Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Three Phase Controlled Rectifiers2003
Enviado por
Sai Pranahita BhaskarapantuluDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Three Phase Controlled Rectifiers2003
Enviado por
Sai Pranahita BhaskarapantuluDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
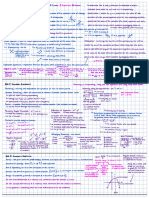
V
AN
V
CN
V
BN
120
0
120
0
120
0
RN AN
YN BN
BN CN
v v
v v
v v
=
=
=
T 1
T 2
T 3
R
load
3- supply
Phase
Voltages
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo
(=0 )
Vo
(30+ )
Va Vb Vc
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Phase
Voltages
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo
(=0 )
Vo
(30+ )
Va Vb Vc
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
( )
( )
( )
0
1
0
2
0
3
0
30
6
5
150
6
7
270
6
2
Each thytistor conducts for 120 or radians
3
T is triggered at t
T is triggered at t
T is triggered at t
t
e o o
t
e o o
t
e o o
t
| |
= + = +
|
\ .
| |
= + = +
|
\ .
| |
= + = +
|
\ .
( )
5
6
6
If the reference phase voltage is
sin , the average or dc output
voltage for continuous load current is calculated
using the equation
3
sin .
2
RN an m
dc m
v v V t
V V t d t
t
o
t
o
e
e e
t
+
+
= =
(
(
=
(
(
}
( )
( )
5
6
6
5
6
6
3
sin .
2
3
cos
2
3 5
cos cos
2 6 6
m
dc
m
dc
m
dc
V
V t d t
V
V t
V
V
t
o
t
o
t
o
t
o
e e
t
e
t
t t
o o
t
+
+
+
+
(
(
=
(
(
(
(
=
(
(
(
| | | |
= + + +
| |
(
\ . \ .
}
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
0 0
0
Note from the trigonometric relationship
cos cos .cos sin .sin
5 5
cos cos sin sin
6 6
3
2
co
cos 150 cos sin 150 sin
3
2
cos 30
s .cos sin sin
6 6
.cos
m
dc
m
dc
A
V
V
B A B A B
V
V
t t
o o
t
t t
o
o
o
o
t
o
+ =
(
| | | |
+
| |
(
\ . \ .
(
=
(
| | | |
+
( | |
\ . \ .
+
=
( )
( )
0
sin 30 sin o
(
(
(
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0
0 0
0
0
0
0
0 0
Note: cos 1
cos 180 30 cos sin 180 30 sin
3
2
cos 30 .cos sin 30 sin
cos 30 cos sin 30 sin
3
2
cos 30 .cos sin 30 s
80 30 cos 30
sin 180 30 sin 30
in
m
dc
m
dc
V
V
V
V
o o
t
o o
o o
t
o o
=
(
+
(
=
(
+
(
+ +
(
=
(
+
( )
( )
( )
( ) ( )
( )
0
3
2cos 30 cos
2
3 3
2 cos
2 2
3 3 3
3 cos cos
2 2
3
cos
2
Where 3 Max. line to line supply voltage
m
dc
m
dc
m m
dc
Lm
dc
Lm m
V
V
V
V
V V
V
V
V
V V
o
t
o
t
o o
t t
o
t
(
=
(
=
(
(
= =
=
= =
( )
( )
( )
1
5
2
6
2 2
6
1
2
The rms value of output voltage is found by
using the equation
3
sin .
2
and we obtain
1 3
3 cos 2
6 8
m
O RMS
m
O RMS
V V t d t
V V
t
o
t
o
e e
t
o
t
+
+
(
(
=
(
(
(
= +
(
}
R-L
load
T 1 T 3 T 5
T 4
T 2
T 6
A
B
C
6 - pulse combinations are:
(6,1) (1,2) (2,3) (3,4) (4,5) (5,6)
Io
R-L
load
T 1 T 3 T 5
T 4 T 6
A
B
C
When thyristors T1 & T6 conducts
T 2
A T1 RL T6 B
Io
R-L
load
T 1 T 3 T 5
T 4 T 6
A
B
C
When thyristors T1 & T2 conducts
T 2
A T1 RL T2 C
Io
R-L
load
T 1 T 3 T 5
T 4 T 6
A
B
C
When thyristors T2 & T3 conducts
T 2
B T3 RL T2 C
Io
R-L
load
T 1 T 3 T 5
T 4 T 6
A
B
C
When thyristors T3 & T4 conducts
T 2
B T3 RL T4 A
Io
R-L
load
T 1 T 3 T 5
T 4 T 6
A
B
C
When thyristors T4 & T5 conducts
T 2
C T5 RL T4 A
Io
R-L
load
T 1 T 3 T 5
T 4 T 6
A
B
C
When thyristors T5 & T6 conducts
T 2
C T5 RL T6 B
Io
Line
Voltages
Phase
Voltages
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Line
Voltages
Vo
(=0 )
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
VCB VCA VAB VBA VBC VAC
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo
(=60 )
Io
Line
Voltages
Vo
(=0 )
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
VCB VCA VAB VBA VBC VAC
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo
(=60 )
Io
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Line
Voltages
Vo
(=90 )
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo
(=120 )
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Line
Voltages
Vo
(=90 )
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo
(=120 )
The output load voltage consists of 6 voltage
pulses over a period of 2t radians, Hence the
average output voltage is calculated as
( )
2
6
6
. ;
2
3 sin
6
dc O
O dc
O ab m
V V v d t
v v V t
t
o
t
o
e
t
t
e
+
+
= =
| |
= = +
|
\ .
}
( )
2
6
mL
max
3
3 sin .
6
3 3 3
cos cos
Where V 3 Max. line-to-line supply vo
The maximum average dc output voltage is
obtained for a delay angle
ltage
3 3
0,
3
dc m
m mL
dc
m
m m
dm
dc
V V t d t
V V
V
V
V V
V V
t
o
t
o
t
e e
t
o o
t
o
t
t
+
+
| |
= +
|
\ .
= =
=
=
=
= = =
}
L
t
( )
( )
1
2
2
2
6
The normalized average dc output voltage is
cos
The rms value of the output voltage is found from
6
.
2
dc
dcn n
dm
O
O rms
V
V V
V
V v d t
t
o
t
o
o
e
t
+
+
= = =
(
(
=
(
(
}
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
1
2
2
2
6
1
2
2
2 2
6
1
2
6
.
2
3
3 sin .
2 6
1 3 3
3 cos 2
2 4
ab
O rms
m
O rms
m
O rms
V v d t
V V t d t
V V
t
o
t
o
t
o
t
o
e
t
t
e e
t
o
t
+
+
+
+
(
(
=
(
(
(
| | (
= +
|
(
\ .
(
| |
= +
|
|
\ .
}
}
For four quadrant operation in many industrial variable speed dc
drives , 3 phase dual converters are used.
Used for applications up to 2 mega watt output power level.
Dual converter consists of two 3 phase full converters which are
connected in parallel & in opposite directions across a common load.
+I0
-I0
+V0
-V0
Conv. 1
Inverting
o
1
> 90
0
Conv. 1
Rectifying
o
1
< 90
0
Conv. 2
Rectifying
o
2
< 90
0
Conv. 2
Inverting
o
2
> 90
0
The Dual Converter is operated such that:
One conv. should be Converter
One conv. should be Inverter
{1 < 90}
{2 > 90}
i.e, 1+2= 180
Conditions:
1. O/P voltage mag. of 2 converters should be same.
2. Polarities should be same.
i.e, Vo = Vo1 = -Vo2
Non Circulating current mode:
only one converter is in operation at a time, and it alone
carries the entire load current.
No Reactor is used between two converters.
Circulating current mode:
A reactor is inserted between two reactors. This
reactor limits the magnitude of circulating current
to a reasonable value.
load
V0
T 11 T 13 T1 5
T1 4
T1 2
T1 6 T 21 T 23 T 25
T 24 T 22
T 26
A
B
C C
B
A
V01 V02
Lr
2
Lr
2
Vr
Vr
2 2
Line
Voltages
Vo1
(=60 )
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
VCB
VCA VAB VBA VBC VAC
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo2
(=120 )
Io
Line
Voltages
Vo1
(=60 )
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
VCB
VCA VAB VBA VBC VAC
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo2
(=120 )
Vo=Vo1+Vo2
Vo2 (=120 )
2
Line
Voltages
Vo1
(=60 )
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
VCB
VCA VAB VBA VBC VAC
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo2
(=120 )
Vo=Vo1+Vo2
Vo2 (=120 )
2
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Line
Voltages
Vr
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Ic = Vr dt
Ic
1 2
3 sin sin
6 2
3 cos
6
The circulating current can be calculated by
using the equation
r O O ab bc
r m
r m
v v v v v
v V t t
v V t
t t
e e
t
e
= + =
(
| | | |
= +
| |
(
\ . \ .
| |
=
|
\ .
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( )
( )
1
1
6
6
1
max
1
.
1
3 cos .
6
3
sin sin
6
3
t
r r
r
t
r m
r
m
r
r
m
r
r
i t v d t
L
i t V t d t
L
V
i t t
L
V
i
L
e
t
o
e
t
o
e
e
t
e e
e
t
e o
e
e
+
+
=
| |
=
|
\ .
(
| |
=
|
(
\ .
=
}
}
Because of Source Inductance effect, overlap conduction
of thyristors takes place.
At an instant, 3 thyristors will conduct
i.e, 2 thyristors from +ve group & 1 thyristor from -ve group
(or)
2 thyristors from -ve group & 1 thyristor from +ve group
So, .output voltage decreases.
R-L
load
T 1 T 3 T 5
T 4
T 2
T 6
A
B
C
Negative
Group
Positive
Group
+ve Group
Line
Voltages
Without
Ls
=0
= 0
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
With Ls
=0
= 30
T1 T3 T5
T6 T2 T4 T6
I1 I3 I5
I6 I2 I4 I6
-ve Group
Vo
Ph-A
Decrease in output voltage due to overlap angle:
Vo = Area of the triangle
Vo = 6x (1/2) 0Vl d(t)
VO = 3Ls
Io
Io
For 3- full bridge conv. With R-L Load without Ls
VO = 33 Vm cos
Therefore, Avg. o/p voltage with overlap angle (or) Source Inductance
VO(avg) = 33 Vm cos
3Ls
Io
3 Phase semiconverters are used in Industrial dc drive
applications upto 120kW power output.
Single quadrant operation is possible.
Power factor decreases as the delay angle increases.
Power factor is better than that of 3 phase half wave
converter.
R-L
load
T 1 T 3 T 5
D 4
D 2
D 6
A
B
C
Io
R-L
load
T 1 T 3 T 5
D 4
D6
A
B
C
When thyristors T1 & T6 conducts
D 2
A T1 RL T6 B
Io
Line
Voltages
Vo
(=30 )
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
VCB VCA VAB VBA VBC VAC
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo
(=60 )
Io
Line
Voltages
Vo
(=30 )
AB AC BC BA CA CB
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
VCB VCA VAB VBA VBC VAC
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Vo
(=60 )
Iph A
1,2 3,4 5,6
Phase A
For Inductive LOAD
To derive an Expression for the
Average Output Voltage of 3 Phase
Semiconverter for o > t / 3
and Discontinuous Output Voltage
( )
( )
7
6
6
7
6
6
For and discontinuous output voltage:
3
the Average output voltage is found from
3
.
2
3
3 sin
2 6
dc ac
dc m
V v d t
V V t d t
t
t
o
t
t
o
t
o
e
t
t
e e
t
+
+
>
(
(
=
(
(
| |
(
=
|
(
\ .
}
}
( )
( )
( )
max
3 3
1 cos
2
3
1 cos
2
3 Max. value of line-to-line supply voltage
The maximum average output voltage that occurs at
a delay angle of 0 is
3 3
m
dc
mL
dc
mL m
m
dm
dc
V
V
V
V
V V
V
V V
o
t
o
t
o
t
= +
= +
= =
=
= =
( )
( )
( )
1
7
2
6
2
6
The normalized average output voltage is
0.5 1 cos
The rms output voltage is found from
3
.
2
dc
n
dm
ac
O rms
V
V
V
V v d t
t
t
o
o
e
t
+
= = +
(
(
=
(
}
( )
( )
( )
1
7
2
6
2 2
6
1
2
3
3 sin
2 6
3 sin 2
3
4 2
m
O rms
m
O rms
V V t d t
V V
t
t
o
t
e e
t
o
t o
t
+
(
| |
(
=
|
(
\ .
(
| |
= +
|
(
\ .
}
Você também pode gostar
- Evaluation of Genetic Algorithm Based Solar Tracking System For Photovoltaic PanelsDocumento5 páginasEvaluation of Genetic Algorithm Based Solar Tracking System For Photovoltaic PanelsSai Pranahita BhaskarapantuluAinda não há avaliações
- A New Efficient Reconfiguration Approach Based On Genetic Algorithm in PV SystemsDocumento6 páginasA New Efficient Reconfiguration Approach Based On Genetic Algorithm in PV SystemsSai Pranahita BhaskarapantuluAinda não há avaliações
- Maximum Power Point Tracking Using GA-Optimized Artificial Neural Network For Solar PV SystemDocumento5 páginasMaximum Power Point Tracking Using GA-Optimized Artificial Neural Network For Solar PV SystemSai Pranahita BhaskarapantuluAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To Genetic AlgorithmsDocumento26 páginasAn Introduction To Genetic AlgorithmsSai Pranahita BhaskarapantuluAinda não há avaliações
- DC DCP V ArchitecturesDocumento13 páginasDC DCP V ArchitecturesSai Pranahita BhaskarapantuluAinda não há avaliações
- D StatcomDocumento29 páginasD StatcomSai Pranahita Bhaskarapantulu100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- 3107 Enthusiast Score Advanced Paper-2 (E+H) JADocumento56 páginas3107 Enthusiast Score Advanced Paper-2 (E+H) JAsonu goyalAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial DistillationDocumento3 páginasTutorial DistillationManu Indivare Nundoolall100% (1)
- CONTEXT PLUS - HFC227ea Systems - SALES BROCHURE - 01-17Documento4 páginasCONTEXT PLUS - HFC227ea Systems - SALES BROCHURE - 01-17Ronny HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile Communications: Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDocumento108 páginasMobile Communications: Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systemsradislamy-1Ainda não há avaliações
- GPS 2Documento6 páginasGPS 2Arnold Alexander GarzonAinda não há avaliações
- Boiler Efficiency PresentationDocumento13 páginasBoiler Efficiency PresentationAhmad Sabree Abdul BasitAinda não há avaliações
- B.pharmacy Project SD of GlimepirideDocumento12 páginasB.pharmacy Project SD of Glimepiridemanvitha varmaAinda não há avaliações
- PL-SQL FunctionsDocumento130 páginasPL-SQL Functionswasim ahmed100% (1)
- Excel FunctionsDocumento13 páginasExcel Functionsfhlim2069Ainda não há avaliações
- Differentiation Questions and AnswerDocumento10 páginasDifferentiation Questions and AnswerNazurah Kamaruzzaman KamariAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Project: Made By:-Shubham Class: - Viii-CDocumento25 páginasMaths Project: Made By:-Shubham Class: - Viii-CsivaAinda não há avaliações
- Resolución de Problema en FísicaDocumento4 páginasResolución de Problema en FísicaCindy ChiribogaAinda não há avaliações
- Opc Da Client ManualDocumento29 páginasOpc Da Client ManualantoAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook Remote Server ManagementDocumento10 páginasEbook Remote Server ManagementPiruletoAinda não há avaliações
- Supertester 680 RDocumento39 páginasSupertester 680 Rdomingos.sanchezAinda não há avaliações
- The Difference Between Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous StatesDocumento9 páginasThe Difference Between Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous StatesFikriZalsyaAinda não há avaliações
- Sound Intensity Level CalculationDocumento10 páginasSound Intensity Level CalculationvenkateswaranAinda não há avaliações
- thống số cụm phanh sau 777E KYDDocumento2 páginasthống số cụm phanh sau 777E KYDlongcpqn95Ainda não há avaliações
- Stephanie Florescu - MPM2D Summary SheetDocumento2 páginasStephanie Florescu - MPM2D Summary Sheetstephanie.florescuAinda não há avaliações
- BBBBBDocumento11 páginasBBBBBAlfredo ErguetaAinda não há avaliações
- Velocity Analysis-Instantaneous Center MDocumento7 páginasVelocity Analysis-Instantaneous Center MSuman_SamadderAinda não há avaliações
- ASHRAE Table9 Hot Water Demand PDFDocumento1 páginaASHRAE Table9 Hot Water Demand PDFsenthilkumar_5425717Ainda não há avaliações
- Linear Programming: Simplex Method: Dr. R. K Singh Professor, Operations Management MDI, GurgaonDocumento58 páginasLinear Programming: Simplex Method: Dr. R. K Singh Professor, Operations Management MDI, GurgaonvsyoiAinda não há avaliações
- TUNAY Manuscript PrefinalDocumento94 páginasTUNAY Manuscript PrefinalC100% (1)
- Function Modules Available in MM & EWMDocumento3 páginasFunction Modules Available in MM & EWMgopalaaraoAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Practice Guideline On Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyponatremia PDFDocumento12 páginasClinical Practice Guideline On Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyponatremia PDFLuis Mochas HClAinda não há avaliações
- FSX Cessna 172SP OldDocumento4 páginasFSX Cessna 172SP Oldaccgh5Ainda não há avaliações
- Brochure - Digilogic Systems PVT Ltd.Documento28 páginasBrochure - Digilogic Systems PVT Ltd.ManojGRamakrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Datasheet en 20170526Documento9 páginasDatasheet en 20170526LODELBARRIO RDAinda não há avaliações