1.Whether MNCs should maintain expatriates in the home country benefits programmes, particularly if these prog are not tax deductible;
2. Whether MNCs have the option of enrolling expatriates in the host country benefits 3. Whether host country legislations regarding termination of employment affects the employee benefits entitlement. 4. Whether home country or the host country is responsible for the social security benefits, which country should pay the benefits; Allowances one common allowance is the payment for differences between the home country and the overseas assignment. This allowance is designed to provide standard of living that he or she enjoyed in the home country, and it may include expenses such relocation, housing, education and hardship.
Taxes MNCs generally select one of the following approaches to handle international taxation : 1. Tax equalisation firms withhold an amount equal to the home country tax obligation of the expatriate, and pay all the taxes in the host country. 2. Tax protection the employee pays up to the amount of taxes he or she would pay on remuneration in the home country.
Você também pode gostar
- SalaryDocumento13 páginasSalarydharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- B4002job AnalysisDocumento19 páginasB4002job Analysisdharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- Job AnalysisDocumento8 páginasJob Analysisdharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- Advertising Legends - Bill Bernbach: BeginningsDocumento5 páginasAdvertising Legends - Bill Bernbach: Beginningsdharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 6 SDMDocumento34 páginasModule 6 SDMdharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- Shop Floor PlanningDocumento19 páginasShop Floor Planningdharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- Shop Floor PlanningDocumento19 páginasShop Floor Planningdharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- SH Aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa AreDocumento82 páginasSH Aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa Aredharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- Advertising & Society: - Brand Communication in India Is Like SnakeDocumento15 páginasAdvertising & Society: - Brand Communication in India Is Like Snakedharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- Advertising: - Defining Advertising - Need - Scope - ObjectivesDocumento16 páginasAdvertising: - Defining Advertising - Need - Scope - Objectivesdharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- Module-3 Part 2SCSDocumento6 páginasModule-3 Part 2SCSdharm287Ainda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Skills Development & Employment Equity - ACTOMDocumento8 páginasSkills Development & Employment Equity - ACTOMDevon Antony HeuerAinda não há avaliações
- PaySlip of JanuaryDocumento1 páginaPaySlip of JanuaryBharat YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Gr7 Outline & Essay - Task 4Documento2 páginasGr7 Outline & Essay - Task 4Vũ Nhật MinhAinda não há avaliações
- Organizational Behavioral Practices in Aci Pharamaciutical Ltd.Documento36 páginasOrganizational Behavioral Practices in Aci Pharamaciutical Ltd.tsopuewu0% (2)
- Case #1 - Manila Electric Co. V QuisimbingDocumento9 páginasCase #1 - Manila Electric Co. V QuisimbingChey DumlaoAinda não há avaliações
- HOLIDAY INN MANILA v. NLRCDocumento2 páginasHOLIDAY INN MANILA v. NLRCrobbyAinda não há avaliações
- Macroeconomic Stability, Inclusive Growth and Employment: Thematic Think Piece Ilo, Unctad, Undesa, WtoDocumento12 páginasMacroeconomic Stability, Inclusive Growth and Employment: Thematic Think Piece Ilo, Unctad, Undesa, WtoKasun DulanjanaAinda não há avaliações
- CSC Form 7 (Inspired) - School Clearance-1Documento3 páginasCSC Form 7 (Inspired) - School Clearance-1Angel Agnes MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Peter Viney, Karen Viney - Handshake WorkbookDocumento88 páginasPeter Viney, Karen Viney - Handshake WorkbookFrancesco Castagna100% (2)
- 01-LUS-HSE-WG3-432-001.19 - Lusail HSE General RequirementsDocumento38 páginas01-LUS-HSE-WG3-432-001.19 - Lusail HSE General RequirementsthomsonAinda não há avaliações
- Saint Mary's UniversityDocumento2 páginasSaint Mary's Universityjun junAinda não há avaliações
- RECRUITMENT AND SELECTION McqsDocumento6 páginasRECRUITMENT AND SELECTION Mcqsalostguy1100% (1)
- Assessment Application Form 1Documento2 páginasAssessment Application Form 1jelly marie floresAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting For LaborDocumento21 páginasAccounting For LaborCharlaign MalacasAinda não há avaliações
- Becmen Service Exporter and Promotion V Cuaresma Case DigestDocumento4 páginasBecmen Service Exporter and Promotion V Cuaresma Case DigestMaricris GalingganaAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Nekepte 2Documento18 páginasRevised Nekepte 2theodrosbaby100% (1)
- Questionnaire Job StressDocumento3 páginasQuestionnaire Job Stressprktharani100% (1)
- Job Interview PreparationDocumento26 páginasJob Interview PreparationShah VickyAinda não há avaliações
- SAQA US 15034 - Confined SpaceDocumento3 páginasSAQA US 15034 - Confined Spacejacobus_louw4329Ainda não há avaliações
- Ambit Engineering Salary Contract Rate Index August 2013Documento17 páginasAmbit Engineering Salary Contract Rate Index August 2013Marino CrisAinda não há avaliações
- (Update) Chapter 10 - Inheritance and PolymorphismDocumento4 páginas(Update) Chapter 10 - Inheritance and PolymorphismEng SayidAinda não há avaliações
- Final Project Report Format SY HRMDocumento6 páginasFinal Project Report Format SY HRMyogeshthakurAinda não há avaliações
- International HRM-British AirwaysDocumento20 páginasInternational HRM-British AirwaysShreyankaRai100% (2)
- IMPORTANCE of TrainingDocumento7 páginasIMPORTANCE of Trainingshaikhelina1595Ainda não há avaliações
- Free Modern HR Presentation TemplateDocumento8 páginasFree Modern HR Presentation TemplatetaraselvamAinda não há avaliações
- A Note On Amendment To The Payment of Bonus ActDocumento3 páginasA Note On Amendment To The Payment of Bonus Actjaskaran singhAinda não há avaliações
- Key Functions of An HR DepartmentDocumento12 páginasKey Functions of An HR Departmentaiman MAinda não há avaliações
- Contractor's Red Book - EHSSQ Requirement PDFDocumento90 páginasContractor's Red Book - EHSSQ Requirement PDFAhmedHussainQureshiAinda não há avaliações
- 20170927090928talent Management W2Documento19 páginas20170927090928talent Management W2Bum MieAinda não há avaliações
- UAE Qualifications FrameworkDocumento8 páginasUAE Qualifications FrameworkTonyP1958Ainda não há avaliações