Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Signal Processing
Enviado por
Karthik V KalyaniDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Signal Processing
Enviado por
Karthik V KalyaniDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Basics of Signal Processing
SIGNAL SOURCE
RECEIVER
describe waves in terms of their significant features
understand the way the waves originate
effect of the waves
will the people in the boat notice ?
ACTION
frequency = 1/T
= speed of sound T, where T is a period
sine wave
period (frequency)
amplitude
phase
f (t) = Asin(2tt /T +|)
f (t) = Asin(et +|)
Asin(et + t /2)
= Acos(et)
sine cosine
Phase u
Sinusoidal grating of image
Fourier idea
describe the
signal by a sum
of other well
defined signals
T
O
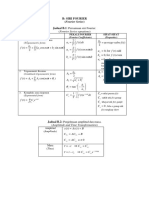
Fourier Series
A periodic function as an infinite weighted
sum of simpler periodic functions!
f (t) = w
i
i=0
f
i
(t)
A good simple function
T
i
=T
0
/ i
f
i
(t ) = sin(ie
0
t +|),
where e
0
= 2t / T
0
f (t) = k
i
sin(ie
0
i=1
+
n
)
= [b
i
i=1
sin(ie
0
) + a
i
cos(ie
0
)]
= Re
c
i
e
je
0
n
i=0
,
c complex
e.t.c. ad infinitum
f (t) = k
i
sin(ie
0
i=1
+
n
) = [b
i
i=1
sin(ie
0
) + a
i
cos(ie
0
)]
T=1/f
e.t.c
T=1/f
e.t.c
Fouriers Idea
Describe complicated function as a weighted sum of simpler functions!
-simpler functions are known
-weights can be found
Simpler functions - sines and cosines are orthogonal on period T, i.e.
f(mt) f(nt)
0
T
}
dt = 0 for m= n
period T period T
0
+
-
0
+
-
0
+
-
x
0
+ +
- -
x
0
+ +
=
0
+ +
- -
=
area is positive (T/2) area is zero
=
f(t) = DC + a
i
cos(
2tit
T
) +b
1
sin(
2tit
T
)
(
(
=
i=1
DC +a
1
cos(
2tt
T
) +b
1
sin(
2tt
T
) +a
2
cos(
4tt
T
) +b
2
sin(
4tt
T
) +a
3
cos(
6tt
T
) +b
3
sin(
6tt
T
) +.........
f(t)sin(
2tt
T
)dt
0
T
}
= {DC
0
T
}
sin(
2tt
T
) +a
1
cos(
2tt
T
)sin(
2tt
T
) +b
1
sin(
2tt
T
)sin(
2tt
T
) +a
2
cos(
4tt
T
)sin(
2tt
T
) +b
2
sin(
4tt
T
)sin(
2tt
T
) +.........} dt
0 0 b
1
T/2 0 0
area=b
1
T/2
area=b
2
T/2
f(t) =DC+f
1
(t) +f
2
(t) =DC+b
1
- sinet +b
2
- sin2et
sin
2
0
T
}
(
t
T
) dt =
T
2
T=2t
+
-
+ +
+ + + +
+
+
+
+
+ +
- -
- - - -
f(t)
f(t) sin(2t)
f(t) sin(4t)
area = DC area = b
1
T/2 area = b
2
T/2
Aperiodic signal
T
0
frequency spacing f
0
0
Discrete spectrum becomes continuous (Fourier integral)
0 1/T
0
2/T
0
frequency
0 1/T
0
2/T
0
frequency
Phase spectrum Magnitude spectrum
Spacing of spectral components is f
0
=1/T
0
sampling
22 samples per 4.2 ms 0.19 ms per sample 5.26 kHz
t
s
=1/f
s
Sampling
> 2 samples per period,
f
s
> 2 f
T = 10 ms (f = 1/T=100 Hz)
Sinusoid is characterized by three parameters
1. Amplitude
2. Frequency
3. Phase
We need at least three samples per the period
T = 10 ms (f = 1/T=100 Hz)
t
s
= 7.5 ms (f
s
=133 Hz < 2f )
Undersampling
T = 40 ms
(f= 25 Hz)
Sampling of more complex signals
period period
highest frequency
component
Sampling must be at the frequency which is higher than the
twice the highest frequency component in the signal !!!
f
s
> 2 f
max
Sampling
1. Make sure you know what is the highest
frequency in the signal spectrum f
MAX
2. Chose sampling frequency f
s
> 2 f
MAX
NO NEED TO SAMPLE ANY FASTER !
Periodicity in one domain implies discrete representation in the dual domain
0 1/T 2/T
frequency
Magnitude spectrum T
frequency
F
=1/t
s
f
s
= 1/T
time
t
s
T
Sampling in time implies periodicity in frequency !
=
=
1
0
2
1
) ( ) (
N
n
N
kn
j
N
e k X n x
t
=
1
0
2
1
) ( ) (
N
n
N
kn
j
N
e n x k X
t
Discrete and periodic in both domains (time and frequency)
DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM
Recovery of analog signal
Digital-to-analog converter (sample-and-hold)
Low-pass filtering
0.000000000000000
0.309016742003550
0.587784822932543
0.809016526452407
0.951056188292881
1.000000000000000
0.951057008296553
0.809018086192214
0.587786969730540
0.309019265716544
0.000000000000000
-0.309014218288380
-0.587782676130406
-0.809014966706903
-0.951055368282511
-1.000000000000000
-0.951057828293529
-0.809019645926324
-0.587789116524398
-0.309021789427363
-0.000000000000000
Quantization
11 levels
21 levels
111 levels
a part of vowel /a/
16 levels (4 bits) 32 levels (5 bits) 4096 levels (12 bits)
Quantization
Quantization error = difference between the
real value of the analog signal at sampling
instants and the value we preserve
Less error less quantization distortion
Você também pode gostar
- Basics of Signal Processing: Understanding Waves, Sampling, and Fourier AnalysisDocumento28 páginasBasics of Signal Processing: Understanding Waves, Sampling, and Fourier AnalysisNilesh PatilAinda não há avaliações
- 2203BPS - Final Exam2009 - Solutions (1) 2Documento7 páginas2203BPS - Final Exam2009 - Solutions (1) 2samAinda não há avaliações
- Ss Unit 4Documento32 páginasSs Unit 4yeluricharan27Ainda não há avaliações
- Week04Module03 FourierTransformsDocumento13 páginasWeek04Module03 FourierTransformsrra127Ainda não há avaliações
- XCFNNDocumento105 páginasXCFNNVenky MaxAinda não há avaliações
- SS Unit IVDocumento34 páginasSS Unit IVKarteek PattaswamiAinda não há avaliações
- Signals Sampling TheoremDocumento3 páginasSignals Sampling TheoremPranjal DubeyAinda não há avaliações
- ECE 5520 Lecture 2Documento37 páginasECE 5520 Lecture 2lamdinh261Ainda não há avaliações
- Handout - 02 (CT)Documento2 páginasHandout - 02 (CT)Mohian RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier Series NfcietDocumento11 páginasFourier Series Nfcietapi-19788618Ainda não há avaliações
- Solved Problems: EE160: Analog and Digital CommunicationsDocumento145 páginasSolved Problems: EE160: Analog and Digital CommunicationsZoryel Montano33% (3)
- Signals Sampling TheoremDocumento3 páginasSignals Sampling TheoremRavi Teja AkuthotaAinda não há avaliações
- Sampling: G GT GT TT GT TTDocumento5 páginasSampling: G GT GT TT GT TTsayed Tamir janAinda não há avaliações
- S&S L5Documento77 páginasS&S L5Aalaa Hussein HamidAinda não há avaliações
- Analog Communication - FM DemodulatorsDocumento3 páginasAnalog Communication - FM DemodulatorskhalidAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier Series PresentationDocumento81 páginasFourier Series PresentationRajithNimali100% (1)
- Fourier Series Lecture on Periodic Functions and Fourier Series DecompositionDocumento183 páginasFourier Series Lecture on Periodic Functions and Fourier Series DecompositionRameez ArshadAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Fourier SeriesDocumento43 páginas6 Fourier SeriesutpAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier Series Objectives and ExamplesDocumento17 páginasFourier Series Objectives and ExamplesShaundre NeoAinda não há avaliações
- CLC - Fourier Series and Integral FourierDocumento24 páginasCLC - Fourier Series and Integral FourierNam GiangAinda não há avaliações
- Unit IiDocumento39 páginasUnit IiAnbazhagan SelvanathanAinda não há avaliações
- 3.0 Fourier SeriesDocumento17 páginas3.0 Fourier SeriesKarmughillaan ManimaranAinda não há avaliações
- Ch6 SamplingDocumento70 páginasCh6 SamplingKushagra BhargavaAinda não há avaliações
- Ch6 Sampling PDFDocumento70 páginasCh6 Sampling PDFVarshaIyerAinda não há avaliações
- CongthucthhtDocumento5 páginasCongthucthhtcholachaAinda não há avaliações
- Signals Sampling TheoremDocumento8 páginasSignals Sampling TheoremSheelaj BabuAinda não há avaliações
- Convolution and system interconnectionsDocumento5 páginasConvolution and system interconnectionsGeorge KaragiannidisAinda não há avaliações
- Half-Wave Symmetry in Periodic SignalsDocumento2 páginasHalf-Wave Symmetry in Periodic Signalshussain ghaziAinda não há avaliações
- DemodulatorsDocumento2 páginasDemodulatorskhalidAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 - Fourier Analysis: J.R. Wilson January 7, 2018Documento15 páginasChapter 10 - Fourier Analysis: J.R. Wilson January 7, 2018Roy VeseyAinda não há avaliações
- SheetDocumento2 páginasSheetKardelen GündoğanAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier Series BreakdownDocumento21 páginasFourier Series BreakdownAina Rashidi0% (1)
- Ee 2006Documento44 páginasEe 2006Karuppusamy MariAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1Documento64 páginasLecture 1loochaoAinda não há avaliações
- Series de FourierDocumento2 páginasSeries de FourierJeanmarco Felipe Manrique PurizacaAinda não há avaliações
- Trigonometric Fourier Series & Fourier Series Properties: Spring 2014 Type The Document TitleDocumento10 páginasTrigonometric Fourier Series & Fourier Series Properties: Spring 2014 Type The Document TitleAbdul RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Analog Communication - Angle ModulationDocumento17 páginasAnalog Communication - Angle Modulationjeremy oswaldAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Fourier Series1Documento40 páginasChapter 3 Fourier Series1EyobAinda não há avaliações
- Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) : Mahendra Singh ThakurDocumento14 páginasAmplitude Shift Keying (ASK) : Mahendra Singh ThakurMahendra SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Measurement and InstrumentationDocumento61 páginasMeasurement and InstrumentationNikhil WaghalkarAinda não há avaliações
- Signals Basics ExplainedDocumento17 páginasSignals Basics ExplainedMaulinduAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet 1Documento1 páginaSheet 1Cem BizAinda não há avaliações
- SheetDocumento1 páginaSheetCem BizAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - Analog Communication Technique - AM ModulatorsDocumento5 páginas2 - Analog Communication Technique - AM ModulatorsasdqwAinda não há avaliações
- Ch4-Amplitude ModulationDocumento62 páginasCh4-Amplitude Modulationarchana belgeAinda não há avaliações
- GM Signal&systemDocumento93 páginasGM Signal&systemBhaskar SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter1 AssignmentDocumento2 páginasChapter1 Assignmentchanvikey0% (1)
- Linear Regression for Tidal Harmonic AnalysisDocumento23 páginasLinear Regression for Tidal Harmonic AnalysisShinta AyuningtyasAinda não há avaliações
- 3.Fourier series _gibbs phenomenaDocumento5 páginas3.Fourier series _gibbs phenomenaSPECIFIED With SIMFLIFICATIONAinda não há avaliações
- 27 First Order Circuit With Non Constant SourcesDocumento20 páginas27 First Order Circuit With Non Constant Sourceshirmay sandesaraAinda não há avaliações
- Attachment Fourier SeriesDocumento2 páginasAttachment Fourier Seriesahmad hazimAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier SeriesDocumento46 páginasFourier SeriesSiddhanth VenugopalAinda não há avaliações
- Seminar 0: Fourier Transform, Convolution, CorrelationDocumento2 páginasSeminar 0: Fourier Transform, Convolution, CorrelationDavid Omelette du FromageAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment#3Documento2 páginasAssignment#3Amit SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Productivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionNo EverandProductivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionAinda não há avaliações
- Tables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesNo EverandTables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesNo EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesNota: 1.5 de 5 estrelas1.5/5 (2)
- Solution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringNo EverandSolution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99Ainda não há avaliações
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Lab ReportDocumento28 páginasDSP Lab ReportKaaviyaAinda não há avaliações
- Load Flow Solution With Nominal Tap Setting: OutputDocumento10 páginasLoad Flow Solution With Nominal Tap Setting: OutputrajaAinda não há avaliações
- The MLbookDocumento160 páginasThe MLbookNick Corona100% (2)
- Chapter 3 SolutionsDocumento18 páginasChapter 3 SolutionsMichaelAinda não há avaliações
- ME4242 NeurocontrollersDocumento110 páginasME4242 NeurocontrollersSee Tze SamAinda não há avaliações
- Implementation of Singly Linked ListDocumento57 páginasImplementation of Singly Linked ListDeelip KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 2Documento2 páginasAssignment 2Faisal AtaAinda não há avaliações
- Autonomous Indoor Navigation Robot PDFDocumento15 páginasAutonomous Indoor Navigation Robot PDFAkshyaAinda não há avaliações
- Armitage & Ober. 2010Documento9 páginasArmitage & Ober. 2010lina maaria lopezAinda não há avaliações
- Regression Modeling Strategies - E-Bok - Frank E Harrell ... - BokusDocumento2 páginasRegression Modeling Strategies - E-Bok - Frank E Harrell ... - BokusasdlasjdlkaAinda não há avaliações
- Nonagonal Neutrosophic Numbers and Their Applications using TOPSISDocumento21 páginasNonagonal Neutrosophic Numbers and Their Applications using TOPSISAliAinda não há avaliações
- Path Planning Algorithms For Unmanned Aerial VehiclesDocumento4 páginasPath Planning Algorithms For Unmanned Aerial VehiclesEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Deep Learning For Image DenoisingDocumento10 páginasDeep Learning For Image DenoisingBusiness with EarthangerAinda não há avaliações
- The Enigma MachineDocumento12 páginasThe Enigma Machineapi-615372446Ainda não há avaliações
- Flood Frequency Analysis: Global Flood Risk Under Climate Change, 2013Documento9 páginasFlood Frequency Analysis: Global Flood Risk Under Climate Change, 2013Anwaar SafdarAinda não há avaliações
- Aliasing - Siemens PLM Community - 367750Documento8 páginasAliasing - Siemens PLM Community - 367750Vili KamenovaAinda não há avaliações
- Finite Element Primer For Engineers: Mike Barton & S. D. RajanDocumento26 páginasFinite Element Primer For Engineers: Mike Barton & S. D. Rajanibrahim alshaikhAinda não há avaliações
- Implementation of Neural Network Back Propagation Training Algorithm On FPGADocumento19 páginasImplementation of Neural Network Back Propagation Training Algorithm On FPGAMix RuksinAinda não há avaliações
- Input Output RevisionDocumento7 páginasInput Output Revisionarya SRAinda não há avaliações
- Isye 6669 HW 2: 1 2 3 3 I 1 I 2 I 1 4 J 2 Ij I 3 T 1 X T! 1 K 1 2 K 1 3 I 1 I J 1 I+J 4 N 2 N+2 M N N MDocumento2 páginasIsye 6669 HW 2: 1 2 3 3 I 1 I 2 I 1 4 J 2 Ij I 3 T 1 X T! 1 K 1 2 K 1 3 I 1 I J 1 I+J 4 N 2 N+2 M N N MMalik KhaledAinda não há avaliações
- MST Linear Programming FormulationDocumento3 páginasMST Linear Programming FormulationKushagra AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Resource Optimization:: Action PlanDocumento13 páginasResource Optimization:: Action Plangpatil1356Ainda não há avaliações
- ANN Lab ManualDocumento35 páginasANN Lab Manualsegnumutra100% (3)
- Finite DifferenceDocumento11 páginasFinite DifferenceAlex IskandarAinda não há avaliações
- Vo Van Duc (FGW DN) - 301625 - 0-Đã Chuyển ĐổiDocumento38 páginasVo Van Duc (FGW DN) - 301625 - 0-Đã Chuyển ĐổiĐức VănAinda não há avaliações
- r05320201 Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento8 páginasr05320201 Digital Signal ProcessingSRINIVASA RAO GANTAAinda não há avaliações
- B Tree Exo + SolDocumento5 páginasB Tree Exo + SolRe Sab RinaAinda não há avaliações
- Solver Ops Research Class 1Documento7 páginasSolver Ops Research Class 1Anupam DasAinda não há avaliações
- VTU - B Tech - 18mat21 Advanced Calculus and Numerical Methods - FirstRanker - Com 2Documento3 páginasVTU - B Tech - 18mat21 Advanced Calculus and Numerical Methods - FirstRanker - Com 2Monster ManAinda não há avaliações