Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
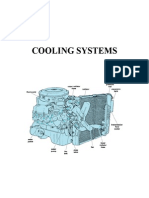
Engine Cooling Systems
Enviado por
Pujara ManishDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Engine Cooling Systems
Enviado por
Pujara ManishDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
5.
Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Engine Cooling Systems
This presentation will explore: Cooling Systems Cooling System Components Fans Coolant Characteristics
ClassAct SRS enabled.
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
What is (are) the function(s) of a cooling system?
Bring the engine to normal operating temperature as quickly as possible
Best performance Lower emissions
Maintain proper engine operating temperature Provides a means of warming the passenger compartment Next > This slide developed by
G.Giguere Jan. 2007
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
What are the two types of cooling systems commonly used on internal combustion engines?
Liquid cooled Air cooled View CDX Air and Liquid Cooling System video
Next >
This slide developed by G.Giguere Jan. 2007
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Air or Water
Cylinder air cooling fins.
Large surface area transfers heat to surrounding air.
Water jacket to circulate coolant.
Coolant / water and antifreeze mix.
Better control of engine temperature.
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Question 1
Which of the following is NOT expected to remove heat from a cylinder?
A) Engine block fins B) Transmission oil C) Water and antifreeze mixture D) Surrounding air
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Cooling System
Combustion (flame) temperatures in cylinders up to 4500F (2500C).
Normal coolant temperature 180-210F (80-100C).
Coolant radiates excess heat to the air.
This slide has been modified by Air flow is fan assisted. G.Giguere Jan. 2007
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Question 2
What is the normal maximum temperature of the coolant in a water cooled system?
A) 80 F B) 100 F C) 210 F D) 4500 F
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Water Pump
Leak (vent) bore
Drive pulley
Main shaft Seal
Bearings Impeller
Water pump housing
This slide has been modified by G.Giguere Jan. 2007
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Water Flow
Conventional coolant flow is upward past the cylinders.
Pipes to passenger compartment heater
Coolant flows out from cylinder head to radiator.
Water pump draws coolant from radiator and forces it back into cylinder block.
Reverse flow cooling is in opposite direction.
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Question 3
The water pump normally forces the coolant from the cylinder block through the radiator. Is this true or false?
Answer True or False.
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Radiator
Hoses connect radiator to cylinder block and heater.
Thermostat prevents coolant flow to the radiator during warm-up.
Radiator transfers heat to the outside air.
Fan(s) draw air through radiator.
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Thermostat
When cold - thermostat closed. Route to radiator cut off. Bypass allows coolant to circulate around engine. When hot - wax-filled pellet expands and opens thermostat. Coolant allowed to flow to radiator and by-pass port is blocked.
To top hose and radiator
When installing vertically mounted thermostats, be sure the vent is in the upper-most position.
By-pass port Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Question 4
What position will the thermostat be in just after the engine has been started first thing in the morning?
A) Half open B) Closed C) Open
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Downflow
Tanks are on top and bottom.
Coolant flows down through core tubes.
Core tubes
Coolant flows out of bottom tank back to engine.
Automatic transmission oil coolers are at bottom.
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Crossflow
Tanks are on sides.
Allows lower hood line.
Core tubes run horizontally.
Transmission oil cooler may be positioned in side tank.
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Question 5
Which of the following would indicate that you were looking at a crossflow radiator?
A) The core tubes are vertical B) The radiator is mounted horizontally C) The transmission oil cooler is at the bottom D) The tanks are on the sides
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Hoses
Flexible hoses carry coolant between radiator, engine block and heater core.
Upper hose from the radiator is connected to the cylinder head.
Hoses carry coolant to passenger compartment heater.
Lower hose from radiator is connected to water pump. Expansion tank keeps system topped up.
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Types of Hoses
Two types of radiator hoses: Molded (pre-formed), Flexible (universal).
Flexible type can be bent.
Support spring often fitted inside flexible hose.
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Question 6
A flexible hose can replace a molded hose as long as it is the same length and diameter. Is this true or false?
Answer True or False.
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Radiator Cap
Pressurizes system which raises the boiling point.
(3F per pound of pressure)
Pressure valve opens at specified pressure.
(See cap 12-16 psi)
Excess coolant released to expansion tank.
This slide has been modified by G.Giguere Jan. 2007
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Question 7
What would be the effect of a weak spring in a radiator cap?
A) Water would boil at a lower temperature B) Water would boil at a higher temperature C) The cap would fall off D) The engine would stop immediately
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Closed Cooling System
When engine is hot, excess coolant flows to expansion tank reservoir.
When engine cools, vacuum valve opens to allow coolant back to radiator top tank.
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Engine-Powered Fan
Main purpose is to generate air flow across radiator core tubes.
Bolts to water pump hub.
May have a spacer. Fluid coupling and thermostatic clutches slip when cooling fan action is unnecessary.
Coolant is below operating temperature and/or at high speeds
This slide has been modified by G.Giguere Jan. 2007
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Question 8
The principal function of an engine-powered fan is to blow air across the cylinder block. Is this true or false?
Answer True or False.
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Electric Cooling Fan
Temperature sending unit
Uses DC motor and thermostat switch. Low temperature: Low temperature indication.
Thermostat switch open.
High temperature:
High temperature indication. Thermostat switch closed. Current feeds fan motor.
Thermostat switch Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Question 9
Which of these statements about a thermostatic switch on an auto cooling system is true?
A) It controls the temperature display B) It turns the fan on when it is cold C) It is located at the highest point of the cooling system D) It is connected between the battery and the fan
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Antifreeze
Normal temperature range for water to remain liquid.
Boiling
Increases under pressure.
Advantages of antifreeze: Prevents winter freezing. Resists rust and corrosion. Lubricates water pump.
This slide has been modified by G.Giguere Jan 2007
Freezing
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Types of Antifreeze
Ethylene Glycol Based:
Extended Life (Organic Acid Technology)
Various colors
Dex-Cool (for GM and other specific makes)
Often orange
Both are highly toxic/deadly Sweet smelling and tasting
Propylene Glycol Based:
Environmentally Friendly (Low-Tox)
This slide developed by G.Giguere Jan 2007
Next >
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Antifreeze/Water Ratios
50/50 mix:
Most commonly recommended by automotive manufacturers Protects from about -34F to + about 265F
70/30 mix:
Protects from about -84F to about +276F
100% Antifreeze will slush at +10F Improper mix may cause an erroneous ECT input signal to PCM Next >
This slide developed by G.Giguere Jan. 2007
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Question 10
What is the effect of adding antifreeze to the cooling system?
A) Raising the freezing point of the water B) Lowers the boiling point of the water C) Lowers the freezing point of the water D) Increases corrosion in the engine block
5. Engine Cooling Systems Automotive Components & Operation
Summary
You should now be aware of: Cooling Systems
Cooling System Components
Fans
Coolant Characteristics
End >
Você também pode gostar
- Plant Utilities Assistant: Passbooks Study GuideNo EverandPlant Utilities Assistant: Passbooks Study GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Lect02 - Engine Cooling SystemDocumento19 páginasLect02 - Engine Cooling SystemMaunish Shah100% (1)
- Cooling SystemDocumento56 páginasCooling SystemPuneet Gautam100% (5)
- Automobile Engineering - Engine Cooling SystemsDocumento16 páginasAutomobile Engineering - Engine Cooling SystemsAhmed Zawad Shovon50% (2)
- Lecture 1 - Diesel Engine Power PlantDocumento60 páginasLecture 1 - Diesel Engine Power PlantbarryAinda não há avaliações
- Me Lab ReportDocumento20 páginasMe Lab ReportJassondemapan100% (1)
- 1) Introduction To Cooling System in IC Engine 2) Types of Cooling System A) Air Cooling System B) Water Cooling SystemDocumento21 páginas1) Introduction To Cooling System in IC Engine 2) Types of Cooling System A) Air Cooling System B) Water Cooling SystemRahul PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of OverheatingDocumento46 páginasEffects of OverheatingSajjad Hossain ShuvoAinda não há avaliações
- Cooling and Lubrication Systems PDFDocumento30 páginasCooling and Lubrication Systems PDFManprita Basumatary100% (1)
- Master CylinderDocumento2 páginasMaster CylinderAfit KenshyAinda não há avaliações
- Starting SystemDocumento21 páginasStarting SystemNikunj Yagnik100% (1)
- Basic Information, Diesel EnginesDocumento90 páginasBasic Information, Diesel EnginesThang Tong100% (1)
- Engine Cooling SystemDocumento28 páginasEngine Cooling SystemSagar Dadhich100% (1)
- What Is EngineDocumento25 páginasWhat Is EngineSajib Chandra RoyAinda não há avaliações
- 02-Engine Mechanical SystemDocumento96 páginas02-Engine Mechanical Systemsalvador341100% (1)
- Parts of An Automobile and The FunctionDocumento11 páginasParts of An Automobile and The Functionrajronson6938100% (8)
- Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle.Documento5 páginasTroubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle Troubleshooting in cooling system of an automotive vehicle.Karanbir Singh100% (1)
- Automobile - Full Notes - 6TH PDFDocumento179 páginasAutomobile - Full Notes - 6TH PDFShailesh RajuAinda não há avaliações
- Engine Lubrication SystemDocumento29 páginasEngine Lubrication SystemAnonymous xjV1llZSAinda não há avaliações
- Automotive Radiator - Full-LibreDocumento10 páginasAutomotive Radiator - Full-LibreLalitVohraAinda não há avaliações
- DiffrentialDocumento15 páginasDiffrentialAuto Teaser100% (1)
- Lab Manual: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocumento46 páginasLab Manual: Department of Mechanical EngineeringsrknotesAinda não há avaliações
- Ats 4Documento231 páginasAts 4gillian marbebeAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Visit Maruti Suzuki in GurgaonDocumento20 páginasIndustrial Visit Maruti Suzuki in Gurgaonnitin garg100% (1)
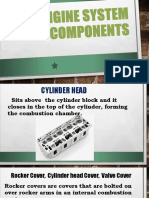
- Engine System ComponentsDocumento33 páginasEngine System Componentsgatul denaenAinda não há avaliações
- Cooling System PDFDocumento7 páginasCooling System PDFdhirendra singh100% (2)
- How Differential WorksDocumento23 páginasHow Differential Worksjohnplaya1234100% (1)
- Sistem Kemudi & RemDocumento171 páginasSistem Kemudi & RemAndikaAinda não há avaliações
- Identifying Engine Systems andDocumento67 páginasIdentifying Engine Systems andBasil BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Sistem PengapianDocumento16 páginasSistem PengapianArdianto BahtiarAinda não há avaliações
- The Battery: SubjectDocumento36 páginasThe Battery: SubjectporkfaceAinda não há avaliações
- Compresor AC SanDen Service Guide Rev.2Documento30 páginasCompresor AC SanDen Service Guide Rev.2MArco Zaragoza100% (2)
- Lighting System, Electrical Instruments and Accessories: HeadlightsDocumento2 páginasLighting System, Electrical Instruments and Accessories: HeadlightsjimmyAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Component CarDocumento12 páginasBasic Component CarFery Budi SatriaAinda não há avaliações
- Torque ConvertorDocumento81 páginasTorque Convertoranupthatta100% (1)
- Gasoline Engine Operation, Parts, and SpecificationsDocumento51 páginasGasoline Engine Operation, Parts, and SpecificationsKien Trinh100% (1)
- Point of No Return - Returnless Fuel Injection SystemsDocumento5 páginasPoint of No Return - Returnless Fuel Injection SystemsrxhughesAinda não há avaliações
- Fuel Injection System in Automobile EnginesDocumento8 páginasFuel Injection System in Automobile EnginesBrendan BrodieAinda não há avaliações
- AutomotiveDocumento259 páginasAutomotiveNavasca RandeeAinda não há avaliações
- Diesel Engine - FundamentalDocumento20 páginasDiesel Engine - FundamentalSoumen BhattaAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Automotive Engine MaintenanceDocumento22 páginas4 Automotive Engine MaintenanceThiruselvan Ayyadorai100% (1)
- Causes of Engine Bearing Failure PDFDocumento15 páginasCauses of Engine Bearing Failure PDFManuel Roberto Chirinos ValerAinda não há avaliações
- Diesel Smoke - WOF Failure?: Home Specials Products Services Events Gallery ContactDocumento2 páginasDiesel Smoke - WOF Failure?: Home Specials Products Services Events Gallery Contactben razAinda não há avaliações
- Clutch SystemDocumento14 páginasClutch SystemSteven Ortiz LapizAinda não há avaliações
- How Diesel Engines WorkDocumento23 páginasHow Diesel Engines WorkBabu Stunner100% (1)
- Automotive Power Tools Ingersoll Rand - UnlockedDocumento68 páginasAutomotive Power Tools Ingersoll Rand - Unlockedamerquip100% (1)
- Engine Cooling SystemDocumento5 páginasEngine Cooling SystemAnoj pahathkumburaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic BatteryDocumento16 páginasBasic BatteryAnton Mariastono50% (2)
- CH 08 - Four-Wheel-Drive SystemsDocumento36 páginasCH 08 - Four-Wheel-Drive SystemsRevanth BhattaramAinda não há avaliações
- Steering System and TyresDocumento32 páginasSteering System and TyresFraolAinda não há avaliações
- Air Conditioning System For Your CarDocumento9 páginasAir Conditioning System For Your CarSanjeev GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Cooling SystemDocumento10 páginasCooling SystemVenu Gopal VegiAinda não há avaliações
- Cylinder and CrankcaseDocumento90 páginasCylinder and CrankcaseLTE002Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Power Tools EquipmentDocumento13 páginasChapter 4 Power Tools EquipmentpapipapiiAinda não há avaliações
- Automobile Engg QuestionsDocumento7 páginasAutomobile Engg QuestionssonawanepmsAinda não há avaliações
- Ic Engine NotesDocumento60 páginasIc Engine Notessamarth motka100% (1)
- Ignition System BasicsDocumento27 páginasIgnition System BasicsRajesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Engine Coolant SystemDocumento10 páginasEngine Coolant SystemJohnAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 Cooling Systems of Ic Engines: StructureDocumento8 páginasUnit 5 Cooling Systems of Ic Engines: StructureAdib Sa-idiAinda não há avaliações
- Report Car Cooling SystemDocumento31 páginasReport Car Cooling SystemOdie Sani Muharman100% (1)
- Scilab TutorialDocumento55 páginasScilab TutorialMichael Villame100% (1)
- Lect 3Documento20 páginasLect 3Pujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- FDM Lecturenotes-4Documento34 páginasFDM Lecturenotes-4Muralikrishnan GMAinda não há avaliações
- ME 11.industrial EngineeringDocumento198 páginasME 11.industrial EngineeringHaren ParmarAinda não há avaliações
- (7 8) FinsDocumento25 páginas(7 8) FinsSalam AlbaradieAinda não há avaliações
- Handout 1 Architecture of A Computer: With MarkupDocumento20 páginasHandout 1 Architecture of A Computer: With MarkupPujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- 33 Budget in Brief GujaratiDocumento20 páginas33 Budget in Brief GujaratiPujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- 10 - D - K - Pandey & AbhayarajDocumento3 páginas10 - D - K - Pandey & AbhayarajPujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- Flow Measuring DevicesDocumento6 páginasFlow Measuring DevicesPujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- UPSC IAS Pre LAST 5 Year Papers General StudiesDocumento96 páginasUPSC IAS Pre LAST 5 Year Papers General StudiesSundeep MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Main Passes of HimalayasDocumento3 páginasMain Passes of HimalayasPujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- Steam TurbineDocumento24 páginasSteam TurbinePujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- Roll No. 130150119002Documento11 páginasRoll No. 130150119002Pujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- CH 07 PDFDocumento15 páginasCH 07 PDFDrRaanu SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Engine Emission - 1Documento13 páginasEngine Emission - 1Pujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- The Two-Phase Microchannel PDFDocumento5 páginasThe Two-Phase Microchannel PDFPujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1Documento8 páginasUnit 1somesh1984Ainda não há avaliações
- Centrifugal Compressors MAN-GEDocumento20 páginasCentrifugal Compressors MAN-GEIbc Cbs Ibc CbsAinda não há avaliações
- Shri B. H. Gardi College of Engineering & TechnologyDocumento4 páginasShri B. H. Gardi College of Engineering & TechnologyPujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- Assembly Line BalancingDocumento11 páginasAssembly Line BalancingAnonymous zQMzqJKAinda não há avaliações
- Vapor Pressure and BoilingDocumento6 páginasVapor Pressure and BoilingPujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- Mel341 38Documento20 páginasMel341 38Pujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To Material Science & EngineeringDocumento16 páginasIntro To Material Science & EngineeringAnkur Yash100% (1)
- The Two-Phase Microchannel PDFDocumento5 páginasThe Two-Phase Microchannel PDFPujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- Temperature MeasurementDocumento40 páginasTemperature MeasurementMohammed Abd El RazekAinda não há avaliações
- Mole ConceptDocumento39 páginasMole ConceptYanique GibbsAinda não há avaliações
- Steam TurbineDocumento24 páginasSteam TurbinePujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamic PumpsDocumento62 páginasDynamic PumpsRaunaq AroraAinda não há avaliações
- Manufacturing ProcessesDocumento44 páginasManufacturing ProcessesPujara Manish0% (1)
- Chapter+1.Gases-part1 2023Documento35 páginasChapter+1.Gases-part1 2023NOXOLO NOMBULELO WENDY NGXONGOAinda não há avaliações
- Definitions - Topic 4 Mechanics and Materials - AQA Physics A-LevelDocumento3 páginasDefinitions - Topic 4 Mechanics and Materials - AQA Physics A-LevelLaud FumhandaAinda não há avaliações
- 1994 - Kemp - Scale-Up of Pneumatic Conveying DryersDocumento20 páginas1994 - Kemp - Scale-Up of Pneumatic Conveying DryersGuilherme Venturi RonchiAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulics and River Engineering Assignment (Submission Date: Within May 15, 2020) Long Questions, Answer in Own Words As Far As PracticableDocumento2 páginasHydraulics and River Engineering Assignment (Submission Date: Within May 15, 2020) Long Questions, Answer in Own Words As Far As PracticableNitish ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Problem 2.50 PDFDocumento2 páginasProblem 2.50 PDFKauê BrittoAinda não há avaliações
- Steam Pipe Failure Investigation ReportDocumento21 páginasSteam Pipe Failure Investigation ReportMohd Saiful Izwan100% (1)
- Life - Prediction - of - Gas - Turbine - Materials PDFDocumento68 páginasLife - Prediction - of - Gas - Turbine - Materials PDFRafael Garcia IllescasAinda não há avaliações
- ME 601 - Stress Analysis Assignment 1 - Review of Strength of Materials Due Date: 27/07/2015, at The Beginning of The ClassDocumento6 páginasME 601 - Stress Analysis Assignment 1 - Review of Strength of Materials Due Date: 27/07/2015, at The Beginning of The Classfatty acidAinda não há avaliações
- PT 2023 Past QuestionDocumento7 páginasPT 2023 Past QuestionTSOG MHAinda não há avaliações
- Concrete Design I Chapter Three Shear Analysis and Design of BeamsDocumento7 páginasConcrete Design I Chapter Three Shear Analysis and Design of BeamsamyarAinda não há avaliações
- Chap9 NPT Grand Canonical Ensemble v04Documento12 páginasChap9 NPT Grand Canonical Ensemble v04Paramita HaldarAinda não há avaliações
- In Line Vs Cross Flow PDFDocumento8 páginasIn Line Vs Cross Flow PDFakhmadmarufnurAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Five Energy BalancesDocumento51 páginasLecture Five Energy BalancesHebron DawitAinda não há avaliações
- Computers and Structures: Alexandre Luis Braun, Armando Miguel AwruchDocumento18 páginasComputers and Structures: Alexandre Luis Braun, Armando Miguel AwruchSiti Rohani IsdrisAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Summative Test Based On TOS Science 3 2021Documento6 páginasRevised Summative Test Based On TOS Science 3 2021Henry Kahal Orio Jr.100% (1)
- BLEVEDocumento1 páginaBLEVEFerdinand Jude DcunhaAinda não há avaliações
- Toyota Land Cruiser 1998-2007 - Air+ConditioningDocumento113 páginasToyota Land Cruiser 1998-2007 - Air+ConditioningseowshengAinda não há avaliações
- VRF Mv6R: Heat Recovery Outdoor UnitsDocumento10 páginasVRF Mv6R: Heat Recovery Outdoor UnitsTony NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Me 423 - Computational Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer: Spring 2018/2019Documento41 páginasMe 423 - Computational Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer: Spring 2018/2019HassanKMAinda não há avaliações
- A NoteDocumento106 páginasA NoteKenneth SantiagoAinda não há avaliações
- BucklingDocumento8 páginasBucklingalphading100% (1)
- Cehdra 1 Obe Syllabus T2 2019 2020Documento6 páginasCehdra 1 Obe Syllabus T2 2019 2020Jemina SamsonAinda não há avaliações
- Adiabatic Wall Temperature Evaluation in A High Speed TurbineDocumento9 páginasAdiabatic Wall Temperature Evaluation in A High Speed TurbineSaadAinda não há avaliações
- Forced Circulation EvaporatorsDocumento11 páginasForced Circulation EvaporatorsFurqan MughalAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier's Law: A T T (LDocumento8 páginasFourier's Law: A T T (LEzioSilvestreAinda não há avaliações
- Körting Multistage-Steam-Jet-Vacuum-Ejectors PDFDocumento5 páginasKörting Multistage-Steam-Jet-Vacuum-Ejectors PDF何恭彥Ainda não há avaliações
- 4th ExamDocumento1 página4th Examquice reviewAinda não há avaliações
- 338-Article Text-1751-2-10-20080123Documento16 páginas338-Article Text-1751-2-10-20080123FurqanAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics II (MEng 3306)Documento2 páginasFluid Mechanics II (MEng 3306)Addisu DagneAinda não há avaliações
- Objective Type Questions With AnswersDocumento29 páginasObjective Type Questions With AnswersNikka LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Welcome to the United States of Anxiety: Observations from a Reforming NeuroticNo EverandWelcome to the United States of Anxiety: Observations from a Reforming NeuroticNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (10)
- The House at Pooh Corner - Winnie-the-Pooh Book #4 - UnabridgedNo EverandThe House at Pooh Corner - Winnie-the-Pooh Book #4 - UnabridgedNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (5)
- You Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherNo EverandYou Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherAinda não há avaliações
- Sexual Bloopers: An Outrageous, Uncensored Collection of People's Most Embarrassing X-Rated FumblesNo EverandSexual Bloopers: An Outrageous, Uncensored Collection of People's Most Embarrassing X-Rated FumblesNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (7)
- The Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionNo EverandThe Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (44)
- The Most Forbidden Knowledge: 151 Things NO ONE Should Know How to DoNo EverandThe Most Forbidden Knowledge: 151 Things NO ONE Should Know How to DoNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- The Book of Bad:: Stuff You Should Know Unless You’re a PussyNo EverandThe Book of Bad:: Stuff You Should Know Unless You’re a PussyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- 1,001 Facts that Will Scare the S#*t Out of You: The Ultimate Bathroom ReaderNo Everand1,001 Facts that Will Scare the S#*t Out of You: The Ultimate Bathroom ReaderNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (48)
- Pickup Lines: The Ultimate Collection of the World's Best Pickup Lines!No EverandPickup Lines: The Ultimate Collection of the World's Best Pickup Lines!Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Travel: The Worst-Case Scenario Survival Handbook: How to Survive Runaway Camels, UFO Abductions, High-Rise Hotel Fires, LeechesNo EverandTravel: The Worst-Case Scenario Survival Handbook: How to Survive Runaway Camels, UFO Abductions, High-Rise Hotel Fires, LeechesNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (126)
- The Smartest Book in the World: A Lexicon of Literacy, A Rancorous Reportage, A Concise Curriculum of CoolNo EverandThe Smartest Book in the World: A Lexicon of Literacy, A Rancorous Reportage, A Concise Curriculum of CoolNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (14)
- Sex, Drugs, and Cocoa Puffs: A Low Culture ManifestoNo EverandSex, Drugs, and Cocoa Puffs: A Low Culture ManifestoNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (1428)
- My Man, Jeeves, The Inimitable Jeeves and Right Ho, Jeeves - THREE P.G. Wodehouse Classics! - UnabridgedNo EverandMy Man, Jeeves, The Inimitable Jeeves and Right Ho, Jeeves - THREE P.G. Wodehouse Classics! - UnabridgedAinda não há avaliações
- What I Was Doing While You Were Breeding: A MemoirNo EverandWhat I Was Doing While You Were Breeding: A MemoirNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (117)




































































































































![The Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/711420909/198x198/ba98be6b93/1712018618?v=1)









