Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Dasar Opamp
Enviado por
Maulana HidayatullahDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Dasar Opamp
Enviado por
Maulana HidayatullahDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
KULIAH MINGGU ke 9
Elektronika Dasar
1
OPERASIONAL AMPLIFIER
OP-AMP
Jurusan Teknik Elektro
2012
2
Op-amp : suatu IC analog
+
_
Input 1
Input 2
output
+ V
CC
- V
EE
SIMBOL
SIFAT IDEAL
3
Ideally,
1. No current can enter terminals
V
+
or V
-
. Called infinite input
impedance.
2. V
out
=A(V
+
- V
-
) with A
3. In a circuit
V
+
is forced equal to V
-
4. An opamp needs two voltages
to power it V
cc
and -V
ee
.
A
V
OUT
= (AV - AV )
= A (V - V )
+
+
-
-
4
Operational Amplifier (Op Amp)
An operational amplifier (Op Amp)
is an integrated circuit of a
complete amplifier circuit.
Op amps have an extremely high
gain (A=10
5
typically).
Op amps also have a high input
impedance (R=4 M , typically)
and a low output impedance
(in order of 100 , typically) .
-
+
V
i1
V
out
A
B
V
i2
( )A V V V
i i out 1 2
=
5
Characters of Operational
Amplifiers
high open loop gain
high input impedance
low output impedance
low input offset voltage
low temperature coefficient of
input offset voltage
low input bias current
wide bandwidth
large common mode rejection
ratio (CMRR)
1 2 3 4
8
7 6 5
Offset null
Offset null
Not used
6
Q1 Q2
D1
D2
Q3
R
2
R
1
R
3
R
4
Q5
C1
R
5
Q4
7
8
Voltage Output from an Amplifier
The linear range of an
amplifier is finite, and limited
by the supply voltage and the
characteristics of the
amplifier.
A
Linear
region
Non-linear
region
V
out
V
in
Daerah Linier ini sangat Kecil
If an amplifier is driven
beyond the linear range
(overdriven), serious errors
can result if the gain is
treated as a constant.
Kalau A = 10
6
dan V
CC
= 12 Volt
maka daerah linier = 24 V
V
in
= V
2
-V
1
OPAMP: COMPARATOR
(bekerja di daerah jenuh)
9
V
out
=A(V
in
V
ref
)
If V
in
>V
ref
, V
out
= + but practically
hits +ve power supply = V
cc
If V
in
<V
ref
, V
out
= - but practically
hits ve power supply = -V
ee
V
cc
-V
ee
V
IN
V
REF
Application: detection of a complex signal in ECG
A (gain)
very high
V
out
A
10
OPAMP: ANALYSIS
The key to op amp analysis is simple
1. No current can enter op amp input terminals.
=> Because of infinite input impedance
2. The +ve and ve (non-inverting and inverting)
inputs are forced to be at the same potential.
=> Because of infinite open loop gain
3. Use the ideal op amp property in all your
analysis
11
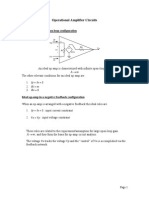
Inverting Amplifier
(bekerja di daerah linier)
Point B is grounded, point A is
called Virtual Grounded.
Voltage across R
1
is V
in
, and
across R
F
is V
out.
The output node voltage
determined by Kirchhoff's
Current Law (KCL).
Circuit voltage gain determined
by the ratio of R
1
and R
F.
1
R
R
V
V
G
F
in
out
= =
-
+
V
in
V
out
R
1
R
F
A
B
F
F
R R
R R
R
+
=
1
1
3
12
PENGUAT INVERTING
(bekerja di daerah linier)
Kondisi fisik
1
R
2
R
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
input
output
R
3
13
OPAMP: INVERTING
AMPLIFIER
1. V
-
= V
+
2. As V
+
= 0, V
-
= 0 (VG)
3. As no current can
enter V
-
and from
Kirchoffs Ist law, I
1
=I
2
.
4. I
1
= (V
IN
- V
-
)/R
1
= V
IN
/R
1
5. I
2
= (0 - V
OUT
)/R
2
= -V
OUT
/R
2
=> V
OUT
= -I
2
R
2
6. From 3 and 6, V
OUT
= -I
2
R
2
= -I
1
R
2
= -V
IN
R
2
/R
1
(NEG)
7. Therefore V
OUT
= (-R
2
/R
1
)V
IN
14
Analysis of Inverting Amplifier
Ideal transfer characteristics:
-
+
V
in
V
out
R
1
R
F
A
B
R
i
+
i
F
i
1
i
-
-
0 = =
+
i i
+
=V V
F F
i i i i = + =
1
F
out
F
IN
R
V V
i and
R
V V
i
=
=
1
1
0 0 0 = = =
+ +
V V i
F
out IN
R
V
R
V
=
1
or
1
R
R
V
V
F
in
out
=
V
IN
KCL at A:
15
OPAMP: NON INVERTING AMPLIFIER
(bekerja di daerah linier)
1. V
-
= V
+
2. As V
+
= V
IN
, V
-
= V
IN
3. As no current can enter
V
-
and from Kirchoffs Ist
law, I
1
=I
2
.
4. I
1
= V
x
/R
1
=V
IN
/R
1
5. I
2
= (V
OUT
- V
IN
)/R
2
V
OUT
= V
IN
+ I
2
R
2
6. V
OUT
= I
1
R
1
+ I
2
R
2
= (R
1
+R
2
)I
1
= (R
1
+R
2
)V
IN
/R
1
7. Therefore V
OUT
= (1 + R
2
/R
1
)V
IN
(tak berlawanan)
V
x
16
Op-amp circuit is a voltage divider.
Noninverting Amplifier
-
+
V
in
V
out
R
1
R
F
A
B
F
out A
R R
R
V V
+
=
1
1
1
1
R
R
V
V
G
F
in
out
+ = =
Circuit voltage gain determined by the ratio of R
1
and R
F.
Point V
A
equals to V
in
.
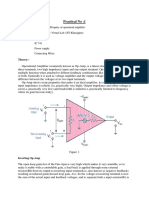
OPAMP : VOLTAGE FOLLOWER (BUFER)
(bekerja di daerah linier)
17
V
+
= V
IN
.
V
-
= V
+
Thus V
out
= V
-
= V
+
= V
IN
!!!!
So whats the point ?
The point is, due to the infinite input impedance of
an op amp, no current at all can be drawn from
the circuit before V
IN
. Thus this part is effectively
isolated.
Very useful for interfacing to high impedance
sensors such as microelectrode, microphone
i =0
18
Differential Amplifier
Point B is grounded, so does point A
(very small).
Voltage across R
1
is V
1
, and across R
2
is V
2.
Normally: R
1
= R
2
, and R
F
= R
3.
Commonly used as a single op-amp
instrumentation amplifier.
) (
1 2
1
V V
R
R
V
F
out
=
R
F
-
+
V
1
V
out
R
1
A
B
R
3
V
2
R
2
19
Analysis of an Instrumentation
Amplifier
Design a single op-amp instrumentation
amplifier.
R
1
= R
2
, R
F
= R
3
Determine the instrumentation gain.
-
+
V
1
V
out
R
1
R
F
A
B
R
3
V
2
R
2
A
F
OUT A A
i
R
V V
R
V V
1
1
3 2
2
R
V
i
R
V V
B
B
B
= +
0 =
B A
i i
2
2
3 1
1
R
V V
R
V
R
V V
R
V V
B B
F
OUT A A
+
( ) ( ) ( )
1
1 2
R
V V V V
R
V V V
B A
F
B A OUT
=
) (
1 2
1
V V
R
R
V
F
out
=
B A
V V ~
SUMMING AMPLIFIER
(
+ + =
3
3
2
2
1
1
V
R
R
V
R
R
V
R
R
V
F F F
out
20
V
OUT
= -R
f
(V
1
/R
1
+ V
2
/R
2
+ + V
n
/R
n
)
I
f
Recall inverting
amplifier and
I
f
= I
1
+ I
2
+ + I
n
Summing amplifier is a good example of analog circuits serving as analog
computing amplifiers (analog computers)!
Note: analog circuits can add, subtract, multiply/divide (using logarithmic
components, differentiat and integrate in real time and continuously.
21
For the following circuit, calculate the
input resistance.
R1
Rf
R2
V
in
V
out
22
INSTRUMENTATION
AMPLIFIER
23
INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER
Inverting
amplifier
Non-inverting
amplifier
very high
input
impedance
- So, you can
connect to
sensors
Differential amplifier ->
it rejects common-mode
interference -> so you
can reject noise
Gain in the multiple stages: i.e.
High Gain so, you can
amplify small signals
INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER:
STAGE 1
24
I
1
Recall virtual ground of opamps
I
1
= (V
1
V
2
)/R
1
Recall no current can enter
opamps and Kirchoffs current law
I
2
= I
3
= I
1
Recall Kirchoffs voltage law
V
OUT
= (R
1
+ 2R
2
)(V
1
V
2
)/R
1
= (V
1
V
2
)(1+2R
2
/R
1
)
I
2
I
3
I
1
INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER:
STAGE 2
25
I
1
Recall virtual ground of opamps
and voltage divider
V
-
= V
+
= V
B
R
4
/(R
3
+ R
4
)
Recall no current can enter
opamps
(V
A
V
-
)/R
3
= (V
-
V
OUT
)/R
4
Solving,
V
OUT
= (V
A
V
B
)R
4
/R
3
I
2
I
3
V
A
V
B
26
INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER:
COMPLETE
V
OUT
= (V
1
V
2
)(1 + 2R
2
/R
1
)(R
4
/R
3
)
27
As force is applied on the sensor, the value of the variable resistor
changes which results in a specific voltage output.
Gain = Vout/Vin = 1 Resistor Values for the Inverting OP-Amp can
be changed to modify gain of converter or to amplify the signal of
interest.
Analog Signal Conditioner
(Current to Voltage Converter, LM-324)
+5 VDC
Sensor
Variable Resistor
4.7k
10k
10k
5k
V
out
0-5
VDC
I
1
I
2
I
3
28
KOMPARATOR
Rangkaian komparator digunakan untuk membandingkan
tegangan masukan dan tegangan referensi.
Tegangan keluaran hanya ada dua kondisi yaitu tegangan
tinggi atau rendah (negatif). Kondisi ini ditentukan oleh
besarnya tegangan masukan apakah lebih tinggi terhadap
tegangan referensi atau lebih rendah.
Persoalan dalam komparator sederhana adalah stabilitas. Bila
tegangan masukan bervariasi sekitar tegangan referensi maka
tegangan keluaran akan berubah-ubah tidak stabil.
Hal tersebut dapat dihilangkan dengan rangkaian schmitt.
29
KOMPARATOR SEDERHANA
30
KURVA HUBUNGAN TEGANGAN
Vi < Vr
Vo = +Vsat
Vi > Vr
Vo = -Vsat
Vr>0
31
KURVA HUBUNGAN TEGANGAN
Vi < Vr
Vo = +Vsat
Vi > Vr
Vo = -Vsat
Vi
Vo
Vr=0
32
KURVA HUBUNGAN TEGANGAN
Vi < Vr
Vo = +Vsat
Vi > Vr
Vo = -Vsat
Vi
Vo
Vr<0
33
STABILITAS KOMPARATOR
SEDERHANA
V
cc
/2
V
in
R
V
cc
R
Teganga
n
masukan
Tegangan
keluaran
V
CC
/2
34
RANGKAIAN SCHMITT
Positive Feedback
Rangkaian ini disebut komparator
Schmitt trigger.
Rangkaian resistor membuat positive
feedback.
R
V
out
R
V
out
/2
V
in
35
CARA KERJA Schmitt trigger
Anggap tegangan masukan kecil, tegangan keluaran menjadi tinggi.
Bila V
out
is 4 V, maka masukan non-inverting V
+
adalah 2 Volt.
Kondisi keluaran tetap selama V
in
kurang dari 2 Volt.
Bila V
in
diperbesar sehingga lebih besar dari 2 V, maka V
out
akan nol, dan V
+
akan
nol juga. Kondisi output ini akan tetap, selama V
in
lebih besar 2 V.
R
V
out
R
V
out
/2
V
in
36
TAK STABIL
37
STABIL
histerisis
38
STABIL
39
STABIL
40
RANGKAIAN dan OUTPUT
41
KETERANGAN SCHMITT
Schmitt trigger adalah sebuah aplikasi comparator yang
mengubah tagangan keluaran menjadi negatif bila
mtegangan masukan lebih besar tegangan referensi.
Kemudian menggunakan negative feedback untuk
mencegah agar tegangan keluaran tdk kembali ke
kondisi semula saat tegangan kembali kurang dari
tegangan referensi, sampai nanti masukan lebih kecil
dari yang ditentukan.
42
A
P
L
I
K
A
S
I
43
PERHITUNGAN
Kerja Schmitt trigger merupakan proses komparasi dengan
threshold ganda. Persamaan arus di titik A:
Karena hanya 2 pers, maka harus ada satu R yang ditentukan
dulu.
Ingat : V
out
= V
CC
saat V
in
diatas batas atas (V
2
)
V
out
= -V
EE
saat V
in
dibawah batas bawah (V
2
).
44
u
LM741
45
NOMOR KAKI
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
KESIMPULAN
Op-amp dapat digunakan sebagai :
1. Penguat INVERTING
2. Penguat NON INVERTING
3. BUFER
4. Penguat PENJUMLAH
5. Penguat INSTRUMENTASI
6. Pengubah ARUS KE TEGANGAN atau
sebaliknya
7. KOMPARATOR
53
PR
Buktikan rumus untuk menghitung R
1
, R
2
dan R
3
pada komparator Schmitt (slide 41), bila batas
atas dan batas bawah diketahui.
Rencanakanlah sebuah komparator Schmitt
dengan menggunakan sebuah op-amp, yang
menggunakan single supply 5 Volt. Batas
tegangan yang dideteksi adalah diatas 3 Volt
memberikan tegangan output tinggi, dan
dibawah 1 Volt menghasilkan tegangan output
rendah. Tentukan nilai R yang diperlukan.
54
Você também pode gostar
- Dasar OpampDocumento54 páginasDasar OpampAdri Muhaimin AfifAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Ainda não há avaliações
- Op Amp ApplicationDocumento24 páginasOp Amp ApplicationPutra ArisandyAinda não há avaliações
- Operational Amplifiers: Basic Building Block Black BoxDocumento27 páginasOperational Amplifiers: Basic Building Block Black BoxAyesha GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Nota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (3)
- Lic Lab ManualDocumento89 páginasLic Lab ManualKALAIMATHI100% (1)
- Differential Amplifier FundamentalsDocumento50 páginasDifferential Amplifier FundamentalsabhinavthedhimanAinda não há avaliações
- Analogue controller op-ampDocumento36 páginasAnalogue controller op-ampFaissalAinda não há avaliações
- Sistec: Sagar Group of InstitutionsDocumento28 páginasSistec: Sagar Group of InstitutionsdeeptimalviyaAinda não há avaliações
- OP-AMP APPLICATIONS: AMPLIFIERS, FOLLOWER, SUMMER & SUBTRACTORDocumento11 páginasOP-AMP APPLICATIONS: AMPLIFIERS, FOLLOWER, SUMMER & SUBTRACTORVijayakumar KAinda não há avaliações
- OpampDocumento36 páginasOpampjainamshahAinda não há avaliações
- Opamp LectureDocumento32 páginasOpamp Lecturesft_15Ainda não há avaliações
- L01 Operational AmplifierDocumento27 páginasL01 Operational AmplifierRamaDinakaranAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Operational AmplifiersDocumento32 páginasIntroduction to Operational Amplifiersjaya1816100% (1)
- ch-3 OpampDocumento12 páginasch-3 OpampS KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Op AmpsDocumento47 páginasOp Ampssuresh_karthik_9Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1 - Intro To Op AmpsDocumento14 páginasLecture 1 - Intro To Op AmpsRap JaviniarAinda não há avaliações
- Design An Inverting and Non Inverting Amplifier.Documento8 páginasDesign An Inverting and Non Inverting Amplifier.Sudeep NayakAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 - OpAmpDocumento7 páginasChapter 6 - OpAmpOm PrakashAinda não há avaliações
- Lic Unit 1 (1) eDocumento114 páginasLic Unit 1 (1) eganeshAinda não há avaliações
- Signal Conditioning Op-AmpsDocumento41 páginasSignal Conditioning Op-AmpsSaleem Haddad100% (1)
- Basic AppsDocumento10 páginasBasic AppsajayganeshAinda não há avaliações
- Makalah Signal ConditioningDocumento64 páginasMakalah Signal Conditioningw4w4n_s3mk4n1s4Ainda não há avaliações
- UNIT 3-Cluster - 4Documento67 páginasUNIT 3-Cluster - 4Anvesh MagantiAinda não há avaliações
- Expetiment 1 AIC (KTU)Documento7 páginasExpetiment 1 AIC (KTU)Kirti ArunAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter3 Op Amp (1) 80911Documento62 páginasChapter3 Op Amp (1) 80911Azman Mat HussinAinda não há avaliações
- Op Amp 2Documento14 páginasOp Amp 2Dhileepan SankarAinda não há avaliações
- Chap4 1 Op Amps2Documento26 páginasChap4 1 Op Amps2ADEL OUBAinda não há avaliações
- Third Analogue ElectronicsDocumento30 páginasThird Analogue ElectronicsKifaru Micro-electronicsAinda não há avaliações
- OPampDocumento16 páginasOPampDarshan Iyer NAinda não há avaliações
- Applications of OP AMPDocumento40 páginasApplications of OP AMPVarun VarmaAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT3 - Introduction To IC Technology - 290617 - EditedDocumento82 páginasUNIT3 - Introduction To IC Technology - 290617 - EditedKISHAN SHUKLAAinda não há avaliações
- Chap4a OpAmpDocumento37 páginasChap4a OpAmpAl AidenAinda não há avaliações
- Opaamp NewwwDocumento20 páginasOpaamp NewwwArpita SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- OPAMP741: Structure and Applications of the Operational Amplifier 741Documento45 páginasOPAMP741: Structure and Applications of the Operational Amplifier 741Rau Muống XàoAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On OP-AMPDocumento17 páginasPresentation On OP-AMPRashmi MittalAinda não há avaliações
- Djukarna Stkip Surya Serpong, BantenDocumento34 páginasDjukarna Stkip Surya Serpong, BantenjainamshahAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Table of ContentsDocumento15 páginas1 Table of ContentsDarkrunner ZerooAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Op-Amp PDFDocumento23 páginasIntroduction To Op-Amp PDFJeswant TSAinda não há avaliações
- Topik 10 - Op-AmpDocumento24 páginasTopik 10 - Op-AmpSulthan ShalahuddinAinda não há avaliações
- OPAMPDocumento24 páginasOPAMPEr Akhilesh SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Ics Basic SimulaDocumento47 páginasIcs Basic Simulasumi36117Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit - 6 Operational Amplifier: Fig.6.1 Symbol of Op-AmpDocumento12 páginasUnit - 6 Operational Amplifier: Fig.6.1 Symbol of Op-AmpJovita LasradoAinda não há avaliações
- Op Amp ReportDocumento57 páginasOp Amp ReportvenkateshAinda não há avaliações
- Operational AmplifierDocumento29 páginasOperational AmplifierTaha Al-abedAinda não há avaliações
- Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp)Documento26 páginasOperational Amplifier (Op-Amp)Md ArifAinda não há avaliações
- OPAMP Lab ReportDocumento8 páginasOPAMP Lab Reportsara khanAinda não há avaliações
- Aim Lab Used Components: Practical No:1Documento12 páginasAim Lab Used Components: Practical No:1Sominath HarneAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 7 Power Amplifier BBN 10205 (Done)Documento6 páginasLab 7 Power Amplifier BBN 10205 (Done)Zhamir ZhakwanAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment - 05Documento17 páginasExperiment - 05Sagar SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic AppsDocumento10 páginasBasic AppsHendra LeosuAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment - 4: Name: Sonu Kumar Keshri Roll No: 1904026 Section:ECE 1 Course Code: ECL3501Documento10 páginasExperiment - 4: Name: Sonu Kumar Keshri Roll No: 1904026 Section:ECE 1 Course Code: ECL3501Sonu Kumar KeshriAinda não há avaliações
- Intro Op AmpDocumento44 páginasIntro Op AmpNimish PrabhakarAinda não há avaliações
- LIC Manual PDFDocumento55 páginasLIC Manual PDFmekalajesiAinda não há avaliações
- Operational Amplifiers: Magic Rules Application ExamplesDocumento20 páginasOperational Amplifiers: Magic Rules Application ExamplesSami MagbobAinda não há avaliações
- Conditioning CircuitsDocumento57 páginasConditioning CircuitsakozyAinda não há avaliações
- LAB 1 Op AmpDocumento11 páginasLAB 1 Op AmpamirulAinda não há avaliações
- EEE 209 - Operational Amplifiers Lab ReportDocumento20 páginasEEE 209 - Operational Amplifiers Lab ReportLester Garcia100% (1)
- Will CHRO roles lead to more CEO positionsDocumento1 páginaWill CHRO roles lead to more CEO positionsMaulana HidayatullahAinda não há avaliações
- Product KeyDocumento1 páginaProduct Keymanoj_yadav191985Ainda não há avaliações
- DCS OverviewDocumento23 páginasDCS OverviewMaulana HidayatullahAinda não há avaliações
- Price List Produk Lab Listrik 2011Documento4 páginasPrice List Produk Lab Listrik 2011Maulana HidayatullahAinda não há avaliações
- Elektronika Dasar: Jurusan Teknik Elektro Fakultas Teknik UGM 2012Documento47 páginasElektronika Dasar: Jurusan Teknik Elektro Fakultas Teknik UGM 2012Maulana HidayatullahAinda não há avaliações
- Ir3245 PDFDocumento58 páginasIr3245 PDFMaulana HidayatullahAinda não há avaliações
- Create One-Line Diagram in ETAPDocumento36 páginasCreate One-Line Diagram in ETAPjopaypagas80% (35)
- Ourlog 8905Documento1 páginaOurlog 8905jazz72484Ainda não há avaliações
- SAAD Lab 3Documento27 páginasSAAD Lab 3Sondos SaidAinda não há avaliações
- Design Secrets of The Worlds Best e Government WebsitesDocumento17 páginasDesign Secrets of The Worlds Best e Government WebsitesKoGku AndreiAinda não há avaliações
- N270L3Documento6 páginasN270L3hotfuryAinda não há avaliações
- Firmware/OSDocumento2 páginasFirmware/OSFrankuu PalapagAinda não há avaliações
- Nxbook PDFDocumento256 páginasNxbook PDFzhenshisAinda não há avaliações
- Cfe 011Documento174 páginasCfe 011MUHAMMAD TAUFIQAinda não há avaliações
- Paper0406 Ducted FanDocumento8 páginasPaper0406 Ducted FanSCALPEL DRAWINGAinda não há avaliações
- M-DRO PC Digital Readout Interface: Technical InformationDocumento20 páginasM-DRO PC Digital Readout Interface: Technical InformationCarlos Gabriel EstergaardAinda não há avaliações
- Pass Task 3.1: Drawing Program - Drawing: Swinburne University of TechnologyDocumento9 páginasPass Task 3.1: Drawing Program - Drawing: Swinburne University of TechnologyHiếu PhanAinda não há avaliações
- PTC Creo Tolerance Analysis DatasheetDocumento3 páginasPTC Creo Tolerance Analysis DatasheetSajjad4434Ainda não há avaliações
- Impact of Practical Skills On Academic Performance A Data-Driven AnalysisDocumento20 páginasImpact of Practical Skills On Academic Performance A Data-Driven AnalysisMarcelino Halili IIIAinda não há avaliações
- NetSim 9 User ManualDocumento40 páginasNetSim 9 User ManualJose Miguel GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Sp. Reserve MagazineDocumento21 páginasSp. Reserve MagazineViraf DasturAinda não há avaliações
- Create Excel Files CDocumento29 páginasCreate Excel Files CSaka Kely100% (1)
- IBM Global Services - Training Center - Hortolândia: Mainframe: Z/VM ConceptsDocumento47 páginasIBM Global Services - Training Center - Hortolândia: Mainframe: Z/VM ConceptsDie001Ainda não há avaliações
- CRM BOL Z Creation FinalDocumento14 páginasCRM BOL Z Creation FinalKavindra Joshi100% (1)
- Chapter-5-Working With Typical Operating System BookbackanswerDocumento5 páginasChapter-5-Working With Typical Operating System BookbackanswervenusrinivassAinda não há avaliações
- Ic3 1Documento11 páginasIc3 1Ngô DiễmAinda não há avaliações
- Exporting Blender Models To ThreeJS and WebGLDocumento5 páginasExporting Blender Models To ThreeJS and WebGLGerman BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Car Audio DEH X2850UIDocumento2 páginasCar Audio DEH X2850UIDaniel MrzAinda não há avaliações
- Rms Keyboards Documentation v1.0: 4 Features 4 Download and Installation of Software 5Documento19 páginasRms Keyboards Documentation v1.0: 4 Features 4 Download and Installation of Software 5GeraintAinda não há avaliações
- Mikrobasic ManualDocumento207 páginasMikrobasic Manualfkimya100% (1)
- GTU Microcontroller Embedded Systems CourseDocumento2 páginasGTU Microcontroller Embedded Systems CourseAshok ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Blockchain Technology For Transparency in Agri-Food Supply Chain Use Cases, Limitations, and Future DirectionsDocumento15 páginasBlockchain Technology For Transparency in Agri-Food Supply Chain Use Cases, Limitations, and Future DirectionsJosé Arcenio Moreno MartínezAinda não há avaliações
- English 7 ModuleDocumento21 páginasEnglish 7 ModuleJaycelyn BaduaAinda não há avaliações
- Bentley Installation GuideDocumento15 páginasBentley Installation GuideToribioGomezAinda não há avaliações
- CpuDocumento1 páginaCpuAimee HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Credit Card Fraud Detection System Using CNNDocumento7 páginasCredit Card Fraud Detection System Using CNNIJRASETPublicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Amber Tools 12Documento535 páginasAmber Tools 12Anna VeraAinda não há avaliações